你了解SonarQube 吗
文章目录
- 你了解SonarQube 吗
- 一、介绍
- 二、idea代码检测工具SonarLint
- 安装方法
- 使用方法
- 三、常见的Sonar解决方法
- Unused "private" fields should be removed
- Sections of code should not be "commented out"
- Useless imports should be removed
- Track uses of "TODO" tags
- Source files should not have any duplicated blocks
- Throwable.printStackTrace(...) should not be called
- Standard outputs should not be used directly to log anything
- String literals should not be duplicated
- Constant names should comply with a naming convention
- Generic exceptions should never be thrown
- Package names should comply with a naming convention
- The diamond operator ("<>") should be used
- Collection.isEmpty() should be used to test for emptiness
- Type parameter names should comply with a naming convention
- Cognitive Complexity of methods should not be too high
- Unused local variables should be removed
- Dead stores should be removed
- Local variables should not be declared and then immediately returned or thrown
- Local variable and method parameter names should comply with a naming convention
- Utility classes should not have public constructors
- Collapsible "if" statements should be merged
- Modifiers should be declared in the correct order
- Lamdbas containing only one statement should not nest this statement in a block
- Methods should not be empty
- Fields in a "Serializable" class should either be transient or serializable
- Empty arrays and collections should be returned instead of null
- Unused method parameters should be removed
- Try-catch blocks should not be nested
- Ternary operators should not be nested
- Field names should comply with a naming convention
- String function use should be optimized for single characters
- Local variables should not shadow class fields
一、介绍
SonarQube 是一种广泛使用的代码检查工具,可以评估代码的质量和安全性,并提供改进建议。它支持多种编程语言,如Java、JavaScript、C++、Python等,可以使用各种规则和检查器来分析代码。SonarQube 还支持 IDE 和 CI/CD 工具的集成,可以与 Jenkins、GitLab、GitHub 等集成使用。SonarQube 有开源社区版和商业版,其中社区版可以免费下载和使用。
在使用 SonarQube 进行代码检查时,可以通过启动 SonarQube 服务器,使用 SonarQube 插件或 Maven、Gradle 等构建工具来进行代码分析。SonarQube 会分析代码,检查是否存在代码质量问题、安全漏洞和潜在的错误,例如重复代码、代码复杂度过高、安全漏洞、可维护性问题等。检查结果会展示在 SonarQube 的网站或 IDE 插件中,提供清晰的报告和指导,帮助开发人员优化和改进代码质量。
Sonar可以从以下七个维度检测代码质量,而作为开发人员至少需要处理前5种代码质量问题
- 不遵循代码标准 sonar可以通过PMD,CheckStyle,Findbugs等等代码规则检测工具规范代码编写
- 潜在的缺陷 sonar可以通过PMD,CheckStyle,Findbugs等等代码规则检测工具检测出潜在的缺陷
- 糟糕的复杂度分布 文件、类、方法等,如果复杂度过高将难以改变,这会使得开发人员难以理解它们 且如果没有自动化的单元测试,对于程序中的任何组件的改变都将可能导致需要全面的回归测试
- 重复 显然程序中包含大量复制粘贴的代码是质量低下的,sonar可以展示源码中重复严重的地方
- 注释不足或者过多 没有注释将使代码可读性变差,特别是当不可避免地出现人员变动时,程序的可读性将大幅下降 而过多的注释又会使得开发人员将精力过多地花费在阅读注释上,亦违背初衷
- 缺乏单元测试 sonar可以很方便地统计并展示单元测试覆盖率
- 糟糕的设计 通过sonar可以找出循环,展示包与包、类与类之间相互依赖关系,可以检测自定义的架构规则 通过sonar可以管理第三方的jar包,可以利用LCOM4检测单个任务规则的应用情况, 检测耦合。
二、idea代码检测工具SonarLint
安装方法
在File找到Setting,找到Plugins在Marketplace中输入 SonarLint,安装即可

使用方法
在项目上右键,然后找到SonarLint,点击生成代码检测报告

之后在底部就能看检测出来的错误、漏洞等,像这样

点击具体项,可查看相应规则
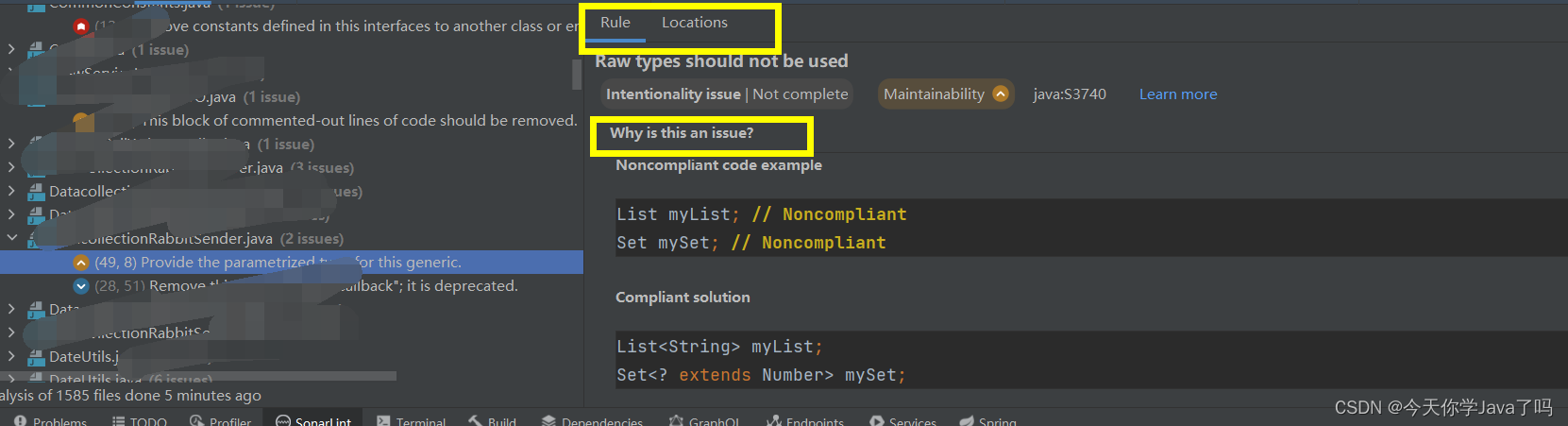
三、常见的Sonar解决方法
Unused “private” fields should be removed
