文章目录
- 前言
- 一、雷达检测
- 二、Matlab 仿真
- 1、高斯和瑞利概率密度函数
- ①、MATLAB 源码
- ②、仿真
- 2、归一化门限相对虚警概率的曲线
- ①、MATLAB 源码
- ②、仿真
- 3、检测概率相对于单个脉冲 SNR 的关系曲线
- ①、MATLAB 源码
- ②、仿真
- 4、改善因子和积累损失相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
- ①、改善因子相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- ②、积累损失相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- 5、起伏目标检测概率
- ①、Swerling V 型目标的检测
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- ②、Swerling Ⅰ 型目标的检测
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- 3)MATLAB 源码
- 4)仿真
- ③、Swerling Ⅱ 型目标的检测
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- ④、Swerling Ⅲ 型目标的检测
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- ⑤、Swerling Ⅳ 型目标的检测
- 1)MATLAB 源码
- 2)仿真
- 三、资源自取
前言
本文对雷达检测的内容以思维导图的形式呈现,有关仿真部分进行了讲解实现。
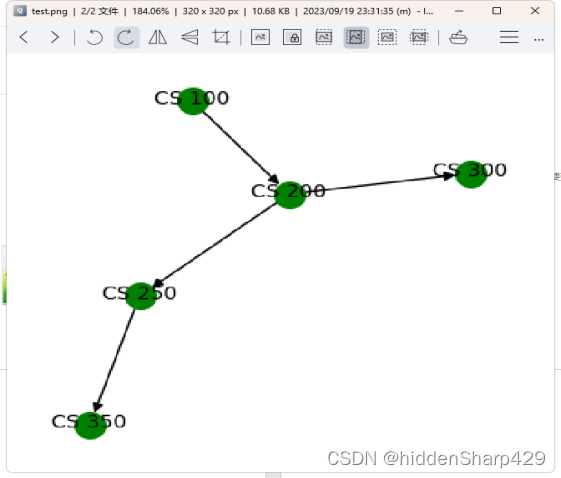
一、雷达检测
思维导图如下图所示,如有需求请到文章末尾端自取。

二、Matlab 仿真
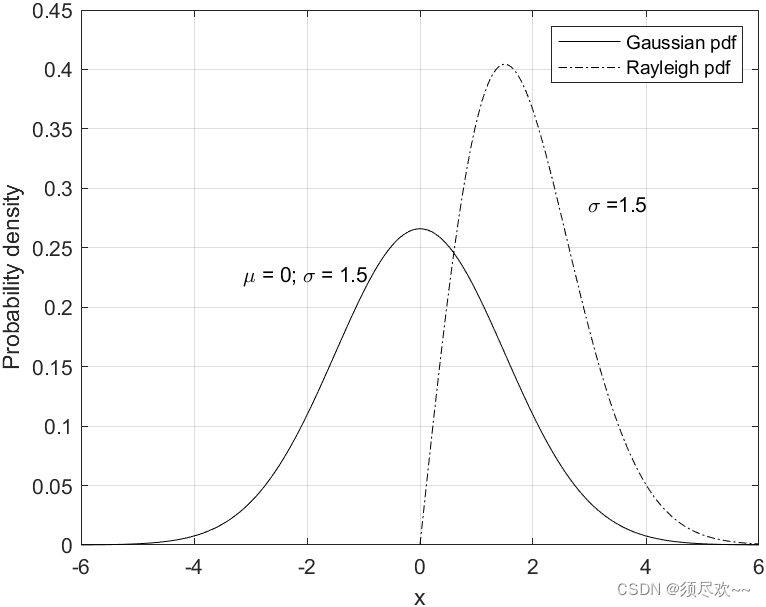
1、高斯和瑞利概率密度函数
瑞利概率密度函数: f ( x ) = x σ 2 e − x 2 2 σ 2 f(x)=\frac{x}{\sigma^2}e^{-\frac{x^2}{2\sigma^2}} f(x)=σ2xe−2σ2x2
高斯概率密度函数: f ( x ) ≈ 1 2 π σ 2 e − ( x − μ ) 2 2 σ 2 f(x) \approx \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}e^{-\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}} f(x)≈2πσ21e−2σ2(x−μ)2
x x x 是变量, μ \mu μ 是均值, σ \sigma σ 是方差
①、MATLAB 源码
clear all
close all
xg = linspace(-6,6,1500); % randowm variable between -4 and 4
xr = linspace(0,6,1500); % randowm variable between 0 and 8
mu = 0; % zero mean Gaussain pdf mean
sigma = 1.5; % standard deviation (sqrt(variance)
ynorm = normpdf(xg,mu,sigma); % use MATLAB funtion normpdf
yray = raylpdf(xr,sigma); % use MATLAB function raylpdf
plot(xg,ynorm,'k',xr,yray,'k-.');
grid
legend('Gaussian pdf','Rayleigh pdf')
xlabel('x')
ylabel('Probability density')
gtext('\mu = 0; \sigma = 1.5')
gtext('\sigma =1.5')
②、仿真
2、归一化门限相对虚警概率的曲线
虚警概率: P f a = e − V T 2 2 ψ 2 P_{fa}=e^{\frac{-V_T^2}{2\psi^2}} Pfa=e2ψ2−VT2
