1. 定义路由注解
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// @Target用来表示注解作用范围,超过这个作用范围,编译的时候就会报错。
// @Target(ElementType.TYPE)——接口、类、枚举、注解,@Target(ElementType.METHOD)——方法
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface DBRouter {
String key() default "";
}
首先我们需要自定义一个注解,用于放置在需要被数据库路由的方法上。
它的使用方式是通过方法配置注解,就可以被我们指定的 AOP 切面进行拦截,拦截后进行相应的数据库路由计算和判断,并切换到相应的操作数据源上。
//使用
@Mapper
public interface IUserDao {
@DBRouter(key = "userId")
User queryUserInfoByUserId(User req);
@DBRouter(key = "userId")
void insertUser(User req);
}
2 解析路由配置
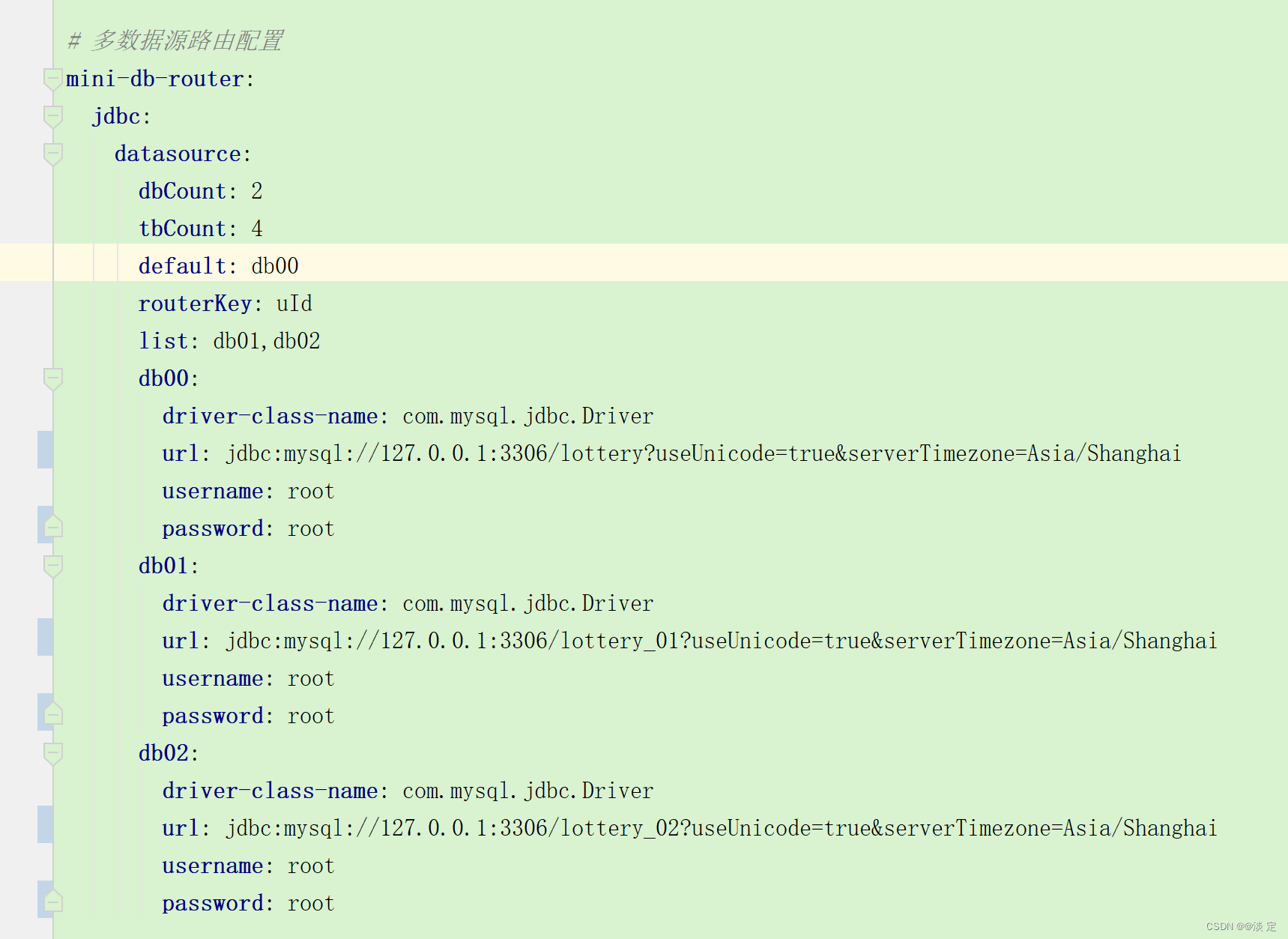
//对于这种自定义较大的信息配置,就需要使用到
org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware 接口,
来获取配置文件并提取需要的配置信息
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
String prefix = "router.jdbc.datasource.";
dbCount = Integer.valueOf(environment.getProperty(prefix + "dbCount"));
tbCount = Integer.valueOf(environment.getProperty(prefix + "tbCount"));
String dataSources = environment.getProperty(prefix + "list");
for (String dbInfo : dataSources.split(",")) {
Map<String, Object> dataSourceProps = PropertyUtil.handle(environment, prefix + dbInfo, Map.class);
//配置信息的提取,并存放到 dataSourceMap 中便于后续使用
dataSourceMap.put(dbInfo, dataSourceProps);
}
}
3. 数据源切换
//支持动态切换数据源
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
// 创建数据源
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
for (String dbInfo : dataSourceMap.keySet()) {
Map<String, Object> objMap = dataSourceMap.get(dbInfo);
targetDataSources.put(dbInfo, new DriverManagerDataSource(objMap.get("url").toString(), objMap.get("username").toString(), objMap.get("password").toString()));
}
// 设置数据源
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(new DriverManagerDataSource(defaultDataSourceConfig.get("url").toString(), defaultDataSourceConfig.get("username").toString(), defaultDataSourceConfig.get("password").toString()));
return dynamicDataSource;
}
2-3步骤:
这里是一个简化的创建案例,把基于从配置信息中读取到的数据源信息,进行实例化创建。
数据源创建完成后存放到 DynamicDataSource 中,它是一个继承了 AbstractRoutingDataSource 的实现类,这个类里可以存放和读取相应的具体调用的数据源信息
4. 切面拦截
// AOP 的切面拦截中需要完成;数据库路由计算、扰动函数加强散列、计算库表索引、
设置到 ThreadLocal 传递数据源
@Around("aopPoint() && @annotation(dbRouter)")
public Object doRouter(ProceedingJoinPoint jp, DBRouter dbRouter) throws Throwable {
String dbKey = dbRouter.key();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(dbKey)) throw new RuntimeException("annotation DBRouter key is null!");
// 计算路由
String dbKeyAttr = getAttrValue(dbKey, jp.getArgs());
int size = dbRouterConfig.getDbCount() * dbRouterConfig.getTbCount();
// 扰动函数;在 JDK 的 HashMap 中,对于一个元素的存放,需要进行哈希散列。
