搭建项目
建立一个Djano项目,建立一个app,建立路径,视图函数大多为render,
Ajax的创建
urls.py
path('index/',views.index),
path('index2/',views.index2),views.py
def index(request):
return render(request,'01.html')
def index2(request):
return render(request,'02.html')01.html
readyState共有五个返回值【0 1 2 3 4】,
0:ajax对象创建成功
1:准备请求结束
2 3 4:服务器接收请求,服务器解析,服务器响应请求【这三步都在监听回调函数中触发】
除了服务器响应外,还要确认资源
200:成功访问【201,204等】
300:服务器有多个可以响应客户端请求的资源【304,307等】
404:访问资源不存在【400,401等】
500: 服务器奔溃【505等】
<body>
<button>send</button>
<script>
document.querySelector('button').onclick=function(){
// 1 创建ajax对象
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest(); //0
console.log('new',xhr.readyState);
// 2 准备请求xhr.open('get/post','地址',是否异步);
xhr.open('get','/index2/',true);// 1
console.log('get',xhr.readyState);
// 3 发送请求
xhr.send();
// 4 监听回调函数
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
// 判断状态执行到哪一步了 0 1 2 3 4
console.log('函数',xhr.readyState);//打印 2 3 4
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
console.log(xhr.status);
if(xhr.status === 200){
// 响应数据
console.log(xhr.response) //返回的数据
}
}
}
}
</script>
</body>执行python manage.py runserver
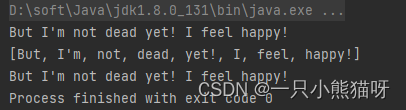
浏览器点击send,看控制台是否打印【02.html如下显示】

传递参数【get/post】
urls.py
#传递参数get/post
path('p/',views.p),#send
path('p2/',views.p2),#backviews.py
注意post与get请求
def p(request):
return render(request,'03.html')
def p2(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
print('进入post请求')
user = request.POST.get('name')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
print(user,pwd)
return render(request, '04.html', {'name': user, 'password': pwd})
print('进入get请求')
user=request.GET.get('name')
pwd=request.GET.get('pwd')
return render(request,'04.html',{'name':user,'password':pwd})03.html
get请求大致不变【url携带参数】
post请求必须携带参数,所以参数是放在data中,并且要避免csrf-token的验证,给请求头除了原本的'Content-type'还要加上csrf的验证,参数直接由send方法发送
转义字符是英文输入法下的 ~ 键
<body>
{% csrf_token %}
用户名:<input type="text"><br>
密码:<input type="password">
<button id="login">send</button>
<script>
document.querySelector('button').onclick=function (){
var name=document.querySelector('input[type=text]').value
var pwd=document.querySelector('input[type=password]').value
console.log(name,pwd)
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest();
{#get请求#}
{#var urls=`/p2/?name=${ name }&pwd=${ pwd } `{# `在笔记本tab上面的那个键 #}
{#xhr.open('get',urls,true)#}
{#xhr.send()#}
{#post请求#}
xhr.open('post','/p2/',true)
var csrf=document.querySelector('input[type=hidden]').value
data=`&${ name }&pwd=${ pwd }`
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8')
xhr.setRequestHeader('X-CSRFToken', csrf);
xhr.send(data)
xhr.onreadystatechange=function (){
console.log(xhr.status)
console.log(xhr.readyState)
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status === 200){
console.log(xhr.response)
}
}
}
}
</script>
</body>04.html
<body>
用户名{{ name }}
密码{{ password }}
</body>异步
open的第三个参数
预留加载位置【例如网络不佳情况下的图片加载失败】,还能执行其它函数
<body>
<script>
// 同步
{#var str="hello world!"#}
{#for(var i=0;i<100;i++){#}
{# console.log(i)#}
{# } #}
{#console.log(str)#}
// 异步
var str2='hello world2'
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get','/index2/',true)
xhr.send()
{#代码跳过该函数,向下执行 ,异步加载要请求的 #}
xhr.onreadystatechange=function (){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status === 200){
console.log(xhr.response)
}
}
}
for(var i=0;i<100;i++){
console.log(i)
}
console.log(str2)
</script>
</body>获取与解析本地Json
 建立json文件
建立json文件
{
"total": 4,
"data": [
{
"name": "三国演义",
"category": "文学",
"desc": "一个军阀混战的年代"
},{
"name": "三国演义2",
"category": "文学2",
"desc": "一个军阀混战的年代2"
}
],
"obj": {"adf": "adf"}
}Json文件中必需使用双引号,最后一个数据不加逗号,比如在data中的列表中第一个字典,最后一行数据不能加逗号否则报Uncaught SyntaxError: Expected double-quoted property name in JSON...
