ncurse的引入
ncurse的概念
ncurse(new curses)是一套编程库,它提供了一系列的函数,以便使用者调用它们去生成基于文本的用户界面。 ncurses是一个能提供功能键定义(快捷键),屏幕绘制以及基于文本终端的图形互动功能的动态库。ncurses用得最多的地方是linux内核编译之前的内核配置,ncurses早已淡出舞台,甚至体验感完爆ncurses的C图形库GTK、C++图形库QT也区趋于落伍嵌入式设备上的Android 系统。这个游戏只是使用ncurses并不以学习它为目的,主要还是通过这个游戏锻炼我们C语言的能力。
ncurse的格式
#include <curses.h>//记得包含头文件
int main()
{
initscr();//ncurse界面的初始化函数
printw("this is a test:n");//在ncurse模式下的printf
getch();//等待用户输入,如果没有这句话,程序就退出来了,看不到运行结果,也就是看不到上面的那句话
endwin();//程序退出,调用改函数来恢复shell终端的显示,如果没有这句话,shell终端字乱码,会坏掉
return 0;
}
ncurse的编译
ncurse的编译需要在文件名.c后加-lcurses
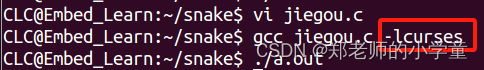
上述格式代码编译结果如下:

nurses的上下左右键值获取及演示
如果不用nurses,那么每次输入上下左右得输入回车小蛇才会有反应,而运用nurses只需输入上下左右小蛇便会做出反应,提高灵敏度,因为该项目键盘中只需用到上下左右,所以我们只需获得上下左右键值即可。
进入nurses头文件方式
vi /usr/include/curses.h上下左右键值宏定义
#define KEY_DOWN 0402
#define KEY_UP 0403
#define KEY_LEFT 0404
#define KEY_RIGHT 0405
代码演示
#include <curses.h>
int main()
{
int key;
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);//函数调用→接受功能键,是否接收(1是接收)
while(1)
{
key = getch();
switch(key)
{
case 0402:
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case 0403:
printw("UP\n");
break;
case 0404:
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case 0405:
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
endwin();
return 0;
}编译结果
地图规划

地图边界
代码演示
#include <curses.h>
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
gameMap();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
代码运行结果:

贪吃蛇节点身子


代码演示
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct snakebody
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct snakebody *next;
};
struct snakebody *head;
struct snakebody *tail;
int snakeNode(int i,int j)
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;//指向链表头
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j)
{
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else if(snakeNode(hang,lie))
{
printw("[]");//蛇结点身子的出现
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct snakebody *new = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;//新的节点赋给尾的下一个
tail = new;//当尾后面没有节点时,新节点就是尾
}
void initSnake()//身子初始化
{
head = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
head->hang = 2;
head->lie = 2;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;//一开始头就是尾
addNode();//头已经定义 调用一次该函数,就是多一节
addNode();
addNode();
}
int main()
{
initcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
代码运行结果:
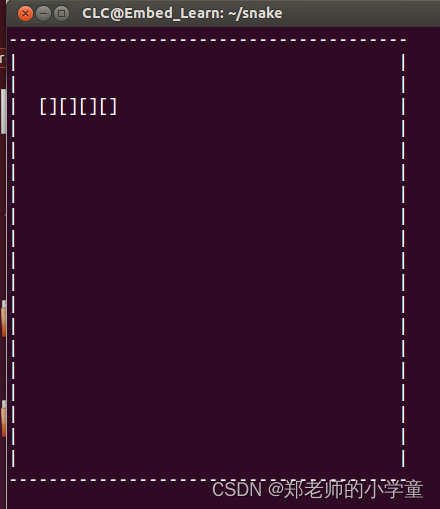
贪吃蛇的移动和“复活”
完成了地图规划就应该对蛇进行操控使得更加有体验感 接下来一步一步让代码使得体验更加逼真。
实现贪吃蛇向右移动
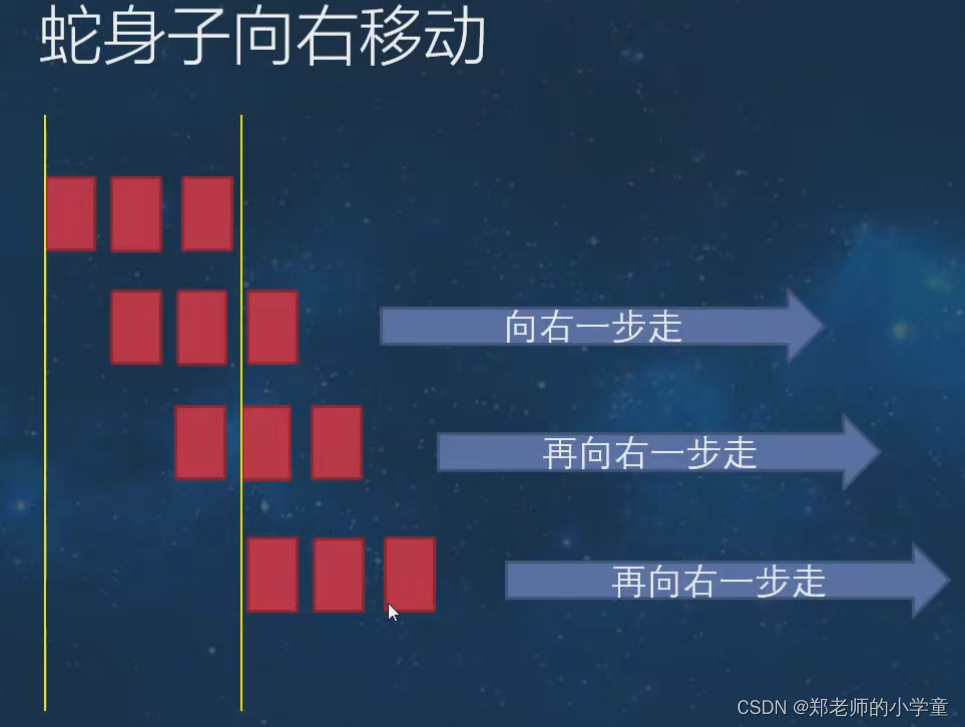
向右移动主要分为两个步骤:第一个是头结点删除,使得第二个结点成为头结点;第二个是新结点从尾部加入。代码如下:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
move(0,0);//每次偏移时在地图里展现出来
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else if(snakeNode(hang,lie))
{
printw("[]");
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct snakebody *new = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
head = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
head->hang = 2;
head->lie = 2;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;//删除头结点
free(p);//对删除的头结点进行空间内存释放
}
void movesnake()
{
addNode();//在尾部增加结点
deletNode();/调用删除头结点函数
}
int main()
{
int control;
initcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
while(1)
{
control = getch();
if(control == KEY_RIGHT)
{
movesnake();
gameMap();//偏移后刷新地图