门限电压: V T = 2 ψ 2 l n ( 1 P f a ) V_T=\sqrt{2\psi^2ln(\frac{1}{P_{fa}})} VT=2ψ2ln(Pfa1)
注: V T V_T VT 为门限电压, ψ 2 \psi^2 ψ2 为方差
①、MATLAB 源码
close all
clear all
logpfa = linspace(.01,250,1000);
var = 10.^(logpfa ./ 10.0);
vtnorm = sqrt( log (var));
semilogx(logpfa, vtnorm,'k')
grid
②、仿真
横坐标为
l
o
g
(
1
/
P
f
a
)
log(1/P_{fa})
log(1/Pfa)
纵坐标为
V
T
2
ψ
2
\frac{V_T}{\sqrt{2\psi^2}}
2ψ2VT
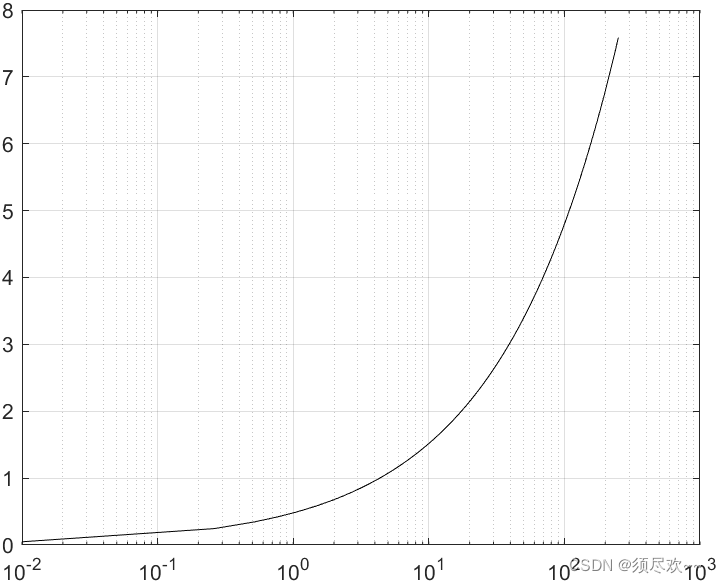
从图中可以明显看出, P f a P_{fa} Pfa 对门限值的小变化非常敏感
3、检测概率相对于单个脉冲 SNR 的关系曲线
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
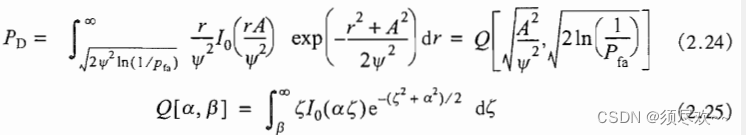
Q
Q
Q 称为
M
a
r
c
u
m
Q
Marcum Q
MarcumQ 函数。
①、MATLAB 源码
marcumsq.m
function PD = marcumsq (a,b)
% This function uses Parl's method to compute PD
max_test_value = 5000.;
if (a < b)
alphan0 = 1.0;
dn = a / b;
else
alphan0 = 0.;
dn = b / a;
end
alphan_1 = 0.;
betan0 = 0.5;
betan_1 = 0.;
D1 = dn;
n = 0;
ratio = 2.0 / (a * b);
r1 = 0.0;
betan = 0.0;
alphan = 0.0;
while betan < 1000.,
n = n + 1;
alphan = dn + ratio * n * alphan0 + alphan;
betan = 1.0 + ratio * n * betan0 + betan;
alphan_1 = alphan0;
alphan0 = alphan;
betan_1 = betan0;
betan0 = betan;
dn = dn * D1;
end
PD = (alphan0 / (2.0 * betan0)) * exp( -(a-b)^2 / 2.0);
if ( a >= b)
PD = 1.0 - PD;
end
return
prob_snr1.m
% This program is used to produce Fig. 2.4
close all
clear all
for nfa = 2:2:12
b = sqrt(-2.0 * log(10^(-nfa)));
index = 0;
hold on
for snr = 0:.1:18
index = index +1;
a = sqrt(2.0 * 10^(.1*snr));
pro(index) = marcumsq(a,b);
end
x = 0:.1:18;
set(gca,'ytick',[.1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .75 .8 .85 .9 ...
.95 .9999])
set(gca,'xtick',[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18])
loglog(x, pro,'k');
end
hold off
xlabel ('Single pulse SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
grid
②、仿真
