目录
- DSP开发例程: logbuf_print_to_uart
- 新建工程
- 源码编辑
- app.cfg
- os.c
- main.c
- 调试
- 说明
DSP开发例程: logbuf_print_to_uart
SYS/BIOS 提供了 xdc.runtime.Log, xdc.runtime.LoggerBuf 和 xdc.runtime.LoggerSys 这几个模块用于日志记录. 日志信息在 应用程序调试和状态监控中非常实用. 日志记录函数相较于 System_printf() 占用的时间更短, 且可以区分事件的等级, 如: Info, Warning 和 Error 等.
此例程实现将 SYS/BIOS 日志信息通过串口输出, 并在 EVM6678L 开发板上进行了测试. 例程源码可从我的 gitee 仓库上克隆或下载. 点击 DSP 开发教程(0): 汇总查看其他例程说明.
新建工程
此示例工程直接在 sys_print_to_uart 工程基础上修改.
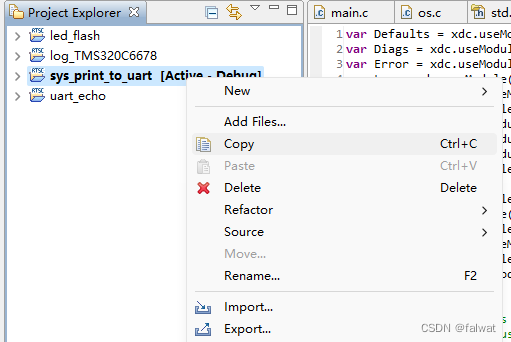
- 选中 sys_print_to_uart 工程, 右键选择 Copy 或 使用快捷键
Ctrl+C复制工程.
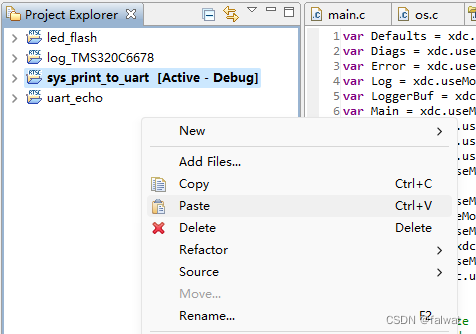
- 在工程浏览视图中, 右键选择 Paste 或使用快捷键
Ctrl+V粘贴工程.
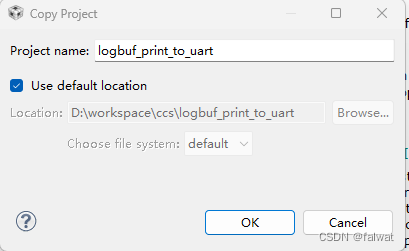
- 在弹出的 Copy Project 对话框中 修改工程名为: logbuf_print_to_uart, 点击 OK.
- 删除 logbuf_print_to_uart 工程中的 Debug目录, 右键选择 Build Project, 编译此工程.
源码编辑
app.cfg
- 使用 XGCONF 打开 app.cfg 文件.
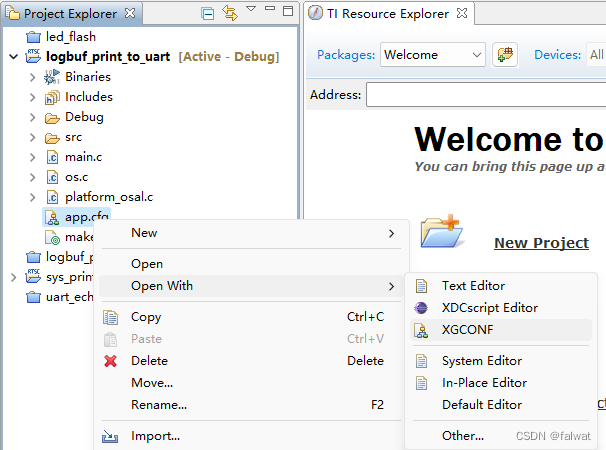
- 点击 logger0.
