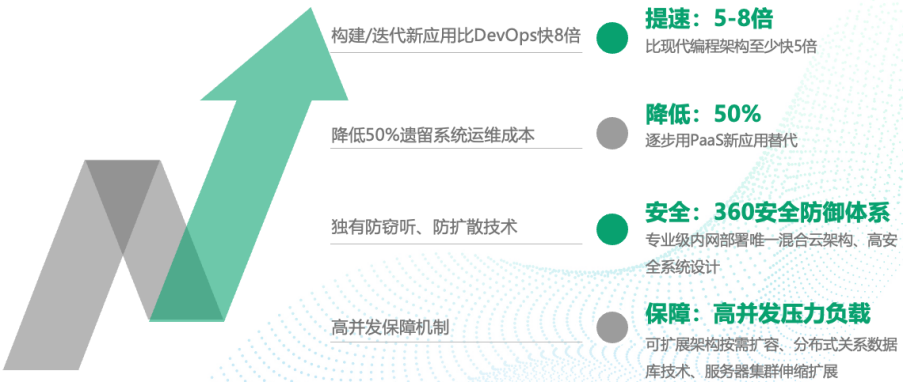
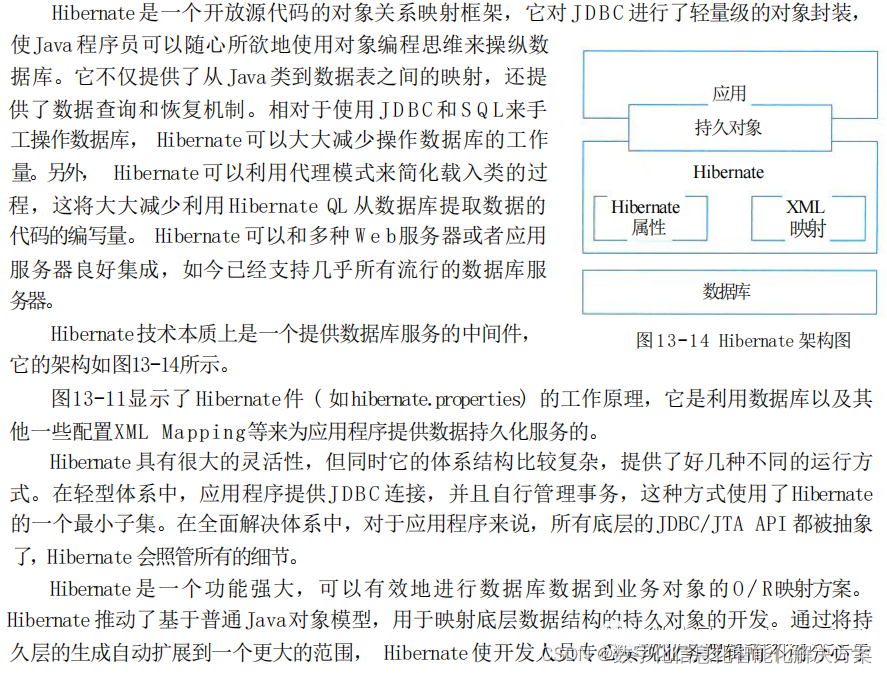
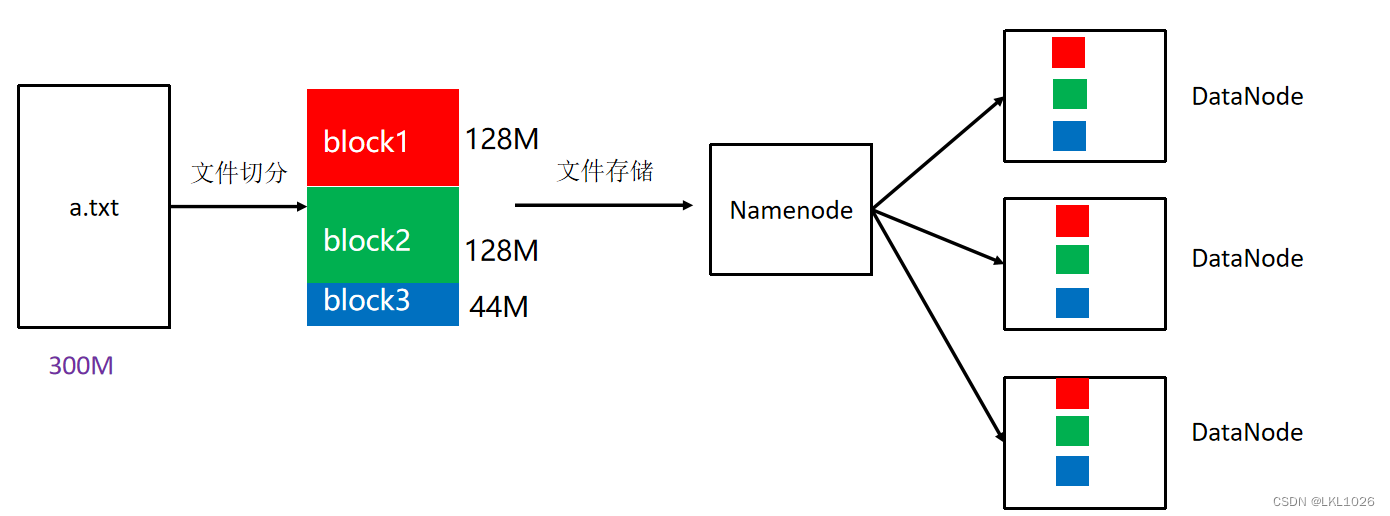
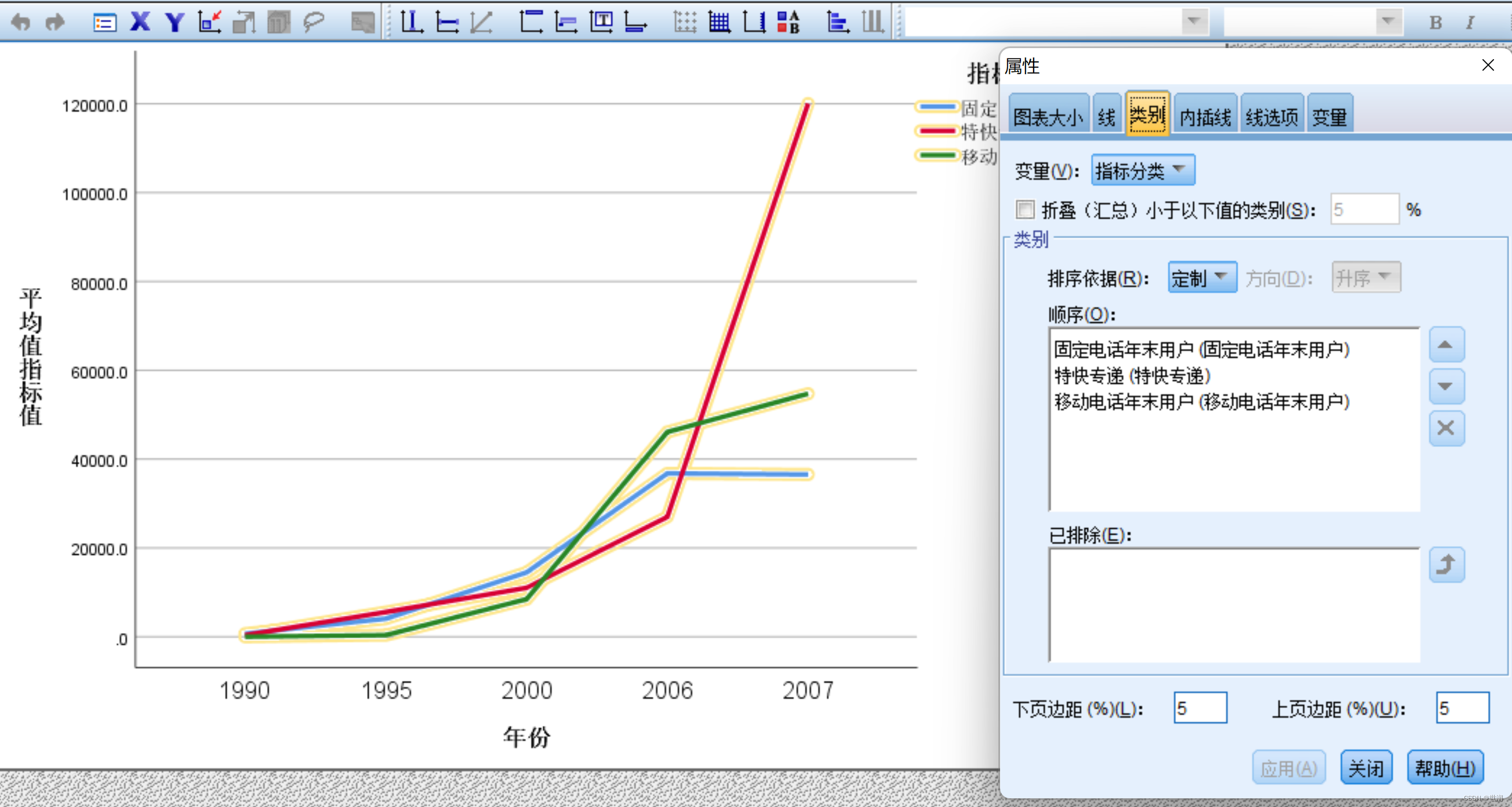
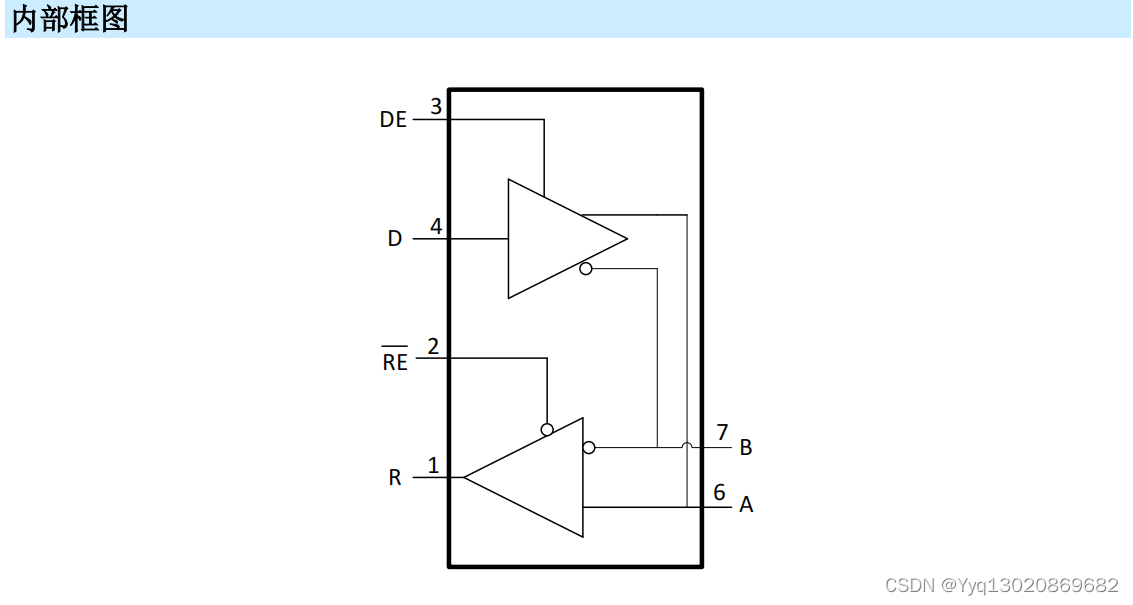
欧式聚类是一种基于距离的聚类算法,可以将点云中距离较近的点聚集在一起,形成一个簇。
在PCL库中,欧式聚类的实现原理是将点云中的每个点看作一个向量,然后计算这些向量之间的欧式距离。欧式距离是指两个向量之间的距离,用公式表示为:d(x,y) = sqrt((x1-y1)^2 + (x2-y2)^2 + … + (xn-yn)^2)。在点云处理中,向量的维度通常是3,因为点云中的每个点都有三个坐标值(x、y、z)。
欧式聚类算法需要指定一个阈值,用于确定哪些点应该被聚集在一起。如果两个点之间的距离小于阈值,则它们被认为是相邻的,可以被聚集在一起。如果两个点之间的距离大于阈值,则它们被认为是不相邻的,不能被聚集在一起。
PCL库中的欧式聚类算法可以基于KD-Tree进行加速,KD-Tree是一种对数据点在k维空间中划分的数据结构,通过将空间划分为多个小部分,可以有效地进行最近邻查找。在构建KD-Tree时,会选择数据点在某一维度上的中值作为切分超平面,将中值左侧的数据点挂在其左子树,中值右侧的数据点挂在其右子树,直到所有数据点挂载完毕。然后,可以利用KD-Tree来加速欧式聚类算法,通过搜索KD-Tree中的最近邻节点来找到距离较近的点。

下面是一个使用PCL中的欧式聚类进行分割的示例代码:
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// Read in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_f (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
