基于 SSM + Spring Boot + Thymeleaf 开发的论坛社区网站
项目概述
本项目是依据 2019 年牛客项目,基于 SSM + Spring Boot + Thymeleaf 开发的论坛社区网站,网站实现了如下功能:
- 使用 Spring Email + Interceptor + Spring Security 等实现网站权限模块开发,完成注册、登录、退出、状态、设置、授权等功能。
- 实现网站核心功能,包括首页、帖子、评论、私信、敏感词过滤、全局异常处理、统一日志记录。
- 使用 Redis 实现其他功能模块,包括点赞、关注、网站数据统计、缓存优化,其中缓存主要为:验证码、登录凭证、会话信息。
- 引入 Kafka 的目的主要是为了异步生产消费事件,包括评论、点赞、关注时的系统通知,以及 Elasticsearch 服务器的更新。
- 使用 Elasticsearch 实现全文搜索。
- 基于 Quartz 定时任务实现热帖排行;使用 Caffeine 做热帖服务器缓存,提升性能。
后面我会罗列一些我认为的重点,梳理项目的后台实现步骤。
总结图如下:

项目难度
本人是把这个项目作为学校工程实践前的热身项目。整个项目约需 1 个月,可作为 Java 练手项目,快速了解热门框架和组件的基本使用。项目可改进的地方有很多,最后会提到。
实现步骤
权限模块
首页
首页进行帖子的展示,依据一般后台开发业务流程进行实现:数据库建表->Java 对应 entity 实体类->mapper 层接口-> 接口对应的 XML 文件实现 crud 逻辑(Mybatis)->service 层->controller 层-> 页面。

分页
通过 Page 类封装分页逻辑:
public class Page {
//当前页码,默认1
private int current = 1;
//每页显示上限,默认10
private int limit = 10;
//数据总数
private int rows;
//查询路径,复用分页链接
private String path;
public int getCurrent() {
return current;
}
public void setCurrent(int current) {
if(current >= 1) {
this.current = current;
}
}
public int getLimit() {
return limit;
}
public void setLimit(int limit) {
if(limit >= 1 && limit <= 100) {
this.limit = limit;
}
}
public int getRows() {
return rows;
}
public void setRows(int rows) {
if(rows >= 0) {
this.rows = rows;
}
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
/**
* 获取当前页的起始行
* @return
*/
public int getOffset() {
return (current - 1) * limit;
}
/**
* 获取总页数
* @return
*/
public int getTotal() {
if(rows % limit == 0) {
return rows / limit;
} else {
return rows /limit + 1;
}
}
/**
* 获取起始页码
* @return
*/
public int getFrom() {
int from = current - 2;
return Math.max(from, 1);
}
/**
* 获取终止页码
* @return
*/
public int getTo() {
int to = current + 2;
return Math.min(to, getTotal());
}
}
前台传来的 current 等参数通过 controller 的 Page 类参数进行封装,从而实现页面跳转。该模块可用于其他地方大量复用。
HomeController 层对于 Page 类的使用:
@RequestMapping(value = "/index", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getIndexPage(Model model, Page page) {
page.setRows(discussPostService.findDiscussPostRows(0));
page.setPath("/index");
List<DiscussPost> list = discussPostService.findDiscussPosts(0, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit());
List<Map<String,Object>> discussPosts = new ArrayList<>();
if(list != null) {
for(DiscussPost discussPost : list) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("post", discussPost);
map.put("user", userService.findUserById(discussPost.getUserId())); //这里也可以在map层做级联查询调出user数据
discussPosts.add(map);
}
}
model.addAttribute("discussPosts", discussPosts);
//model加page可以省略
return "/index";
}
邮箱注册
对前台传来的注册表单数据进行判重判空和数据库匹配后,如果能注册,将用户数据插入数据库:
//注册
user.setSalt(NcCommunityUtil.generateUUID().substring(0,5));
user.setPassword(NcCommunityUtil.md5(user.getPassword() + user.getSalt()));
user.setType(0); //普通用户
user.setStatus(0); //还未激活
user.setActivationCode(NcCommunityUtil.generateUUID());
user.setHeaderUrl(String.format("http://images.nowcoder.com/head/%dt.png", new Random().nextInt(1000)));
user.setCreateTime(new Date());
userMapper.insertUser(user);
注意:密码的存储是经过加盐和 md5 加密的,防止密码泄露。数据库存储了该用户的盐和加密的密码。
然后发送激活邮件:
//发送激活邮件
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("email", user.getEmail());
context.setVariable("url", domain + contextPath + "/activation/" + user.getId() + "/" + user.getActivationCode()); //激活链接
String content = templateEngine.process("/mail/activation", context);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mailClient.sendMail(user.getEmail(), "激活账号", content);
}
}).start(); //由于发送邮件太慢,直接交给多线程去处理
mailClient 工具类封装了 JavaMailSender 进行邮箱激活,需要在配置文件中进行邮箱 SMTP 服务的配置。这里用子线程去发送邮件,防止卡顿时间过长。
邮箱里的激活链接即是通过"/activation/{userId}/{code}"访问路径修改用户的 status 字段,使其可用。
登录
登录时检查信息正确性的逻辑和注册时基本一致,需要对账号进行非空、存在和激活的判断,对验证码进行判断,对密码进行非空和正确的判断,以及是否有 rememberMe。登陆成功后生成 LoginTicket 存入数据库,记录了用户 ID、ticket、过期时间等,ticket 字段会被放入 cookie 中。
LoginTicket 登录凭证之所以存入数据库,是考虑到了 session 在分布式环境下请求分发导致的会话状态无法保持的问题。
验证码
使用 Google 提供的 Kaptcha 实现验证码,登录时要检查验证码,逻辑如下:
-
生成图片时存入 session(后面用 Redis 优化):
