目录:
- SpringBoot入门案例(Idea联网版)
- SpringBoot入门案例(官网创建版)
- SpringBoot入门案例(阿里云版)
- SpringBoot入门案例(手工制作版)
- 教你一招,隐藏文件或文件夹
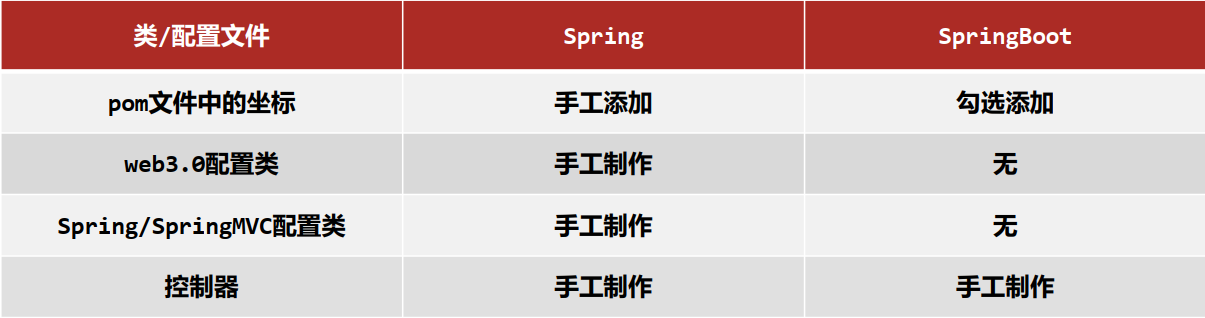
- 入门案例解析:parent
- 入门案例解析:starter
- 入门案例解析:引导类
- 入门案例解析:辅助功能
- REST风格简介
- RESTfuI入门案例
- RESTful快速开发
- 复制模块
- 属性配置方式
- 基础配置
- 3种配置文件类型
- 配置文件加载优先级
- 属性提示消失解决方案
- yaml数据格式
- 读取yaml单一属性数据
- yaml文件中的变量引用
- 读取yaml全部属性数据
- 读取yaml引用类型属性数据
- SpringBoot整合JUnit
- 整合JUnit--classes属性
- SpringBoot整合MyBatis
- SpringBoot整合MyBatis常见问题处理
- SpringBoot整合MyBatisPlus
- SpringBoot整合Druid
- SSMP整合案例制作分析
1.SpringBoot入门案例(Idea联网版)
