本文主要介绍base_lcoal_planner功能包中LocalPlannerUtil类的getLocalPlan函数,以及其调用的transformGlobalPlan函数、prunePlan函数的相关内容
一、getLocalPlan函数
getLocalPlan函数的源码如下:
bool LocalPlannerUtil::getLocalPlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& transformed_plan) {
//get the global plan in our frame
if(!base_local_planner::transformGlobalPlan(
*tf_,
global_plan_,
global_pose,
*costmap_,
global_frame_,
transformed_plan)) {
ROS_WARN("Could not transform the global plan to the frame of the controller");
return false;
}
//now we'll prune the plan based on the position of the robot
if(limits_.prune_plan) {
base_local_planner::prunePlan(global_pose, transformed_plan, global_plan_);
}
return true;
}
下面对函数的主要功能和步骤进行介绍
1. 函数签名:
bool LocalPlannerUtil::getLocalPlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& transformed_plan)
2. 函数参数:
- global_pose:机器人在全局坐标系中的当前位置,通常表示为位姿信息(包括位置和方向)。
- transformed_plan:函数将转换后的局部路径规划存储在此参数中。
3. 函数功能:
这个函数的主要功能是获取机器人的局部路径规划的初始参考路径,并存储在 transformed_plan 中。函数执行以下步骤:
- 首先,它调用名为 transformGlobalPlan 的函数来将全局路径规划 global_plan_ 转换为机器人的局部路径规划,结果存储在 transformed_plan 中。注意:transformed_plan中的坐标依然为全局坐标系
- 如果转换失败(transformGlobalPlan 返回 false),函数打印警告消息并返回 false
- 接下来,如果 limits_.prune_plan 为真,函数会调用名为 prunePlan 的函数,以根据机器人的当前位置修剪局部路径规划。这将确保局部路径规划与机器人的当前位置对齐。
- 最后,函数返回 true,表示成功获取局部路径规划。
4. 返回值:
- 如果获取局部路径规划成功,函数返回 true。
- 如果获取失败,函数返回 false,并在需要时输出警告消息。
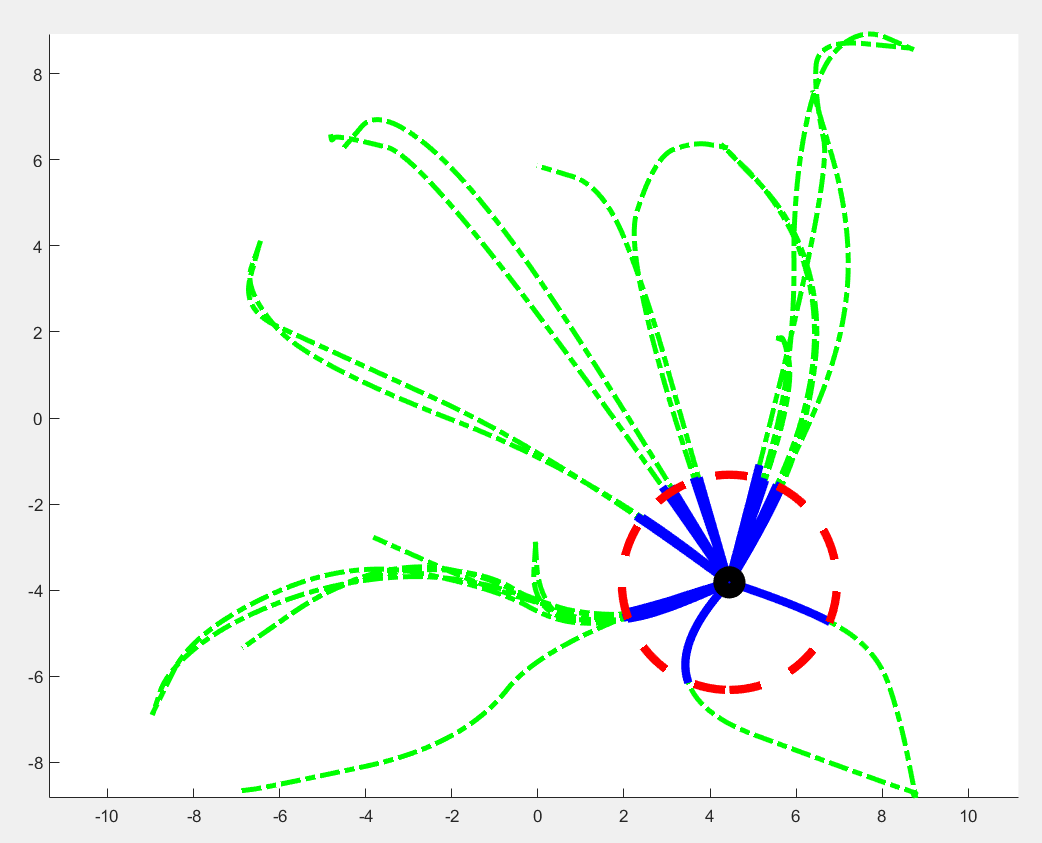
5. 函数效果示意
为了方便大家理解,我从实际运行过程中导出了转换前后的数据,绘制了以下图像,下图中的绿色虚线是一些列全局路径规划器规划的路径,蓝色实线是其对应的经过getLocalPlan函数后,得到的局部初始路径transformed_plan,从图中可以发现getLocalPlan函数对全局路径进行了裁剪,仅取与当前点距离小于局部地图一半尺寸的部分,在下图示例中,局部地图的设定尺寸为5x5m,下图中红色虚线圆圈的半径为5/2=2.5m。
需要注意的是,尽管transformed_plan中存储着局部初始路径,但其坐标的坐标系依然为全局坐标系
二、transformGlobalPlan 函数
transformGlobalPlan 函数的源码如下:
bool transformGlobalPlan(
const tf2_ros::Buffer& tf,
const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& global_plan,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose,
const costmap_2d::Costmap2D& costmap,
const std::string& global_frame,
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& transformed_plan){
transformed_plan.clear();
if (global_plan.empty()) {
ROS_ERROR("Received plan with zero length");
return false;
}
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& plan_pose = global_plan[0];
try {
// get plan_to_global_transform from plan frame to global_frame
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped plan_to_global_transform = tf.lookupTransform(global_frame, ros::Time(),
plan_pose.header.frame_id, plan_pose.header.stamp, plan_pose.header.frame_id, ros::Duration(0.5));
//let's get the pose of the robot in the frame of the plan
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped robot_pose;
tf.transform(global_pose, robot_pose, plan_pose.header.frame_id);
//we'll discard points on the plan that are outside the local costmap
double dist_threshold = std::max(costmap.getSizeInCellsX() * costmap.getResolution() / 2.0,
costmap.getSizeInCellsY() * costmap.getResolution() / 2.0);
unsigned int i = 0;
double sq_dist_threshold = dist_threshold * dist_threshold;
