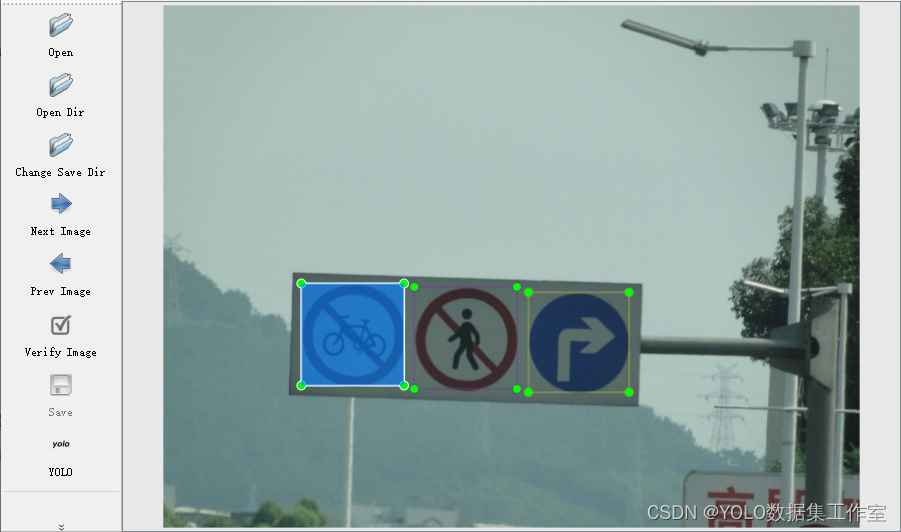
文章目录
- 引言
- 演进路线
- 邻域搜索,NS
- 变邻域搜素,VDNS
- 大邻域搜索,LNS
- 自适应大邻域搜索,ALNS
- 代码实现
- 34个国内城市的TSP
- 测试集XQF131
- 相关阅读
引言
之前介绍的差分进化算法和蚁群算法分别适用于求解连续优化问题和组合优化问题,它们都属于基于种群进化的智能优化算法。
除此之外,智能优化算法中还有一大类,即基于单点出发的智能优化算法,比如模拟退火算法、禁忌搜索算法和邻域搜索算法等。本文将着重介绍其中一个邻域搜索算法:自适应大邻域搜索算法(Adaptive large neighborhood search,ALNS)。
选择ALNS的主要原因包含三个:ALNS中很多参数设计的逻辑是自适应的,比较符合长期发展的需要;从行业实践来看,菜鸟的车辆路径规划引擎入围过2021年Franz Edelman杰出成就奖(被称为运筹学界“奥斯卡”),其核心算法就是ALNS,因此ALNS看起来比较有前景;之前我自己做过变邻域搜索算法的项目实践,效果还不错,而ALNS听名字就比变邻域搜索更加高级,因此也有动力去学习ALNS。
正文见下。
演进路线
在网上搜索邻域搜索算法,能看到很多相关的名词,比如邻域、变邻域和大邻域等,对于我这种一知半解的人来说,着实有些让人费解。本着追根溯源的思路,我详细学习了大佬Pisinger的综述性文章(其实是书的其中一章):Large Neighborhood Search。概念众多,个人认为,了解清楚以下4个就足够了:邻域搜索(NS)、变邻域搜素(VDNS)、大邻域搜索(LNS)和自适应大邻域搜索(ALNS)。
邻域搜索,NS
邻域这个词应该不难理解,本质就是在当前解 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0 附近的一些区域。至于如何定义区域,则需要看实际问题的特征。
如果 x \pmb x x 是连续的,可以定义邻域是距离 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0 不超过1的空间范围,当 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0 是一维时,例如 x 0 = 2 x_0=2 x0=2,此时邻域就是 [ 1 , 3 ] [1,3] [1,3];当 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0 是二维时,例如 x 0 = [ 2 , 2 ] \pmb x_0=[2,2] x0=[2,2],此时邻域就是圆心为 [ 2 , 2 ] [2,2] [2,2]、半径为1的圆。
