1、元素偏移量 offset 系列
1.1、offset 概述
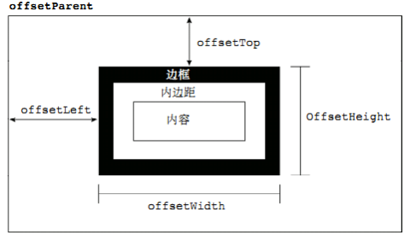
offset 翻译过来就是偏移量, 我们使用 offset系列相关属性可以动态的得到该元素的位置(偏移)、大小等。
- 获得元素距离带有定位父元素的位置
- 获得元素自身的大小(宽度高度)
- 注意:返回的数值都不带单位
| offset系列属性 | 作用 |
| element.offsetParent | 返回作为该元素带有定位的父级元素,如果父级都没有定位则返回body |
| element.offsetTop | 返回元素相对带有定位父元素上方的偏移 |
| element.offsetLeft | 返回元素相对带有定位父元素左边框的偏移 |
| element.offsetWidth | 返回自身包括padding、边框、内容区的宽度,返回数值不带单位 |
| element.offsetHeight | 返回自身包括padding、边框、内容区的高度,返回数值不带单位 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.father {
/* position: relative; */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 150px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: purple;
margin-left: 45px;
}
.w {
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
margin: 0 auto 200px;
padding: 10px;
border: 15px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
<div class="w"></div>
<script>
// offset 系列
var father = document.querySelector('.father');
var son = document.querySelector('.son');
// 1.可以得到元素的偏移 位置 返回的不带单位的数值
console.log(father.offsetTop);
console.log(father.offsetLeft);
// 它以带有定位的父亲为准 如果么有父亲或者父亲没有定位 则以 body 为准
console.log(son.offsetLeft);
var w = document.querySelector('.w');
// 2.可以得到元素的大小 宽度和高度 是包含padding + border + width
console.log(w.offsetWidth);
console.log(w.offsetHeight);
// 3. 返回带有定位的父亲 否则返回的是body
console.log(son.offsetParent); // 返回带有定位的父亲 否则返回的是body
console.log(son.parentNode); // 返回父亲 是最近一级的父亲 亲爸爸 不管父亲有没有定位
</script>
</body>
</html>1.2、offset 与 style 区别
offset
-
offset 可以得到任意样式表中的样式值
-
offset 系列获得的数值是没有单位的
-
offsetWidth 包含padding+border+width
-
offsetWidth 等属性是只读属性,只能获取不能赋值
-
所以,我们想要获取元素大小位置,用offset更合适
style
-
style 只能得到行内样式表中的样式值
-
style.width 获得的是带有单位的字符串
-
style.width 获得不包含padding和border 的值
-
style.width 是可读写属性,可以获取也可以赋值
-
所以,我们想要给元素更改值,则需要用style改变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="width: 200px;"></div>
<script>
// offset与style的区别
var box = document.querySelector('.box');
console.log(box.offsetWidth);
console.log(box.style.width);
// box.offsetWidth = '300px';
box.style.width = '300px';
</script>
</body>
</html>1.3、案例:获取鼠标在盒子内的坐标
-
我们在盒子内点击,想要得到鼠标距离盒子左右的距离。
-
首先得到鼠标在页面中的坐标(e.pageX, e.pageY)
-
其次得到盒子在页面中的距离 ( box.offsetLeft, box.offsetTop)
-
用鼠标距离页面的坐标减去盒子在页面中的距离,得到 鼠标在盒子内的坐标
-
如果想要移动一下鼠标,就要获取最新的坐标,使用鼠标移动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 我们在盒子内点击, 想要得到鼠标距离盒子左右的距离。
// 首先得到鼠标在页面中的坐标( e.pageX, e.pageY)
// 其次得到盒子在页面中的距离(box.offsetLeft, box.offsetTop)
// 用鼠标距离页面的坐标减去盒子在页面中的距离, 得到 鼠标在盒子内的坐标
var box = document.querySelector('.box');
box.addEventListener('mousemove', function(e) {
// console.log(e.pageX);
// console.log(e.pageY);
// console.log(box.offsetLeft);
var x = e.pageX - this.offsetLeft;
var y = e.pageY - this.offsetTop;
this.innerHTML = 'x坐标是' + x + ' y坐标是' + y;
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1.4、案例:模态框拖拽
弹出框,我们也称为模态框。
1.点击弹出层,会弹出模态框, 并且显示灰色半透明的遮挡层。