double sq_dist = 0;
//we need to loop to a point on the plan that is within a certain distance of the robot
while(i < (unsigned int)global_plan.size()) {
double x_diff = robot_pose.pose.position.x - global_plan[i].pose.position.x;
double y_diff = robot_pose.pose.position.y - global_plan[i].pose.position.y;
sq_dist = x_diff * x_diff + y_diff * y_diff;
if (sq_dist <= sq_dist_threshold) {
break;
}
++i;
}
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped newer_pose;
//now we'll transform until points are outside of our distance threshold
while(i < (unsigned int)global_plan.size() && sq_dist <= sq_dist_threshold) {
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& pose = global_plan[i];
tf2::doTransform(pose, newer_pose, plan_to_global_transform);
transformed_plan.push_back(newer_pose);
double x_diff = robot_pose.pose.position.x - global_plan[i].pose.position.x;
double y_diff = robot_pose.pose.position.y - global_plan[i].pose.position.y;
sq_dist = x_diff * x_diff + y_diff * y_diff;
++i;
}
}
catch(tf2::LookupException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("No Transform available Error: %s\n", ex.what());
return false;
}
catch(tf2::ConnectivityException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("Connectivity Error: %s\n", ex.what());
return false;
}
catch(tf2::ExtrapolationException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("Extrapolation Error: %s\n", ex.what());
if (!global_plan.empty())
ROS_ERROR("Global Frame: %s Plan Frame size %d: %s\n", global_frame.c_str(), (unsigned int)global_plan.size(), global_plan[0].header.frame_id.c_str());
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool getGoalPose(const tf2_ros::Buffer& tf,
const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& global_plan,
const std::string& global_frame, geometry_msgs::PoseStamped &goal_pose) {
if (global_plan.empty())
{
ROS_ERROR("Received plan with zero length");
return false;
}
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& plan_goal_pose = global_plan.back();
try{
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped transform = tf.lookupTransform(global_frame, ros::Time(),
plan_goal_pose.header.frame_id, plan_goal_pose.header.stamp,
plan_goal_pose.header.frame_id, ros::Duration(0.5));
tf2::doTransform(plan_goal_pose, goal_pose, transform);
}
catch(tf2::LookupException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("No Transform available Error: %s\n", ex.what());
return false;
}
catch(tf2::ConnectivityException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("Connectivity Error: %s\n", ex.what());
return false;
}
catch(tf2::ExtrapolationException& ex) {
ROS_ERROR("Extrapolation Error: %s\n", ex.what());
if (global_plan.size() > 0)
ROS_ERROR("Global Frame: %s Plan Frame size %d: %s\n", global_frame.c_str(), (unsigned int)global_plan.size(), global_plan[0].header.frame_id.c_str());
return false;
}
return true;
}
下面对函数的主要功能和步骤进行介绍
1. 函数签名:
bool transformGlobalPlan(
const tf2_ros::Buffer& tf,
