👨🎓个人主页:研学社的博客
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
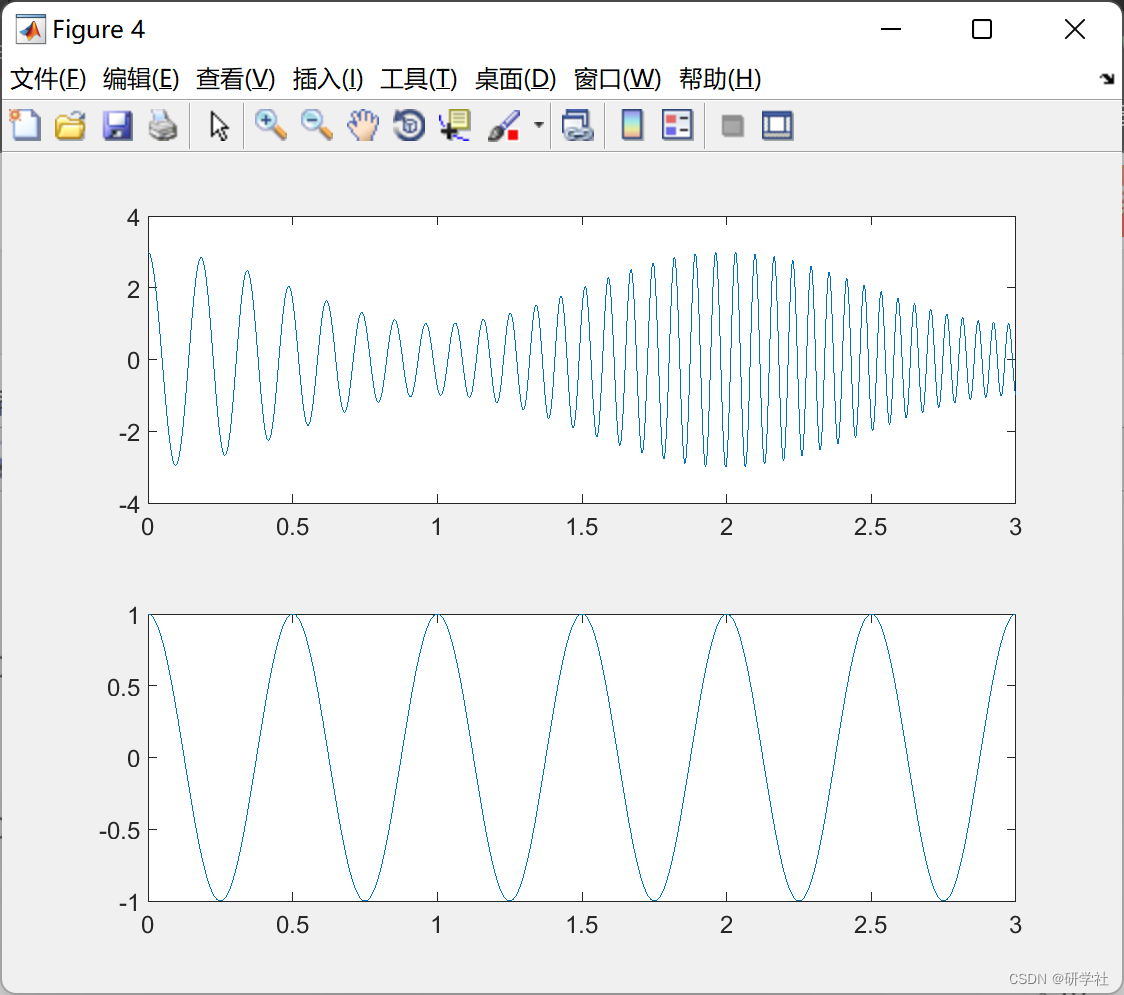
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
💥1 概述