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}贪吃蛇撞墙回到起始位置
这里先实现蛇在水平方向的偏移,如果蛇的尾结点碰到地图边界,则让其初始化。代码如下
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void initcurses()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
struct snakebody
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct snakebody *next;
};
struct snakebody *head = NULL;
struct snakebody *tail = NULL;
int snakeNode(int i,int j)
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j)
{
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else if(snakeNode(hang,lie))
{
printw("[]");
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct snakebody *new = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct snakebody *p;
while(head != NULL)//蛇撞墙后初始化时原来的身子还占内存空间,需对其进行释放
{
p = head;//指向链表头
head = head->next;//遍历整个链表
free(p);//释放整个链表内存空间
}
head = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void movesnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20)
{
initSnake();//蛇撞到边界时初始化
}
}
int main()
{
int control;
initcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
while(1)
{
control = getch();
if(control == KEY_RIGHT)
{
movesnake();
gameMap();
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
贪吃蛇的自由移动
线程的引入
若要蛇的移动和按键检测同时进行,用两个while循环是无法实现的,其只会执行第一个循环中的内容,此时就得需要用到线程。线程是Linux中常见的函数库,在此项目中的作用是能够使两个循环同时进行。线程的定义格式是pthread_t+任意名字,创建线程格式是pthread_create(前面的任意名字取地址,NULL,循环的名字,NULL)同时线程有独自的头文件和链接库,如下:
void* changeDir()
{
}
pthread_t t1;
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,changeDir,NULL);#include <pthread.h>gcc a.c -lcurses -lpthread自由移动代码演示:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
void initcurses()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
noecho();//ncurses自带的函数,作用是不让无关信息出现在显示屏上
}
struct snakebody
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct snakebody *next;
};
struct snakebody *head = NULL;
struct snakebody *tail = NULL;
int key;
int dir;
int snakeNode(int i,int j)
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j)
{
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else if(snakeNode(hang,lie))
{
printw("[]");
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("key=%d\n",key);
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct snakebody *new = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
new->next = NULL;
switch(dir)
{
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;//蛇向上,行减一即可
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;//蛇向下,行加一即可
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;//蛇向左,列减一即可
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;//蛇向右,行加一即可
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct snakebody *p;
dir = RIGHT;
while(head != NULL)
{
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void movesnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20)
{
initSnake();
}
}
void* refreshJiemian()
{
while(1)
{
movesnake();
gameMap();
refresh();//ncurses自带刷新函数
usleep(100000);//每个100000us向右移动一次
}
}
void turn(int direction)
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction))//abs是一个运算符 表示的是参数的绝对值
//如果输入方向的绝对值等于蛇前进方向的绝对值,则蛇的路径不发生改变
//如果输入方向的绝对值不等于蛇前进方向的绝对值,则原有方向改变成输入方向
{
dir = direction;
}
}
void* changeDir()
{
while(1)
{
key = getch();
switch(key)
{
case 0402:
turn(DOWN);//调用turn函数,并将方向传过去,判断输入方向与原有方向绝对值是否一致
break;
case 0403:
turn(UP);
break;
case 0404:
turn(LEFT);
break;