检测概率相对于单个脉冲 S N R SNR SNR 的关系曲线对于 P f a P_{fa} Pfa的个数值:
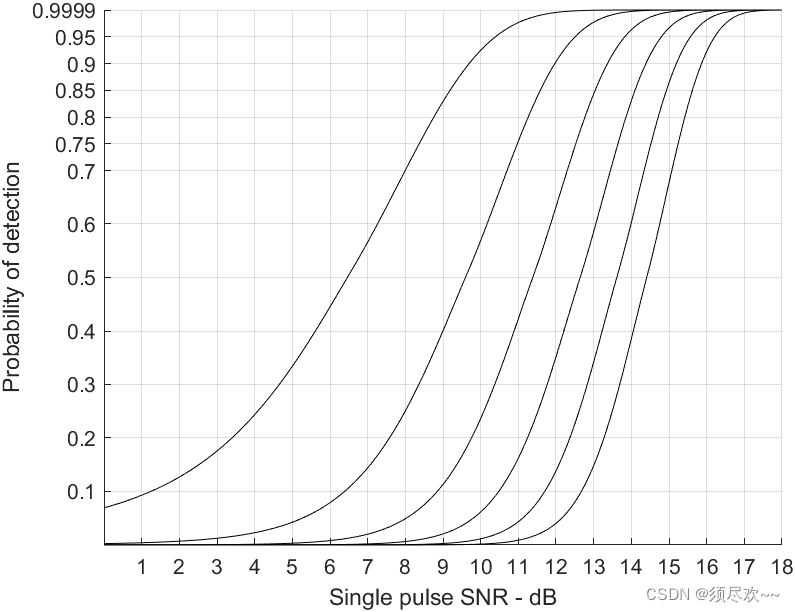
6 条曲线的
P
f
a
P_{fa}
Pfa 从左到右依次是
1
0
−
2
,
1
0
−
4
,
1
0
−
6
,
1
0
−
8
,
1
0
−
10
,
1
0
−
12
10^{-2},10^{-4},10^{-6},10^{-8},10^{-10},10^{-12}
10−2,10−4,10−6,10−8,10−10,10−12,可以看到随着 SNR 信噪比的增加,检测概率逐渐增大,此外,虚警概率越小,随着信噪比的增加,检测概率增加的越快。
4、改善因子和积累损失相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
I ( n p ) I(n_p) I(np) 称为积累改善因子
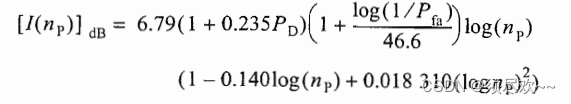

①、改善因子相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
1)MATLAB 源码
improv_fac.m
function impr_of_np = improv_fac (np, pfa, pd)
% This function computes the non-coherent integration improvment
% factor using the empirical formula defind in Eq. (2.48)
fact1 = 1.0 + log10( 1.0 / pfa) / 46.6;
fact2 = 6.79 * (1.0 + 0.253 * pd);
fact3 = 1.0 - 0.14 * log10(np) + 0.0183 * (log10(np))^2;
impr_of_np = fact1 * fact2 * fact3 * log10(np);
return
fig2_6a.m
% This program is used to produce Fig. 2.6a
% It uses the function "improv_fac"
clear all
close all
pfa1 = 1.0e-2;
pfa2 = 1.0e-6;
pfa3 = 1.0e-10;
pfa4 = 1.0e-13;
pd1 = .5;
pd2 = .8;
pd3 = .95;
pd4 = .999;
index = 0;
for np = 1:1:1000
index = index + 1;
I1(index) = improv_fac (np, pfa1, pd1);
I2(index) = improv_fac (np, pfa2, pd2);
I3(index) = improv_fac (np, pfa3, pd3);
I4(index) = improv_fac (np, pfa4, pd4);
end
np = 1:1:1000;
semilogx (np, I1, 'k', np, I2, 'k--', np, I3, 'k-.', np, I4, 'k:')
%set (gca,'xtick',[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 20 30 100]);
xlabel ('Number of pulses');
ylabel ('Improvement factor in dB')
legend ('pd=.5, nfa=e+2','pd=.8, nfa=e+6','pd=.95, nfa=e+10','pd=.999, nfa=e+13');
grid
2)仿真
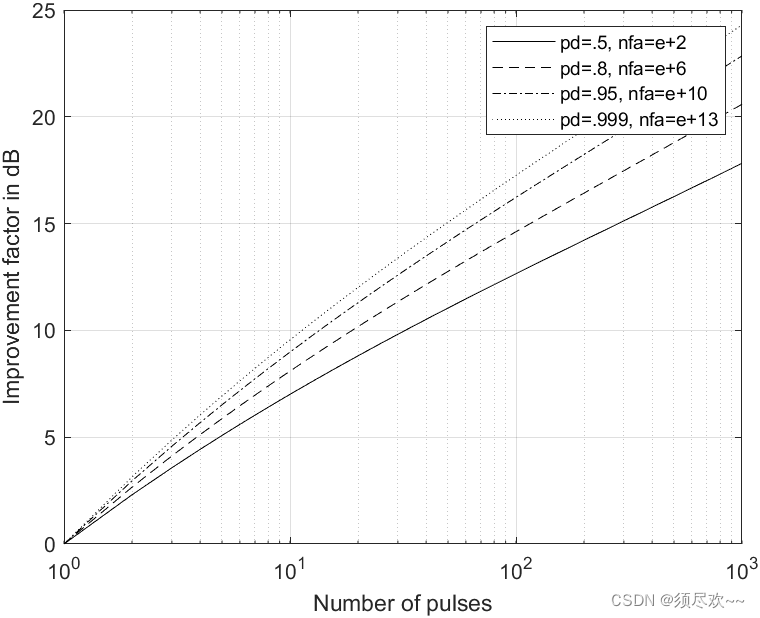
可以看到随着非相干积累脉冲数的增多,改善因子逐渐增大;在同一脉冲数的情况下,随着检测概率和虚警概率的增大,则改善因子也会逐渐增大
②、积累损失相对于非相干积累脉冲数的关系曲线
1)MATLAB 源码
% This program is used to produce Fig. 2.6b
% It uses the function "improv_fac".
