简介
TimerQueue
通过timerfd实现的定时器功能,为EventLoop扩展了一系列runAt,runEvery,runEvery等函数TimerQueue中通过std::set维护所有的Timer,也可以使用优先队列实现
muduo的TimerQueue是基于timerfd_create实现,这样超时很容易和epoll结合起来。等待超时事件保存在set集合中,注意set集合的有序性,从小到大排列,整个对TimerQueue的处理也就是对set集合的操作。实现TimerQueue用了3个set,分别是等待超时事件set,活跃事件set,被撤销定时set。主要是STL的一些操作。
主要成员及属性解析
主要接口
- addTimer
向定时器中添加Timer
Timer是一个封装了回调函数和时间的类
通过内部实现addTimerInLoop保证线程安全
- cancel
从定时器中移除某个Timer
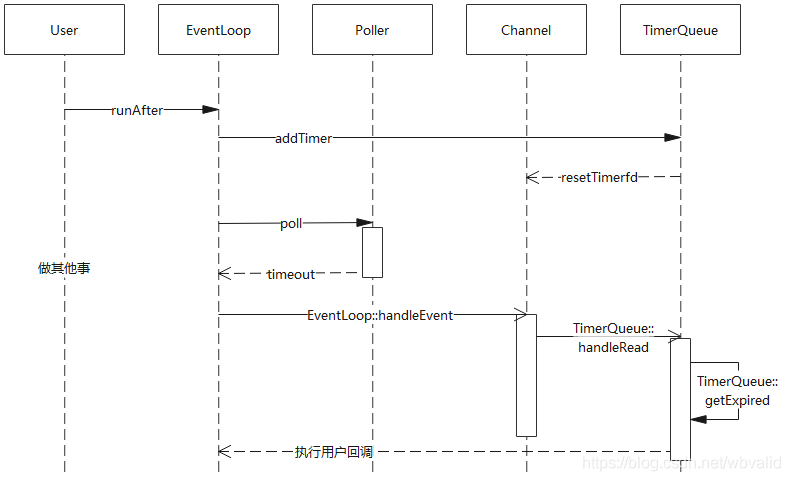
- 核心实现:getExpired
从timers_集合中移除已经到期的Timer
- 核心实现:handleRead
向timerfdChannel注册的回调函数
在timerfd触发可读时间时,也就是定时器到期的时候执行
会调用getExpired,并依次执行返回的所有Timer中的回调
主要成员
- timerfdChannel_
用来唤醒计时器的Channel,维护了一个timerfd,注册了TimerQueue::handleRead回调
- std::set<std::pair<Timestamp, Timer*>> timers_
使用std::set容器来取得最近将要超时的Timer,从而决定是否resetTimerfd
TimerQueue执行用户回调的时序图:
源码剖析
TimerQueue.h
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
// This is an internal header file, you should not include this.
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H
#define MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include "muduo/base/Mutex.h"
#include "muduo/base/Timestamp.h"
#include "muduo/net/Callbacks.h"
#include "muduo/net/Channel.h"
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class EventLoop;
class Timer;
class TimerId;
///
/// A best efforts timer queue.
/// No guarantee that the callback will be on time.
///
class TimerQueue : noncopyable
{
public:
explicit TimerQueue(EventLoop* loop);
~TimerQueue();
///
/// Schedules the callback to be run at given time,
/// repeats if @c interval > 0.0.
///
/// Must be thread safe. Usually be called from other threads.
//添加定时事件
TimerId addTimer(TimerCallback cb,
Timestamp when,
double interval);
//取消定时事件
void cancel(TimerId timerId);
private:
// FIXME: use unique_ptr<Timer> instead of raw pointers.
// This requires heterogeneous comparison lookup (N3465) from C++14
// so that we can find an T* in a set<unique_ptr<T>>.
