目录
1. 构造函数
1.1 list ()
1.2 list (size_t n, const T& val = T())
1.3 list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
2. bool empty() const
3. size_type size() const
4. T& front()
4. T& back()
5. void push_front (const T& val)
6. void pop_front()
7. void push_back (const T& val)
8. void pop_back()
9. 迭代器
10. iterator insert (iterator pos, const T& val)
11. void insert (iterator pos, size_t n, const T& val)
12. iterator erase (iterator pos)
13. void swap (list& x)
14. void resize (size_t n, const T& val = T())
15. void clear()
16. 下面的这些函数都很好理解
16.1 void remove (const T& val)
16.2 void unique()
16.2 void merge(list& x)
16.3 void sort()
16.4 void reverse()
list 的介绍,来源:list - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
1. list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
2. list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向 其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3. list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高 效。
4. 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率 更好。
5. 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list 的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间 开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这 可能是一个重要的因素)
1. 构造函数
1.1 list ()
这里的 T 是模板参数,list 可以存储任意类型的数据嘛。
通过 list 的简介,我们知道 list 的底层其实是一个带头双向循环链表 (以下简称双链表),在定义 list 的时候,我们需要初始化一个哨兵位的头结点。哨兵位的头结点不存储有效数据。无参构造就是用来初始化哨兵位的头结点的!
1.2 list (size_t n, const T& val = T())
这个构造函数可以初始化一个长度为 n 的,值均为 val 的双链表。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt(5, 8);
//输出:8 8 8 8 8
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}1.3 list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
这个构造函数可以用一段迭代器区间来初始化双链表。构造的区间:[first, last)。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
list<int> lt(arr.begin(), arr.end());
//输出:1 2 3 4 5
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}2. bool empty() const
判断一个链表是不是空链表!如果有有效数据,返回 true,反之返回 false。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt1;
cout << lt1.empty() << endl; //输出:1
list<int> lt2(5, 8);
cout << lt2.empty() << endl; //输出:0
return 0;
}3. size_type size() const