2.点击关闭按钮,可以关闭模态框,并且同时关闭灰色半透明遮挡层。
3.鼠标放到模态框最上面一行,可以按住鼠标拖拽模态框在页面中移动。
4.鼠标松开,可以停止拖动模态框移动
案例分析:
-
点击弹出层, 模态框和遮挡层就会显示出来 display:block;
-
点击关闭按钮,模态框和遮挡层就会隐藏起来 display:none;
-
在页面中拖拽的原理:鼠标按下并且移动, 之后松开鼠标
-
触发事件是鼠标按下mousedown,鼠标移动mousemove 鼠标松开 mouseup
-
拖拽过程: 鼠标移动过程中,获得最新的值赋值给模态框的left和top值,这样模态框可以跟着鼠标走了
-
鼠标按下触发的事件源是最上面一行,就是 id 为 title
-
鼠标的坐标减去 鼠标在盒子内的坐标, 才是模态框真正的位置。
-
鼠标按下,我们要得到鼠标在盒子的坐标。
-
鼠标移动,就让模态框的坐标 设置为 :鼠标坐标 减去盒子坐标即可,注意移动事件写到按下事件里面。
-
鼠标松开,就停止拖拽,就是可以让鼠标移动事件解除
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.login-header {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 30px;
}
ul,
li,
ol,
dl,
dt,
dd,
div,
p,
span,
h1,
h2,
h3,
h4,
h5,
h6,
a {
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
}
.login {
display: none;
width: 512px;
height: 280px;
position: fixed;
border: #ebebeb solid 1px;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
background: #ffffff;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px #ddd;
z-index: 9999;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
.login-title {
width: 100%;
margin: 10px 0px 0px 0px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 18px;
position: relative;
cursor: move;
}
.login-input-content {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.login-button {
width: 50%;
margin: 30px auto 0px auto;
line-height: 40px;
font-size: 14px;
border: #ebebeb 1px solid;
text-align: center;
}
.login-bg {
display: none;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: fixed;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3);
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #000000;
}
.login-button a {
display: block;
}
.login-input input.list-input {
float: left;
line-height: 35px;
height: 35px;
width: 350px;
border: #ebebeb 1px solid;
text-indent: 5px;
}
.login-input {
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0px 0px 20px 0px;
}
.login-input label {
float: left;
width: 90px;
padding-right: 10px;
text-align: right;
line-height: 35px;
height: 35px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.login-title span {
position: absolute;
font-size: 12px;
right: -20px;
top: -30px;
background: #ffffff;
border: #ebebeb solid 1px;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="login-header"><a id="link" href="javascript:;">点击,弹出登录框</a></div>
<div id="login" class="login">
<div id="title" class="login-title">登录会员
<span><a id="closeBtn" href="javascript:void(0);" class="close-login">关闭</a></span>
</div>
<div class="login-input-content">
<div class="login-input">
<label>用户名:</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" name="info[username]" id="username" class="list-input">
</div>
<div class="login-input">
<label>登录密码:</label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请输入登录密码" name="info[password]" id="password" class="list-input">
</div>
</div>
<div id="loginBtn" class="login-button"><a href="javascript:void(0);" id="login-button-submit">登录会员</a></div>