如果 x \pmb x x 是离散的,例如 x 0 = [ 2 , 2 ] \pmb x_0=[2,2] x0=[2,2],可以定义邻域是某一个分量向左或向右移动1个单位,此时邻域便包括: [ 1 , 2 ] 、 [ 3 , 2 ] 、 [ 2 , 1 ] [1,2]、[3,2]、[2,1] [1,2]、[3,2]、[2,1] 和 [ 2 , 3 ] [2,3] [2,3]。
有了邻域后,就可以做邻域搜索了,其含义就是在邻域内找到最好的解 x ⋆ \pmb x ^{\star} x⋆,从而更新 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0。
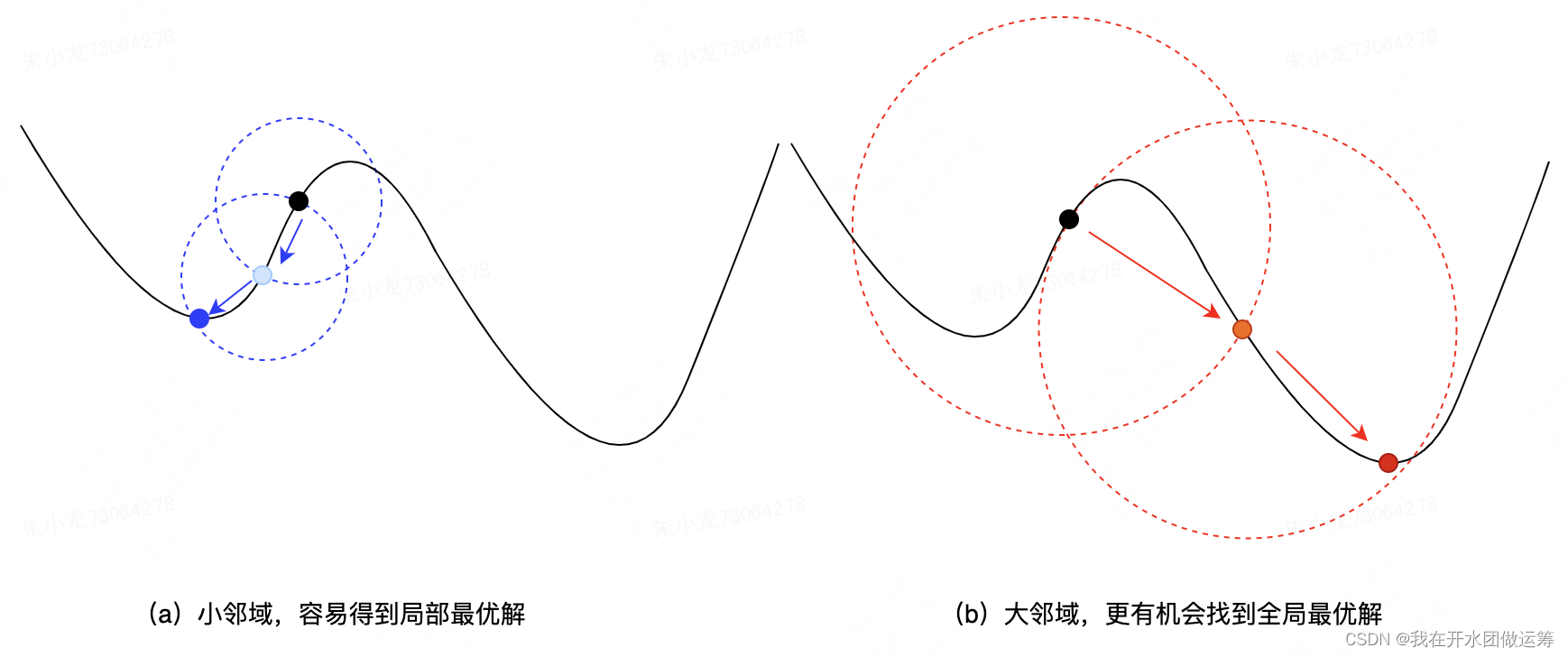
邻域搜索的核心是设计出合理的邻域,下图显示了不同邻域下最终得到不同解的示意图。基本结论为:邻域越大,越有机会找到全局最优解,但是为此也需要花费更多的计算时间。
再举个TSP中的邻域实例:2-opt。假设当前解为
A
−
B
−
C
−
D
−
E
−
F
−
G
−
H
−
A
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-A
A−B−C−D−E−F−G−H−A
随机选择选择两个点,假设是4和7,对应D和G,此时可以将当前解拆成如下3段
A
−
B
−
C
,
D
−
E
−
F
−
G
,
H
−
A
A-B-C,\quad D-E-F-G,\quad H-A
A−B−C,D−E−F−G,H−A
2-opt的定义是,前后两段保持不变,中间一段进行翻转,然后重新拼接起来,即
A
−
B
−
C
−
G
−
F
−
E
−
D
−
H
−
A
A-B-C-G-F-E-D-H-A
A−B−C−G−F−E−D−H−A
变邻域搜素,VDNS
如果邻域空间随着问题规模的增长成指数型增长,或者邻域空间本身就比较大,那么通常会被定义为VLSN(very large-scale neighbourhood search)。针对VLSN,要实现邻域的完全遍历,几乎不太现实,因此就需要一些新的解决方案。
变邻域搜索(Variable-Depth Neighborhood Search, VDNS)便是其中一种。其基本思路为:首先在 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0的小邻域内搜索,如果有更优解,则更新 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0为 x 1 \pmb x_1 x1,然后在 x 1 \pmb x_1 x1的小邻域内重新搜索;如果没有更优解,则扩大 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0的邻域,继续搜索,找到更优解后,更新 x 0 \pmb x_0 x0并回到小邻域搜索。
