1、数据类型简介
1.1为什么需要数据类型
不同的数据占用的存储空间不同,为了充分利用存储空间,便于把数据分成所需内存大小不同的数据,定义了不同的数据类型
1.2变量的数据类型
js是弱类型(动态语言)的语言,不需要提前声明变量的类型,在程序运行过程中,类型会被自动确定
所以js的变量的数据类型是只有程序在运行过程中,根据等号右边的值来确定的
所以同一个变量的数据类型可以变化
var x=10;//int
x="xiaomi";//字符串
1.3基本数据类型
Number \ Boolean \Undefined\Null

1.3.1数字型Number
整型和浮点型
0八进制:0~7 010–转为10进制=8
0x十六进制:0-9,A-F,0xa转为10进制=10
a.数字型范围
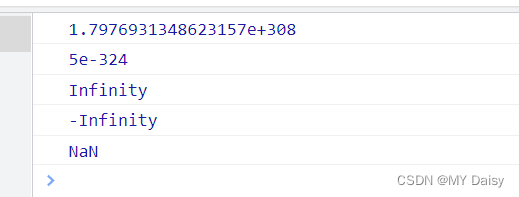
最大值:Number.MAX_VALUE;
最小值:Number.MIN_VALUE;
无穷大 :Infinity
非数字:NaN
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
//最大值
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE);
//数值型最小值
console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE);
//无穷大 Infinity
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE*2);
// 负无穷大 -Infinity
console.log(-Number.MAX_VALUE*2);
//非数字 NaN
console.log('aaa'-100);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
b.isNaN
isNaN()方法用来判断非数字,并且返回一个值,如果是数字,返回的就是false,如果不是数字返回的是true
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
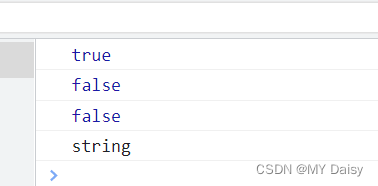
console.log(isNaN('12a'));//true
console.log(isNaN('12'));//false
console.log(isNaN(12));//false
console.log(typeof('12'));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.3.2 字符串型String
可以用单引号或双引号,推荐用单引号。
a.特殊用法:
字符串嵌套,外单内双或内单外双
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
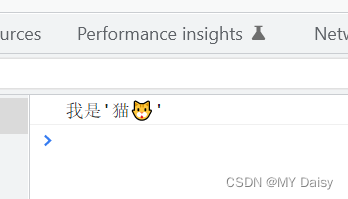
<script>
var str="我是'猫🐱'";
console.log(str);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
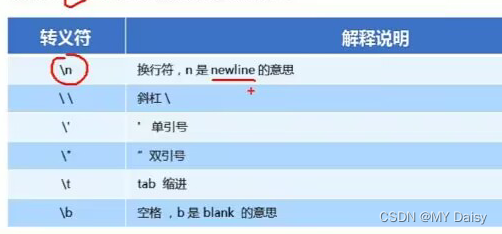
b.字符串转义符
以\开头
\n \ ’ " \t \b
\b表示空的格子,不是空格
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
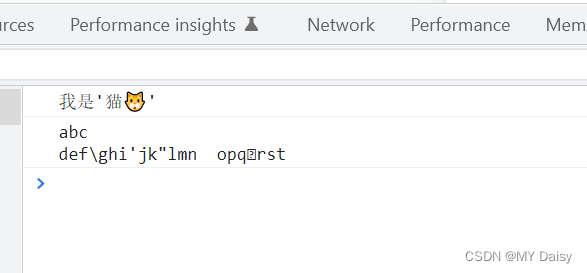
var str="我是'猫🐱'";
console.log(str);
var str1='abc\ndef\\ghi\'jk\"lmn\topq\brst';
console.log(str1);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
c.练习1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
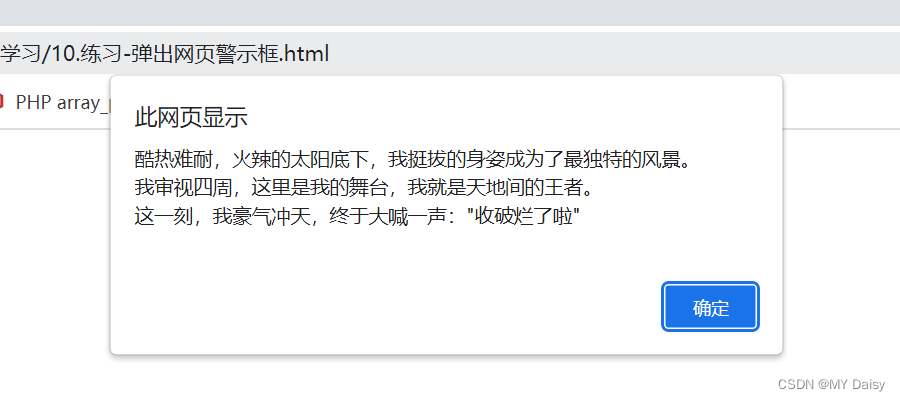
var text='酷热难耐,火辣的太阳底下,我挺拔的身姿成为了最独特的风景。\n我审视四周,这里是我的舞台,我就是天地间的王者。\n这一刻,我豪气冲天,终于大喊一声:"收破烂了啦"';
alert(text);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
