本节介绍,使用python实现接口自动化实现。
思路:讲接口数据存放在excel文档中,读取excel数据,将每一行数据存放在一个个列表当中。然后获取URL,header,请求体等数据,进行请求发送。
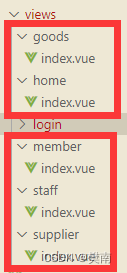
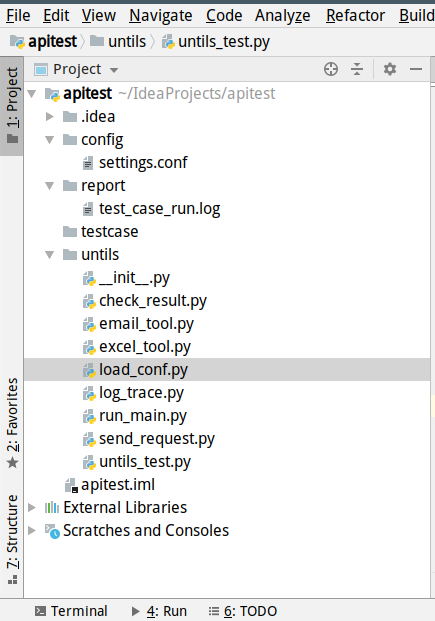
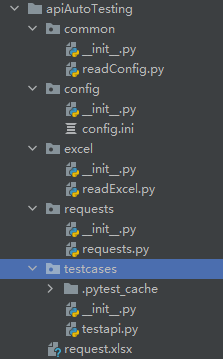
结构如下
excel文档内容如下:

一、Common与Config包
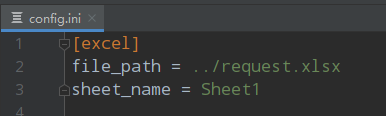
Config里面的config.ini主要存放的默认的路径内容等,如excel文件的地址,工作簿名称
Common里面主要是一些通用的方法,目前只需要读取config里面的数据
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | import configparser
import os.path
#读取config里面的数据
class ReadConfig:
def __init__(self):
self.filePath = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)))+"\\config\\config.ini"
print(self.filePath)
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.config.read(self.filePath,encoding='utf-8')
def get_data(self,section,key):
return self.config.get(section,key)
def get_list(self,section):
return self.config.items(section)
if __name__ == '__main__':
conf = ReadConfig()
print(conf.get_data("excel", "file_path"))
|
二、excel包
主要是实现读取excel表格数据,此处用的是openpyxl进行实现
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | import openpyxl
class ReadExcel:
def __init__(self,excel_path,sheet_name):
self.excel_path = excel_path
self.sheet_name = sheet_name
def get_data(self,row):
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.excel_path)
sh = workbook[self.sheet_name]
data = []
for c in list(sh.rows)[row]:
data.append(c.value)
return data
if __name__ == '__main__':
ex = ReadExcel('request.xlsx','Sheet1')
print(ex.get_data(0))
print(ex.get_data(1))
print(ex.get_data(2))
print(ex.get_data(3))
print(ex.get_data(4))
|
三、requests包
主要用于发送请求,这里只写了常用的get post请求,需要可以加其他的。
由于post请求体有多种,此处只区分了两种,其他的可以加上。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import json
import requests
class Request:
def get_url(self,url,headers=None,paras=None):
if url==None:
print("URL地址为空")
elif paras == None:
r = requests.get(url,headers=headers,params=paras)
else:
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers, params=json.loads(paras))
return r
def post_url(self,url,content_type,headers=None,payload=None):
if url==None:
print("URL地址为空")
else:
if content_type == "application/json":
payload_json = json.dumps(payload)
r = requests.post(url,headers=headers,data=payload_json)
elif content_type =="application/x-www-form-urlencoded":
r = requests.post(url,headers=headers,data=payload)
else:
print("no this content-type")
return r
def choose_method(self,method,url,content_type,headers=None,payload=None):
if method == "get":
return self.get_url(url,headers,payload)
elif method == "post":
return self.post_url(url,content_type,headers,payload)
else:
print("no this method request")
|
四、testcases包
使用pytest框架进行自动化测试
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import json
import pytest
from autoStruct.apiAuto.common.requests import Request
from autoStruct.apiAutoTesting.common.readConfig import ReadConfig
from autoStruct.apiAutoTesting.excel.readExcel import ReadExcel
class TestApi:
def setup_class(self):
file_path = ReadConfig().get_data('excel', 'file_path')
sheet_name = ReadConfig().get_data('excel', 'sheet_name')
self.ex = ReadExcel(file_path, sheet_name)
@pytest.mark.parametrize('num',[1,2,3,4,5])
def testcase(self,num):
data = self.ex.get_data(num)
print(data)
if data[3]==None:
r = Request().choose_method(data[1],data[0],data[4],json.loads(data[2]),data[3])
else:
r = Request().choose_method(data[1], data[0], data[4], json.loads(data[2]), json.loads(data[3]))
print(r.text)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['-vs','testapi.py'])
|
Python接口自动化测试零基础入门到精通(2023最新版)