下图是一个VDNS的实例。通过在2处的3次邻域扩充,找到了更优解3。
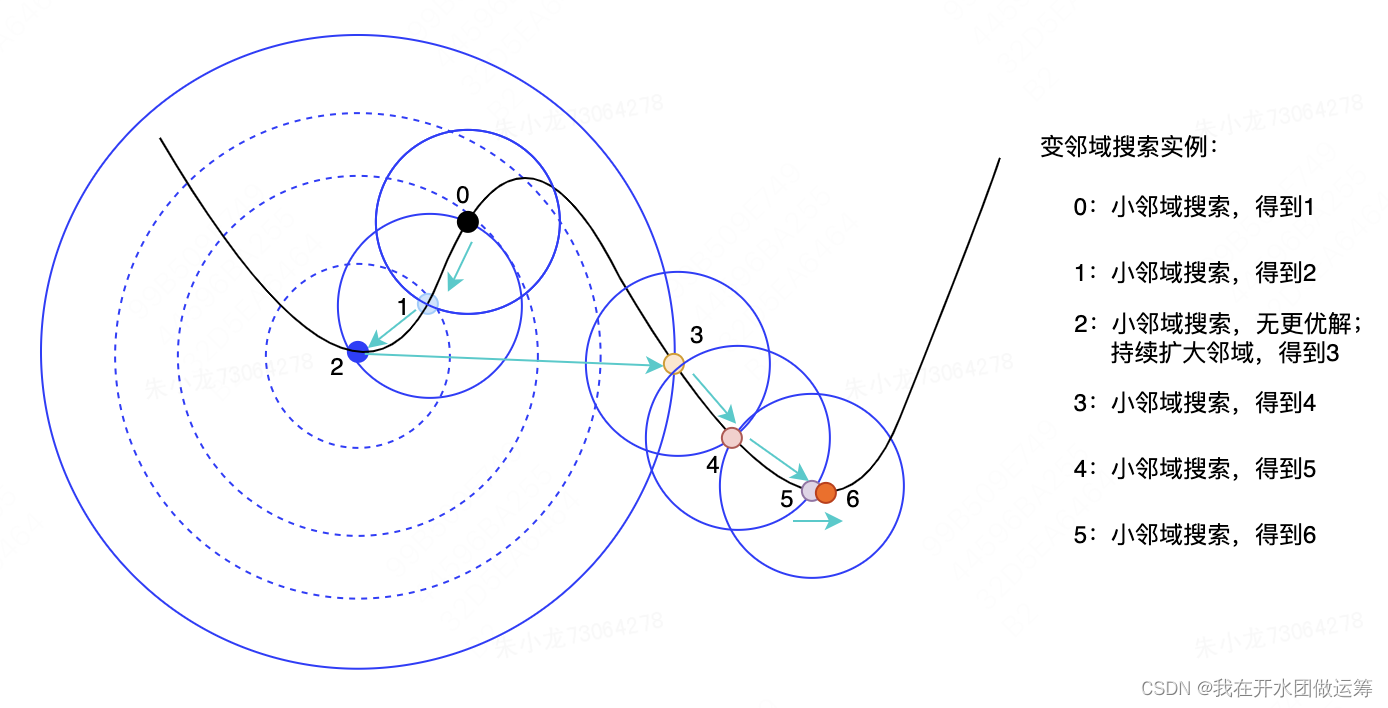
大邻域搜索,LNS
大邻域搜索(Large Neighborhood Search, LNS)可以理解为求解VLSN的另一种解决方案,而且主要用来求解组合优化问题。这里直接使用原文中的VRP实例来描述LNS的实现过程。
VRP,vehicle routing problem,车辆路径问题,是非常经典的一类组合优化问题,可以简单描述为:一个中心点和多个客户,主要目标是使用尽量少的车和行驶尽量短的距离,或花费尽量少的成本,基本约束是要拜访完所有客户并且车辆最终返回中心点,如果再加入其他约束,如每辆车有装载限制,则被称为CVRP问题,如果继续加入约束,还可以扩展至VRP-TW等。
下图是一个VRP解的实例。图中的方块为中心点,一共21个客户,使用了4辆车,分别拜访了6(蓝绿)、3(红)、5(蓝)和7(紫)个客户。从图上看,很多车辆间的路径是交叉的,并不美观,大致判断总行驶距离是有优化空间的。那具体该如何优化呢?
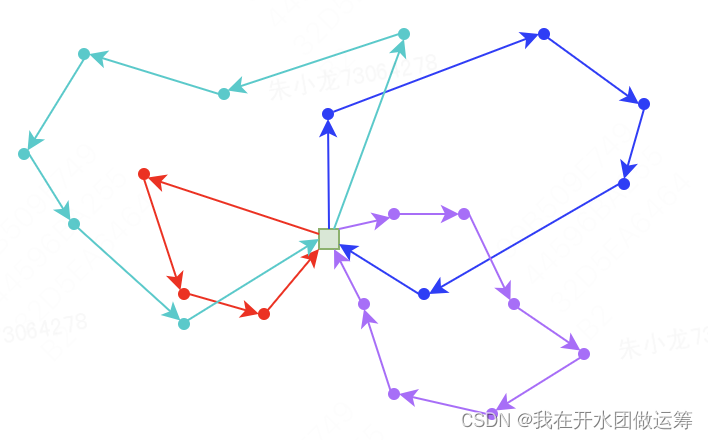
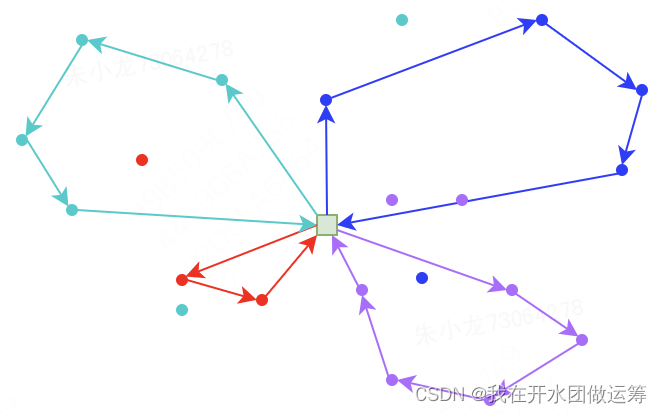
接着,对破坏后的解,进行repair操作,将被删除的客户重新插入到路径中,保证约束的满足,得到一个测试解。下图的方案是贪心策略:将被删除的客户插入到总路径最短的位置中。
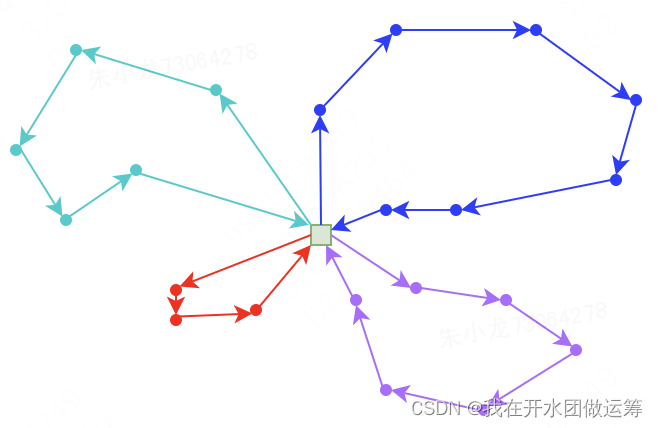
然后,比较当前解和测试解的指标大小,如果指标更优,则将当前解更新为测试解,否则便不更新。
此后,重新进行destroy+repair,直至满足终止条件,退出优化。
下图是LNS的伪代码。目标函数为最小化
c
(
x
)
c(x)
c(x);第4行的
d
(
x
)
d(x)
d(x)指的是destroy,
r
(
d
(
x
)
)
r(d(x))
r(d(x))指的是repair;尤其需要注意的是这里有三个
x
x
x:
x
x
x指的是当前解,
x
t
x^t
xt指的是基于当前解
x
x
x + destroy + repair产生的测试解,
x
b
x^b
xb指的是截至当前的历史最优解;另外,在第5行还有个
accept
(
x
t
,
x
)
\text{accept}(x^t,x)
accept(xt,x)函数,表明是否更新当前解
x
x
x,还需要一个判断,我们刚刚说的判断指标是否更优是最初的版本,后续版本更倾向于借鉴模拟退火算法中的设计思路:产生一个随机数,如果其值低于