RLMD 是一种改进的局部均值分解,由一组优化策略提供支持。优化策略可以处理LMD中的边界条件、包络估计和筛选停止准则。它同时从混合信号中提取一组单分量信号(称为乘积函数)及其相关的解调信号(即AM信号和FM信号),与其他自适应信号处理方法(如EMD)相比,这是最吸引人的特征。RLMD可用于时频分析。
📚2 运行结果
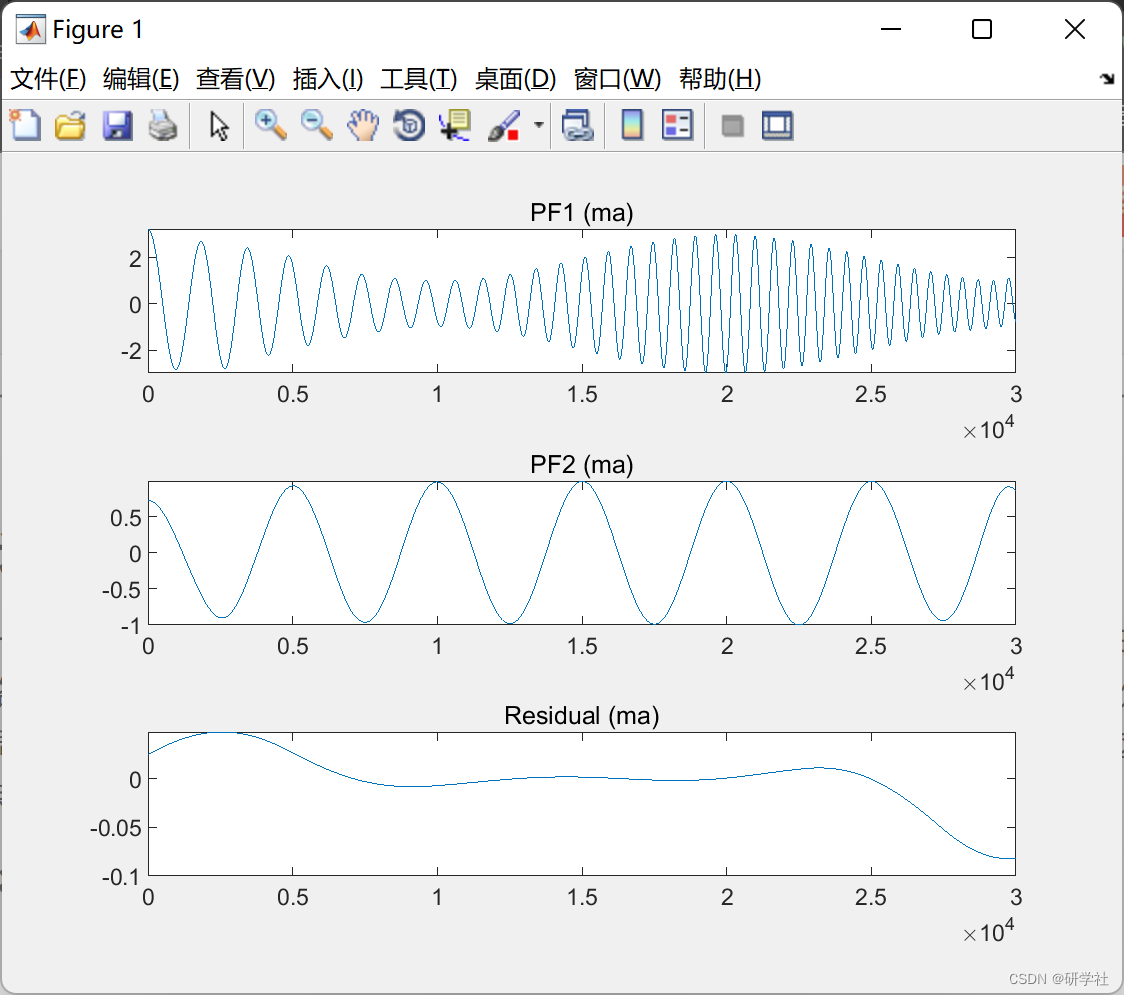