</div>
<!-- 遮盖层 -->
<div id="bg" class="login-bg"></div>
<script>
// 1. 获取元素
var login = document.querySelector('.login');
var mask = document.querySelector('.login-bg');
var link = document.querySelector('#link');
var closeBtn = document.querySelector('#closeBtn');
var title = document.querySelector('#title');
// 2. 点击弹出层这个链接 link 让mask 和login 显示出来
link.addEventListener('click', function() {
mask.style.display = 'block';
login.style.display = 'block';
})
// 3. 点击 closeBtn 就隐藏 mask 和 login
closeBtn.addEventListener('click', function() {
mask.style.display = 'none';
login.style.display = 'none';
})
// 4. 开始拖拽
// (1) 当我们鼠标按下, 就获得鼠标在盒子内的坐标
title.addEventListener('mousedown', function(e) {
var x = e.pageX - login.offsetLeft;
var y = e.pageY - login.offsetTop;
// (2) 鼠标移动的时候,把鼠标在页面中的坐标,减去 鼠标在盒子内的坐标就是模态框的left和top值
document.addEventListener('mousemove', move)
function move(e) {
login.style.left = e.pageX - x + 'px';
login.style.top = e.pageY - y + 'px';
}
// (3) 鼠标弹起,就让鼠标移动事件移除
document.addEventListener('mouseup', function() {
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', move);
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>2、元素可视区 client 系列
2.1、client概述
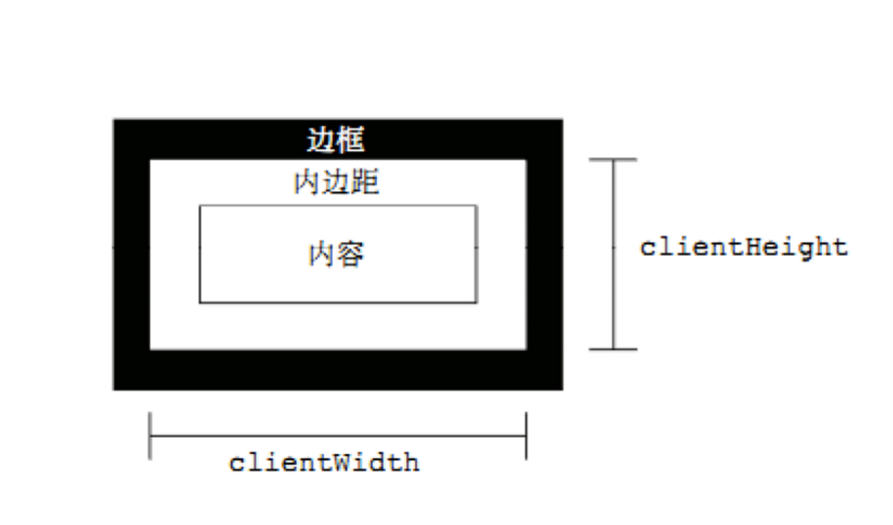
client 翻译过来就是客户端,我们使用 client 系列的相关属性来获取元素可视区的相关信息。通过 client 系列的相关属性可以动态的得到该元素的边框大小、元素大小等。
| client系列属性 | 作用 |
| element.clientTop | 返回元素上边框的大小 |
| element.clientLeft | 返回元素左边框的大小 |
| element.clientWidth | 返回自身包括padding、内容区的宽度,不含边框,返回数值不带单位 |
| element.clientHeight | 返回自身包括padding、内容区的高度,不含边框,返回数值不带单位 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
border: 10px solid red;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
// client 宽度 和我们offsetWidth 最大的区别就是 不包含边框
var div = document.querySelector('div');
console.log(div.clientWidth);
</script>
</body>
</html>2.2、立即执行函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1.立即执行函数: 不需要调用,立马能够自己执行的函数
function fn() {
console.log(1);
}
fn();
// 2. 写法 也可以传递参数进来
// 1.(function() {})() 或者 2. (function(){}());
(function(a, b) {
console.log(a + b);
var num = 10;
})(1, 2); // 第二个小括号可以看做是调用函数
(function sum(a, b) {
console.log(a + b);
var num = 10; // 局部变量
}(2, 3));
// 3. 立即执行函数最大的作用就是 独立创建了一个作用域, 里面所有的变量都是局部变量 不会有命名冲突的情况
</script>
</body>
</html>3、元素滚动 scroll 系列
3.1、scroll 概述
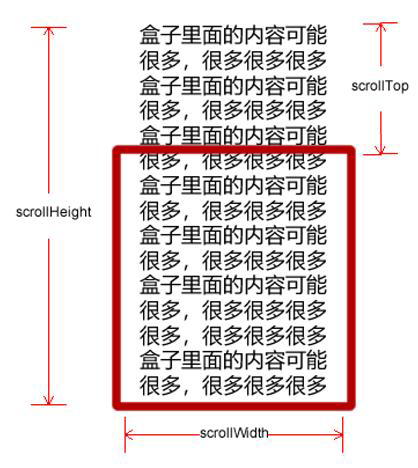
scroll 翻译过来就是滚动的,我们使用 scroll 系列的相关属性可以动态的得到该元素的大小、滚动距离等。
| scroll系列属性 | 作用 |
| element.scrollTop | 返回被卷去的上侧距离,返回数值不带单位 |
| element.scrollLeft | 返回被卷去的左侧距离,返回数值不带单位 |
| element.scrollWidth | 返回自身实际的宽度,不含边框,返回数值不带单位 |
| element.scrollHeight | 返回自身实际的高度,不含边框,返回数值不带单位 |
3.2、页面被卷去的头部
如果浏览器的高(或宽)度不足以显示整个页面时,会自动出现滚动条。当滚动条向下滚动时,页面上面被隐藏掉的高度,我们就称为页面被卷去的头部。滚动条在滚动时会触发 onscroll事件。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
border: 10px solid red;
padding: 10px;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容 我是内容
</div>
<script>
// scroll 系列