e
−
(
c
(
x
t
)
−
c
(
x
)
)
/
T
e^{-(c(x^t)-c(x))/T}
e−(c(xt)−c(x))/T(
T
T
T为外部参数),即使指标没有更优,也会将当前解更新为测试解,这样当前解便有机会跳出局部最优解,找到更优解。

自适应大邻域搜索,ALNS
从LNS的设计逻辑来看,算法的核心是设计出匹配具体问题的destroy和repair算子。针对repair,常用的算子不多,主要就随机和贪心两类策略;但针对destroy,算子的数量就有些大了:首先需要确定的是destroy的比例,还是以上一节的VRP问题为例,一共21个客户,如果destroy比例为10%,则需要删除2个客户;然后还要确定删除哪两个,这就有420种情况,如果destroy比例为20%,那就有143640种情况。所以,如何在每次迭代时找出恰当的destroy和repair算子,就显得尤为重要。
ALNS的目标是根据具体问题的特征,自适应地找到最恰当的算子。其设计思路可以理解为:开始阶段先罗列可以选择的所有算子,并且不同算子的选择概率是完全相同的;此后如果某个算子能带来更大的指标提升,该算子被选择的概率就会提升,从而有更大的概率在后续的迭代中被使用。
下图是ALNS的伪代码。相比LNS,主要变化为:第2、4和12行。第2行中的 ρ − \rho^- ρ−指的是选择不同destroy算子的概率, ρ + \rho^+ ρ+指的是选择不同repair算子的概率。迭代开始时,他们均被设置为1,即被选择的概率保持相同;每一轮迭代后,都会对它们进行更新,即第12行,更新逻辑稍微复杂,稍后再细说。第4行中的 Ω − \Omega^- Ω−指的是destroy算子的集合, Ω + \Omega^+ Ω+指的是repair算子的集合,当前轮次选择哪一个destroy和repair,采用轮盘赌的方式确定,即 ρ − \rho^- ρ−和 ρ + \rho^+ ρ+的概率越大,被选中的概率越大。
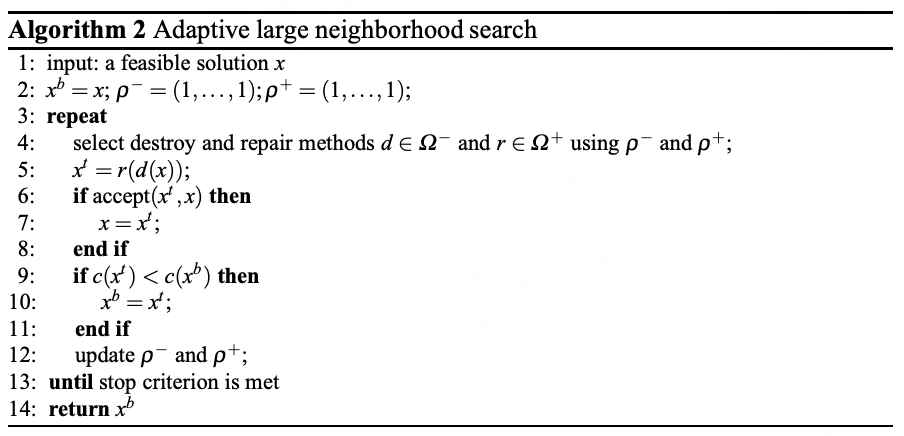
回到
ρ
−
\rho^-
ρ−和
ρ
+
\rho^+
ρ+的更新逻辑。为了让它们的更新和指标提升程度挂上勾,需要先引入一个额外参数
Ψ
=
{
w
1
,
测试解为历史最优解
w
2
,
测试解不是历史最优解,但是优于当前解
w
3
,
当前解更新为测试解
w
4
,
测试解较差,当前解不更新
\Psi=\left\{ \begin{aligned} w_1, & 测试解为历史最优解 \\ w_2, & 测试解不是历史最优解,但是优于当前解 \\ w_3, & 当前解更新为测试解 \\ w_4, & 测试解较差,当前解不更新 \end{aligned} \right.