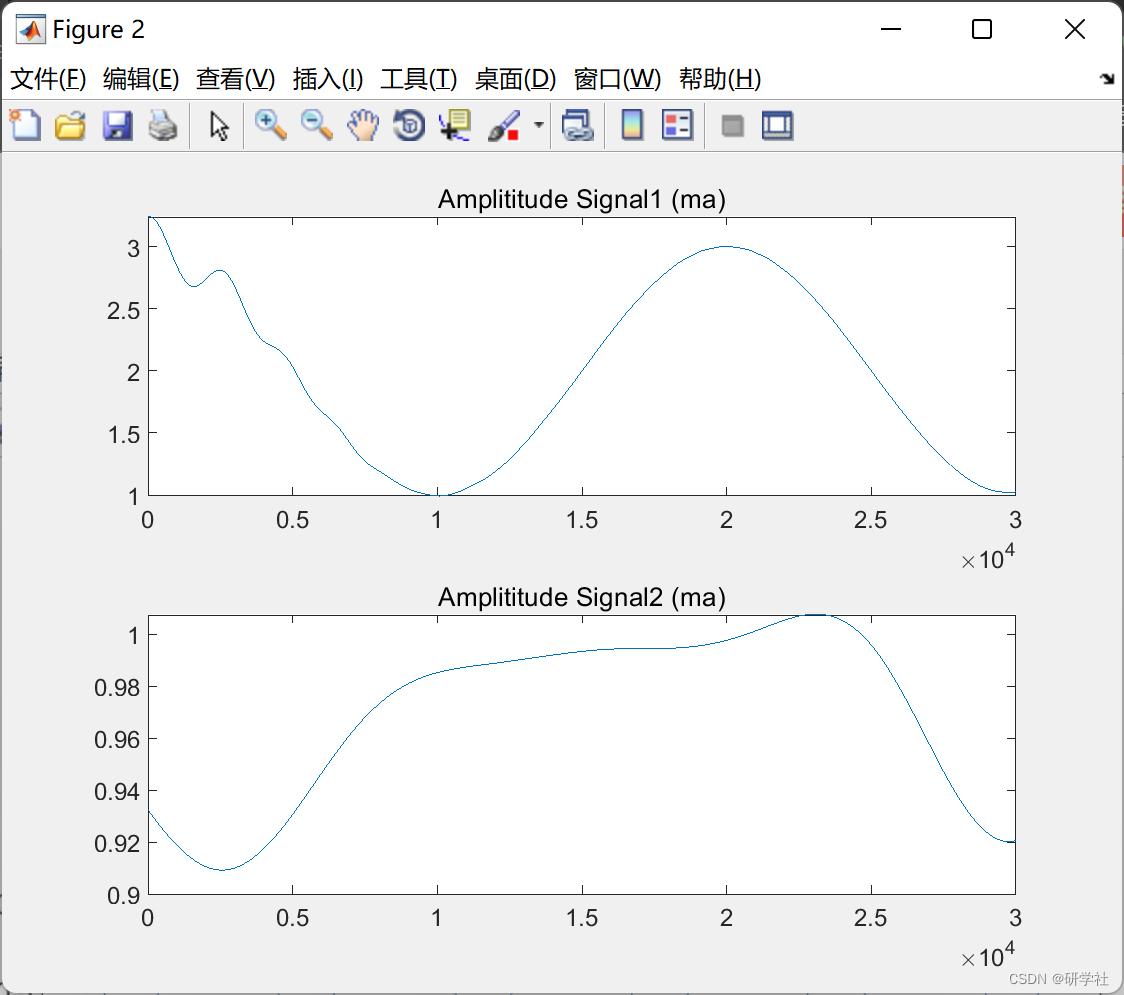
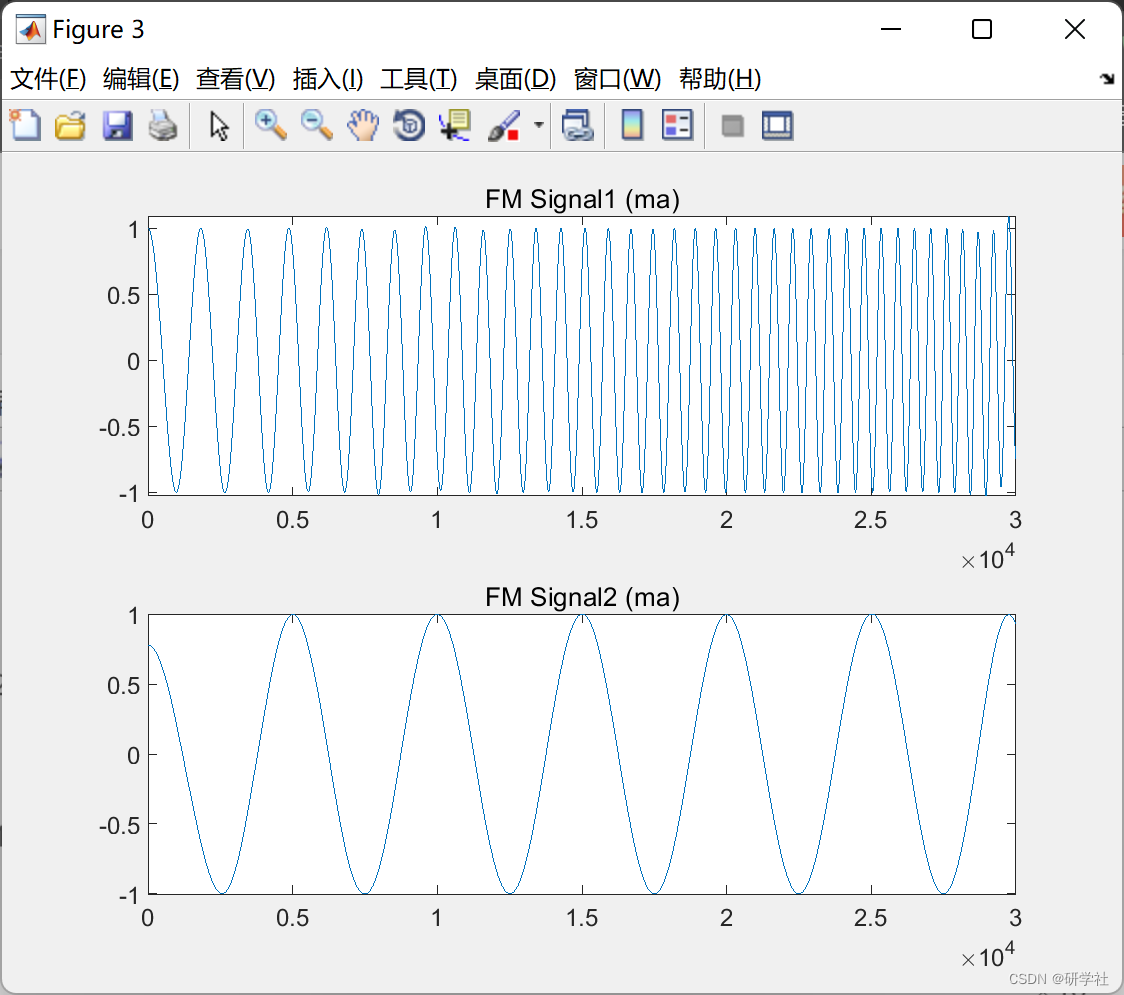
部分代码:
[x, display, stop_thre, sifting_stopping_mode, max_iter, max_pfs, smooth_mode,...