@RequestMapping(path = "/kaptcha", method = RequestMethod.GET) public void getKaptcha(HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) { String text = kaptchaProducer.createText(); BufferedImage image = kaptchaProducer.createImage(text); //验证码存入session session.setAttribute("kaptcha", text); //图片输出给浏览器,不用关闭流,springmvc会自动做 response.setContentType("image/png"); try { OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream(); //javax的用于图片输出的工具 ImageIO.write(image,"png",os); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error("响应验证码失败:" + e.getMessage()); } } -
登录时从 session 中取值和表单值进行比对即可。
状态保持
登录后需要进行状态保持,可以用前面提到的登录凭证 +Interceptor+ThreadLocal 实现:
public class LoginTicketInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String ticket = CookieUtil.getValue(request, "ticket");
if(ticket != null) {
LoginTicket loginTicket = userService.findLoginTicket(ticket);
//查询凭证是否有效
if(loginTicket != null && loginTicket.getStatus() == 0 && loginTicket.getExpired().after(new Date())) {
//本次请求中持有该用户
User user = userService.findUserById(loginTicket.getUserId());
hostHolder.setUser(user);
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
if(user != null && modelAndView != null) {
modelAndView.addObject("loginUser", user);
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
hostHolder.clear();
}
}
拦截器在 preHandle 时检查 cookies 中是否有有效 ticket,有的话就在当前请求中持有用户信息。HostHolder 类封装了 ThreadLocal< User >,ThreadLocal 的目的:Tomcat 服务器会使用独立线程去处理每个请求,因此需要隔离多请求多用户,防止信息混乱。
拦截器在 postHandle 时若发现该次请求中有用户信息,需要在 modelAndView 中添加用户信息以保持状态。
在 afterCompletion 清空信息即可。
设置头像
File 文件上传,修改用户的头像链接使其可以通过 url 访问头像图片。图片存放位置可暂存本地,后改为云服务器。
@RequestMapping(path = "upload",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String uploadHeader(MultipartFile headerimage, Model model) {
if(headerimage == null) {
model.addAttribute("error", "您未选择图片!");
return "/site/setting";
}
String filename = headerimage.getOriginalFilename();
String suffix = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".")); //.png等后缀
if(StringUtils.isBlank(suffix)) {
model.addAttribute("error", "文件格式不正确!");
return "/site/setting";
}
//生成随机访问url
filename = NcCommunityUtil.generateUUID() + suffix;
//上传头像
File file = new File(uploadPath + "/" + filename);
try {
headerimage.transferTo(file);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("上传文件失败:" + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("上传文件失败,服务器异常!", e);
}
//更新headerUrl(web访问路径)
//http://localhost:8080/nccommunity/user/header/xxx.png
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
String headerUrl = domain + contextPath + "/user/header/" + filename;
userService.updateHeader(user.getId(), headerUrl);
return "redirect:/index";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/header/{filename}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void getHeader(@PathVariable("filename") String filename, HttpServletResponse response) {
filename = uploadPath + "/" + filename; //服务器实际存放头像位置
String suffix = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
System.out.println(suffix);
//注意这里只能用传统的文件io方法而不能用验证码的ImageIO.write(image,"png",os);因为第一个参数类型不满足
response.setContentType("image/" + suffix);
try(
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filename);
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
) {
byte[] buffer =new byte[1024];
int b = 0;
while((b=fis.read(buffer))!= -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, b);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("读取头像失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
简单的权限管理
设置页面和修改头像请求显然必须登录才能使用,可以通过注解进行简单的权限管理:
自定义@LoginRequired 注解类,并添加到需要权限的方法上,然后通过拦截器进行判定。在访问当前方法时若有该注解则必须是已登录状态:
public class LoginRequiredInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if(handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
LoginRequired loginRequired = method.getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class);
if(loginRequired != null && hostHolder.getUser() == null) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/login");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
发帖评论私信
发帖和评论为论坛核心功能,此外要能支持用户的私信。
敏感词过滤
基于 Trie 树数据结构,该模块可用于帖子、评论、私信等。
public class SensitiveFilter {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SensitiveFilter.class);