SpringBoot入门程序开发
- SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
SpringBoot基础配置
1.创建新模块,选择Spring Initializr,并配置模块相关基础信息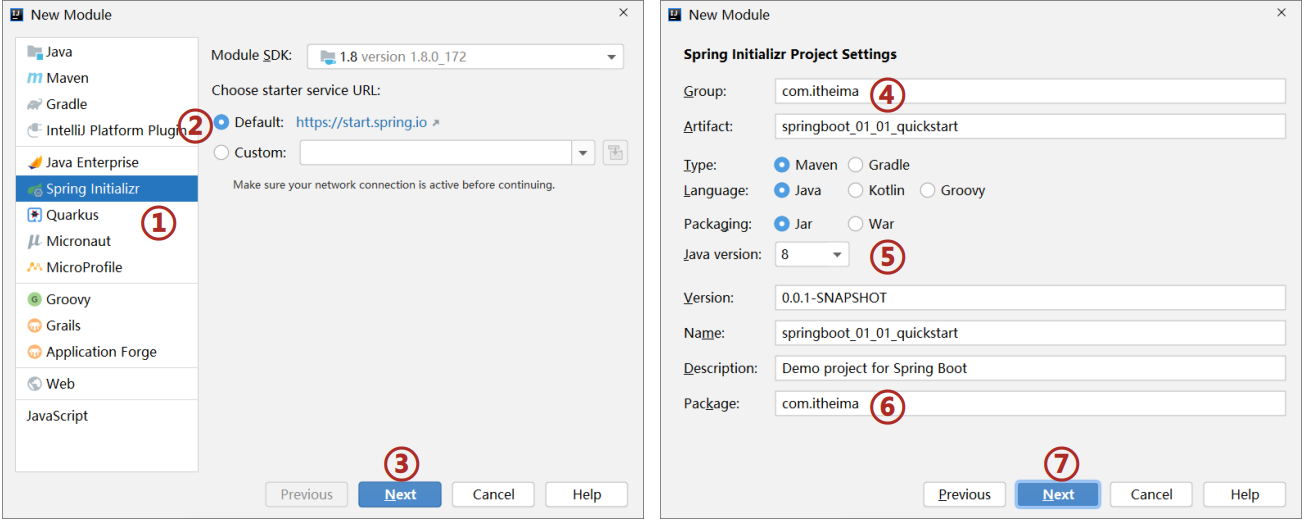
2.选择当前模块需要使用的技术集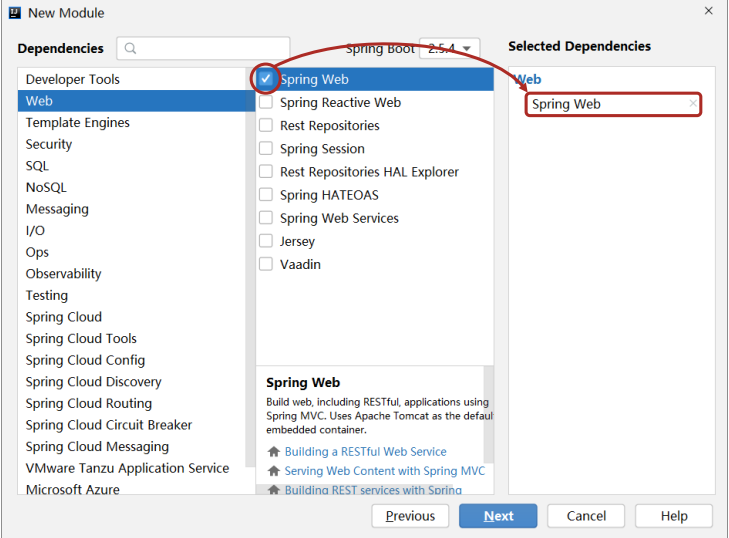
3.开发控制器类
//Rest模式
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
return "springboot is running...";
}
}4.运行自动生成的Application类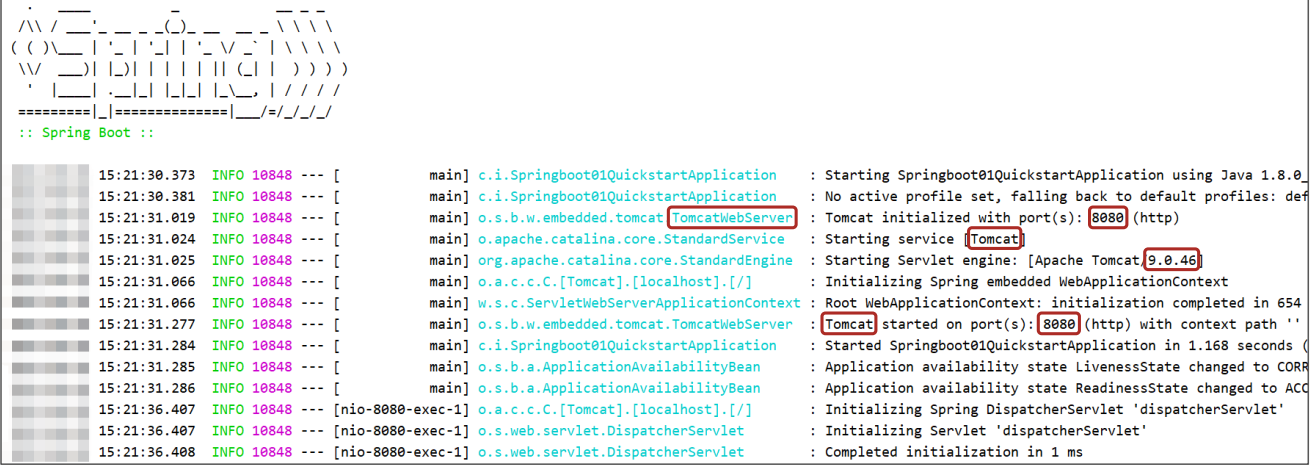
5.运行结果:
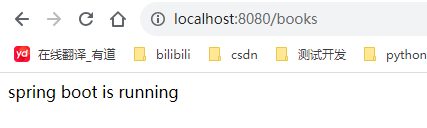
入门案例
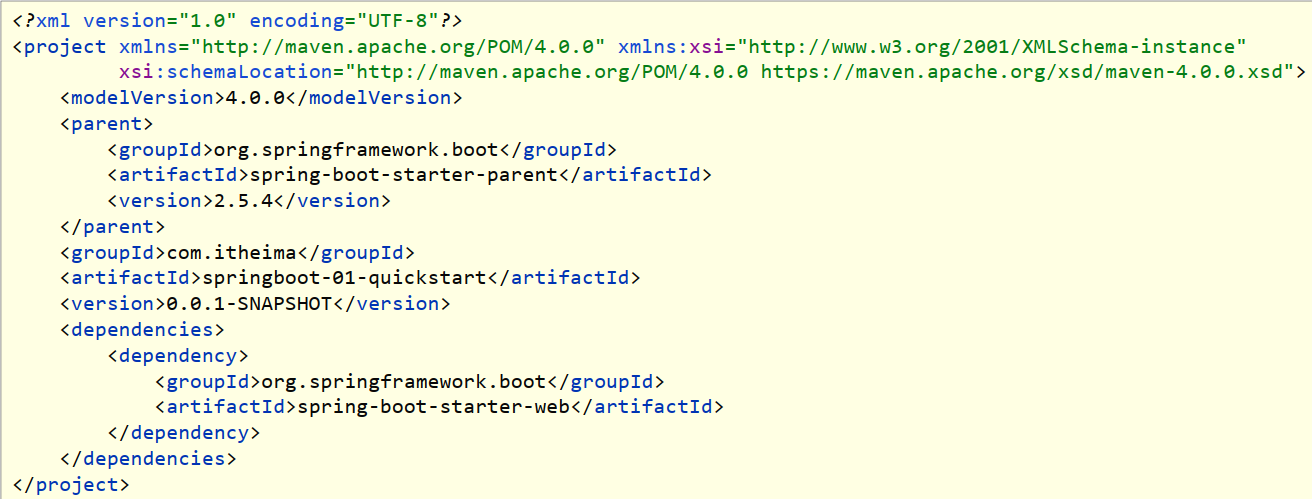
最简SpringBoot程序所包含的基础文件
-
pom.xml文件
-
Application类