urls.py
#ajax获取本地json数据-解析显示页面
path('gjson/', views.Jsond, name='gjson'),
path('huoqu/',views.huoqu),views.py
def huoqu(request):
return render(request,'06.html')
def Jsond(request):#报错
with open('static/data.json', 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
response = JsonResponse(data)
# 设置X-Content-Type-Options头部
response['X-Content-Type-Options'] = 'nosniff'
return response'X-Content-Type-Options':nosniff确保浏览器按照指定的选项来处理响应的内容类型,以提高安全性。
不加报ncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token 'o', "nosniff" is not valid JSON
json也可以写为这样,不过要导入JsonResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
def Jsond(request):#JsonResponse(json文件)
with open('static/data.json', 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
return JsonResponse(data)06.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h3{
color:orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">click</button>
<ul>
{# 将json数据插入#}
</ul>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick=function (){
// 清空ul
document.querySelector('ul').innerHTML=''
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get','/static/data.json')
xhr.send()
xhr.onreadystatechange=function (){
console.log(xhr.status)
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status === 200){
{#console.log(xhr.response) //字符串#}
var obj = JSON.parse(xhr.response);
{#console.log(obj)#}
var arr=obj.data
var str=''
for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
console.log(arr[i].name)
{#console.log(arr[i].category)#}
{#console.log(arr[i].desc)#}
{#方法1 创建li标签#}
{#var lis=document.createElement('li')#}
{#lis.innerHTML=`<h3>${arr[i].name}</h3><p>${ arr[i].desc}</p>`#}
{##}
{#方法1 追加给ul#}
{#document.querySelector('ul').appendChild(lis)#}
{#方法2 字符串拼接#}
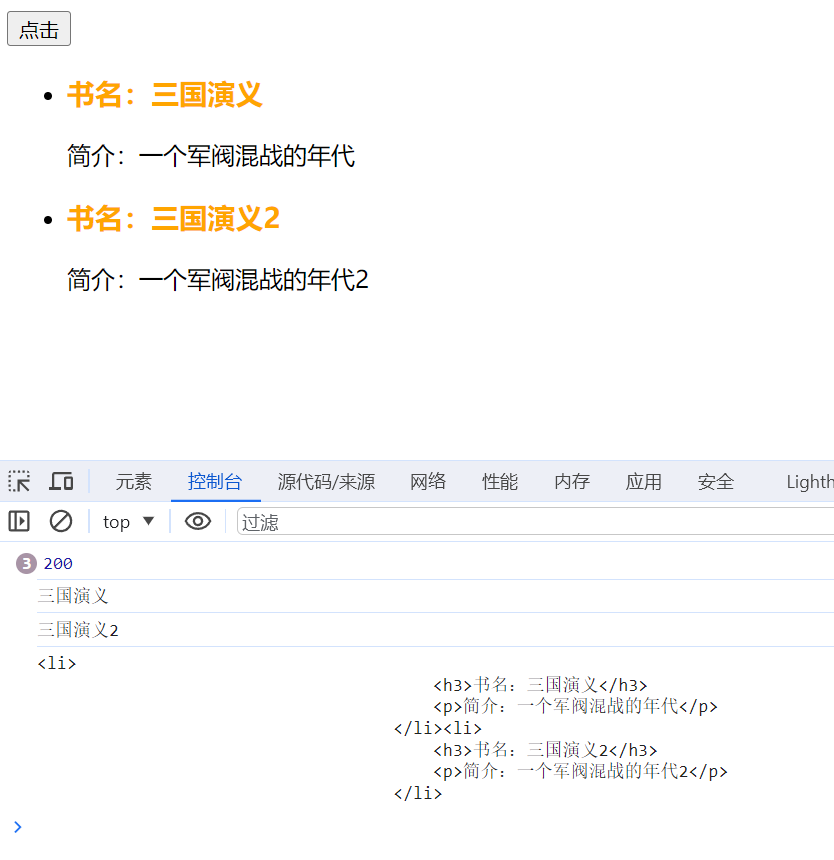
str+=`<li>
<h3>书名:${arr[i].name}</h3>
<p>简介:${ arr[i].desc}</p>
</li>`;
}
console.log(str)
document.querySelector('ul').innerHTML=str
}
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html> 将获取到的json数据传入li,加进先前准备好的ul中