var div = document.querySelector('div');
console.log(div.scrollHeight);
console.log(div.clientHeight);
// scroll滚动事件当我们滚动条发生变化会触发的事件
div.addEventListener('scroll', function() {
console.log(div.scrollTop);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>3.3、案例:仿淘宝固定右侧侧边栏
-
原先侧边栏是绝对定位
-
当页面滚动到一定位置,侧边栏改为固定定位
-
页面继续滚动,会让 返回顶部显示出来
案例分析:
- 需要用到页面滚动事件 scroll 因为是页面滚动,所以事件源是document
- 滚动到某个位置,就是判断页面被卷去的上部值。
- 页面被卷去的头部:可以通过window.pageYOffset 获得 如果是被卷去的左侧window.pageXOffset
- 注意,元素被卷去的头部是element.scrollTop , 如果是页面被卷去的头部 则是 window.pageYOffset
- 其实这个值 可以通过盒子的 offsetTop可以得到,如果大于等于这个值,就可以让盒子固定定位了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.slider-bar {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 300px;
margin-left: 600px;
width: 45px;
height: 130px;
background-color: pink;
}
.w {
width: 1200px;
margin: 10px auto;
}
.header {
height: 150px;
background-color: purple;
}
.banner {
height: 250px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.main {
height: 1000px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
span {
display: none;
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="slider-bar">
<span class="goBack">返回顶部</span>
</div>
<div class="header w">头部区域</div>
<div class="banner w">banner区域</div>
<div class="main w">主体部分</div>
<script>
//1. 获取元素
var sliderbar = document.querySelector('.slider-bar');
var banner = document.querySelector('.banner');
// banner.offestTop 就是被卷去头部的大小 一定要写到滚动的外面
var bannerTop = banner.offsetTop
// 当我们侧边栏固定定位之后应该变化的数值
var sliderbarTop = sliderbar.offsetTop - bannerTop;
// 获取main 主体元素
var main = document.querySelector('.main');
var goBack = document.querySelector('.goBack');
var mainTop = main.offsetTop;
// 2. 页面滚动事件 scroll
document.addEventListener('scroll', function() {
// console.log(11);
// window.pageYOffset 页面被卷去的头部
// console.log(window.pageYOffset);
// 3 .当我们页面被卷去的头部大于等于了 172 此时 侧边栏就要改为固定定位
if (window.pageYOffset >= bannerTop) {
sliderbar.style.position = 'fixed';
sliderbar.style.top = sliderbarTop + 'px';
} else {
sliderbar.style.position = 'absolute';
sliderbar.style.top = '300px';
}
// 4. 当我们页面滚动到main盒子,就显示 goback模块
if (window.pageYOffset >= mainTop) {
goBack.style.display = 'block';
} else {
goBack.style.display = 'none';
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>3.4、页面被卷去的头部兼容性解决方案
需要注意的是,页面被卷去的头部,有兼容性问题,因此被卷去的头部通常有如下几种写法:
-
声明了 DTD,使用 document.documentElement.scrollTop
-
未声明 DTD,使用 document.body.scrollTop
-
新方法 window.pageYOffset和 window.pageXOffset,IE9 开始支持
function getScroll() {
return {
left: window.pageXOffset || document.documentElement.scrollLeft || document.body.scrollLeft||0,
top: window.pageYOffset || document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop || 0
};
}
使用的时候 getScroll().left4、三大系列总结
- offset系列 经常用于获得元素位置 offsetLeft offsetTop
- client经常用于获取元素大小 clientWidth clientHeight
- scroll 经常用于获取滚动距离 scrollTop scrollLeft
- 注意页面滚动的距离通过 window.pageXOffset 获得