这个函数可以获取双链表的长度。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt2(5, 8);
cout << lt2.size() << endl; //输出:5
return 0;
}4. T& front()
这个函数可以获取双链表的第一个有效元素。有 const 和非 const 两个版本,支持普通对象和 const 对象的调用。

#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
list<int> lt(arr.begin(), arr.end());
cout << lt.front() << endl; //输出:1
return 0;
}4. T& back()
这个函数可以获取双链表的最后一个有效元素。有 const 和非 const 两个版本,支持普通对象和 const 对象的调用。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> arr;
arr.push_back(1);
arr.push_back(2);
arr.push_back(3);
arr.push_back(4);
arr.push_back(5);
list<int> lt(arr.begin(), arr.end());
cout << lt.back() << endl; //输出:5
return 0;
}5. void push_front (const T& val)
双链表头插元素。因为之前我们都用 C 语言实现过双链表,学习 list 的使用就非常简单啦!
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_front(4);
lt.push_front(3);
lt.push_front(2);
lt.push_front(1);
//输出:1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}6. void pop_front()
双链表头删元素。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_front(4);
lt.push_front(3);
lt.push_front(2);
lt.push_front(1);
//输出:1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
lt.pop_front();
//输出:2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}7. void push_back (const T& val)
双链表尾插元素。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//输出:1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}8. void pop_back()
双链表尾删元素。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//输出:1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
lt.pop_back();
//输出:1 2 3
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}9. 迭代器
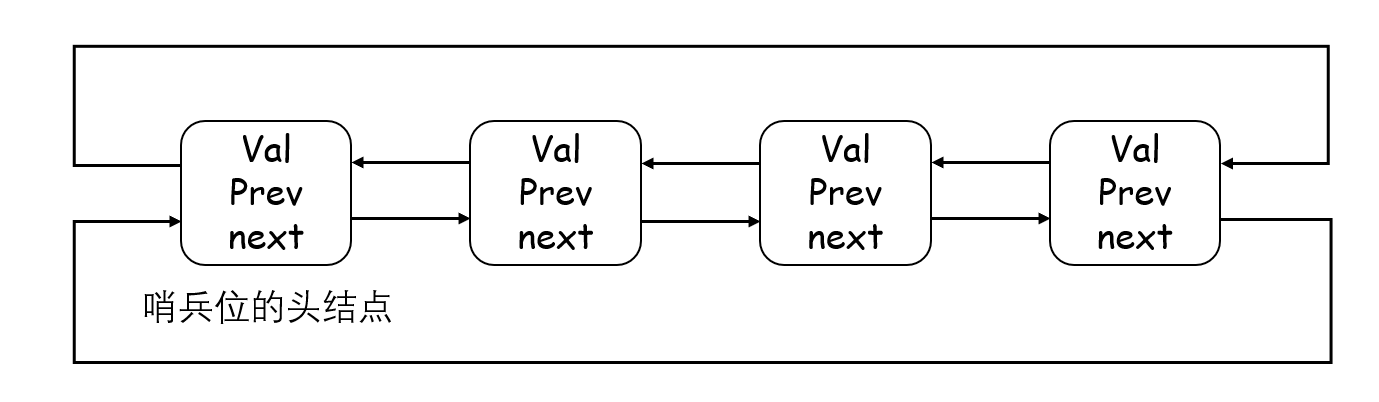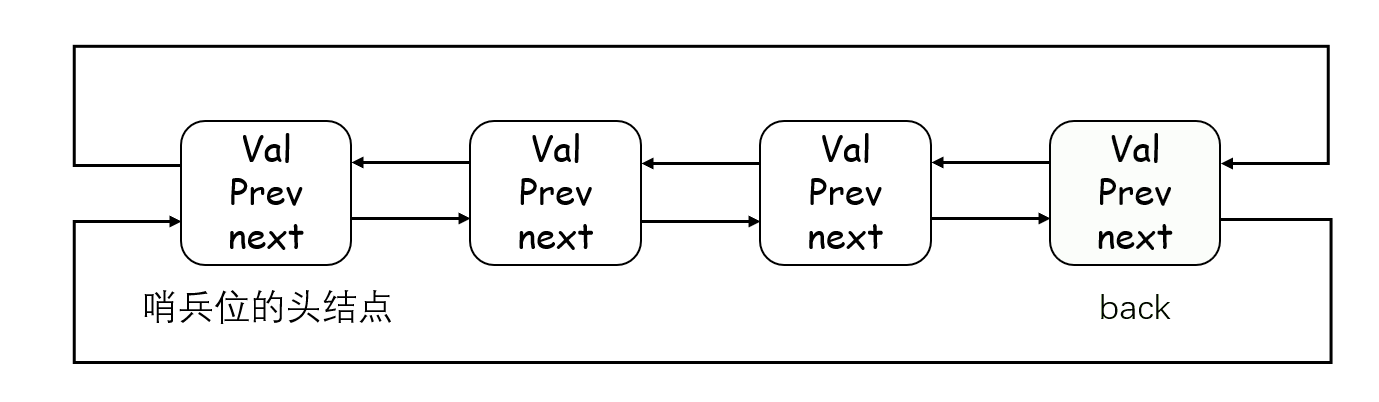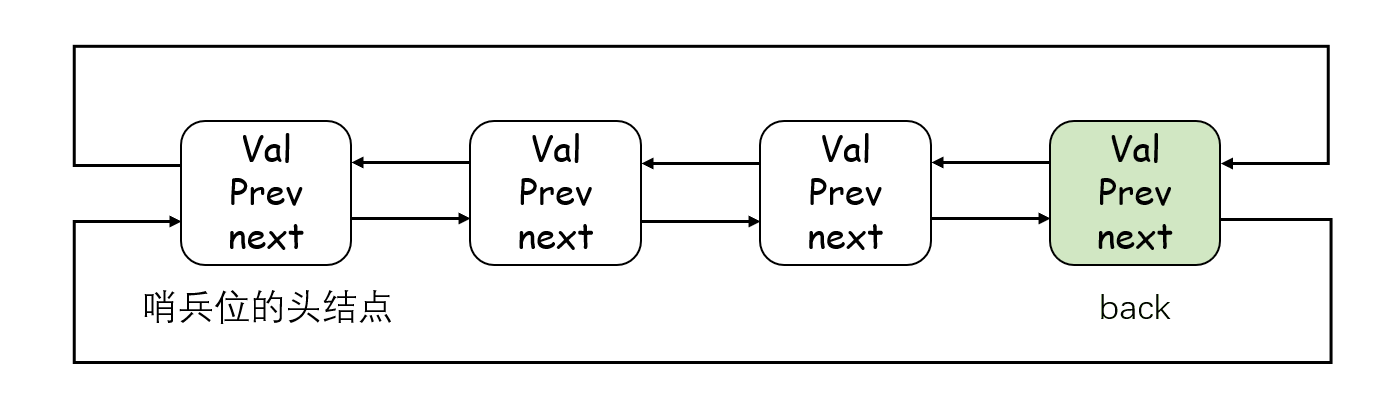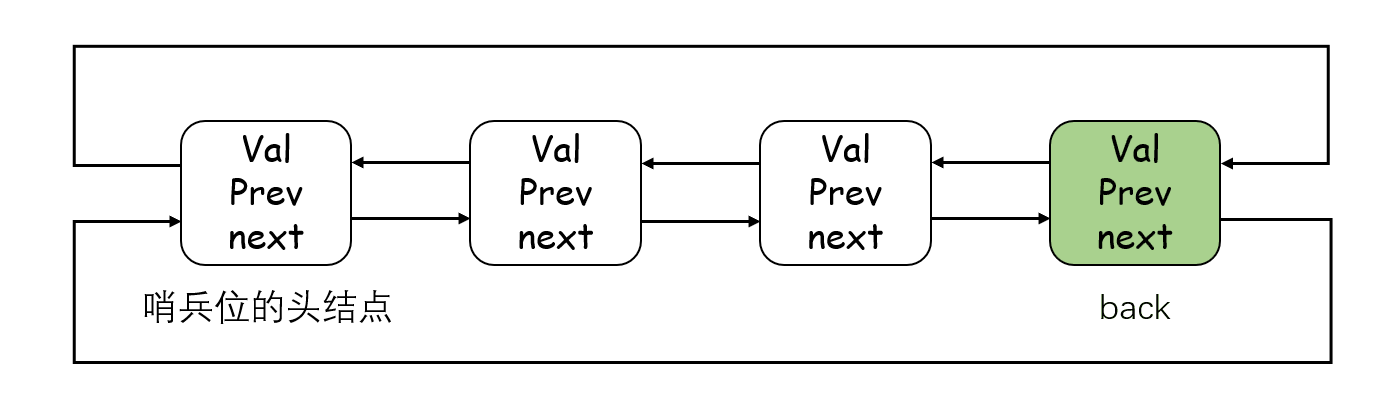
list 的迭代器就不是简单的原生指针了。因为他的物理空间并不连续,因此 list 的迭代器需要进行封装,使得迭代器解引用能够返回节点存储的数据,使得迭代器加加,指向下一个节点,等等。具体的操作到我们模拟实现 list 的时候再说。
下面的图是 list 迭代器 begin() 与 end() 迭代器对应的双链表节点。
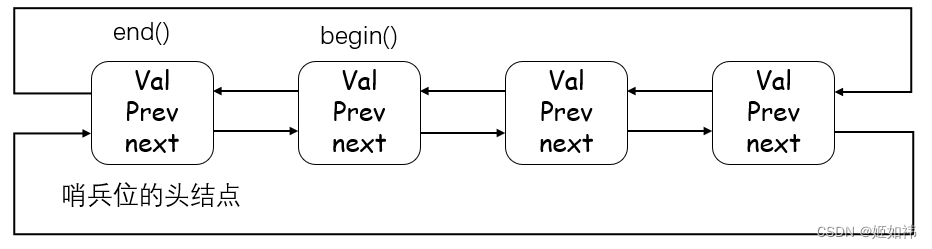
10. iterator insert (iterator pos, const T& val)
这个函数可以在 list 的 pos 位置处,插入一个值为 val 的元素。返回值就是返回新插入的元素的位置对应的迭代器。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//在begin() 的位置插入 0 ,相当于头插
lt.insert(lt.begin(), 0);