d.字符串长度
length属性获取字符串长度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
var str="I am 里";
console.log(str.length);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
e.字符串拼接+号
数值型+字符串=字符串
数值型+数值型=数值型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
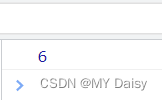
console.log("我今年"+18+"岁");
console.log(12+12);
console.log('12'+'12');
var age=23;
console.log("我今年"+age);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.3.3 布尔型Boolean
有两个值:true和false
boolean类型做加法运算:true作为1,false作为0
做拼接时,还是true/false
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
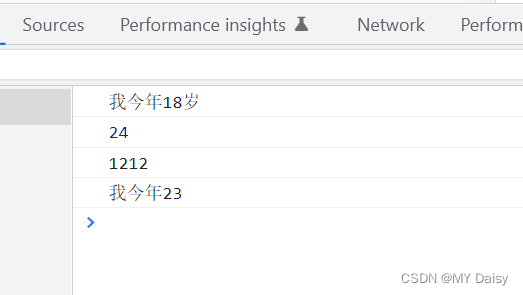
var flag1=true;
var flag2=false;
console.log(flag1+1);//2
console.log(flag2+1);//1
console.log('aa'+flag1);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.3.4 Undefined和NULL
undefined
undefined:一个变量声明但没有赋值,会有一个默认的undefined与字符串相加=字符串
undefined与数值相加=NaN
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
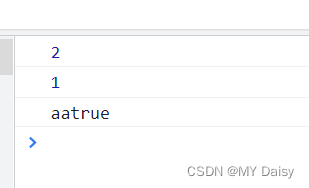
var text;
console.log(text+"我们");
console.log(text+1);//NaN
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
NULL
NULL+字符串=字符串
NULL+数值=数值
NULL+undefined=NaN
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
var space=null;
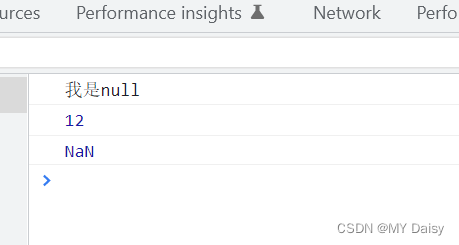
console.log("我是"+space);
console.log(12+space);
console.log(space+undefined);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.4获取变量的数据类型
使用typeof获取变量的数据类型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
var num=10;
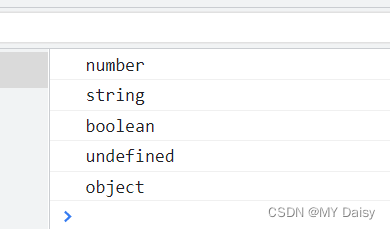
console.log(typeof num);//number
var str="100";
console.log(typeof str);//string
var flag=true;
console.log(typeof flag);//boolean
var und=undefined;
console.log(typeof und);//undefined
var non=null;
console.log(typeof non);//object
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.5 字面量
字面量就是表示如何表达这个值
数字字面量:8,9 ,10
字符串字面量:’前端’
布尔
字面量:true,false
1.6数据类型转换
把一种数据类型的变量转成另一种数据类型
转换的3种方式:
- 转换为字符串类型
- 转换为数字型
- 转换为布尔型
(1)转换为字符串类型
最常用的是加号拼接,这种方式叫隐式转换