Ψ=⎩
⎨
⎧w1,w2,w3,w4,测试解为历史最优解测试解不是历史最优解,但是优于当前解当前解更新为测试解测试解较差,当前解不更新
然后便可以按如下公式进行更新
ρ
−
\rho^-
ρ−和
ρ
+
\rho^+
ρ+
ρ
−
=
λ
ρ
−
+
(
1
−
λ
)
Ψ
\rho^- = \lambda \rho^- + (1-\lambda )\Psi
ρ−=λρ−+(1−λ)Ψ
ρ
+
=
λ
ρ
+
+
(
1
−
λ
)
Ψ
\rho^+ = \lambda \rho^+ + (1-\lambda )\Psi
ρ+=λρ++(1−λ)Ψ
此处,
λ
\lambda
λ的含义可以类比蚁群算法中信息素的挥发系数。
需要说明的是,为了保证更大的 Ψ \Psi Ψ能让 ρ − \rho^- ρ−和 ρ + \rho^+ ρ+也更大,一般要求 w 1 > w 2 > w 3 > w 4 w_1>w_2>w_3>w_4 w1>w2>w3>w4。
代码实现
34个国内城市的TSP
上一篇介绍蚁群算法的文章中,计算实例是国内34个主要城市的TSP问题。其中,蚁群算法得到的最优解是15944.43,使用ortools得到的全局最优解是15614.84。
本节也使用该实例,以此初步评估ALNS的能力。以下是python实现的代码。其中,destroy算子有3个:随机筛选N个城市、删除距离最大的N个城市和随机删除连续的N个城市;repair算子有2个:随机插入和贪心插入,不过考虑到随机插入的效果大概率比较差,所以代码中实际只使用了贪心插入,设置方式参见代码第138行。代码的可扩展性比较好,如果想调整destroy和repair算子,只需要调整第66行的destroy函数和109行的repair函数即可。
import copy
import math
import time
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 计算TSP总距离
def dis_cal(path, dist_mat):
distance = 0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
distance += dist_mat[path[i]][path[i + 1]]
distance += dist_mat[path[-1]][path[0]]
return distance
# 随机删除N个城市
def random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 随机选择N个城市,并删除
removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), destroy_city_cnt)
for i in removed_index:
removed_cities.append(new_x[i])
x.remove(new_x[i])
return removed_cities
# 删除距离最大的N个城市
def max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 计算顺序距离并排序
dis = []
for i in range(len(new_x) - 1):
dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[i]][new_x[i + 1]])
dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[-1]][new_x[0]])
sorted_index = np.argsort(np.array(dis))
# 删除最大的N个城市
for i in range(destroy_city_cnt):
removed_cities.append(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])
x.remove(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])
return removed_cities
# 随机删除连续的N个城市
def continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 随机选择N个城市,并删除
removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)-destroy_city_cnt), 1)[0]
for i in range(removed_index + destroy_city_cnt, removed_index, -1):
removed_cities.append(new_x[i])
x.remove(new_x[i])
return removed_cities
# destroy操作
def destroy(flag, x, destroy_city_cnt):
# 三个destroy算子,第一个是随机删除N个城市,第二个是删除距离最大的N个城市,第三个是随机删除连续的N个城市
removed_cities = []
if flag == 0:
# 随机删除N个城市
removed_cities = random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
elif flag == 1:
# 删除距离最大的N个城市
removed_cities = max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
elif flag == 2:
# 随机删除连续的N个城市
removed_cities = continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
return removed_cities
# 随机插入
def random_insert(x, removed_cities):
insert_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), len(removed_cities))
for i in range(len(insert_index)):
x.insert(insert_index[i], removed_cities[i])
# 贪心插入
def greedy_insert(x, removed_cities):
dis = float('inf')
insert_index = -1
for i in range(len(removed_cities)):
# 寻找插入后的最小总距离
for j in range(len(x) + 1):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
new_x.insert(j, removed_cities[i])
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) < dis:
dis = dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat)
insert_index = j
# 最小位置处插入
x.insert(insert_index, removed_cities[i])
dis = float('inf')
# repair操作
def repair(flag, x, removed_cities):
# 两个repair算子,第一个是随机插入,第二个贪心插入
if flag == 0:
random_insert(x, removed_cities)
elif flag == 1:
greedy_insert(x, removed_cities)
# 选择destroy算子
def select_and_destroy(destroy_w, x, destroy_city_cnt):
# 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子
prob = destroy_w / np.array(destroy_w).sum()
seq = [i for i in range(len(destroy_w))]
destroy_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]
# destroy操作
removed_cities = destroy(destroy_operator, x, destroy_city_cnt)
return x, removed_cities, destroy_operator
# 选择repair算子
def select_and_repair(repair_w, x, removed_cities):
# # 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子
prob = repair_w / np.array(repair_w).sum()
seq = [i for i in range(len(repair_w))]
repair_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]
# repair操作:此处设定repair_operator=1,即只使用贪心策略
repair(1, x, removed_cities)
return x, repair_operator
# ALNS主程序
def calc_by_alns(dist_mat):
# 模拟退火温度
T = 100
# 降温速度
a = 0.97
# destroy的城市数量
destroy_city_cnt = int(len(dist_mat) * 0.1)
# destroy算子的初始权重
destroy_w = [1, 1, 1]
# repair算子的初始权重
repair_w = [1, 1]
# destroy算子的使用次数
destroy_cnt = [0, 0, 0]
# repair算子的使用次数
repair_cnt = [0, 0]