If a private field is declared but not used in the program, it can be considered dead code and should therefore be removed. This will improve maintainability because developers will not wonder what the variable is used for.
Note that this rule does not take reflection into account, which means that issues will be raised on private fields that are only accessed using the reflection API.
Noncompliant Code Example
public class MyClass {
private int foo = 42;
public int compute(int a) {
return a * 42;
}
}
Compliant Solution
public class MyClass {
public int compute(int a) {
return a * 42;
}
}
Exceptions
The Java serialization runtime associates with each serializable class a version number, called serialVersionUID , which is used during deserialization to verify that the sender and receiver of a serialized object have loaded classes for that object that are compatible with respect to serialization.
A serializable class can declare its own serialVersionUID explicitly by declaring a field named serialVersionUID that must be static, final, and of type long. By definition those serialVersionUID fields should not be reported by this rule:
public class MyClass implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
}
Moreover, this rule doesn't raise any issue on annotated fields.
Sections of code should not be “commented out”
Programmers should not comment out code as it bloats programs and reduces readability.
Unused code should be deleted and can be retrieved from source control history if required.
See
MISRA C:2004, 2.4 - Sections of code should not be "commented out".
MISRA C++:2008, 2-7-2 - Sections of code shall not be "commented out" using C-style comments.
MISRA C++:2008, 2-7-3 - Sections of code should not be "commented out" using C++ comments.
MISRA C:2012, Dir. 4.4 - Sections of code should not be "commented out"
Useless imports should be removed
The imports part of a file should be handled by the Integrated Development Environment (IDE), not manually by the developer.
Unused and useless imports should not occur if that is the case.
Leaving them in reduces the code's readability, since their presence can be confusing.
Noncompliant Code Example
package my.company;
import java.lang.String; // Noncompliant; java.lang classes are always implicitly imported
import my.company.SomeClass; // Noncompliant; same-package files are always implicitly imported
import java.io.File; // Noncompliant; File is not used
import my.company2.SomeType;
import my.company2.SomeType; // Noncompliant; 'SomeType' is already imported
class ExampleClass {
public String someString;
public SomeType something;
}
Exceptions
Imports for types mentioned in comments, such as Javadocs, are ignored.
Track uses of “TODO” tags
TODO tags are commonly used to mark places where some more code is required, but which the developer wants to implement later.
Sometimes the developer will not have the time or will simply forget to get back to that tag.