clear all
close all
pfa1 = 1.0e-12;
pfa2 = 1.0e-12;
pfa3 = 1.0e-12;
pfa4 = 1.0e-12;
pd1 = .5;
pd2 = .8;
pd3 = .95;
pd4 = .99;
index = 0;
for np = 1:1:1000
index = index+1;
I1 = improv_fac (np, pfa1, pd1);
i1 = 10.^(0.1*I1);
L1(index) = -1*10*log10(i1 ./ np);
I2 = improv_fac (np, pfa2, pd2);
i2 = 10.^(0.1*I2);
L2(index) = -1*10*log10(i2 ./ np);
I3 = improv_fac (np, pfa3, pd3);
i3 = 10.^(0.1*I3);
L3(index) = -1*10*log10(i3 ./ np);
I4 = improv_fac (np, pfa4, pd4);
i4 = 10.^(0.1*I4);
L4 (index) = -1*10*log10(i4 ./ np);
end
np = 1:1:1000;
semilogx (np, L1, 'k', np, L2, 'k--', np, L3, 'k-.', np, L4, 'k:')
axis tight
xlabel ('Number of pulses');
ylabel ('Integration loss - dB')
legend ('pd=.5, nfa=e+12','pd=.8, nfa=e+12','pd=.95, nfa=e+12','pd=.99, nfa=e+12');
grid
2)仿真

可以看到随着非相干积累脉冲数的增多,积累损失逐渐增大;在同一脉冲数的情况下,随着检测概率的增大,则积累损失会逐渐减小
5、起伏目标检测概率
①、Swerling V 型目标的检测
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
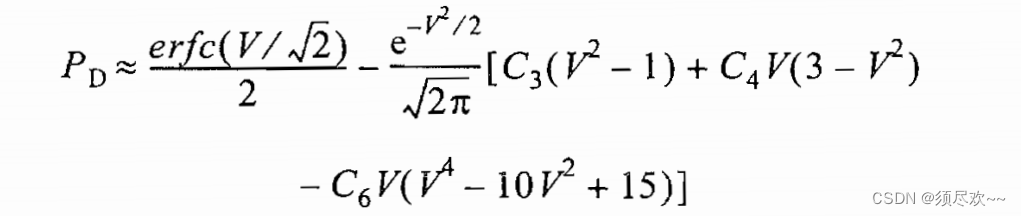
n p = 1 , 10 n_p=1,10 np=1,10 时检测概率相对于 SNR 的曲线
1)MATLAB 源码
pd_swerling5.m
function pd = pd_swerling5 (input1, indicator, np, snrbar)
% This function is used to calculate the probability of detection
% for Swerling 5 or 0 targets for np>1.
if(np == 1)
'Stop, np must be greater than 1'
return
end
format long
snrbar = 10.0.^(snrbar./10.);
eps = 0.00000001;
delmax = .00001;
delta =10000.;
% Calculate the threshold Vt
if (indicator ~=1)
nfa = input1;
pfa = np * log(2) / nfa;
else
pfa = input1;
nfa = np * log(2) / pfa;
end
sqrtpfa = sqrt(-log10(pfa));
sqrtnp = sqrt(np);
vt0 = np - sqrtnp + 2.3 * sqrtpfa * (sqrtpfa + sqrtnp - 1.0);
vt = vt0;
while (abs(delta) >= vt0)
igf = incomplete_gamma(vt0,np);
num = 0.5^(np/nfa) - igf;
temp = (np-1) * log(vt0+eps) - vt0 - factor(np-1);
deno = exp(temp);
vt = vt0 + (num / (deno+eps));
delta = abs(vt - vt0) * 10000.0;
vt0 = vt;
end
% Calculate the Gram-Chrlier coeffcients
temp1 = 2.0 .* snrbar + 1.0;
omegabar = sqrt(np .* temp1);
c3 = -(snrbar + 1.0 / 3.0) ./ (sqrt(np) .* temp1.^1.5);
c4 = (snrbar + 0.25) ./ (np .* temp1.^2.);
c6 = c3 .* c3 ./2.0;
V = (vt - np .* (1.0 + snrbar)) ./ omegabar;
Vsqr = V .*V;
val1 = exp(-Vsqr ./ 2.0) ./ sqrt( 2.0 * pi);
val2 = c3 .* (V.^2 -1.0) + c4 .* V .* (3.0 - V.^2) -...
c6 .* V .* (V.^4 - 10. .* V.^2 + 15.0);
q = 0.5 .* erfc (V./sqrt(2.0));
pd = q - val1 .* val2;
fig2_9.m
close all
clear all
pfa = 1e-9;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
b = sqrt(-2.0 * log(pfa));
index = 0;
for snr = 0:.1:20
index = index +1;
a = sqrt(2.0 * 10^(.1*snr));
pro(index) = marcumsq(a,b);
prob205(index) = pd_swerling5 (pfa, 1, 10, snr);
end
x = 0:.1:20;
plot(x, pro,'k',x,prob205,'k:');
axis([0 20 0 1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('np = 1','np = 10')
grid
2)仿真
n
p
=
1
,
10
n_p=1,10
np=1,10 时检测概率相对于 SNR 的曲线
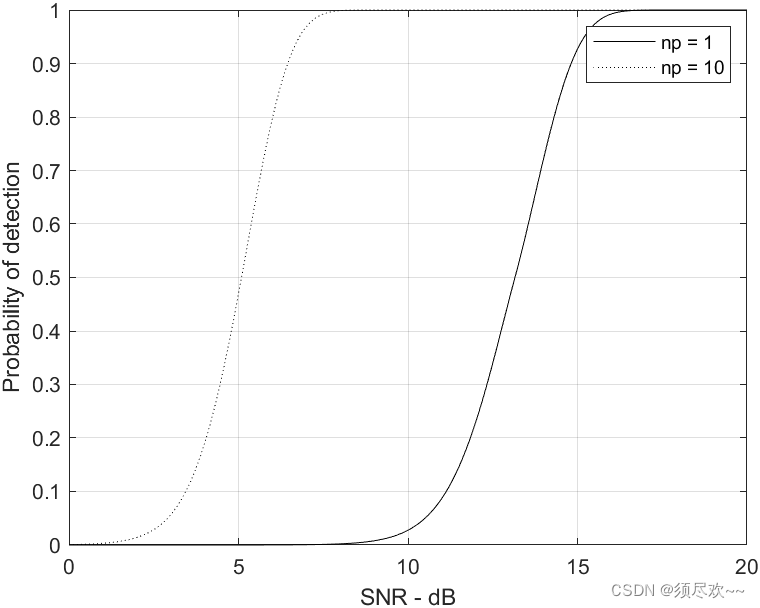
注意到为了获得同样的检概率,10 个脉冲非相干积累比单个脉冲需要更少的 SNR。
②、Swerling Ⅰ 型目标的检测
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
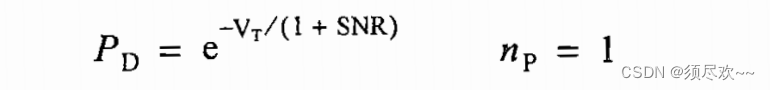
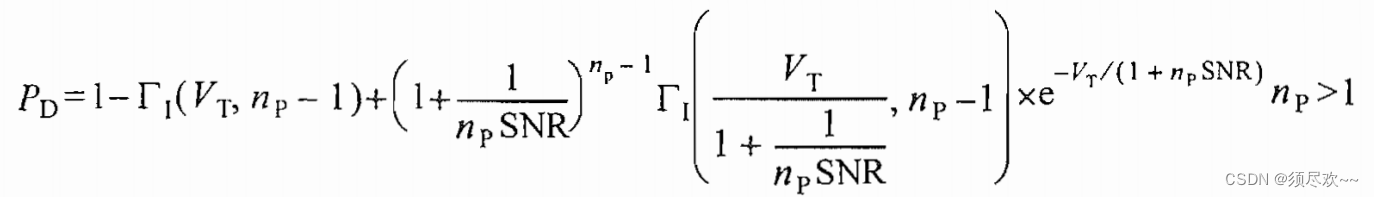
1)MATLAB 源码
pd_swerling2.m
function pd = pd_swerling2 (nfa, np, snrbar)
% This function is used to calculate the probability of detection
% for Swerling 2 targets.