typedef std::pair<Timestamp, Timer*> Entry;
typedef std::set<Entry> TimerList;
typedef std::pair<Timer*, int64_t> ActiveTimer;
typedef std::set<ActiveTimer> ActiveTimerSet;
//在workloop中执行实际添加的定时事件的回调函数
void addTimerInLoop(Timer* timer);
//在workloop中执行实际删除定时事件的回调函数
void cancelInLoop(TimerId timerId);
// called when timerfd alarms
//定时器超时时候被调用处理事件的回调函数
void handleRead();
// move out all expired timers
//获取所有的超时事件
std::vector<Entry> getExpired(Timestamp now);
//重置刷新定时器列表
void reset(const std::vector<Entry>& expired, Timestamp now);
//将一个定时事件加入到定时列表中
bool insert(Timer* timer);
//所属loop的指针
EventLoop* loop_;
//timerfd文件描述符
const int timerfd_;
//存储timerfd事件的channel
Channel timerfdChannel_;
// Timer list sorted by expiration
//按过期时间排序的定时器列表
TimerList timers_;
// for cancel()
//存储活跃定时事件的容器
ActiveTimerSet activeTimers_;
//正在处理超时事件的标志
bool callingExpiredTimers_; /* atomic */
//存储所有需要取消定时事件的容器
ActiveTimerSet cancelingTimers_;
};
} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo
#endif // MUDUO_NET_TIMERQUEUE_H
TimerQueue.cc
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved.
// http://code.google.com/p/muduo/
//
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
#ifndef __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS
#define __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS
#endif
#include "muduo/net/TimerQueue.h"
#include "muduo/base/Logging.h"
#include "muduo/net/EventLoop.h"
#include "muduo/net/Timer.h"
#include "muduo/net/TimerId.h"
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
namespace detail
{
//创建一个timerfd
int createTimerfd()
{
//创建一个timerFd,设置为单调,非阻塞,fork+exec关闭fd
int timerfd = ::timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC,
TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
if (timerfd < 0)
{
LOG_SYSFATAL << "Failed in timerfd_create";
}
return timerfd;
}
//计算定时器触发还有多长
struct timespec howMuchTimeFromNow(Timestamp when)
{
//当前时间与when的时间间隔
int64_t microseconds = when.microSecondsSinceEpoch()
- Timestamp::now().microSecondsSinceEpoch();
if (microseconds < 100)//100起步
{
microseconds = 100;
}
struct timespec ts;
//秒
ts.tv_sec = static_cast<time_t>(
microseconds / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
//纳秒
ts.tv_nsec = static_cast<long>(
(microseconds % Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond) * 1000);
return ts;
}
void readTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp now)
{
//在timerfd在读取8字节
uint64_t howmany;
ssize_t n = ::read(timerfd, &howmany, sizeof howmany);
LOG_TRACE << "TimerQueue::handleRead() " << howmany << " at " << now.toString();
if (n != sizeof howmany)
{
LOG_ERROR << "TimerQueue::handleRead() reads " << n << " bytes instead of 8";
}
}
//重置定时器超时时间戳
void resetTimerfd(int timerfd, Timestamp expiration)
{
// wake up loop by timerfd_settime()
struct itimerspec newValue;
struct itimerspec oldValue;
memZero(&newValue, sizeof newValue);
memZero(&oldValue, sizeof oldValue);
newValue.it_value = howMuchTimeFromNow(expiration);
//设置下一次定时事件的到达时间
int ret = ::timerfd_settime(timerfd, 0, &newValue, &oldValue);
if (ret)
{
LOG_SYSERR << "timerfd_settime()";
}
}
} // namespace detail
} // namespace net
} // namespace muduo
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
using namespace muduo::net::detail;
TimerQueue::TimerQueue(EventLoop* loop)
: loop_(loop),
timerfd_(createTimerfd()),
timerfdChannel_(loop, timerfd_),
timers_(),
callingExpiredTimers_(false)
{
//设置读事件的回调函数
timerfdChannel_.setReadCallback(
std::bind(&TimerQueue::handleRead, this));
// we are always reading the timerfd, we disarm it with timerfd_settime.