This rule is meant to track those tags and to ensure that they do not go unnoticed.
Noncompliant Code Example
void doSomething() {
// TODO
}
See
MITRE, CWE-546 - Suspicious Comment
Source files should not have any duplicated blocks
An issue is created on a file as soon as there is at least one block of duplicated code on this file
Throwable.printStackTrace(…) should not be called
Throwable.printStackTrace(...) prints a Throwable and its stack trace to some stream. By default that stream
System.Err , which could inadvertently expose sensitive information.
Loggers should be used instead to print Throwable s, as they have many advantages:
Users are able to easily retrieve the logs.
The format of log messages is uniform and allow users to browse the logs easily.
This rule raises an issue when printStackTrace is used without arguments, i.e. when the stack trace is printed to the default stream.
Noncompliant Code Example
try {
/* ... */
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // Noncompliant
}
Compliant Solution
try {
/* ... */
} catch(Exception e) {
LOGGER.log("context", e);
}
Standard outputs should not be used directly to log anything
When logging a message there are several important requirements which must be fulfilled:
The user must be able to easily retrieve the logs
The format of all logged message must be uniform to allow the user to easily read the log
Logged data must actually be recorded
Sensitive data must only be logged securely
If a program directly writes to the standard outputs, there is absolutely no way to comply with those requirements. That's why defining and using a dedicated logger is highly recommended.
Noncompliant Code Example
System.out.println("My Message"); // Noncompliant
Compliant Solution
logger.log("My Message");
See
CERT, ERR02-J. - Prevent exceptions while logging data
String literals should not be duplicated
Duplicated string literals make the process of refactoring errorprone, since you must be sure to update all occurrences.
On the other hand, constants can be referenced from many places, but only need to be updated in a single place.
Noncompliant Code Example
With the default threshold of 3:
public void run() {
prepare("action1"); // Noncompliant - "action1"
is duplicated 3 times
execute("action1");
release("action1");
}
@SuppressWarning("all") // Compliant - annotations are excluded
private void method1() { /* ... */ }
@SuppressWarning("all")
private void method2() { /* ... */ }
public String method3(String a) {
System.out.println("'" + a + "'"); // Compliant - literal "'" has less than 5 characters and is excluded
return ""; // Compliant - literal "" has less than 5 characters and is excluded
}
Compliant Solution
private static final String ACTION_1 = "action1"; // Compliant
public void run() {
prepare(ACTION_1); // Compliant
execute(ACTION_1);
release(ACTION_1);
}
Exceptions
To prevent generating some false-positives, literals having less than 5 characters are excluded.
Constant names should comply with a naming convention
Shared coding conventions allow teams to collaborate efficiently.
This rule checks that all constant names match a provided regular expression.
Noncompliant Code Example
With the default regular expression ^[A-Z][A-Z0-9]*(_[A-Z0-9]+)*$ :
public class MyClass {
public static final int first = 1;
}
public enum MyEnum {
first;
}
Compliant Solution
public class MyClass {
public static final int FIRST = 1;
}
public enum MyEnum {
FIRST;
}
Generic exceptions should never be thrown
Using such generic exceptions as Error , RuntimeException ,
Throwable , and Exception prevents calling methods from handling true, system-generated exceptions differently than application-generated errors.
Noncompliant Code Example
public void foo(String bar) throws Throwable { // Noncompliant
throw new RuntimeException("My Message"); // Noncompliant
}
Compliant Solution
public void foo(String bar) {
throw new MyOwnRuntimeException("My Message");
}
Exceptions
Generic exceptions in the signatures of overriding methods are ignored, because overriding method has to follow signature of the throw declaration in the superclass. The issue will be raised on superclass declaration of the method (or won't be raised at all if superclass is not part of the analysis).
@Override
public void myMethod() throws Exception {...}
Generic exceptions are also ignored in the signatures of methods that make calls to methods that throw generic exceptions.
public void myOtherMethod throws Exception {
doTheThing(); // this method throws Exception
}
See
MITRE, CWE-397 - Declaration of Throws for Generic Exception
CERT, ERR07-J. - Do not throw RuntimeException, Exception, or Throwable
Package names should comply with a naming convention
Shared coding conventions allow teams to collaborate efficiently.
This rule checks that all package names match a provided regular expression.