format long
snrbar = 10.0^(snrbar/10.);
eps = 0.00000001;
delmax = .00001;
delta =10000.;
% Calculate the threshold Vt
pfa = np * log(2) / nfa;
sqrtpfa = sqrt(-log10(pfa));
sqrtnp = sqrt(np);
vt0 = np - sqrtnp + 2.3 * sqrtpfa * (sqrtpfa + sqrtnp - 1.0);
vt = vt0;
while (abs(delta) >= vt0)
igf = incomplete_gamma(vt0,np);
num = 0.5^(np/nfa) - igf;
temp = (np-1) * log(vt0+eps) - vt0 - factor(np-1);
deno = exp(temp);
vt = vt0 + (num / (deno+eps));
delta = abs(vt - vt0) * 10000.0;
vt0 = vt;
end
if (np <= 50)
temp = vt / (1.0 + snrbar);
pd = 1.0 - incomplete_gamma(temp,np);
return
else
temp1 = snrbar + 1.0;
omegabar = sqrt(np) * temp1;
c3 = -1.0 / sqrt(9.0 * np);
c4 = 0.25 / np;
c6 = c3 * c3 /2.0;
V = (vt - np * temp1) / omegabar;
Vsqr = V *V;
val1 = exp(-Vsqr / 2.0) / sqrt( 2.0 * pi);
val2 = c3 * (V^2 -1.0) + c4 * V * (3.0 - V^2) - ...
c6 * V * (V^4 - 10. * V^2 + 15.0);
q = 0.5 * erfc (V/sqrt(2.0));
pd = q - val1 * val2;
end
fig2_10.m
clear all
pfa = 1e-9;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
b = sqrt(-2.0 * log(pfa));
index = 0;
for snr = 0:.01:22
index = index +1;
a = sqrt(2.0 * 10^(.1*snr));
pro(index) = marcumsq(a,b);
prob(index) = pd_swerling2 (nfa, 1, snr);
end
x = 0:.01:22;
%figure(10)
plot(x, pro,'k',x,prob,'k:');
axis([2 22 0 1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('Swerling V','Swerling I')
grid
2)仿真
检测概率相对于 SNR,单个脉冲,
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
9
P_{fa}=10^{-9}
Pfa=10−9:

可以看出为了获得与无起伏情况相同的
P
D
P_D
PD,在有起伏时,需要更高的 SNR。
3)MATLAB 源码
pd_swerling1.m
function pd = pd_swerling1 (nfa, np, snrbar)
% This function is used to calculate the probability of detection
% for Swerling 1 targets.
format long
snrbar = 10.0^(snrbar/10.);
eps = 0.00000001;
delmax = .00001;
delta =10000.;
% Calculate the threshold Vt
pfa = np * log(2) / nfa;
sqrtpfa = sqrt(-log10(pfa));
sqrtnp = sqrt(np);
vt0 = np - sqrtnp + 2.3 * sqrtpfa * (sqrtpfa + sqrtnp - 1.0);
vt = vt0;
while (abs(delta) >= vt0)
igf = incomplete_gamma(vt0,np);
num = 0.5^(np/nfa) - igf;
temp = (np-1) * log(vt0+eps) - vt0 - factor(np-1);
deno = exp(temp);
vt = vt0 + (num / (deno+eps));
delta = abs(vt - vt0) * 10000.0;
vt0 = vt;
end
if (np == 1)
temp = -vt / (1.0 + snrbar);
pd = exp(temp);
return
end
temp1 = 1.0 + np * snrbar;
temp2 = 1.0 / (np *snrbar);
temp = 1.0 + temp2;
val1 = temp^(np-1.);
igf1 = incomplete_gamma(vt,np-1);
igf2 = incomplete_gamma(vt/temp,np-1);
pd = 1.0 - igf1 + val1 * igf2 * exp(-vt/temp1);
fig2_11ab.m
clear all
pfa = 1e-11;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
index = 0;
for snr = -10:.5:30
index = index +1;
prob1(index) = pd_swerling1 (nfa, 1, snr);
prob10(index) = pd_swerling1 (nfa, 10, snr);
prob50(index) = pd_swerling1 (nfa, 50, snr);
prob100(index) = pd_swerling1 (nfa, 100, snr);
end
x = -10:.5:30;
plot(x, prob1,'k',x,prob10,'k:',x,prob50,'k--', ...