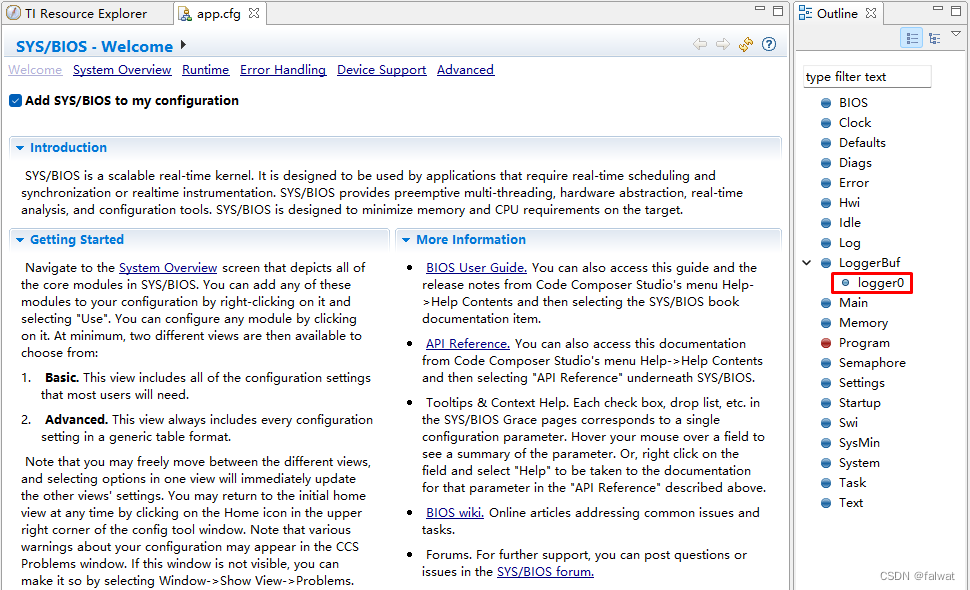 - 将 logger0 的句柄设置为
- 将 logger0 的句柄设置为 logger0.
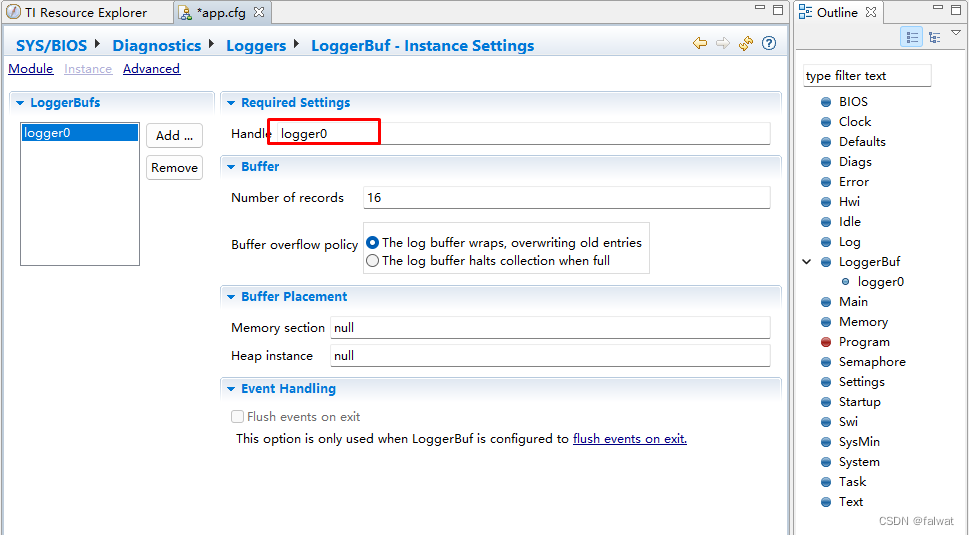 - 点击 Timestamp 模块.
- 点击 Timestamp 模块.

- 勾选 Add Timestamp to my configuration.