Noncompliant Code Example
With the default regular expression ^[a-z_]+(\.[a-z_][a-z0-9_]*)*$ :
package org.exAmple; // Noncompliant
Compliant Solution
package org.example;
The diamond operator (“<>”) should be used
Java 7 introduced the diamond operator ( <> ) to reduce the verbosity of generics code. For instance, instead of having to declare a List 's type in both its declaration and its constructor, you can now simplify the constructor declaration with <> , and the compiler will infer the type.
Note that this rule is automatically disabled when the project's sonar.java.source is lower than 7 .
Noncompliant Code Example
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>(); // Noncompliant
Map<String,List<Integer>> map = new
HashMap<String,List<Integer>>(); // Noncompliant
Compliant Solution
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
Collection.isEmpty() should be used to test for emptiness
Using Collection.size() to test for emptiness works, but using
Collection.isEmpty() makes the code more readable and can be more performant. The time complexity of any isEmpty() method implementation should be O(1) whereas some implementations of size() can be O(n) .
Noncompliant Code Example
if (myCollection.size() == 0) { // Noncompliant
/* ... */
}
Compliant Solution
if (myCollection.isEmpty()) {
/* ... */
}
Type parameter names should comply with a naming convention
Shared naming conventions make it possible for a team to collaborate efficiently. Following the established convention of single-letter type parameter names helps users and maintainers of your code quickly see the difference between a type parameter and a poorly named class.
This rule check that all type parameter names match a provided regular expression. The following code snippets use the default regular expression.
Noncompliant Code Example
public class MyClass<TYPE> { // Noncompliant
<TYPE> void method(TYPE t) { // Noncompliant
}
}
Compliant Solution
public class MyClass<T> {
<T> void method(T t) {
}
}
Cognitive Complexity of methods should not be too high
Cognitive Complexity is a measure of how hard the control flow of a method is to understand. Methods with high Cognitive
Complexity will be difficult to maintain.
See
Cognitive Complexity
Unused local variables should be removed
If a local variable is declared but not used, it is dead code and should be removed. Doing so will improve maintainability because developers will not wonder what the variable is used for.
Noncompliant Code Example
public int numberOfMinutes(int hours) {
int seconds = 0; // seconds is never used
return hours * 60;
}
Compliant Solution
public int numberOfMinutes(int hours) {
return hours * 60;
}
Dead stores should be removed
A dead store happens when a local variable is assigned a value, including null , that is not read by any subsequent instruction.
Calculating or retrieving a value only to then overwrite it or throw it away, could indicate a serious error in the code. Even if it's not an error, it is at best a waste of resources.
Even assigning null to a variable is a dead store if the variable is not subsequently used. Assigning null as a hint to the garbage collector used to be common practice, but is no longer needed and such code should be eliminated.
Noncompliant Code Example
public void pow(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = a;
for(int i= 1, i < b, i++) {
x = x * a; //Dead store because the last return statement should
return x instead of returning a
}
return a;
}
Compliant Solution
public void pow(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) {
return 0;
}
int x = a;
for(int i= 1, i < b, i++) {
x = x * a;
}
return x;
}
Exceptions
This rule ignores initializations to -1, 0, 1, null , empty string ( "" ),
true , and false .
See
MITRE, CWE-563 - Assignment to Variable without Use ('Unused Variable')
CERT, MSC13-C. - Detect and remove unused values
CERT, MSC56-J. - Detect and remove superfluous code and values
Local variables should not be declared and then immediately returned or thrown
Declaring a variable only to immediately return or throw it is a bad practice.
Some developers argue that the practice improves code readability, because it enables them to explicitly name what is being returned. However, this variable is an internal implementation detail that is not exposed to the callers of the method. The method name should be sufficient for callers to know exactly what will be returned.
Noncompliant Code Example
public long computeDurationInMilliseconds() {
long duration = (((hours * 60) + minutes) * 60 + seconds ) * 1000;
return duration;
}
public void doSomething() {
RuntimeException myException = new RuntimeException();
throw myException;
}
Compliant Solution
public long computeDurationInMilliseconds() {
return (((hours * 60) + minutes) * 60 + seconds ) * 1000 ;
}
public void doSomething() {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
Local variable and method parameter names should comply with a naming convention
Shared naming conventions allow teams to collaborate effectively.
This rule raises an issue when a local variable or function parameter name does not match the provided regular expression.
Noncompliant Code Example
With the default regular expression ^[a-z][a-zA-Z0-9]*$ :
public void doSomething(int my_param) {
int LOCAL;
...