x, prob100,'k-.');
axis([-10 30 0 1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('np = 1','np = 10','np = 50','np = 100')
grid
4)仿真
检测概率相对于 SNR,Swerling Ⅰ,
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
8
P_{fa}=10^{-8}
Pfa=10−8
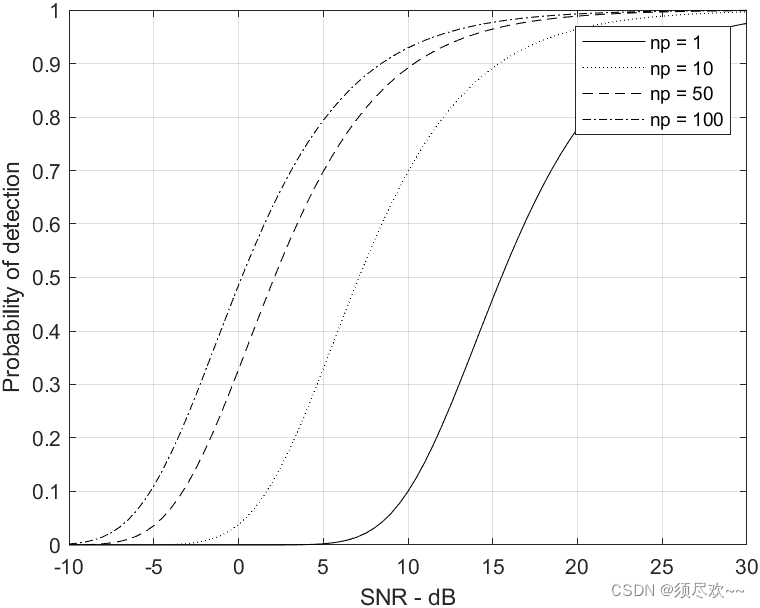
上图显示了
n
p
=
1
,
10
,
50
,
100
n_p=1,10,50,100
np=1,10,50,100 时,检测概率相对于 SNR 的曲线,其中
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
8
P_{fa}=10^{-8}
Pfa=10−8,可以看到
n
p
n_p
np 越大,那么达到同一检测概率的 SNR 越小。
③、Swerling Ⅱ 型目标的检测
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
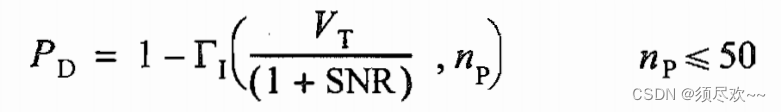
当
n
p
>
50
n_p > 50
np>50 时:
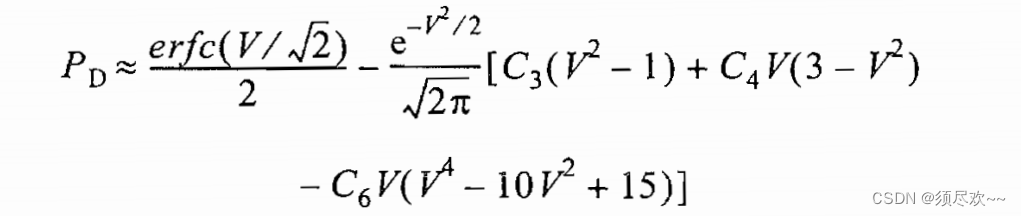
此时:
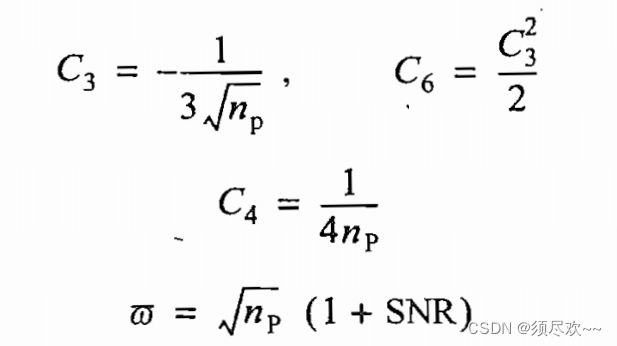
1)MATLAB 源码
fig2_12.m
clear all
pfa = 1e-10;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
index = 0;
for snr = -10:.5:30
index = index +1;
prob1(index) = pd_swerling2 (nfa, 1, snr);
prob10(index) = pd_swerling2 (nfa, 10, snr);
prob50(index) = pd_swerling2 (nfa, 50, snr);
prob100(index) = pd_swerling2 (nfa, 100, snr);
end
x = -10:.5:30;
plot(x, prob1,'k',x,prob10,'k:',x,prob50,'k--', ...
x, prob100,'k-.');
axis([-10 30 0 1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('np = 1','np = 10','np = 50','np = 100')
grid
2)仿真
检测概率相对于 SNR,Swerling Ⅱ,
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
10
P_{fa}=10^{-10}
Pfa=10−10

上图显示了当
n
p
=
1
,
10
,
50
,
100
n_p=1,10,50,100
np=1,10,50,100 时,检测概率作为 SNR 函数的曲线,其中
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
10
P_{fa}=10^{-10}
Pfa=10−10
④、Swerling Ⅲ 型目标的检测
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
n
p
=
1
,
2
n_p=1,2
np=1,2 时:

n
p
>
2
n_p>2
np>2 时:
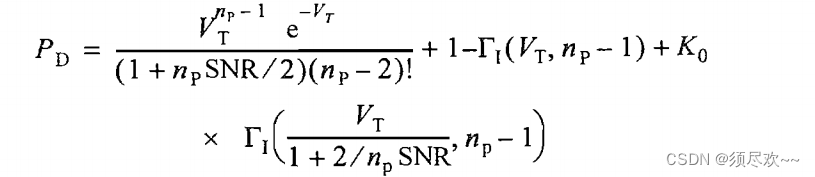
1)MATLAB 源码
pd_swerling3.m
function pd = pd_swerling3 (nfa, np, snrbar)
% This function is used to calculate the probability of detection
% for Swerling 2 targets.
