岛屿数量
- 题解1 DFS(图论经典方法)
- 题解2 BFS(遍历(DFS展开【顺序不同】))
- 题解3 并查集(学习理解)
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
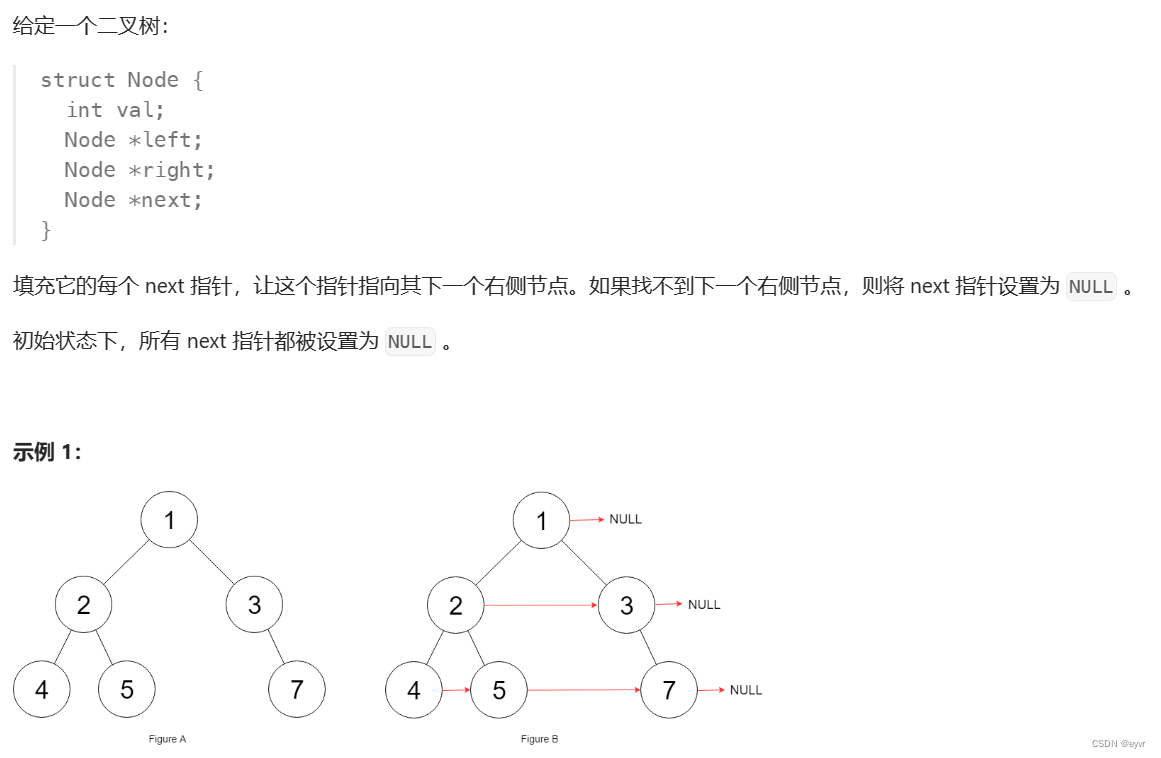
示例 1:
输入:
grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:
grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length- 1 <=
m, n<= 300 - grid[i][j] 的值为 ‘0’ 或 ‘1’
题解1 DFS(图论经典方法)
class Solution {
int l, r;
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int ro, int co){
if(co < 0 || co >= r || ro < 0 || ro >= l || grid[ro][co] == '0')
return;
// 思想:把1附近相连(连通分量)置0
// 相当于visited(面试时需要确定是否可以修改grid)
grid[ro][co] = '0';
dfs(grid, ro, co+1);
dfs(grid, ro+1, co);
dfs(grid, ro-1, co);
dfs(grid, ro, co-1);
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int ret = 0;
l = grid.size();
r = grid[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < l; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < r; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
ret += 1;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
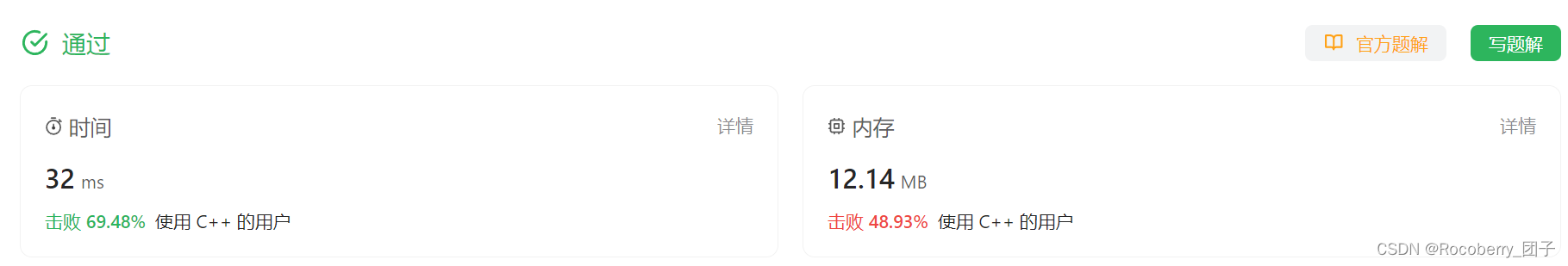
题解2 BFS(遍历(DFS展开【顺序不同】))
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int ret = 0;
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
ret += 1;
grid[i][j] = '0';
// BFS典型ADT
queue<pair<int, int>> nei;
nei.push(make_pair(i, j));
while(! nei.empty()){
auto rc = nei.front();
nei.pop();
int r = rc.first;
int c = rc.second;
if(r >= 1 && grid[r-1][c] == '1'){
nei.push(make_pair(r-1, c));
grid[r-1][c] = '0';
}
if(r+1 < m && grid[r+1][c] == '1'){
nei.push(make_pair(r+1, c));
grid[r+1][c] = '0';
}