| 方式 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| toString() | 转成字符串 | var num=1;alert(num.toString()) |
| String() | 强制转换成字符串 | var num=1;alert(String(num)) |
| 加号拼接 | 和字符串拼接的结果都是字符串 | var num=1;alert(num+“字符串”) |
(2)转换为数字型**
输入promot输入的都是字符型
| 方式 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| parseInt(string) | 将string转为整数类型 | parseInt(“78”) |
| parseFloat(string) | 将string转为浮点类型 | parseInt(“7.8”) |
| Number() | 强制转换将string类型转为数值型 | Number(“12”) |
| js隐式转换 | 算术运算符 -*/ | ‘12’-0 |
在这里插入代码片<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
console.log("parseInt");
// 1.parseInt将接受到的字符串转为数值型
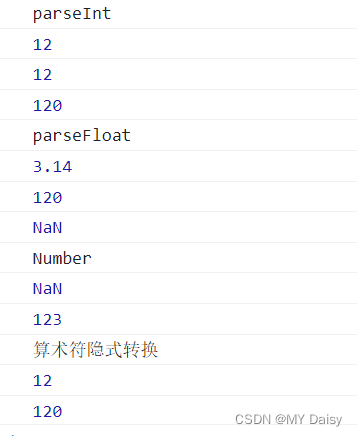
console.log(parseInt('12'));
// 如果是输入的小数值,则转整数类型时,会向下取整'12.5'--12
console.log(parseInt('12.6'));
// 如果输入的是数值+字符串,则转换时留数值,去掉字符串 '120px' --120 'rem120px'--NaN
console.log(parseInt("120px"));
console.log("parseFloat")
//2.parseFloat将接收到的字符转为浮点数
console.log(parseFloat('3.14'));//3.14
console.log(parseFloat('120px'));//120
console.log(parseFloat('rem120'));//NaN
// 3.Number(变量)
console.log("Number")
console.log(Number('123px'));//NaN
console.log(Number('123'));//123
//4.隐式转换
console.log("算术符隐式转换")
console.log('12'-0);//12
console.log('129'-'9');//120
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
(3)转为Boolean类型
| 方式 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean()函数 | 将其他类型转为布尔值 | Boolean(‘true’) |
- 代表空、否定的值会被转为false,如
'' 0 NaN null undefined
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
//转为false
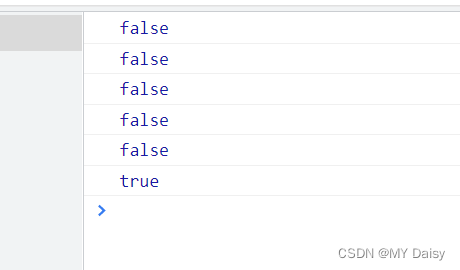
console.log(Boolean(""));
console.log(Boolean(0));
console.log(Boolean(NaN));
console.log(Boolean(null));
console.log(Boolean(undefined));
//转为true,除上述转为false的其他值
console.log(Boolean('aaa'));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
2、扩展
2.1解释型语言和编译型语言
翻译器翻译的方式:编译和解释。两种方式的区别在于翻译的时间点不同
编译器:代码执行前先编译,生成中间代码文件,如java的class文件
解释器:代码运行时进行解释,并立即执行,如javaScript
2.2 标识符、关键字、保留字
标识符:开发人员为变量、属性、函数、参数取得名字。标识符不能是保留字和关键字
关键字:JS本身已经使用的子,如break if else
保留字:预留的关键字,如name let int const