# destroy算子的初始得分
destroy_score = [1, 1, 1]
# repair算子的初始得分
repair_score = [1, 1]
# destroy和repair的挥发系数
lambda_rate = 0.5
# 当前解,第一代,贪心策略生成
removed_cities = [i for i in range(dist_mat.shape[0])]
x = []
repair(1, x, removed_cities)
# 历史最优解解,第一代和当前解相同,注意是深拷贝,此后有变化不影响x,也不会因x的变化而被影响
history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
# 迭代
cur_iter = 0
max_iter = 1000
print(
'cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat), history_best_x))
while cur_iter < max_iter:
# destroy算子
destroyed_x, remove, destroy_operator_index = select_and_destroy(destroy_w, x, destroy_city_cnt)
destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index] += 1
# repair算子
new_x, repair_operator_index = select_and_repair(repair_w, destroyed_x, remove)
repair_cnt[repair_operator_index] += 1
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) <= dis_cal(x, dist_mat):
# 测试解更优,更新当前解
x = new_x
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) <= dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat):
# 测试解为历史最优解,更新历史最优解,并设置最高的算子得分
history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(new_x)
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.5
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.5
else:
# 测试解不是历史最优解,但优于当前解,设置第二高的算子得分
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.2
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.2
else:
if np.random.random() < np.exp((dis_cal(x, dist_mat) - dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat))) / T:
# 当前解优于测试解,但满足模拟退火逻辑,依然更新当前解,设置第三高的算子得分
x = new_x
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.8
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.8
else:
# 当前解优于测试解,也不满足模拟退火逻辑,不更新当前解,设置最低的算子得分
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.5
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.5
# 更新destroy算子的权重
destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] = \
destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \
(1 - lambda_rate) * destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] / destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index]
# 更新repair算子的权重
repair_w[repair_operator_index] = \
repair_w[repair_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \
(1 - lambda_rate) * repair_score[repair_operator_index] / repair_cnt[repair_operator_index]
# 降低温度
T = a * T
# 结束一轮迭代,重置模拟退火初始温度
cur_iter += 1
print(
'cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat), history_best_x))
# 打印ALNS得到的最优解
print(history_best_x)
print(dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat))
if __name__ == '__main__':
original_cities = [['西宁', 101.74, 36.56],
['兰州', 103.73, 36.03],
['银川', 106.27, 38.47],
['西安', 108.95, 34.27],
['郑州', 113.65, 34.76],
['济南', 117, 36.65],
['石家庄', 114.48, 38.03],
['太原', 112.53, 37.87],
['呼和浩特', 111.65, 40.82],
['北京', 116.407526, 39.90403],
['天津', 117.200983, 39.084158],
['沈阳', 123.38, 41.8],
['长春', 125.35, 43.88],
['哈尔滨', 126.63, 45.75],
['上海', 121.473701, 31.230416],
['杭州', 120.19, 30.26],
['南京', 118.78, 32.04],
['合肥', 117.27, 31.86],
['武汉', 114.31, 30.52],
['长沙', 113, 28.21],
['南昌', 115.89, 28.68],
['福州', 119.3, 26.08],
['台北', 121.3, 25.03],
['香港', 114.173355, 22.320048],
['澳门', 113.54909, 22.198951],
['广州', 113.23, 23.16],
['海口', 110.35, 20.02],
['南宁', 108.33, 22.84],
['贵阳', 106.71, 26.57],
['重庆', 106.551556, 29.563009],
['成都', 104.06, 30.67],
['昆明', 102.73, 25.04],
['拉萨', 91.11, 29.97],
['乌鲁木齐', 87.68, 43.77]]
original_cities = pd.DataFrame(original_cities, columns=['城市', '经度', '纬度'])
D = original_cities[['经度', '纬度']].values * math.pi / 180
city_cnt = len(original_cities)
dist_mat = np.zeros((city_cnt, city_cnt))
for i in range(city_cnt):
for j in range(city_cnt):
if i == j:
# 相同城市不允许访问
dist_mat[i][j] = 1000000
else:
# 单位:km
dist_mat[i][j] = 6378.14 * math.acos(
math.cos(D[i][1]) * math.cos(D[j][1]) * math.cos(D[i][0] - D[j][0]) +
math.sin(D[i][1]) * math.sin(D[j][1]))
# ALNS求解TSP
time0 = time.time()
calc_by_alns(dist_mat)
print('使用ALNS求解TSP,耗时: {} s'.format(time.time() - time0))
运行代码后发现,经过不到4s的计算时间,ALNS即可得到全局最优解15614.84。
想了一下,会不会是上述代码中的初始解质量本身比较高,才导致最终的计算效率比较高?目前代码中初始解的计算方案是贪心策略,代码见168到170行。所以把这几行换成
x = [i for i in range(dist_mat.shape[0])]
即初始解只是简单的从小到大排列。然后重新运行代码,发现依然在4秒内就可以得到全局最优解15614.84。
看起来,ALNS的效果还是挺好的。
测试集XQF131
为了进一步评估ALNS的效果,再增加点问题规模。本节使用通用的TSP测试集之一:XQF131。该TSP中包含131个城市点,全局最优解为564。
先尝试调用ortools求解,发现计算了6个小时都没返回优化结果,就放弃继续死磕了。
然后是尝试ALNS,以下是python实现的代码。ALNS的逻辑和上一节保持一致,只是替换了输入数据。
import copy
import math
import time
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 计算TSP总距离
def dis_cal(path, dist_mat):