const std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& global_plan,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose,
const costmap_2d::Costmap2D& costmap,
const std::string& global_frame,
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& transformed_plan
)
2. 参数:
- tf:tf2_ros::Buffer 对象,用于进行坐标变换(Transform)的查询。
- global_plan:全局路径规划的一系列位姿(姿态信息),通常包含从机器人当前位置到目标点的路径。
- global_pose:机器人在全局坐标系中的当前位置,通常表示为位姿信息(包括位置和方向)。
- costmap:局部代价地图,用于检查路径规划中的点是否在局部地图中。
- global_frame:全局坐标系的名称,通常是机器人的地图坐标系。
- transformed_plan:函数将转换后的全局路径规划存储在此参数中。
3. 函数功能:
这个函数的主要功能是将全局路径规划 global_plan 转换为局部路径规划,并存储在 transformed_plan 中。函数执行以下步骤:
- 首先,它清空 transformed_plan,以确保在填充之前不包含任何数据。
- 如果 global_plan 为空,它将打印错误消息并返回 false,表示接收到零长度的路径规划。
- 获取全局路径规划的第一个位姿 plan_pose,通常表示目标点。
- 使用 tf 对象查询全局坐标系 global_frame 到 plan_pose 所在坐标系的坐标变换。这里暂时没有看明白,貌似转换后还是全局坐标系,不清楚此操作的作用
- 计算机器人当前位置 robot_pose 在路径规划坐标系中的姿态,以便确定机器人在哪个位置附近需要开始路径转换。
- 计算一个距离阈值 dist_threshold,它通常是局部代价地图的一半尺寸,用于确定哪些点需要保留在局部路径规划中。
- 使用一个循环,找到全局路径规划中距离机器人位置不超过 dist_threshold 的点,并将它们添加到 transformed_plan 中,同时计算距离并更新 i。
- 最后,函数处理可能的异常,如坐标变换失败,并返回 false,以指示转换失败。
4. 返回值:
- 如果路径转换成功,函数返回 true,并将转换后的路径存储在 transformed_plan 中。
- 如果出现异常或全局路径规划为空,函数返回 false。
三、prunePlan函数
prunePlan函数的源码如下:
void prunePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& global_plan){
ROS_ASSERT(global_plan.size() >= plan.size());
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>::iterator it = plan.begin();
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>::iterator global_it = global_plan.begin();
while(it != plan.end()){
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& w = *it;
// Fixed error bound of 2 meters for now. Can reduce to a portion of the map size or based on the resolution
double x_diff = global_pose.pose.position.x - w.pose.position.x;
double y_diff = global_pose.pose.position.y - w.pose.position.y;
double distance_sq = x_diff * x_diff + y_diff * y_diff;
if(distance_sq < 1){
ROS_DEBUG("Nearest waypoint to <%f, %f> is <%f, %f>\n", global_pose.pose.position.x, global_pose.pose.position.y, w.pose.position.x, w.pose.position.y);
break;
}
it = plan.erase(it);
global_it = global_plan.erase(global_it);
}
}
下面对函数的主要功能和步骤进行介绍
1. 函数签名:
void prunePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& global_pose, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan, std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& global_plan)
2. 参数:
- global_pose:机器人在全局坐标系中的当前位置,通常表示为位姿信息(包括位置和方向)。
- plan:一个存储局部路径规划的一系列位姿(姿态信息),这是局部路径规划器生成的候选路径。
- global_plan:全局路径规划的一系列位姿,通常包含从起点到终点的路径。
3. 函数功能:
这个函数的主要目的是将plan和global_plan修剪,以便将全局路径规划和局部路径规划的起点对齐。它的实现逻辑如下:
- 首先,函数使用断言 ROS_ASSERT 来确保global_plan的大小大于等于plan的大小,因为全局规划必须包括局部规划。
- 接下来,函数使用迭代器遍历plan和global_plan中的位姿信息。
- 对于每个位姿,它计算全局位置 global_pose 与该位姿的距离的平方,这是通过计算差值并计算欧几里德距离的平方来完成的。
- 如果距离的平方小于1(可以根据需要更改阈值),则认为机器人已经接近路径的一部分,函数会停止修剪,这通常意味着机器人已经到达或非常接近路径上的某个点。
- 如果距离的平方大于等于1,函数会将plan和global_plan中的当前位姿从列表中删除,以便继续修剪下一个位姿。
4. 总结:
该函数的目的是将局部路径规划器生成的位姿列表plan修剪到机器人当前位置附近的部分,并且同时将全局路径规划器生成的路径global_plan做相应的修剪,以确保局部路径规划与全局路径规划对齐。这是导航中的一个常见操作,以确保机器人沿着规划路径前进。如果机器人远离路径,函数将删除不再需要的位姿,以节省计算资源。