format long
snrbar = 10.0^(snrbar/10.);
eps = 0.00000001;
delmax = .00001;
delta =10000.;
% Calculate the threshold Vt
pfa = np * log(2) / nfa;
sqrtpfa = sqrt(-log10(pfa));
sqrtnp = sqrt(np);
vt0 = np - sqrtnp + 2.3 * sqrtpfa * (sqrtpfa + sqrtnp - 1.0);
vt = vt0;
while (abs(delta) >= vt0)
igf = incomplete_gamma(vt0,np);
num = 0.5^(np/nfa) - igf;
temp = (np-1) * log(vt0+eps) - vt0 - factor(np-1);
deno = exp(temp);
vt = vt0 + (num / (deno+eps));
delta = abs(vt - vt0) * 10000.0;
vt0 = vt;
end
temp1 = vt / (1.0 + 0.5 * np *snrbar);
temp2 = 1.0 + 2.0 / (np * snrbar);
temp3 = 2.0 * (np - 2.0) / (np * snrbar);
ko = exp(-temp1) * temp2^(np-2.) * (1.0 + temp1 - temp3);
if (np <= 2)
pd = ko;
return
else
temp4 = vt^(np-1.) * exp(-vt) / (temp1 * exp(factor(np-2.)));
temp5 = vt / (1.0 + 2.0 / (np *snrbar));
pd = temp4 + 1.0 - incomplete_gamma(vt,np-1.) + ko * ...
incomplete_gamma(temp5,np-1.);
end

fig2_13.m
clear all
pfa = 1e-9;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
index = 0;
for snr = -10:.5:30
index = index +1;
prob1(index) = pd_swerling3 (nfa, 1, snr);
prob10(index) = pd_swerling3 (nfa, 10, snr);
prob50(index) = pd_swerling3(nfa, 50, snr);
prob100(index) = pd_swerling3 (nfa, 100, snr);
end
x = -10:.5:30;
plot(x, prob1,'k',x,prob10,'k:',x,prob50,'k--', ...
x, prob100,'k-.');
axis([-10 30 0 1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('np = 1','np = 10','np = 50','np = 100')
grid
2)仿真
检测概率相对于 SNR,Swerling Ⅲ,
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
9
P_{fa}=10^{-9}
Pfa=10−9
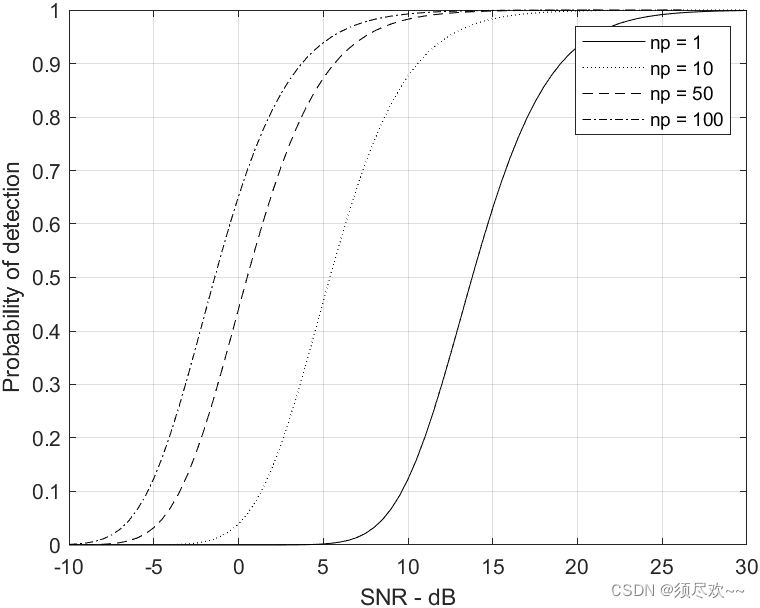
上图显示了当
n
p
=
1
,
10
,
50
,
100
n_p=1,10,50,100
np=1,10,50,100 时,检测概率作为 SNR 函数的曲线,其中
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
9
P_{fa}=10^{-9}
Pfa=10−9
⑤、Swerling Ⅳ 型目标的检测
检测概率
P
D
P_D
PD:
n
p
<
50
n_p <50
np<50 时:

当
n
p
>
50
n_p > 50
np>50 时:
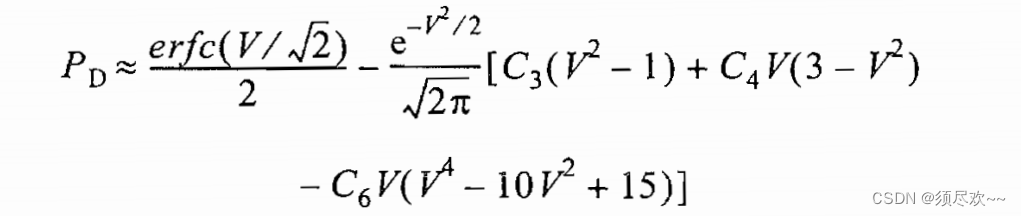
此时:
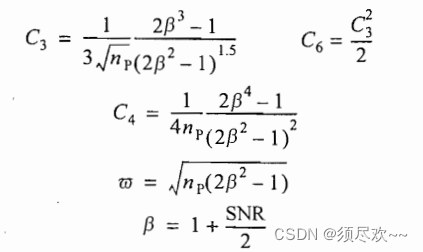
1)MATLAB 源码
pd_swerling4.m
function pd = pd_swerling4 (nfa, np, snrbar)
% This function is used to calculate the probability of detection
% for Swerling 4 targets.