distance = 0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
distance += dist_mat[path[i]][path[i + 1]]
distance += dist_mat[path[-1]][path[0]]
return distance
# 随机删除N个城市
def random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 随机选择N个城市,并删除
removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), destroy_city_cnt)
for i in removed_index:
removed_cities.append(new_x[i])
x.remove(new_x[i])
return removed_cities
# 删除距离最大的N个城市
def max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 计算顺序距离并排序
dis = []
for i in range(len(new_x) - 1):
dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[i]][new_x[i + 1]])
dis.append(dist_mat[new_x[-1]][new_x[0]])
sorted_index = np.argsort(np.array(dis))
# 删除最大的N个城市
for i in range(destroy_city_cnt):
removed_cities.append(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])
x.remove(new_x[sorted_index[-1 - i]])
return removed_cities
# 随机删除连续的N个城市
def continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
removed_cities = []
# 随机选择N个城市,并删除
removed_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)-destroy_city_cnt), 1)[0]
for i in range(removed_index + destroy_city_cnt, removed_index, -1):
removed_cities.append(new_x[i])
x.remove(new_x[i])
return removed_cities
# destroy操作
def destroy(flag, x, destroy_city_cnt):
# 三个destroy算子,第一个是随机删除N个城市,第二个是删除距离最大的N个城市,第三个是随机删除连续的N个城市
removed_cities = []
if flag == 0:
# 随机删除N个城市
removed_cities = random_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
elif flag == 1:
# 删除距离最大的N个城市
removed_cities = max_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
elif flag == 2:
# 随机删除连续的N个城市
removed_cities = continue_n_destroy(x, destroy_city_cnt)
return removed_cities
# 随机插入
def random_insert(x, removed_cities):
insert_index = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), len(removed_cities))
for i in range(len(insert_index)):
x.insert(insert_index[i], removed_cities[i])
# 贪心插入
def greedy_insert(x, removed_cities):
dis = float('inf')
insert_index = -1
for i in range(len(removed_cities)):
# 寻找插入后的最小总距离
for j in range(len(x) + 1):
new_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
new_x.insert(j, removed_cities[i])
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) < dis:
dis = dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat)
insert_index = j
# 最小位置处插入
x.insert(insert_index, removed_cities[i])
dis = float('inf')
# repair操作
def repair(flag, x, removed_cities):
# 两个repair算子,第一个是随机插入,第二个贪心插入
if flag == 0:
random_insert(x, removed_cities)
elif flag == 1:
greedy_insert(x, removed_cities)
# 选择destroy算子
def select_and_destroy(destroy_w, x, destroy_city_cnt):
# 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子
prob = destroy_w / np.array(destroy_w).sum()
seq = [i for i in range(len(destroy_w))]
destroy_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]
# destroy操作
removed_cities = destroy(destroy_operator, x, destroy_city_cnt)
return x, removed_cities, destroy_operator
# 选择repair算子
def select_and_repair(repair_w, x, removed_cities):
# # 轮盘赌逻辑选择算子
prob = repair_w / np.array(repair_w).sum()
seq = [i for i in range(len(repair_w))]
repair_operator = np.random.choice(seq, size=1, p=prob)[0]
# repair操作:此处设定repair_operator=1,即只使用贪心策略
repair(1, x, removed_cities)
return x, repair_operator
# ALNS主程序
def calc_by_alns(dist_mat):
# 模拟退火温度
T = 100
# 降温速度
a = 0.97
# destroy的城市数量
destroy_city_cnt = int(len(dist_mat) * 0.1)
# destroy算子的初始权重
destroy_w = [1, 1, 1]
# repair算子的初始权重
repair_w = [1, 1]
# destroy算子的使用次数
destroy_cnt = [0, 0, 0]
# repair算子的使用次数
repair_cnt = [0, 0]
# destroy算子的初始得分
destroy_score = [1, 1, 1]
# repair算子的初始得分
repair_score = [1, 1]
# destroy和repair的挥发系数
lambda_rate = 0.5
# 当前解,第一代,贪心策略生成
removed_cities = [i for i in range(dist_mat.shape[0])]
x = []
repair(1, x, removed_cities)
# 历史最优解解,第一代和当前解相同,注意是深拷贝,此后有变化不影响x,也不会因x的变化而被影响
history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(x)
# 迭代
cur_iter = 0
max_iter = 1000
print(
'cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat), history_best_x))
while cur_iter < max_iter:
# destroy算子
destroyed_x, remove, destroy_operator_index = select_and_destroy(destroy_w, x, destroy_city_cnt)
destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index] += 1
# repair算子
new_x, repair_operator_index = select_and_repair(repair_w, destroyed_x, remove)
repair_cnt[repair_operator_index] += 1
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) <= dis_cal(x, dist_mat):
# 测试解更优,更新当前解
x = new_x
if dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat) <= dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat):