//替换符号
private static final String REPLACEMENT = "**";
//根节点
private TrieNode rootNode = new TrieNode();
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
try(
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("sensitive-words.txt");//classes类路径
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
) {
String keyword;
while((keyword = reader.readLine()) != null) {
this.addKeyword(keyword);
}
}catch(IOException e) {
logger.error("加载敏感词文件失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 用于过滤文本的敏感词,被外界所调用
* @param text 待过滤文本
* @return 过滤后的文本
*/
public String filter(String text) {
if(StringUtils.isBlank(text)) {
return null;
}
//指针1,指向树
TrieNode tempNode = rootNode;
//指针2
int begin = 0;
//指针3
int position = 0;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(position < text.length()) {
char c = text.charAt(position);
//跳过符号
if(isSymbol(c)) {
//若指针1位于根节点(即position == ),说明过滤判断还没开始,因此该符号可以计入结果
if(tempNode == rootNode) {
sb.append(c);
begin++;
}
//position始终跳过该符号
position++;
continue;
}
tempNode = tempNode.getSubnode(c);
//以begin开头的子字符串不是敏感词
if(tempNode == null) {
sb.append(c);
position = ++begin;
tempNode = rootNode;
} else if(tempNode.isKeywordEnd()) {
//发现敏感词
sb.append(REPLACEMENT);
begin = ++position;
tempNode = rootNode;
} else {
//继续检查
position++;
}
}
//最后的几个字符计入
sb.append(text.substring(begin));
return sb.toString();
}
private class TrieNode {
//关键词结束标识
private boolean isKeywordEnd = false;
//子节点
private Map<Character, TrieNode> subnodes = new HashMap<>();
public boolean isKeywordEnd() {
return isKeywordEnd;
}
public void setKeywordEnd(boolean keywordEnd) {
isKeywordEnd = keywordEnd;
}
//添加子节点操作
public void addSubnode(Character c, TrieNode node) {
subnodes.put(c, node);
}
//获取子节点操作
public TrieNode getSubnode(Character c) {
return subnodes.get(c);
}
}
private void addKeyword(String keyword) {
TrieNode trieNode = rootNode;
for(int i = 0; i < keyword.length(); i++){
char c = keyword.charAt(i);
TrieNode subnode = trieNode.getSubnode(c);
if(subnode == null) {
subnode = new TrieNode();
trieNode.addSubnode(c, subnode);
}
trieNode = subnode;
}
//最后别忘了设置结束标志
trieNode.setKeywordEnd(true);
}
private boolean isSymbol(Character c) {
return !CharUtils.isAsciiAlphanumeric(c) && (c < 0x2E80 || c > 0x9FFF); //0x2E80到0x9FFF为东亚文字
}
}
发帖
异步发送请求,以通过提示框展示提示信息,发帖后台就是普通的 crud。
function publish() {
$("#publishModal").modal("hide");
//获取标题和内容
var title = $("#recipient-name").val();
var content = $("#message-text").val();
//发送异步请求
$.post(
CONTEXT_PATH + "/discuss/add",
{"title":title,"content":content},
function (data) {
data = $.parseJSON(data);
console.log(data);
//提示框内展示返回消息
$("#hintBody").text(data.msg);
//显示提示框
$("#hintModal").modal("show");
//2s后,隐藏
setTimeout(function(){
$("#hintModal").modal("hide");
//刷新页面
if(data.code == 0) {
window.location.reload();
}
}, 2000);
}
)
}
评论
评论分为对帖子的评论(简称评论)和对评论的评论(简称回复)。
评论的 entity 如下:
public class Comment {
private int id;
private int userId;
private int entityType;
private int entityId;
private int targetId;
private String content;
private int status;
private Date createTime;
...
}
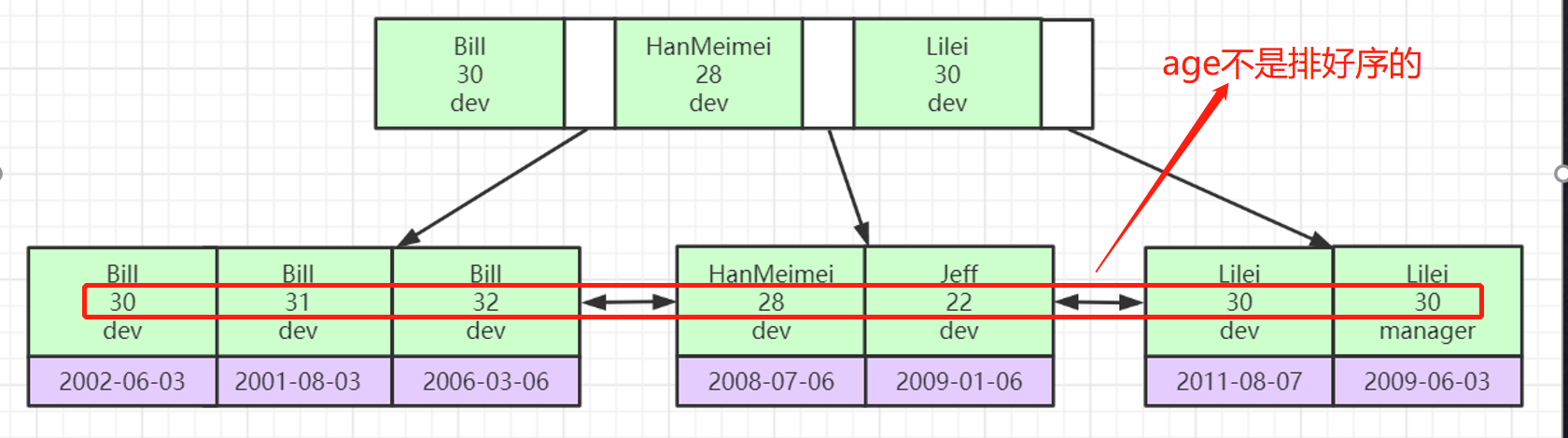
entityType+entityId 指示评论的对象(是帖子还是评论,然后具体 Id 为多少),当 entityType 为评论,且该条评论为回复时有效,为 0 表示该条回复评论的是对帖子的评论,非 0 则是代表该条回复评论的是回复,具体如图:

另外注意,帖子 entity 中有个关于评论的冗余数据,因此有新评论产生时需要通过事务进行更新:
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public int addComment(Comment comment) {
if(comment == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!");
}
comment.setContent(HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(comment.getContent()));
comment.setContent(sensitiveFilter.filter(comment.getContent()));
int rows = commentMapper.insertComment(comment);
//更新帖子的冗余数据
if(comment.getEntityType() == ENTITY_TYPE_POST) {
int count = commentMapper.selectCountByEntity(comment.getEntityType(),comment.getEntityId());
discussPostMapper.updateCommentCount(comment.getEntityId(), count);
}
return rows;
}
私信
私信 entity 如下:
public class Message {
private int id;
private int fromId;
private int toId;
private String conversationId;
private String content;
private int status;
private Date createTime;
...