format long
snrbar = 10.0^(snrbar/10.);
eps = 0.00000001;
delmax = .00001;
delta =10000.;
% Calculate the threshold Vt
pfa = np * log(2) / nfa;
sqrtpfa = sqrt(-log10(pfa));
sqrtnp = sqrt(np);
vt0 = np - sqrtnp + 2.3 * sqrtpfa * (sqrtpfa + sqrtnp - 1.0);
vt = vt0;
while (abs(delta) >= vt0)
igf = incomplete_gamma(vt0,np);
num = 0.5^(np/nfa) - igf;
temp = (np-1) * log(vt0+eps) - vt0 - factor(np-1);
deno = exp(temp);
vt = vt0 + (num / (deno+eps));
delta = abs(vt - vt0) * 10000.0;
vt0 = vt;
end
h8 = snrbar /2.0;
beta = 1.0 + h8;
beta2 = 2.0 * beta^2 - 1.0;
beta3 = 2.0 * beta^3;
if (np >= 50)
temp1 = 2.0 * beta -1;
omegabar = sqrt(np * temp1);
c3 = (beta3 - 1.) / 3.0 / beta2 / omegabar;
c4 = (beta3 * beta3 - 1.0) / 4. / np /beta2 /beta2;;
c6 = c3 * c3 /2.0;
V = (vt - np * (1.0 + snrbar)) / omegabar;
Vsqr = V *V;
val1 = exp(-Vsqr / 2.0) / sqrt( 2.0 * pi);
val2 = c3 * (V^2 -1.0) + c4 * V * (3.0 - V^2) - ...
c6 * V * (V^4 - 10. * V^2 + 15.0);
q = 0.5 * erfc (V/sqrt(2.0));
pd = q - val1 * val2;
return
else
snr = 1.0;
gamma0 = incomplete_gamma(vt/beta,np);
a1 = (vt / beta)^np / (exp(factor(np)) * exp(vt/beta));
sum = gamma0;
for i = 1:1:np
temp1 = 1;
if (i == 1)
ai = a1;
else
ai = (vt / beta) * a1 / (np + i -1);
end
a1 = ai;
gammai = gamma0 - ai;
gamma0 = gammai;
a1 = ai;
for ii = 1:1:i
temp1 = temp1 * (np + 1 - ii);
end
term = (snrbar /2.0)^i * gammai * temp1 / exp(factor(i));
sum = sum + term;
end
pd = 1.0 - sum / beta^np;
end
pd = max(pd,0.);

fig2_14.m
clear all
pfa = 1e-9;
nfa = log(2) / pfa;
index = 0;
for snr = -10:.5:30
index = index +1;
prob1(index) = pd_swerling4 (nfa, 1, snr);
prob10(index) = pd_swerling4 (nfa, 10, snr);
prob50(index) = pd_swerling4(nfa, 50, snr);
prob100(index) = pd_swerling4 (nfa, 100, snr);
end
x = -10:.5:30;
plot(x, prob1,'k',x,prob10,'k:',x,prob50,'k--', ...
x, prob100,'k-.');
axis([-10 30 0 1.1])
xlabel ('SNR - dB')
ylabel ('Probability of detection')
legend('np = 1','np = 10','np = 50','np = 100')
grid
axis tight
2)仿真
检测概率相对于 SNR,Swerling Ⅳ,
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
9
P_{fa}=10^{-9}
Pfa=10−9
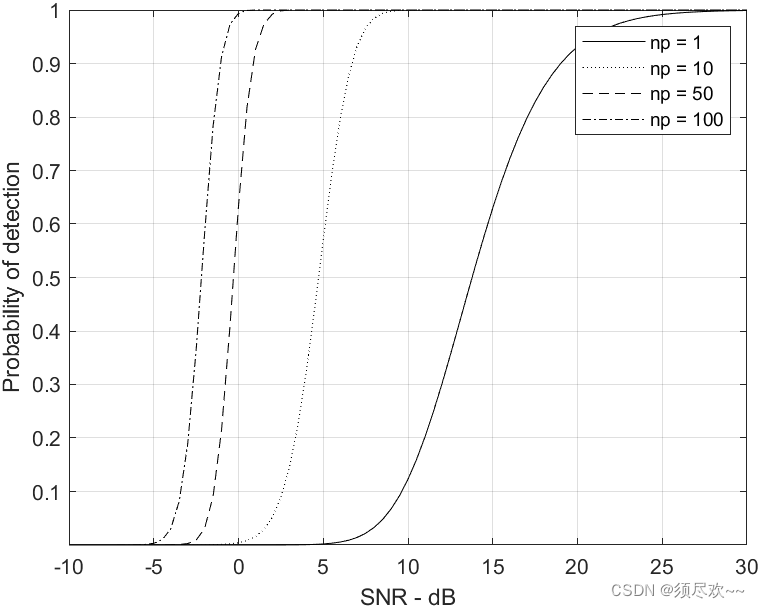
上图显示了当
n
p
=
1
,
10
,
50
,
100
n_p=1,10,50,100
np=1,10,50,100 时,检测概率作为 SNR 函数的曲线,其中
P
f
a
=
1
0
−
9
P_{fa}=10^{-9}
Pfa=10−9
三、资源自取
雷达检测思维导图笔记
我的qq:2442391036,欢迎交流!