case 0405:
turn(RIGHT);
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,refreshJiemian,NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,changeDir,NULL);
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
贪吃蛇的食物及"食"物(结尾)
贪吃蛇食物关心的是其位置和符号,我们这里把符号定义为##,位置可以在蛇的身体结构体定义一个食物结构体,让食物的行、列在地图中被扫描,从而出现食物。食物的出现是随机的,这里需要调用一个函数,是rand(),其作用是生成一个随机数,定义格式在下面代码中展示,同时我们的地图是20x20,只需要使其范围在19以内(0开始)即可,这里运用取余的方法:行列都是20,让生成的随机数对20取余,即%20,那么出现的数的范围就在0到19(刚好为20倍数是为0)。"食"物的根本是判断蛇的尾部的行列值是否与食物行列值一致,如果一致则在吃到那一瞬间新增一个身体结点,不执行删除函数;如果不一致,则按原来一样自由移动。代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <ncurses.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
void initcurses()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
noecho();
}
struct snakebody
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct snakebody *next;
};
struct snakebody *head = NULL;
struct snakebody *tail = NULL;
int key;
int dir;
struct snakebody food;
void initfood()
{
int x = rand()%20;
int y = rand()%20;
food.hang = x;
food.lie = y;
}
int snakeNode(int i,int j)
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j)
{
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
int creatfood(int i,int j)
{
if(food.hang == i && food.lie == j)//如果食物与传进来的参数行列值一样 就运行该函数 该函数主要用于后面地图出现食物符号
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void gameMap()
{
int hang,lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang = 0;hang <20;hang++)
{
if(hang == 0)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang >= 0 && hang <= 18)
{
for(lie = 0;lie <= 20;lie++)
{
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20)
{
printw("|");
}
else if(snakeNode(hang,lie))
{
printw("[]");
}
else if(creatfood(hang,lie))
{
printw("##");//设置食物在地图出现
}
else
{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19)
{
for(lie = 0;lie < 20;lie++)
{
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct snakebody *new = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
new->next = NULL;
switch(dir)
{
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct snakebody *p;
dir = RIGHT;
while(head != NULL)
{
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
initfood();
head = (struct snakebody *)malloc(sizeof(struct snakebody));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
int ifSnakeDie()
{
struct snakebody *p;
p = head;
if(tail->hang < 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20)
{
return 1;//碰到边界则运行该函数,该函数主要用于后面进行碰壁后蛇的初始化
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->hang == tail->hang && p->lie == tail->lie)
{
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void movesnake()
{
addNode();
if(creatfood(tail->hang,tail->lie))//将蛇的尾巴参数传到该函数 相当于蛇吃到食物 则初始化食物
{
initfood();
}
else
{
deletNode();
}
if(ifSnakeDie())
{
initSnake();
}
}
void* refreshJiemian()
{
while(1)
{
movesnake();
gameMap();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
void turn(int direction)
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction))
{
dir = direction;
}
}
void* changeDir()
{
while(1)
{
key = getch();
switch(key)
{
case 0402:
turn(DOWN);
break;
case 0403:
turn(UP);
break;
case 0404:
turn(LEFT);
break;
case 0405:
turn(RIGHT);
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,refreshJiemian,NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,changeDir,NULL);
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}