一、简介
1、缓存介绍
Spring 从 3.1 开始就引入了对 Cache 的支持。定义了 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术。并支持使用 JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们的开发。
其使用方法和原理都类似于 Spring 对事务管理的支持。Spring Cache 是作用在方法上的,其核心思想是,当我们在调用一个缓存方法时会把该方法参数和返回结果作为一个键值对存在缓存中。
2、Cache 和 CacheManager 接口说明
- Cache 接口包含缓存的各种操作集合,你操作缓存就是通过这个接口来操作的。
- Cache 接口下 Spring 提供了各种 xxxCache 的实现,比如:RedisCache、EhCache、ConcurrentMapCache
- CacheManager 定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的 Cache。这些 Cache 存在于 CacheManager 的上下文中。
小结:
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring 会检查指定参数的指定目标方法是否已经被调用过,如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
二、@Cacheable 注解使用详细介绍
1、缓存使用步骤
@Cacheable 这个注解,用它就是为了使用缓存的。所以我们可以先说一下缓存的使用步骤:
1、开启基于注解的缓存,使用 @EnableCaching 标识在 SpringBoot 的主启动类(或配置类)上。
2、标注缓存注解即可
① 第一步:开启基于注解的缓存,使用 @EnableCaching 标注在 springboot 主启动类上
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching/**开启基于注解的缓存*/
@Slf4j
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
log.info("<<=================== 启动成功 ==================>>");
}
}
② 第二步:标注缓存注解
@Cacheable(value = "test",key = "#id")
public String test(Integer id){
System.out.println("经过这里=======>");
return "这是测试"+id;
}
注:这里使用 @Cacheable 注解就可以将运行结果缓存,以后查询相同的数据,直接从缓存中取,不需要调用方法,若数据过期,需要调用方法查询结果返回并缓存
2、常用属性说明
下面介绍一下 @Cacheable 这个注解常用的几个属性:
- cacheNames/value :用来指定缓存组件的名字
- key :缓存数据时使用的 key,可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值。(这个 key 你可以使用 spEL 表达式来编写)
- keyGenerator :key 的生成器。 key 和 keyGenerator 二选一使用
- cacheManager :可以用来指定缓存管理器。从哪个缓存管理器里面获取缓存。
- condition :可以用来指定符合条件的情况下才缓存
- unless :否定缓存。当 unless 指定的条件为 true ,方法的返回值就不会被缓存。当然你也可以获取到结果进行判断。(通过 #result 获取方法结果)
- sync :是否使用异步模式。
- cacheNames/value
用来指定缓存组件的名字,将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,可以是数组的方式,支持指定多个缓存。 - key
缓存数据时使用的 key。默认使用的是方法参数的值。可以使用 spEL 表达式去编写 - keyGenerator
key 的生成器,可以自己指定 key 的生成器,通过这个生成器来生成 key
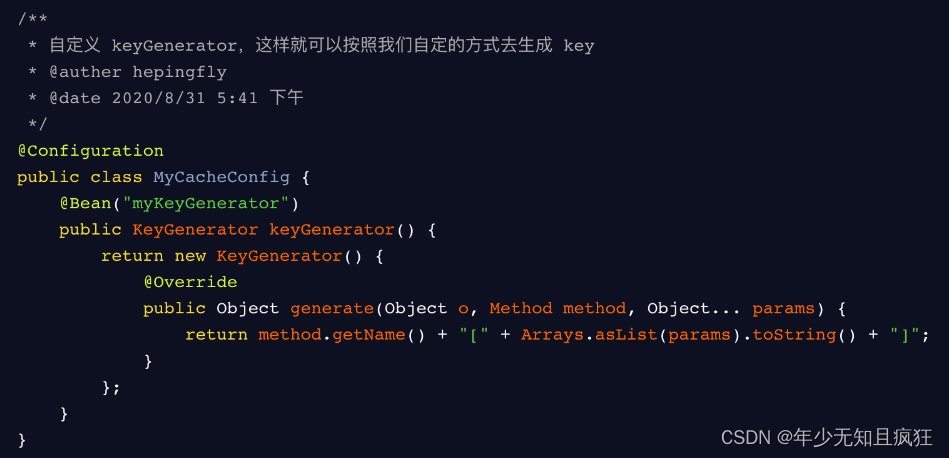
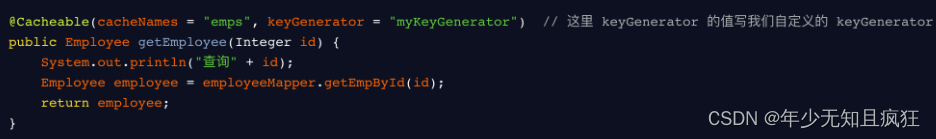
这样放入缓存中的 key 的生成规则就按照你自定义的 keyGenerator 来生成。不过需要注意的是:
@Cacheable 的属性,key 和 keyGenerator 使用的时候,一般二选一。 - condition
符合条件的情况下才缓存。方法返回的数据要不要缓存,可以做一个动态判断。
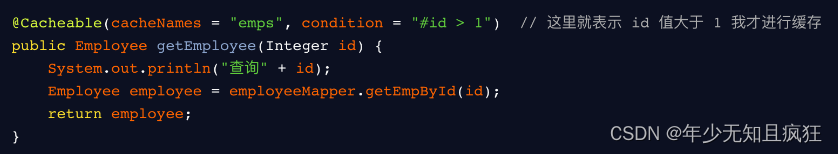
- unless
否定缓存。当 unless 指定的条件为 true ,方法的返回值就不会被缓存。
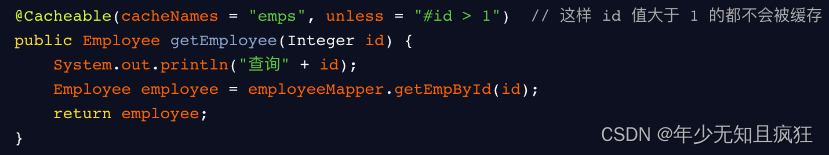
- sync
是否使用异步模式。默认是方法执行完,以同步的方式将方法返回的结果存在缓存中。
前面说过,缓存的 key 支持使用 spEL 表达式去编写,下面总结一下使用 spEL 去编写 key 可以用的一些元数据:
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| methodName | 当前方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | 当前方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | 当前被调用的对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | 当前被调用的对象的class | #root.targetClass |
| args | 当前方法参数组成的数组 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | 当前被调用的方法使用的Cache | #root.caches[0].name |
3、@CachePut和@CacheEvict 注解使用
- @CachePut
将方法返回值存入到缓存中,一般情况下是用在更新操作中,并于Cacheable与CacheEvict配合使用 - @CacheEvict
清除缓存值,一般用在删除或更新操作中,并于Cacheable与CachePut配合使用。并且在@CacheEvict注解中,多了两个参数:
- allEntries - 清除当前value下的所有缓存
- beforeInvocation - 在方法执行前清除缓存
示例代码示例如下:
/**查询,加载缓存*/
@Cacheable(value = "c", key = "123")
public String hello(String name) {
System.out.println("name - " + name);
return "hello " + name;
}
/**更新缓存*/
@CachePut(value = "c", key = "123")
public String put() {
return "hello put";
}
/**删除缓存*/
@CacheEvict(value = "c", key = "123")
public String evict() {
return "hello put";
}
三、配置类(结合Redis作为缓存)
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* 缓存配置类
* */
@EnableCaching /**开启缓存注解*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
/**解决查询缓存转换异常的问题*/
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
/**配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)*/
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))/**设置缓存默认过期时间600秒*/
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
}
}
pom.xml需要Redis依赖:
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
</dependency>
纯属个人经验,喜欢的可以点赞关注,后续见!!!




![[量化投资-学习笔记011]Python+TDengine从零开始搭建量化分析平台-MACD金死叉策略回测](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/675ed52caf504b43a411a08574e48704.png#pic_center)