}
其中 conversationId 由 fromId 和 toId 拼接而成,小 Id 在前,如 111_112,表示 111 和 112 之间的私信。status 记录私信是否已读,当用户进入私信详情页面时,会更新未读私信状态为已读。
@RequestMapping(path = "/detail/{conversationId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getLetterDetail(@PathVariable("conversationId") String conversationId, Page page, Model model){
page.setLimit(5);
page.setPath("/letter/detail/" + conversationId);
page.setRows(messageService.findLetterCount(conversationId));
List<Message> letterList = messageService.findLetters(conversationId, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit());
List<Map<String,Object>> letters = new ArrayList<>();
if(letterList != null) {
for(Message message : letterList) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("letter", message);
map.put("fromUser",userService.findUserById(message.getFromId()));
letters.add(map);
}
}
model.addAttribute("letters", letters);
//私信目标,显示要用
model.addAttribute( "target", getLetterTarget(conversationId));
//设置已读
List<Integer> ids = getLetterIds(letterList);
if(!ids.isEmpty()) {
messageService.readMessage(ids);
}
return "/site/letter-detail";
}
private User getLetterTarget(String conversationId) {
String[] ids = conversationId.split("_");
int d0 = Integer.parseInt(ids[0]);
int d1 = Integer.parseInt(ids[1]);
if(hostHolder.getUser().getId() == d0) {
return userService.findUserById(d1);
} else return userService.findUserById(d0);
}
/**
* 获取当前用户当前会话未读消息的id
* @param letterList
* @return
*/
private List<Integer> getLetterIds(List<Message> letterList) {
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
if(letterList != null) {
for(Message message : letterList) {
if(hostHolder.getUser().getId() == message.getToId() && message.getStatus() == 0) {
ids.add(message.getId());
}
}
}
return ids;
}
统一异常处理
JavaWeb 的思想是异常尽量不处理,而是往上层抛给 controller 去处理。Spring 对此提供了简单支持,若有 4xx 或 5xx 异常,则返回的页面为/error 包下对应的 4xx.html 或 5xx.html。但我们有如下需求:
- 记录错误日志
- 对于异步/非异步提供友好提示
因此我们可以用@ControllerAdvice 注解实现异常处理:
//统一异常处理,1.记录日志 2.对于异步/非异步请求给予友好提示
//如果无上述需求,可以用spring自带的异常处理(error包和404.html/500.html)
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = Controller.class)
public class ExceptionAdvice {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionAdvice.class);
@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class})
public void handlerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
logger.error("服务器发生异常: " + e.getMessage());
for(StackTraceElement element : e.getStackTrace()) {
logger.error(element.toString());
}
String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");
//如果是异步请求,返回普通字符串
if("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {
response.setContentType("application/plain;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write(NcCommunityUtil.getJSONString(1, "服务器异常"));
} else {
//非异步请求
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error");
}
}
}
统一记录日志
我们需要知道哪些用户什么时候对什么方法进行了访问,因此最好能提供日志记录,一个解决思路是对于每个方法都进行硬编码记录日志,但这种思路显然违背了开闭原则,不利于扩展和维护。因此我们可以用 AOP 的思想解决问题,Spring 对此提供了友好支持:
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceLogAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceLogAspect.class);
//任意返回值,service包的任意xxx类的任意方法(任意参数)
@Pointcut("execution(* cn.codingcrea.nccommunity.service.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() {
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//用户[1.2.3.4],在[xxx],访问了[xxx.service.xxx.xxx()].