if(c >= 1 && grid[r][c-1] == '1'){
nei.push(make_pair(r, c-1));
grid[r][c-1] = '0';
}
if(c+1 < n && grid[r][c+1] == '1'){
nei.push(make_pair(r, c+1));
grid[r][c+1] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
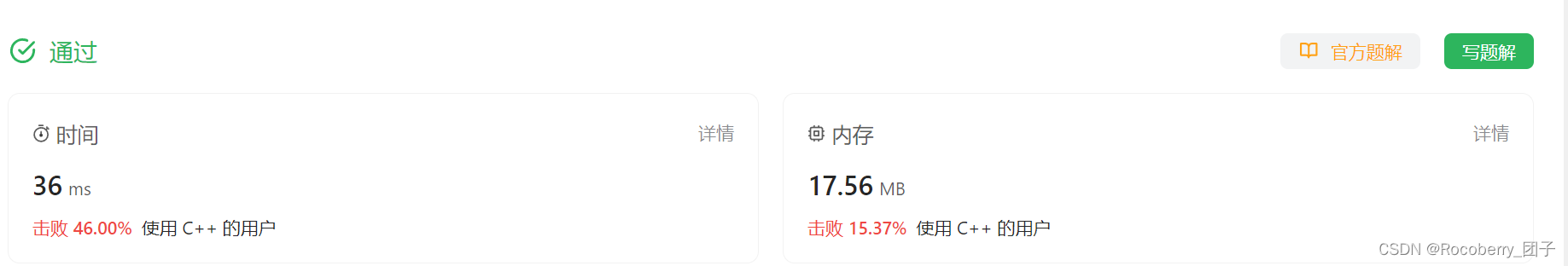
题解3 并查集(学习理解)
class UnionFind {
vector<int> parent;
vector<int> rank;
int count;
public:
UnionFind(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
count = 0;
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
parent.push_back(i * n + j);
++count;
}
else {
parent.push_back(-1);
}
rank.push_back(0);
}
}
}
int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] != i) {
parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
return parent[i];
}
void unite(int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if (rootx != rooty) {
if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) {
swap(rootx, rooty);
}
parent[rooty] = rootx;
if (rank[rootx] == rank[rooty]) rank[rootx] += 1;
--count;
}
}
int getCount() const {
return count;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int nr = grid.size();
if (!nr) return 0;
int nc = grid[0].size();
UnionFind uf(grid);
int num_islands = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
grid[r][c] = '0';
if (r - 1 >= 0 && grid[r-1][c] == '1') uf.unite(r * nc + c, (r-1) * nc + c);
if (r + 1 < nr && grid[r+1][c] == '1') uf.unite(r * nc + c, (r+1) * nc + c);
if (c - 1 >= 0 && grid[r][c-1] == '1') uf.unite(r * nc + c, r * nc + c - 1);
if (c + 1 < nc && grid[r][c+1] == '1') uf.unite(r * nc + c, r * nc + c + 1);
}
}
}
return uf.getCount();
}
};