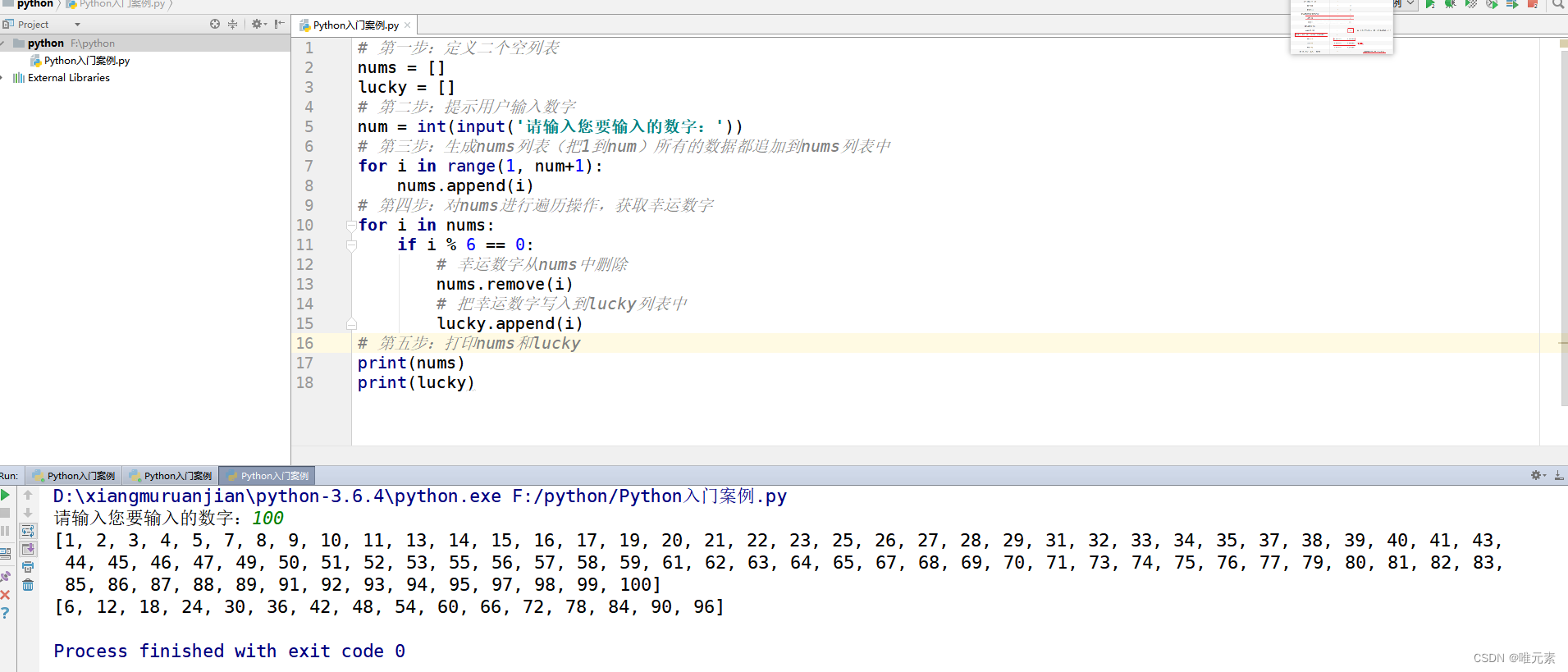
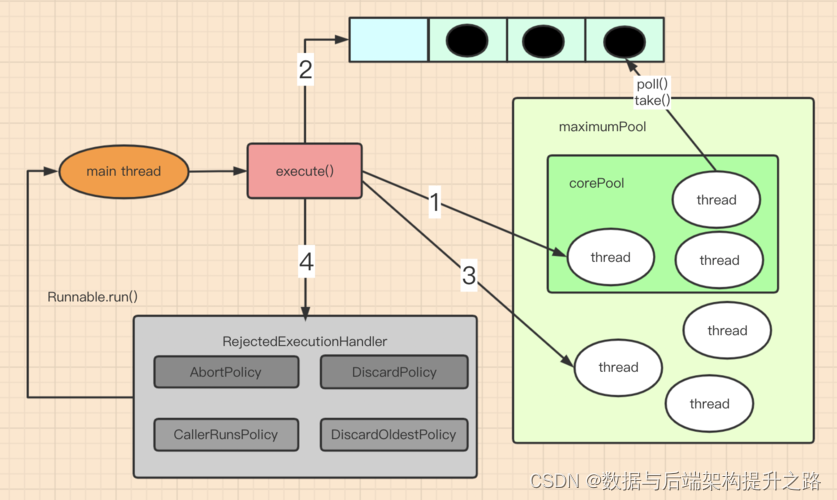
原理图
实现代码
1.线程类(PoolThread)
这个类用于执行任务队列中的任务。
public class PoolThread extends Thread {
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;
private boolean isStopped = false;
public PoolThread(Queue<Runnable> queue) {
taskQueue = queue;
}
public void run() {
while (!isStopped()) {
try {
Runnable runnable;
synchronized (taskQueue) {
while (taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
taskQueue.wait();
}
runnable = taskQueue.poll();
}
runnable.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 异常处理
}
}
}
public synchronized void stopThread() {
isStopped = true;
this.interrupt(); // 中断线程
}
public synchronized boolean isStopped() {
return isStopped;
}
}
2.线程池类(ExtendedThreadPool)
这个类用于管理线程和任务的分配。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class ExtendedThreadPool {
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;
private final List<PoolThread> threads;
private boolean isStopped;
private int maxNumThreadSize;
private int minNumThreadSize;
private int keepAliveTime;
private Timer maintainTimer;
public ExtendedThreadPool(int minNumThreadSize, int maxNumThreadSize, int keepAliveTime) {
this.minNumThreadSize = minNumThreadSize;
this.maxNumThreadSize = maxNumThreadSize;
this.keepAliveTime = keepAliveTime;
this.taskQueue = new LinkedList<>();
this.threads = new ArrayList<>();
this.isStopped = false;
this.maintainTimer = new Timer();
for (int i = 0; i < this.minNumThreadSize; i++) {