# 测试解为历史最优解,更新历史最优解,并设置最高的算子得分
history_best_x = copy.deepcopy(new_x)
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.5
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.5
else:
# 测试解不是历史最优解,但优于当前解,设置第二高的算子得分
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 1.2
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 1.2
else:
if np.random.random() < np.exp((dis_cal(x, dist_mat) - dis_cal(new_x, dist_mat))) / T:
# 当前解优于测试解,但满足模拟退火逻辑,依然更新当前解,设置第三高的算子得分
x = new_x
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.8
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.8
else:
# 当前解优于测试解,也不满足模拟退火逻辑,不更新当前解,设置最低的算子得分
destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] = 0.5
repair_score[repair_operator_index] = 0.5
# 更新destroy算子的权重
destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] = \
destroy_w[destroy_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \
(1 - lambda_rate) * destroy_score[destroy_operator_index] / destroy_cnt[destroy_operator_index]
# 更新repair算子的权重
repair_w[repair_operator_index] = \
repair_w[repair_operator_index] * lambda_rate + \
(1 - lambda_rate) * repair_score[repair_operator_index] / repair_cnt[repair_operator_index]
# 降低温度
T = a * T
# 结束一轮迭代,重置模拟退火初始温度
cur_iter += 1
print(
'cur_iter: {}, best_f: {}, best_x: {}'.format(cur_iter, dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat), history_best_x))
# 打印ALNS得到的最优解
print(history_best_x)
print(dis_cal(history_best_x, dist_mat))
if __name__ == '__main__':
original_cities = [[0, 13],
[0, 26],
[0, 27],
[0, 39],
[2, 0],
[5, 13],
[5, 19],
[5, 25],
[5, 31],
[5, 37],
[5, 43],
[5, 8],
[8, 0],
[9, 10],
[10, 10],
[11, 10],
[12, 10],
[12, 5],
[15, 13],
[15, 19],
[15, 25],
[15, 31],
[15, 37],
[15, 43],
[15, 8],
[18, 11],
[18, 13],
[18, 15],
[18, 17],
[18, 19],
[18, 21],
[18, 23],
[18, 25],
[18, 27],
[18, 29],
[18, 31],
[18, 33],
[18, 35],
[18, 37],
[18, 39],
[18, 41],
[18, 42],
[18, 44],
[18, 45],
[25, 11],
[25, 15],
[25, 22],
[25, 23],
[25, 24],
[25, 26],
[25, 28],
[25, 29],
[25, 9],
[28, 16],
[28, 20],
[28, 28],
[28, 30],
[28, 34],
[28, 40],
[28, 43],
[28, 47],
[32, 26],
[32, 31],
[33, 15],
[33, 26],
[33, 29],
[33, 31],
[34, 15],
[34, 26],
[34, 29],
[34, 31],
[34, 38],
[34, 41],
[34, 5],
[35, 17],
[35, 31],
[38, 16],
[38, 20],
[38, 30],
[38, 34],
[40, 22],
[41, 23],
[41, 32],
[41, 34],
[41, 35],
[41, 36],
[48, 22],
[48, 27],
[48, 6],
[51, 45],
[51, 47],
[56, 25],
[57, 12],
[57, 25],
[57, 44],
[61, 45],
[61, 47],
[63, 6],
[64, 22],
[71, 11],
[71, 13],
[71, 16],
[71, 45],
[71, 47],
[74, 12],
[74, 16],
[74, 20],
[74, 24],
[74, 29],
[74, 35],
[74, 39],
[74, 6],
[77, 21],
[78, 10],
[78, 32],
[78, 35],
[78, 39],
[79, 10],
[79, 33],
[79, 37],
[80, 10],
[80, 41],
[80, 5],
[81, 17],
[84, 20],
[84, 24],
[84, 29],
[84, 34],
[84, 38],
[84, 6],
[107, 27]]
original_cities = np.array(original_cities)
dist_mat = np.zeros((len(original_cities), len(original_cities)))
for i in range(len(original_cities)):
for j in range(len(original_cities)):
if i == j:
dist_mat[i][j] = 100000
else:
dist_mat[i][j] = math.sqrt((original_cities[i][0] - original_cities[j][0]) ** 2 +
(original_cities[i][1] - original_cities[j][1]) ** 2)
# ALNS求解TSP
time0 = time.time()
calc_by_alns(dist_mat)
print('使用ALNS求解TSP,耗时: {} s'.format(time.time() - time0))
运行代码后,可以在3分钟得到589的解,和最优解564之间的gap为4%。对比计算时间和最优解,整体上还是令人满意的。
另外,github上有个大佬也写了ALNS,据称可以在1分钟内得到574的解,和最优解之间的gap仅为2%。他代码的理解成本有些高,我大概学习了一下。部分我觉得不错的思路,已经用在了以上的代码中,建议刚入门ALNS的童鞋可以先看明白我的这篇文章,再去学习他的代码。
相关阅读
差分进化算法:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIyMzc3MjIyMw==&mid=2247484871&idx=1&sn=defa15d216059b478bcd8b5cb2d97880&chksm=e8186e97df6fe781ebf62d1637826c22d675729f794c6675b886d2596b8acc2c4906381b5eba&token=1630762518&lang=zh_CN#rd
蚁群算法:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIyMzc3MjIyMw==&mid=2247484883&idx=1&sn=2a25919d1a20b4783c1d79fdc91ee676&chksm=e8186e83df6fe795f0dc8dcc447f47082720b9e435e6bda0ff262f6575805ee6da2127a4a1e7&token=1630762518&lang=zh_CN#rd
LNS和ALNS:https://backend.orbit.dtu.dk/ws/portalfiles/portal/5293785/Pisinger.pdf
ALNS python版本_1: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40894102/article/details/106794504
ALNS python版本_2: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46651999/article/details/113065064
大佬ALNS实践:https://github.com/N-Wouda/ALNS/blob/master/examples/travelling_salesman_problem.ipynb
菜鸟的车辆路径规划引擎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/344773150
TSP测试集:https://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/vlsi/index.html#XQF131