}
Compliant Solution
public void doSomething(int myParam) {
int local;
...
}
Exceptions
Loop counters are ignored by this rule.
for (int i_1 = 0; i_1 < limit; i_1++) { // Compliant
// ...
}
as well as one-character catch variables:
try {
//...
} catch (Exception e) { // Compliant
}
Utility classes should not have public constructors
Utility classes, which are collections of static members, are not meant to be instantiated. Even abstract utility classes, which can be extended, should not have public constructors.
Java adds an implicit public constructor to every class which does not define at least one explicitly. Hence, at least one non-public constructor should be defined.
Noncompliant Code Example
class StringUtils { // Noncompliant
public static String concatenate(String s1, String s2) {
return s1 + s2;
}
}
Compliant Solution
class StringUtils { // Compliant
private StringUtils() {
throw new IllegalStateException("Utility class");
}
public static String concatenate(String s1, String s2) {
return s1 + s2;
}
}
Exceptions
When class contains public static void main(String[] args) method it is not considered as utility class and will be ignored by this rule.
Collapsible “if” statements should be merged
Merging collapsible if statements increases the code's readability.
Noncompliant Code Example
if (file != null) {
if (file.isFile() || file.isDirectory()) {
/* ... */
}
}
Compliant Solution
if (file != null && isFileOrDirectory(file)) {
/* ... */
}
private static boolean isFileOrDirectory(File file) {
return file.isFile() || file.isDirectory();
}
Modifiers should be declared in the correct order
The Java Language Specification recommends listing modifiers in the following order:
1. Annotations
2. public
3. protected
4. private
5. abstract
6. static
7. final
8. transient
9. volatile
10. synchronized
11. native
12. strictfp
Not following this convention has no technical impact, but will reduce the code's readability because most developers are used to the standard order.
Noncompliant Code Example
static public void main(String[] args) { // Noncompliant
}
Compliant Solution
public static void main(String[] args) { // Compliant
}
Lamdbas containing only one statement should not nest this statement in a block
There are two ways to write lambdas that contain single statement, but one is definitely more compact and readable than the other.
Note that this rule is automatically disabled when the project's sonar.java.source is lower than 8 .
Noncompliant Code Example
x -> {System.out.println(x+1);}
(a, b) -> { return a+b; }
Compliant Solution
x -> System.out.println(x+1)
(a, b) -> a+b //For return statement, the return keyword should also be dropped
Methods should not be empty
There are several reasons for a method not to have a method body:
It is an unintentional omission, and should be fixed to prevent an unexpected behavior in production.
It is not yet, or never will be, supported. In this case an
UnsupportedOperationException should be thrown.
The method is an intentionally-blank override. In this case a nested comment should explain the reason for the blank override.
Noncompliant Code Example
public void doSomething() {
}
public void doSomethingElse() {
}
Compliant Solution
@Override
public void doSomething() {
// Do nothing because of X and Y.
}
@Override
public void doSomethingElse() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
Exceptions
Default (no-argument) constructors are ignored when there are other constructors in the class, as are empty methods in abstract classes.
public abstract class Animal {
void speak() { // default implementation ignored
}
}
Fields in a “Serializable” class should either be transient or serializable
Fields in a Serializable class must themselves be either
Serializable or transient even if the class is never explicitly serialized or deserialized. For instance, under load, most J2EE application frameworks flush objects to disk, and an allegedly
Serializable object with non-transient, non-serializable data members could cause program crashes, and open the door to attackers. In general a Serializable class is expected to fulfil its contract and not have an unexpected behaviour when an instance is serialized.
This rule raises an issue on non- Serializable fields, and on collection fields when they are not private (because they could be assigned non- Serializable values externally), and when they are assigned non- Serializable types within the class.
Noncompliant Code Example
public class Address {
//...
}
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID =
1905122041950251207L;
private String name;
private Address address; // Noncompliant; Address isn't serializable
}
Compliant Solution
public class Address implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID =
2405172041950251807L;
}
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID =
1905122041950251207L;
private String name;
private Address address;
}
Exceptions
The alternative to making all members serializable or transient is to implement special methods which take on the responsibility of properly serializing and de-serializing the object.
This rule ignores classes which implement the following methods:
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
See
MITRE, CWE-594 - Saving Unserializable Objects to Disk
Oracle Java 6, Serializable
Oracle Java 7, Serializable
Empty arrays and collections should be returned instead of null
Returning null instead of an actual array or collection forces callers of the method to explicitly test for nullity, making them more complex and less readable.