//由于不能用request,只能用下面的方法
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = requestAttributes.getRequest();
String ip = request.getRemoteHost();
String now = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());
String target = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
logger.info(String.format("用户[%s],在[%s],访问了[%s].", ip, now, target));
}
}
切入时机可以是 pointcut 调用前(@Before),pointcut 调用后(@After),环绕 pointcut(@Around),return 后(@AfterReturning),异常后(@AfterThrowing)。这里只需@Before 即可。
点赞关注
点赞关注使用较频繁,是通过 Redis 实现的。我们在配置类中将 RedisTemplate<String, Object> 注入 Spring 容器,该 Bean 需要设置 key 和 value 的序列化方式(存入的有可能是对象,采用 JSON 格式进行序列化)。
点赞
点赞用 AJAX 实现,可对帖子也可对评论点赞。根据返回的点赞状态和点赞数量进行正确的局部更新。Service 方法如下:
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//点赞
//entityUserId即被点赞的实体的作者,本来可以通过entityId找,但点赞操作本来是redis操作,这样查会调数据库拉低性能,因此干脆直接作为参数传进来
public void like(int userId, int entityType, int entityId, int entityUserId) {
// String entityLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getEntityLikeKey(entityType, entityId);
// Boolean isMember = redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(entityLikeKey, userId);
// if(isMember) {
// redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(entityLikeKey, userId);
// } else {
// redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(entityLikeKey, userId);
// }
redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations redisOperations) throws DataAccessException {
String entityLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getEntityLikeKey(entityType, entityId);
String userLikeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserLikeKey(entityUserId);
Boolean isMember = redisOperations.opsForSet().isMember(entityLikeKey, userId);
redisOperations.multi();
if(isMember) {
redisOperations.opsForSet().remove(entityLikeKey, userId);
redisOperations.opsForValue().decrement(userLikeKey);
} else {
redisOperations.opsForSet().add(entityLikeKey, userId);
redisOperations.opsForValue().increment(userLikeKey);
}
return redisOperations.exec();
}
});
}
其中 RedisKeyUtil 是一个构造 Redis key 的工具类,生成的 key 是由各个字段用冒号隔开的(Redis 的惯用 key 命名方式)。
我们通过 set 数据结构记录某个实体(如帖子)的点赞用户 Id,此外用一个 string 数据结构记录某个用户获得的赞总数:

这两个数据结构的操作需要用到 Redis 的事务一并实现。
关注
关注的对象可以是用户、帖子、评论。和点赞的区别在于:key 中需要包含关注者和被关注者这两个变量。
Service 层定义 follow 和 unfollow 等方法,试举一例:
public void follow(int userId, int entityType, int entityId) {
redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations redisOperations) throws DataAccessException {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, entityType);
String followerKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFollowerKey(entityType, entityId);
redisOperations.multi();
redisOperations.opsForZSet().add(followeeKey, entityId, System.currentTimeMillis());
redisOperations.opsForZSet().add(followerKey, userId, System.currentTimeMillis());
return redisOperations.exec();
}
});
}
这里要用 zset 数据结构,在进行关注的人/粉丝列表显示的时候,可以根据关注时间进行排序显示。

你可以查看别人的关注列表,并对列表中的用户进行关注。
//查询某用户关注的人
public List<Map<String,Object>> findFollowees(int userId, int offset, int limit) {
String followeeKey = RedisKeyUtil.getFolloweeKey(userId, ENTITY_TYPE_USER);
//注意,虽然这里是Set,但其实返回的实现类是redis自己的,是保证了顺序的
Set<Integer> targetIds = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRange(followeeKey, offset, offset + limit - 1);
if(targetIds == null) {
return null;
}
List<Map<String,Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Integer targetId : targetIds) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
User user = userService.findUserById(targetId);
map.put("user", user);
Double score = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(followeeKey, targetId);
map.put("followTime", new Date(score.longValue()));
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
缓存优化
下面用 Redis 缓存进行了三处地方的性能优化。
代替 session 存储验证码
理由如下:
- 验证码可能会频繁访问和刷新
- 验证码只需要暂存,不需要长期保存
- 如未来涉及到分布式部署,能避免 session 共享的问题。
存验证码("/kaptcha"请求):
//验证码存入session
// session.setAttribute("kaptcha", text);
//验证码存入redis
String kaptchaOwner = NcCommunityUtil.generateUUID();
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("kaptchaOwner", kaptchaOwner);
cookie.setMaxAge(60);
cookie.setPath(contextPath);
response.addCookie(cookie);
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getKaptchaKey(kaptchaOwner);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(redisKey, text, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
登录表单提交时取验证码:
@RequestMapping(path = "/login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(String username, String password, String code, boolean rememberme, Model model,
/*HttpSession session,*/ HttpServletResponse response,
@CookieValue("kaptchaOwner") String kaptchaOwner) {
//验证码
// String kaptcha = (String) session.getAttribute("kaptcha");
String kaptcha = null;
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(kaptchaOwner)) {
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getKaptchaKey(kaptchaOwner);
kaptcha = (String)redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey);
}
...
}
存储登录凭证
每次对网站的请求都会通过拦截器获取登录凭证,因此考虑到凭证的时效性和经常性,可以改为用 Redis 存储凭证而不是用数据库存储。
存储用户信息
同上,每次对网站的请求都会通过拦截器获取登录凭证,然后再获取用户信息以保持登录状态,因此对于 findUserById 这个方法,有必要做 Redis 缓存:
@Component
public class LoginTicketInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String ticket = CookieUtil.getValue(request, "ticket");
if(ticket != null) {
LoginTicket loginTicket = userService. findLoginTicket(ticket);
//查询凭证是否有效
if(loginTicket != null && loginTicket.getStatus() == 0 && loginTicket.getExpired().after(new Date())) {
//本次请求中持有该用户
User user = userService.findUserById(loginTicket.getUserId());
hostHolder.setUser(user);
}
}
return true;
}
...