ma_span, ma_iter_mode, extd_r, x_energy, pfs, ams, fms, iterNum, fvs]...
= initial(x,varargin{:});
% Initialize main loop
i = 0;
xs = x; % copy x to xs for sifting process, reserve original input as x.
nx = length(x);
while i < max_pfs && ~stoplmd(xs, x_energy) % outer loop for PF selection
i = i+1;
% initialize variables used in PF sifting loop
a_i = ones(1,nx);
s_j = zeros(max_iter,nx);
a_ij = zeros(max_iter, nx);
% PF sifting iteration loop
j = 0;
stop_sifting = 0;
s = xs;
while j < max_iter && ~stop_sifting % inner loop for sifting process
j = j+1;
[m_j, a_j, n_extr] = lmd_mean_amp(s, smooth_mode, ma_span, ma_iter_mode,...
extd_r);
% force to stop iter if number of extrema of s is smaller than 3.
if n_extr < 3
break;
end
h_j = s-m_j; % remove mean.
s = h_j./a_j; % demodulate amplitude.
a_i = a_i .* a_j; % mulitiply every ai
a_ij(j, :) = a_i;
s_j(j, :) = s;
[stop_sifting,fvs(i,:)] = is_sifting_stopping(a_j, j, fvs(i,:), sifting_stopping_mode, stop_thre);
end % sift iteration loop
switch sifting_stopping_mode
case {'liu'}
[~, opt0] = min(fvs(i,1:j)); % ***Critical Step***
opt_IterNum = min(j, opt0); % in case iteration stop for n_extr<3
% opt_IterNum = min(j-2, opt0);
otherwise
error('No specifications for sifting_stopping_mode.');
end
ams(i, :) = a_ij(opt_IterNum, :); % save each amplitude modulation function in ams.
fms(i, :) = s_j(opt_IterNum, :); % save each pure frequency modulation function in fms.
pfs(i, :) = ams(i, :).*fms(i, :); % gain Product Funcion.
xs = xs-pfs(i, :); % remove PF just obtained from input signal;
iterNum(i) = opt_IterNum; % record the iteration times taken by of each PF sifing.
end % main loop
pfs(i+1, :) = xs; % save residual in the last row of PFs matrix.
ams(i+1:end,:) = []; fms(i+1:end,:) = []; pfs(i+2:end,:) = []; fvs(i+1:end,:) = [];
ort = io(x, pfs);
% Output visualization
if display == 1
lmdplot(pfs, ams, fms, smooth_mode);
end
end
%--------------------------- built-in functions ---------------------------
% initialize signal and options
function [x, display, stop_thre, sifting_stopping_mode, max_iter, max_pfs, smooth_mode,...
ma_span, ma_iter_mode, extd_r, x_energy, pfs, ams, fms, iterNum, fvs]...
= initial(x,varargin)
% option fields(i.e. name)
optn_fields = {'display', 'stop_thre', 'sifting_stopping_mode', 'max_iter',...
'max_pfs', 'smooth_mode', 'ma_span', 'ma_iter_mode','extd_r', 'fix','fix_h'};
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1] 刘志亮, 金亚强, 左明军, 冯志鹏.基于鲁棒局部均值分解的时频表示,用于多分量AM-FM信号分析。机械系统和信号处理。95: 468-487, 2017.
[2] Smith J S. The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2005, 2(5): 443-454.
[3] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin and P. Goncalves. On empirical mode decomposition and its algorithms. IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing NSIP-03, Grado (I), June 2003













![[hadoop全分布部署]虚拟机Hadoop集群配置/etc/hosts、配置无密码登录(SSH)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8e97f2ac585d4b73875659ddc3ac4de4.png)