//输出:0 1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
//在end() 的位置插入 5 ,相当于尾插
auto it = lt.insert(lt.end(), 5);
cout << *it << endl; //输出:5
//输出:0 1 2 3 4 5
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}11. void insert (iterator pos, size_t n, const T& val)
这个函数可以在 pos 位置插入 n 个值为 val 的节点。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//在begin() 的 位置插入 3 个值为 0 的节点
lt.insert(lt.begin(), 3, 0);
//输出:0 0 0 1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}12. iterator erase (iterator pos)
这个函数可以删除 pos 位置的双链表节点。不可以删除 end() 位置的节点,会报错的!VS2022 做了检查的。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
//相当于头删
lt.erase(lt.begin());
//输出:2 3 4
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}13. void swap (list<T>& x)
这个函数可以交换两个链表。我们实现 list 的时候,list 类中维护的是哨兵位的头结点的指针,交换两个链表的指针就能实现这样的效果。仅限于我们自己实现的 list 类哈!list 实现方式多种多样!
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
list<int> lt2;
lt2.push_back(5);
lt2.push_back(6);
lt2.push_back(7);
lt2.push_back(8);
lt1.swap(lt2);
//输出:5 6 7 8
for (auto e : lt1)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
//输出:1 2 3 4
for (auto e : lt2)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}14. void resize (size_t n, const T& val = T())
stl 库的接口风格都很相似,list 的resize 和 vector,string 的 resize 简直一毛一样。当 n 小于双链表的长度,直接截断,当 n 大于双链表的长度,会用 val 区初始化新插入的节点。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(0);
lt.resize(5, 1);
//输出: 0 1 1 1 1
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}15. void clear()
清空链表,即释放所有链表节点。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(0);
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.clear();
//没有输出
for (auto e : lt)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}16. 下面的这些函数都很好理解
16.1 void remove (const T& val)
移除链表中所有值为 val 的节点。
1 2 3 3 4 5 remove(3) :1 2 4 5。
16.2 void unique()
删除链表中重复的节点。
1 2 2 3 3 4 5 1 remove(3) :1 2 3 4 5 1。
这个函数只能对相邻的重复的数去重。因此多用于已经排好序的 list。
16.2 void merge(list<T>& x)
这个函数用于两个 list 的合并,前提是两个 list 都被排好序了!
例如:
list1:-1 2 3 5 8
list2:0 1 2 4 6 7
合并后的结果:-1 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8。
16.3 void sort()
链表的排序。
16.4 void reverse()
链表的逆置。