}
这样,整个拦截器所调用的方法就不会涉及到数据库了。
但用户信息的存储会涉及到 Redis 和 MySQL 的缓存不一致问题,需要解决:
//1.优先从缓存中取值
private User getCache(int userId) {
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserKey(userId);
return (User)redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey);
}
//2.取不到时初始化缓存数据
private User initCache(int userId) {
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserKey(userId);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(redisKey, user, 3600, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return user;
}
//3.数据变更时清除缓存信息
private void clearCache(int userId) {
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUserKey(userId);
redisTemplate.delete(redisKey);
}
//redis、数据库不一致问题https://developer.aliyun.com/article/712285
//由于该项目涉及到的主要是user信息,所以很难涉及到对同一行的并发访问,可以不采用延时双删等策略
//重试机制?
//这篇比较完善,以后再看:https://www.cnblogs.com/dingpeng9055/p/11562261.html
关于缓存不一致问题,有很多解决方法,这里采用的是:当数据变更时,先更新数据库,再删除缓存。
当然无论是先更新数据库还是先删除缓存,都会有并发访问情况下的不一致问题和第二步操作失败的问题。
前一个问题可以采用延迟双删策略来解决。后一个问题可以用重试机制来解决。详细可以参考博文。
public User findUserById(int id) {
// return userMapper.selectById(id);
User user = getCache(id);
if(user == null) {
user = initCache(id);
}
return user;
}
...
//用户信息变更时
public int updateHeader(int userId, String headerUrl) {
int i = userMapper.updateHeaderUrl(userId, headerUrl);
clearCache(userId);
return i;
}
系统通知
用 Kafka 做消息队列也能对系统进行优化。
原先 Controller 层的一些实现逻辑,可以转移到 EventConsumer 类中实现,享有消息队列异步削峰解耦的优势。例如系统通知的实现,本身和点赞、关注、评论的逻辑关联不强,且这些动作频繁发生,因此可以通过异步实现,提高性能。在例如后面用到的 ES 数据库的更新也可以用消息队列来实现。
比如点赞时:
@RequestMapping(path = "/like",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String like(int entityType, int entityId, int entityUserId, int postId) {
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
likeService.like(user.getId(), entityType, entityId, entityUserId);
//数量
long likeCount = likeService.findEntityLikeCount(entityType, entityId);
//状态
int likeStatus = likeService.findEntityLikeStatus(user.getId(), entityType, entityId);
//返回结果
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("likeCount",likeCount);
map.put("likeStatus", likeStatus);
//触发点赞事件
if(likeStatus == 1) {
Event event = new Event()
.setTopic(TOPIC_LIKE)
.setUserId(hostHolder.getUser().getId())
.setEntityType(entityType)
.setEntityId(entityId)
.setEntityUserId(entityUserId)
.setData("postId", postId);
eventProducer.fireEvent(event);
}
return NcCommunityUtil.getJSONString(0, null, map);
}
生产者:
@Component
public class EventProducer {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
//处理事件
public void fireEvent(Event event) {
//发布消息到指定topic
kafkaTemplate.send(event.getTopic(), JSONObject.toJSONString(event));
}
}
消费者:
@Component
public class EventConsumer implements CommunityConstant {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EventConsumer.class);
@Autowired
private MessageService messageService;
@KafkaListener(topics = {TOPIC_COMMENT,TOPIC_LIKE,TOPIC_FOLLOW})
public void handleCommentMessage(ConsumerRecord record) {
if(record == null || record.value() == null) {
logger.error("消息为空!");
return;
}
Event event = JSONObject.parseObject(record.value().toString(), Event.class);
if(event == null) {
logger.error("消息的格式不对!");
return;
}
Message message = new Message();
message.setFromId(SYSTEM_USER_ID);
message.setToId(event.getEntityUserId());
message.setConversationId(event.getTopic());
message.setCreateTime(new Date());
Map<String, Object> content = new HashMap<>();
content.put("userId", event.getUserId());
content.put("entityType", event.getEntityType());
content.put("entityId",event.getEntityId());
if(!event.getData().isEmpty()) {
for(Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : event.getData().entrySet()) {
content.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
message.setContent(JSONObject.toJSONString(content));
messageService.addMessage(message);
}
}
至于系统消息的查看、列表等实现,则基本与私信的实现差不多。(数据库中 from_id 为 1 表示这不是普通私信而是系统通知)

搜索
Elasticsearch 相当于特殊的数据库,搜索就是对这个数据库的搜索。
ElasticsearchService 需要完成三个方法:save、delete 和 search,重点是 search:
public Map<String, Object> searchDiscussPost(String keyword,int current, int limit) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
NativeSearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
.withQuery(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery(keyword, "title", "content"))
.withSort(SortBuilders.fieldSort("type").order(SortOrder.DESC))
.withSort(SortBuilders.fieldSort("score").order(SortOrder.DESC))