Moreover, in many cases, null is used as a synonym for empty.
Noncompliant Code Example
public static List<Result> getResults() {
return null; // Noncompliant
}
public static Result[] getResults() {
return null; // Noncompliant
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result[] results = getResults();
if (results != null) { // Nullity test required to prevent
NPE
for (Result result: results) {
/* ... */
}
}
}
Compliant Solution
public static List<Result> getResults() {
return Collections.emptyList(); // Compliant
}
public static Result[] getResults() {
return new Result[0];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Result result: getResults()) {
/* ... */
}
}
See
CERT, MSC19-C. - For functions that return an array, prefer returning an empty array over a null value
CERT, MET55-J. - Return an empty array or collection instead of a null value for methods that return an array or collection
Unused method parameters should be removed
Unused parameters are misleading. Whatever the values passed to such parameters, the behavior will be the same.
Noncompliant Code Example
void doSomething(int a, int b) { // "b" is unused
compute(a);
}
Compliant Solution
void doSomething(int a) {
compute(a);
}
Exceptions
The rule will not raise issues for unused parameters: that are annotated with @javax.enterprise.event.Observes in overrides and implementation methods in interface default methods in non-private methods that only throw or that have empty bodies in annotated methods, unless the annotation is @SuppressWarning("unchecked") or @SuppressWarning("rawtypes") , in which case the annotation will be ignored in overridable methods (non-final, or not member of a final class, non-static, non-private), if the parameter is documented with a proper javadoc.
@Override
void doSomething(int a, int b) { // no issue reported on b
compute(a);
}
public void foo(String s) {
// designed to be extended but noop in standard case
}
protected void bar(String s) {
//open-closed principle
}
public void qix(String s) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This method should
be implemented in subclasses");
}
See
MISRA C++:2008, 0-1-11 - There shall be no unused parameters (named or unnamed) in nonvirtual functions.
MISRA C:2012, 2.7 - There should be no unused parameters in functions
CERT, MSC12-C. - Detect and remove code that has no effect or is never executed
Try-catch blocks should not be nested
Nesting try / catch blocks severely impacts the readability of source code because it makes it too difficult to understand which block will catch which exception.
Ternary operators should not be nested
Just because you can do something, doesn't mean you should, and that's the case with nested ternary operations. Nesting ternary operators results in the kind of code that may seem clear as day when you write it, but six months later will leave maintainers (or worse - future you) scratching their heads and cursing.
Instead, err on the side of clarity, and use another line to express the nested operation as a separate statement.
Noncompliant Code Example
public String getTitle(Person p) {
return p.gender == Person.MALE ? "Mr. " : p.isMarried() ? "Mrs. " :
"Miss "; // Noncompliant
}
Compliant Solution
public String getTitle(Person p) {
if (p.gender == Person.MALE) {
return "Mr. ";
}
return p.isMarried() ? "Mrs. " : "Miss ";
}
Field names should comply with a naming convention
Sharing some naming conventions is a key point to make it possible for a team to efficiently collaborate. This rule allows to check that field names match a provided regular expression.
Noncompliant Code Example
With the default regular expression ^[a-z][a-zA-Z0-9]*$ :
class MyClass {
private int my_field;
}
Compliant Solution
class MyClass {
private int myField;
}
String function use should be optimized for single characters
An indexOf or lastIndexOf call with a single letter String can be made more performant by switching to a call with a char argument.
Noncompliant Code Example
String myStr = "Hello World";
// ...
int pos = myStr.indexOf("W"); // Noncompliant
// ...
int otherPos = myStr.lastIndexOf("r"); // Noncompliant
// ...
Compliant Solution
String myStr = "Hello World";
// ...
int pos = myStr.indexOf('W');
// ...
int otherPos = myStr.lastIndexOf('r');
// ...
Local variables should not shadow class fields
Shadowing fields with a local variable is a bad practice that reduces code readability: it makes it confusing to know whether the field or the variable is being used.
Noncompliant Code Example
class Foo {
public int myField;
public void doSomething() {
int myField = 0;
...
}
}
See
CERT, DCL51-J. - Do not shadow or obscure identifiers in subscopes






![[自学记录08*]LDR、HDR与ToneMapping](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4eb14a68616340a186d801650c81be20.png)