threads.add(new PoolThread(taskQueue));
}
for (PoolThread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
maintainThreadPool();
}
public synchronized void execute(Runnable task) {
if (this.isStopped) throw new IllegalStateException("ThreadPool is stopped");
this.taskQueue.add(task);
this.taskQueue.notify();
if (threads.size() < maxNumThreadSize) {
PoolThread newThread = new PoolThread(taskQueue);
threads.add(newThread);
newThread.start();
}
}
private void maintainThreadPool() {
maintainTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (taskQueue) {
// 如果任务多于线程,且线程数小于最大线程数,则增加线程
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty() && taskQueue.size()> threads.size() && threads.size() < maxNumThreadSize) {
PoolThread newThread = new PoolThread(taskQueue);
threads.add(newThread);
newThread.start();
}
// 检查线程是否超过空闲时间,如果是,则移除线程
Iterator<PoolThread> iterator = threads.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
PoolThread thread = iterator.next();
if (thread.isIdleFor(keepAliveTime)) {
iterator.remove();
thread.stopThread();
}
}
}
}
}, 0, keepAliveTime * 1000);
}
public synchronized void stop() {
this.isStopped = true;
for (PoolThread thread : threads) {
thread.stopThread();
}
maintainTimer.cancel();
}
}
上面的代码如何保证线程复用?
任务到达时唤醒: 当一个新任务被添加到队列中并且队列之前是空的,
execute方法会调用taskQueue.notify();,这会唤醒一个正在等待的线程。被唤醒的线程随后会从队列中取出任务并执行。线程不立即终止: 线程在执行完一个任务后不会立即终止。相反,它会再次检查队列是否有新的任务。如果有,线程会继续执行新的任务。
相关文章
【精选】线程池的核心参数和运行机制_线程池的核心参数以及工作机制-CSDN博客
线程池内运行的线程抛异常,线程池会怎么办_线程池线程异常后会结束线程吗-CSDN博客