.withSort(SortBuilders.fieldSort("createTime").order(SortOrder.DESC))
.withPageable(PageRequest.of(current, limit))
.withHighlightFields(
new HighlightBuilder.Field("title").preTags("<em>").postTags("</em>"),
new HighlightBuilder.Field("content").preTags("<em>").postTags("</em>")
).build();
SearchHits<DiscussPost> search = elasticsearchRestTemplate.search(searchQuery, DiscussPost.class);
// 得到查询结果返回的内容
List<SearchHit<DiscussPost>> searchHits = search.getSearchHits();
// 设置一个需要返回的实体类集合
List<DiscussPost> discussPosts = new ArrayList<>();
for(SearchHit<DiscussPost> searchHit : searchHits){
// 高亮的内容
Map<String, List<String>> highLightFields = searchHit.getHighlightFields();
// 将高亮的内容填充到content中
searchHit.getContent().setTitle(highLightFields.get("title") == null ? searchHit.getContent().getTitle() : highLightFields.get("title").get(0));
searchHit.getContent().setContent(highLightFields.get("content") == null ? searchHit.getContent().getContent() : highLightFields.get("content").get(0));
// 放到实体类中
discussPosts.add(searchHit.getContent());
}
long totalCount = elasticsearchRestTemplate.count(searchQuery, DiscussPost.class);
result.put("discussPosts", discussPosts);
result.put("totalCount", totalCount);
return result;
}
其他
认证授权
废弃了之前采用拦截器实现的登录检查,使用 Spring Security 框架来进行统一认证授权管理。Security 底层原理蛮复杂的,我们这里对其进行简单的使用。
授权方面,见 Security 配置类:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter implements CommunityConstant {
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/resources/**");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//授权
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(
"/user/setting",
...
)
.hasAnyAuthority(
AUTHORITY_USER,
AUTHORITY_ADMIN,
AUTHORITY_MODERATOR)
.antMatchers(
"/discuss/top",
"/discuss/wonderful"
)
.hasAnyAuthority(
AUTHORITY_MODERATOR
)
.antMatchers(
"/discuss/delete"
)
.hasAnyAuthority(
AUTHORITY_ADMIN
)
.anyRequest().permitAll()
.and().csrf().disable();
//权限不够时的处理
http.exceptionHandling()
//未登录时
.authenticationEntryPoint(new AuthenticationEntryPoint() {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
...
}
})
//权限不足
.accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
...
}
});
//跳过(覆盖默认)logout功能,让自己的logout逻辑能执行
http.logout().logoutUrl("/xxxxxx");
}
//另外,用户认证逻辑采用我自己的,绕过spring security,但是认证信息我们仍要想办法存到SecurityContext里
}
而用户认证方面,由于我们采用自定义的认证方式,因此无需采用 Security 提供的方式,但我们认证信息仍需要存到 SecurityContext 里,拦截器需要改进:
@Component
public class LoginTicketInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String ticket = CookieUtil.getValue(request, "ticket");
if(ticket != null) {
LoginTicket loginTicket = userService. findLoginTicket(ticket);
//查询凭证是否有效
if(loginTicket != null && loginTicket.getStatus() == 0 && loginTicket.getExpired().after(new Date())) {
//本次请求中持有该用户
User user = userService.findUserById(loginTicket.getUserId());
hostHolder.setUser(user);
//构建用户认证结果,并存入SecurityContext,以便于Security获取
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user, user.getPassword(),
userService.getAuthorities(user.getId()));//自定义方法
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(new SecurityContextImpl(authentication));
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
if(user != null && modelAndView != null) {
modelAndView.addObject("loginUser", user);
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
if(hostHolder.getUser()==null) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
hostHolder.clear();
}
}
认证信息会在 preHandle 加入,afterafterCompletion 处删除,logout 时也会删除。
关于认证信息何时删除的思考:
-
每次在 afterCompletion 时删除:
Security 是基于 Filter 的,如果每次在 afterCompletion 时删除,那么下次请求时首先到达 Filter,由于没有认证信息,会被判定权限不够,直接跳转到登录页面,即使已经登录。
-
在 afterCompletion 时不删除,只在 logout 时删除:
如果这样虽然能保证权限与请求匹配,但是由于登录凭证会过期,用户信息会被清除,但认证信息却不会被清除,用户即使没登录也能访问,显然不合常理。
-
因此正确做法为 afterafterCompletion 处如果没有用户信息就删除认证信息,logout 时也删除。
置顶加精删除
Thymeleaf 有对 Security 的支持,可以从 SecurityContext 从获得权限信息。从而赋予用户不同的权限(置顶、加精、删除)。
网站统计
UV 独立访客统计
使用 Redis 的 HyperLogLog 数据结构去实现,该数据结构的特点是占用内存很小,但会损失一定的统计精度。
使用拦截器,游客每次访问时 Redis 计入该 ip。
统计区间 UV:
public long calculateUV(Date start, Date end) {
if(start == null || end == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!");
}
//整理日期范围内的key
List<String> keyList = new ArrayList<>();
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(start);
while(!calendar.getTime().after(end)) {
String key = RedisKeyUtil.getUVKey(sdf.format(calendar.getTime()));
keyList.add(key);
calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, 1);
}
//合并数据(union去重生成新数据)
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getUVKey(sdf.format(start), sdf.format(end));
redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().union(redisKey, keyList.toArray());
//返回统计结果
return redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().size(redisKey);
}
DAU 日活统计
类似 UV 统计,只是 DAU 统计操作的是 bitmap:
//统计区间内的DAU
public long calculateDAU(Date start, Date end) {
if(start == null || end == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!");
}
//整理日期范围内的key
List<byte[]> keyList = new ArrayList<>();
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(start);
while(!calendar.getTime().after(end)) {
String key = RedisKeyUtil.getDAUKey(sdf.format(calendar.getTime()));
keyList.add(key.getBytes());
calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, 1);
}
//or运算
return(long) redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback() {
@Override
public Object doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getDAUKey(sdf.format(start), sdf.format(end));
connection.bitOp(RedisStringCommands.BitOperation.OR, redisKey.getBytes(),
keyList.toArray(new byte[0][0]));
return connection.bitCount(redisKey.getBytes());
}
});
}
热帖排行
使用 Quartz 实现热帖排行和更新,相比 JDK 的 ScheduledExecutorService 和 Spring 的 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 的优势:
- Quartz 实现定时任务所依赖的参数是保存在数据库中,数据库只有一份,所以不会冲突。
- 而 ScheduledExecutorService 和 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 是基于内存的,在分布式环境中,多台服务器会重复执行定时任务,产生冲突。
热帖排行和更新的实现逻辑如下:
- 帖子的 score 字段计算方法自定义为 log(精华分 + 评论数 * 10+ 点赞数 * 2)+(发布时间-纪元)。
- 一旦涉及到上述 score 会变化的操作,如帖子被设为精华,或帖子有新的评论等,帖子 id 会被放入 Redis 的 set 中。
- 每隔一段时间执行定时任务,会从 set 中 pop 帖子 id 出来进行分数的刷新。
private void refresh(int postId) {
DiscussPost post = discussPostService.findDiscussPostById(postId);
//算分的时候发现被管理员删了
if(post == null) {
logger.error("待刷新帖子不存在: id = " + postId);
return;
}
//是否精华
boolean wonderful = post.getStatus() == 1;
//评论数量
int commentCount = post.getCommentCount();
//点赞数量
long likeCount = likeService.findEntityLikeCount(ENTITY_TYPE_POST, postId);
//计算权重
double w = (wonderful ? 75 : 0) + commentCount * 10 + likeCount * 2;
//分数 = 权重 + 距离天数
double score =
Math.log10(Math.max(w, 1)) + (post.getCreateTime().getTime() - epoch.getTime()) / (1000 * 3600 * 24);
//更新帖子分数
discussPostService.updateScore(postId, score);
//同步搜索数据
post.setScore(score);
elasticSearchService.saveDiscussPost(post);
}
热帖页面根据帖子的 score 进行排序。
头像上传云服务器
头像上传到阿里云 OSS 进行存储,Spring 对此提供了支持。
本地缓存
在实际的部署中,服务器缓存由于就在服务器本机内,因此对性能的提升相比 Redis 更高。
对于热帖等与用户状态无关的内容可以存到本地缓存中。本项目用 Caffeine 实现,主要缓存帖子列表和帖子总数。
需要定义两个缓存管理器,一个针对热帖列表,一个针对帖子总数,可以通过@PostConstruct 进行初始化。
//帖子列表缓存
private LoadingCache<String,List<DiscussPost>> postListCache;
...
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
//初始化帖子列表缓存
postListCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(maxSize)
.expireAfterWrite(expireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build(new CacheLoader<String,List<DiscussPost>>() { //缓存失效的处理
@Nullable
@Override
public List<DiscussPost> load(@NonNull String key) throws Exception {
if(key == null || key.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数错误!");
}
String[] params = key.split(":");
if(params == null || params.length != 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数错误!");
}
int offset = Integer.valueOf(params[0]);
int limit = Integer.valueOf(params[1]);
//这里可以进行二次缓存,后实现
logger.debug("从数据库中查找热帖列表数据。");
return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPosts(0, offset, limit, 1);
}
});
}
...
public List<DiscussPost> findDiscussPosts(int userId, int offset, int limit, int orderMode) {
//热帖排行缓存,userId=0,orderMode=1时
if(userId == 0 && orderMode == 1) {
return postListCache.get(offset + ":" + limit);
}
logger.debug("从数据库中查找热帖列表数据。");
return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPosts(userId, offset, limit, orderMode);
}
用 JMeter 做下小测试,30w 数据的情况下,性能有数倍到数十倍的提升。
服务器部署
需要修改一些路径以适配 Linux 环境。为方便切换,可以使用两套配置文件。
整个项目部署到阿里云 ECS 上(2cpu/4g/CentOS),部署步骤为:
- Java 运行环境安装。
- Maven 安装,把项目发到云服务器再进行 mvn package,可以节省传输流量,因为 package 后的包特别大。
- Tomcat 安装。
- 安装所需组件,包括 MySQL、Redis、Kafka、Elasticsearch。
- 将本地项目 clean 后压缩发送到服务器。
- 项目解压后使用命令 mvn package -Dmaven.test.skip=true 打包,将生成的 war 包放在 Tomcat 的 webapps 文件夹中,部署成功。
♻️ 资源

大小: 322KB
➡️ 资源下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/s1t16/87274224