reader.read ("../table.pcd", *cloud); // 点云文件
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg; // VoxelGrid类在输入点云数据上创建3D体素网格(将体素网格视为一组空间中的微小3D框
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
vg.setInputCloud (cloud); //输入
vg.setLeafSize (0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f); // setLeafSize (float lx, float ly, float lz)
vg.filter (*cloud_filtered); //输出
std::cout << "点云过滤后: " << cloud_filtered->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*滤波后
//创建平面模型分割的对象并设置参数
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); //分割模型
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC); //随机参数估计方法
seg.setMaxIterations (100); //最大的迭代的次数
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.02); //设置阀值
int i=0, nr_points = (int) cloud_filtered->points.size ();
while (cloud_filtered->points.size () > 0.3 * nr_points) // 滤波停止条件
{
seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered); // 输入
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size () == 0)
{
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;
extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices (inliers);
extract.setNegative (false);
extract.filter (*cloud_plane);// [平面
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
// // 移去平面局内点,提取剩余点云
extract.setNegative (true);
extract.filter (*cloud_f);
*cloud_filtered = *cloud_f;
}
// Creating the KdTree object for the search method of the extraction
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices;
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec; //欧式聚类对象
ec.setClusterTolerance (0.02); // 设置近邻搜索的搜索半径为2cm
ec.setMinClusterSize (100); //设置一个聚类需要的最少的点数目为100
ec.setMaxClusterSize (25000); //设置一个聚类需要的最大点数目为25000
ec.setSearchMethod (tree); //设置点云的搜索机制
ec.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
ec.extract (cluster_indices); //从点云中提取聚类,并将点云索引保存在cluster_indices中
//迭代访问点云索引cluster_indices,直到分割出所有聚类
int j = 0;
for (std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin (); it != cluster_indices.end (); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_cluster (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin (); pit != it->indices.end (); ++pit)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back (cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size ();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size () << " data points." << std::endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "../cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ> (ss.str (), *cloud_cluster, false); // 保存文件
j++;
}
return (0);
}
这段代码对点云先进行平面拟合,移去平面局内点,然后欧式聚类提取出各簇点云并保存为不同的pcd.
本系列全部代码的链接