- 保存修改.
os.c
编辑 os.c 源文件, 其内容如下:
/*
* os.c
*
* Created on: 2023-10-26
* Author: falwa
*/
#include <xdc/std.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Log.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/LoggerBuf.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/System.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Text.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Types.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Timestamp.h>
extern LoggerBuf_Handle logger0;
/*
* ======== doPrint ========
*/
Void myLog_doPrint(Log_EventRec *er)
{
Text_RopeId rope;
String fmt;
Bits32 hi, lo;
Types_FreqHz freq;
uint32_t msec;
Timestamp_getFreq(&freq);
/* print timestamp if there is one; ~0 isn't a valid timestamp value */
hi = er->tstamp.hi;
lo = er->tstamp.lo;
msec = (((uint64_t)hi << 32) | lo) / (freq.lo/1000);
System_printf("[%5d.%03ds] ", msec/1000, msec%1000);
/* print event */
rope = Types_getEventId(er->evt); /* the event id is the message rope */
if (rope == 0) {
/* Log_print() event */
System_aprintf((String)iargToPtr(er->arg[0]),
er->arg[1], er->arg[2], er->arg[3], er->arg[4],
er->arg[5], er->arg[6], 0, 0);
}
else {
/* Log_write() event */
fmt = Text_ropeText(rope);
if (Text_isLoaded) {
System_aprintf(fmt, er->arg[0], er->arg[1], er->arg[2], er->arg[3],
er->arg[4], er->arg[5], er->arg[6], er->arg[7]);
}
else {
System_aprintf("{evt: fmt=%p, args=[0x%x, 0x%x ...]}",
fmt, er->arg[0], er->arg[1]);
}
}
System_putch('\n');
}
/*
* ======== LoggerBuf_flush ========
*/
Void myLoggerBuf_flush(LoggerBuf_Object *obj)
{
Int nEntries;
Log_EventRec evtRec;
for (;;) {
nEntries = LoggerBuf_getNextEntry(obj, &evtRec);
if (nEntries == 0) {
break;
}
else {
if (nEntries != -1) {
myLog_doPrint(&evtRec);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 添加此函数到 Idle Thread.
*
* ```xdc
* var Idle = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Idle');
*
* Idle.idleFxns[0] = "&os_systemFlush";
* ```
*/
void os_systemFlush()
{
if (logger0)
myLoggerBuf_flush(logger0);
System_flush();
}
/**
* 将 System_printf() 重定向到 platform_uart_write().
*
* 请在 .cfg 中添加:
* ```
* SysMin.outputFxn = "&os_systemOutput";
* ```
*/
Void os_systemOutput(Char *str, UInt len)
{
UInt i;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
platform_uart_write(str[i]);
}
}
其中新增了两个函数 myLog_doPrint() 和 myLoggerBuf_flush() , 这两个函数参考 C:\ti\xdctools_3_25_03_72\packages\xdc\runtime\LoggerBuf.c 中的 Log_doPrint() 和 LoggerBuf_flush() 进行设计. 其中,
myLog_doPrint()用于调用System_printf()格式化打印一条日志事件;myLoggerBuf_flush()负责调用myLog_doPrint()格式化 并 flush logBuf 中的所有日志事件.
在 os_systemFlush() 函数中调用 myLoggerBuf_flush(logger0); 完成日志的 flush.
main.c
编辑 main.c, 其内容如下:
/*
* ======== main.c ========
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <xdc/std.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Error.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Log.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/System.h>
#include <ti/sysbios/BIOS.h>
#include <ti/sysbios/knl/Task.h>
#include <ti/platform/platform.h>
/*
* ======== taskFxn ========
*/
Void task_ledFlash(UArg a0, UArg a1)
{
int i = 1;
Log_info0("enter task_ledFlash().");
while(1)
{
platform_led(0, PLATFORM_LED_ON, PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
Log_info1("LED 0 ON at %d times.", i);
Task_sleep(500);
platform_led(0, PLATFORM_LED_OFF, PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
Log_info1("LED 0 OFF at %d times.", i);
Task_sleep(500);
i++;
}
}
/**
* 平台初始化
*/
void EVM_init()
{
platform_init_flags init_flags;
platform_init_config init_config;
// plaform initialize
memset(&init_flags, 1, sizeof(platform_init_flags));
init_flags.phy = 0;
memset(&init_config, 0, sizeof(platform_init_config));
if (platform_init(&init_flags, &init_config) != Platform_EOK)
{
printf("Platform failed to initialize, errno = 0x%x \n", platform_errno);
while(1);
}
platform_uart_init();
}
/*
* ======== main ========
*/
Int main()
{
Task_Handle task;
Error_Block eb;
Log_info0("enter main().");
Log_error1("Log_error1(%d)", 1);
Log_warning2("log_warnning2(%d, %d)", 1, 2);
Error_init(&eb);
task = Task_create(task_ledFlash, NULL, &eb);
if (task == NULL) {
System_printf("Task_create() failed!\n");
BIOS_exit(0);
}
BIOS_start(); /* does not return */
return(0);
}
其中 调用了 Log_info#(), Log_error#() 和 Log_warning#() 这几个日志事件记录函数进行测试.