而为了让散列更加均匀,所以添加了扰动函数。
int idx = (size - 1) & (dbKeyAttr.hashCode() ^ (dbKeyAttr.hashCode() >>> 16));
//库表索引;相当于是把一个长条的桶,切割成段,对应分库分表中的库编号和表编号
//公式目的;8个位置,计算出来的是位置在5 那么你怎么知道5是在2库1表
int dbIdx = idx / dbRouterConfig.getTbCount() + 1;
int tbIdx = idx - dbRouterConfig.getTbCount() * (dbIdx - 1);
// 设置到 ThreadLocal
DBContextHolder.setDBKey(String.format("%02d", dbIdx));
DBContextHolder.setTBKey(String.format("%02d", tbIdx));
logger.info("数据库路由 method:{} dbIdx:{} tbIdx:{}", getMethod(jp).getName(), dbIdx, tbIdx);
// 返回结果
try {
return jp.proceed();
} finally {
DBContextHolder.clearDBKey();
DBContextHolder.clearTBKey();
}
}
5. Mybatis 拦截器处理分表
//实现 Interceptor 接口的 intercept 方法,获取StatementHandler、通过自定义注解判
断是否进行分表操作、获取SQL并替换SQL表名 USER 为 USER_03、最后通过反射修改SQL语句
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})})
public class DynamicMybatisPlugin implements Interceptor {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(from|into|update)[\\s]{1,}(\\w{1,})", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取StatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
MetaObject metaObject = MetaObject.forObject(statementHandler, SystemMetaObject.DEFAULT_OBJECT_FACTORY, SystemMetaObject.DEFAULT_OBJECT_WRAPPER_FACTORY, new DefaultReflectorFactory());
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) metaObject.getValue("delegate.mappedStatement");
// 获取自定义注解判断是否进行分表操作
String id = mappedStatement.getId();
String className = id.substring(0, id.lastIndexOf("."));
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
DBRouterStrategy dbRouterStrategy = clazz.getAnnotation(DBRouterStrategy.class);
if (null == dbRouterStrategy || !dbRouterStrategy.splitTable()){
return invocation.proceed();
}
// 获取SQL
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 替换SQL表名 USER 为 USER_03
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(sql);
String tableName = null;
if (matcher.find()) {
tableName = matcher.group().trim();
}
assert null != tableName;
String replaceSql = matcher.replaceAll(tableName + "_" + DBContextHolder.getTBKey());
// 通过反射修改SQL语句
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, replaceSql);
field.setAccessible(false);
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
配置分表注解
@Mapper
//配置后会通过数据库路由组件把sql语句添加上分表字段
@DBRouterStrategy(splitTable = true)
public interface IUserStrategyExportDao {
/**
* 新增数据
* @param userStrategyExport 用户策略
*/
//未配置情况下走默认字段
@DBRouter(key = "uId")
void insert(UserStrategyExport userStrategyExport);
/**
* 查询数据
* @param uId 用户ID
* @return 用户策略
*/
@DBRouter
UserStrategyExport queryUserStrategyExportByUId(String uId);
}