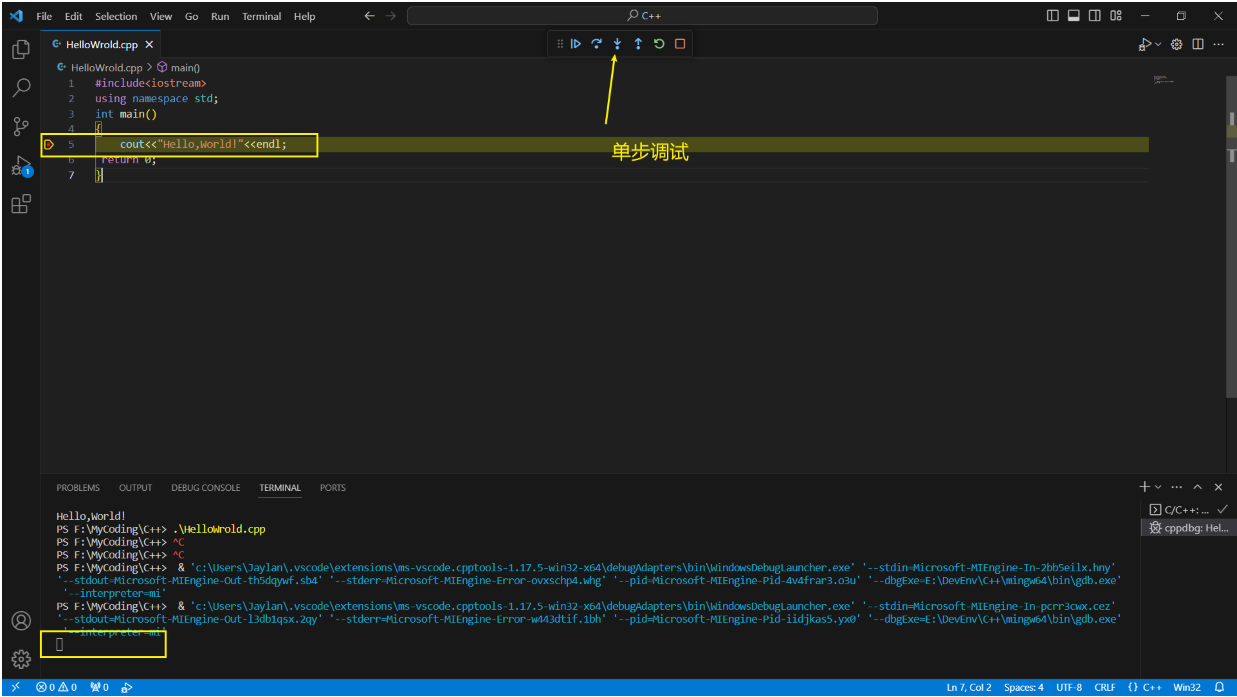
1. 可解的条件 Solvability conditions on b
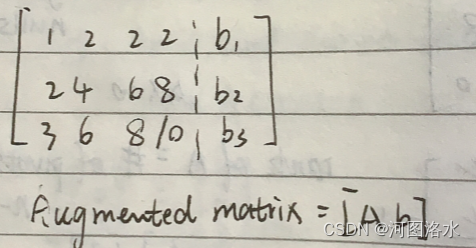
检验Ax=b是否可解的方法是对增广矩阵进行行消元。如果矩阵A的行被完全消去的话,则对应的b的分量也要得0
两条关于b的限制条件(等价)
1. if a comb. of rows of A gives zero row, then same comb. of enties of b must give 0
2. Ax=b solvable when b is in C(A)
2. 通解 Complete solution
to find complete soln's to Ax=b 我们首先检验方程是否可解,然后找到一个特解。将特解和矩阵零空间的向量相加即为方程的通解
2.1. 特解 A particular solution
求Ax=b特解的方法是将自由变量均赋值为0,求解其主变量
xparticular : set all free variables to zero, x2=x4=0
solve Ax=b for pivot variables
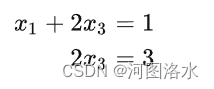
x3=3/2,x1=-2
特解为xp=
2.2. 零空间进行线性组合 Combined with nullspace
Ax=b的通解为: Xc = Xp + Xn

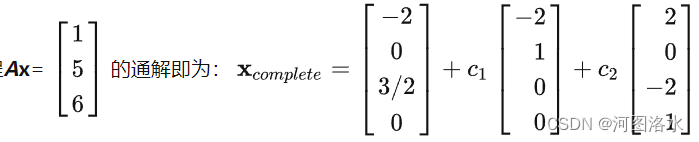
特解 particualr 基础解系special solutions 矩阵的零空间N(A)是R4空间中的二维子空间,方程的解Ax=b构成了穿过xp点并和矩阵零空间平行的“平面“。但该”平面“并不是R4空间的子空间
3. 秩 Rank
矩阵的秩等于矩阵的主元数。如果mxn矩阵的秩为r,则必有r<=m且r<=n
满秩(full rank):
1. 列满秩full column rank means:r=n no free variables
零空间N(A)之内只有零向量。方程无解或者有唯一解xp unique solution if it exists (0 or 1 solution)
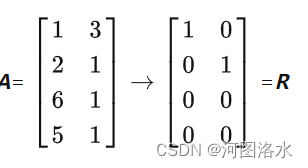
2. 行满秩full row rank means:r=m <n
Can solve Ax=b for every b left with n-r = n-m free variables
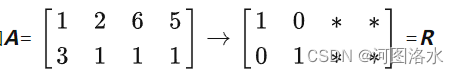
3. 满秩 r=m=n,
矩阵可逆。零空间只有零向量,无论b取何值,方程Ax=b都有唯一解
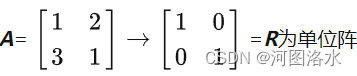 1 solution to Ax=b
1 solution to Ax=b
4. summary:
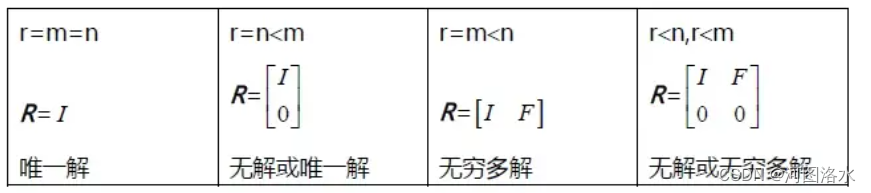
the rank tells you everything about the number of solutions