保存上述更改, 并编译工程.
调试
完成编译后, 在 EVM6678L 上调试.
串口通过USB连接计算机. 请确保 COM_SEL1 跳线设置在正确位置. 且在计算机设备管理器中能够找到对应板卡的串口.
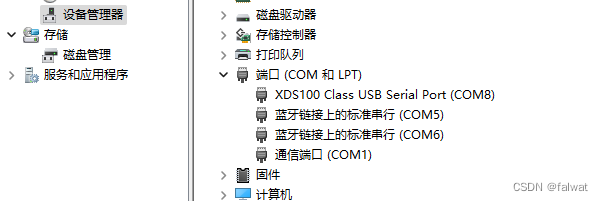
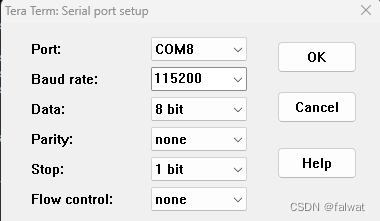
打开串口终端, 连接对应串口, 串口设置如下:
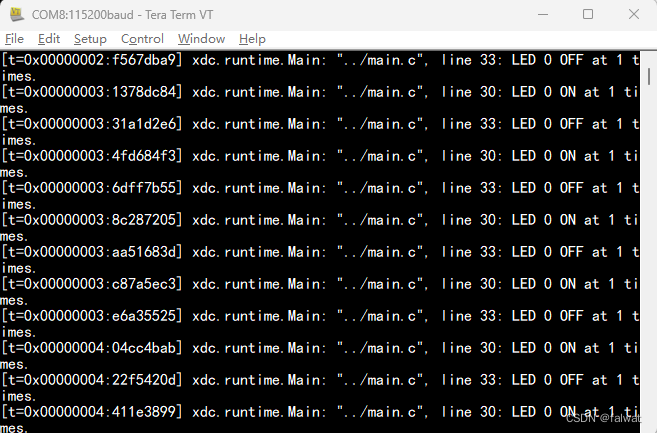
点击运行按钮, 运行程序. 此时在串口终端中能够看到打印的日志信息. 相较于 System_printf(), 增加了 时间戳, 文件名, 行数等信息.
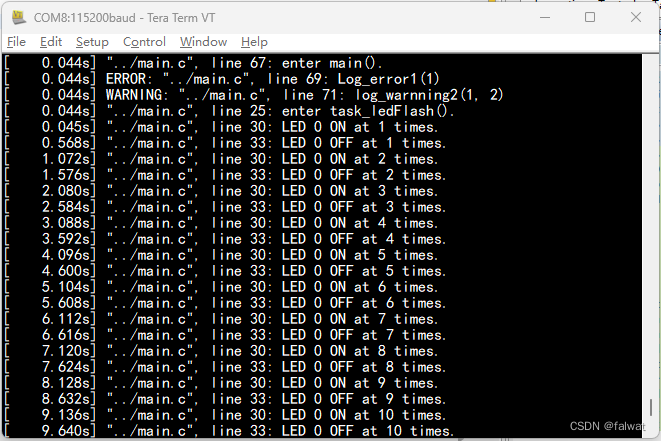
说明
这只是 打印日志信息到串口的一种方式. 启用 xdc.runtime.LoggerSys 模块, 也可以实现日志信息的打印, 不过打印的格式不是很好看, 其中的时间戳是16进制显示的. 看图自行体会.