//监听读事件
timerfdChannel_.enableReading();
}
TimerQueue::~TimerQueue()
{
//取消所有的监听事件
timerfdChannel_.disableAll();
//将自己从polller中移除
timerfdChannel_.remove();
//关闭fd
::close(timerfd_);
// do not remove channel, since we're in EventLoop::dtor();
//释放定时器列表中所有的定时器
for (const Entry& timer : timers_)
{
delete timer.second;
}
}
//添加定时事件
TimerId TimerQueue::addTimer(TimerCallback cb,//超时回调
Timestamp when,//时间戳
double interval)//时间间隔
{
//创建一个定时器
Timer* timer = new Timer(std::move(cb), when, interval);
//添加定时器
loop_->runInLoop(
std::bind(&TimerQueue::addTimerInLoop, this, timer));
return TimerId(timer, timer->sequence());
}
//取消一个定时事件
void TimerQueue::cancel(TimerId timerId)
{
loop_->runInLoop(
std::bind(&TimerQueue::cancelInLoop, this, timerId));
}
void TimerQueue::addTimerInLoop(Timer* timer)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
//将定时事件插入定时器列表
bool earliestChanged = insert(timer);
//如果这个定时事件将会是最先被触发的,那么就重新设置定时器超时时间戳
if (earliestChanged)
{
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, timer->expiration());
}
}
//取消一个定时器
void TimerQueue::cancelInLoop(TimerId timerId)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
//寻找这个定时器
ActiveTimer timer(timerId.timer_, timerId.sequence_);
ActiveTimerSet::iterator it = activeTimers_.find(timer);
if (it != activeTimers_.end())//找到了
{
//删除+释放
size_t n = timers_.erase(Entry(it->first->expiration(), it->first));
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
delete it->first; // FIXME: no delete please
activeTimers_.erase(it);
}
//如果此时正在处理过期事件,那么就将该定时器加入到过期事件列表
else if (callingExpiredTimers_)
{
cancelingTimers_.insert(timer);
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
}
//timer读事件的回调函数
void TimerQueue::handleRead()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
//read timer
readTimerfd(timerfd_, now);
//获取所有超时的定时事件
std::vector<Entry> expired = getExpired(now);
callingExpiredTimers_ = true;
//释放所有过期事件
cancelingTimers_.clear();
// safe to callback outside critical section
//执行所有超时事件的回调函数
for (const Entry& it : expired)
{
it.second->run();
}
callingExpiredTimers_ = false;
//重置定时器列表
reset(expired, now);
}
//获取所有超时的定时事件
std::vector<TimerQueue::Entry> TimerQueue::getExpired(Timestamp now)
{
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
std::vector<Entry> expired;
//获取当前时间戳
Entry sentry(now, reinterpret_cast<Timer*>(UINTPTR_MAX));
//返回指向第一个不小于给定值的元素的迭代器
//也就是通过二分搜索找到第一个时间戳大于当前时间点的迭代器
TimerList::iterator end = timers_.lower_bound(sentry);
assert(end == timers_.end() || now < end->first);
//back_inserter(expired)将获取vector尾部可插入元素的迭代器
//将所有超时事件都复制到vector中
std::copy(timers_.begin(), end, back_inserter(expired));
//删除所有超时事件
timers_.erase(timers_.begin(), end);
//将所有超时事件都从活跃事件列表中摘除
for (const Entry& it : expired)
{
ActiveTimer timer(it.second, it.second->sequence());
size_t n = activeTimers_.erase(timer);
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
return expired;
}
//重置定时器列表
//expired中存放过期的定时器事件
void TimerQueue::reset(const std::vector<Entry>& expired, Timestamp now)
{
Timestamp nextExpire;
for (const Entry& it : expired)
{
ActiveTimer timer(it.second, it.second->sequence());
if (it.second->repeat()
&& cancelingTimers_.find(timer) == cancelingTimers_.end())
{
//如果这个定时事件设置了重复执行,并且没有被取消,
it.second->restart(now);//刷新时间戳
insert(it.second);//加入定时器列表
}
else//否则释放掉
{
// FIXME move to a free list
delete it.second; // FIXME: no delete please
}
}
//如果定时器列表非空,就获取首节点的时间戳
if (!timers_.empty())
{
nextExpire = timers_.begin()->second->expiration();
}
//刷新重置timer的下一次超时时间戳
if (nextExpire.valid())
{
resetTimerfd(timerfd_, nextExpire);
}
}
//将一个定时事件加入到定时列表中
bool TimerQueue::insert(Timer* timer)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
//此变量用来标记这个待插入的定时事件是不是会最早触发的
bool earliestChanged = false;
//获取到该定时器的时间戳
Timestamp when = timer->expiration();
TimerList::iterator it = timers_.begin();
if (it == timers_.end() || when < it->first)
{
earliestChanged = true;
}
{
//将定时事件插入事件列表
std::pair<TimerList::iterator, bool> result
= timers_.insert(Entry(when, timer));
assert(result.second); (void)result;
}
{
//将定时事件插入活跃事件列表
std::pair<ActiveTimerSet::iterator, bool> result
= activeTimers_.insert(ActiveTimer(timer, timer->sequence()));
assert(result.second); (void)result;
}
assert(timers_.size() == activeTimers_.size());
return earliestChanged;
}