package com.example._20231018; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
Spring程序与SpringBoot程序对比
注意:基于idea开发SpringBoot程序需要确保联网且能够加载到程序框架结构
小结:
- 开发SpringBoot程序可以根据向导进行联网快速制作
- SpringBoot程序需要基于JDK8进行制作
- SpringBoot程序中需要使用何种功能通过勾选选择技术
- 运行SpringBoot程序通过运行Application程序入口进行
2.SpringBoot入门案例(官网创建版)
- 基于SpringBoot官网创建项目,地址: https://start.spring.io/
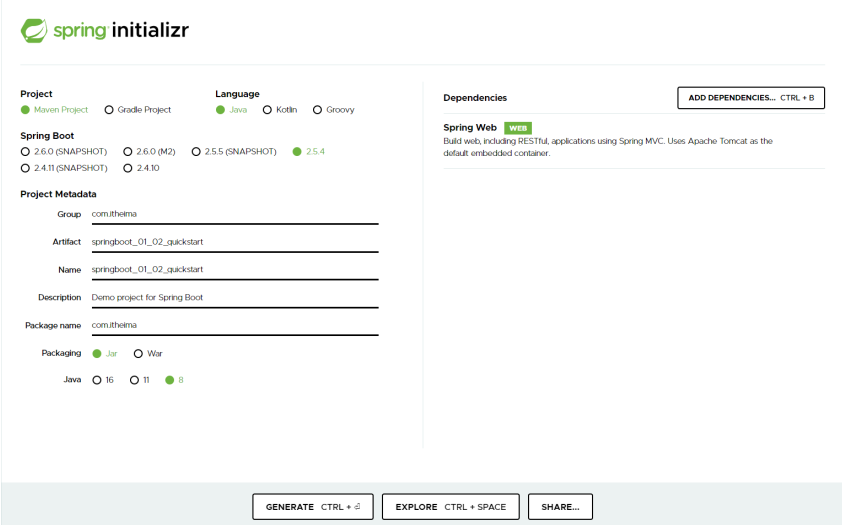
步骤:
- 打开SpringBoot官网,选择Quickstart Your Project
- 创建工程,并保存项目
- 解压项目,通过IDE导入项目
3.SpringBoot入门案例(阿里云版)
- 基于SpringBoot官网创建项目,地址: https://start.spring.io/
- 基于阿里云创建项目,地址: https://start.aliyun.com
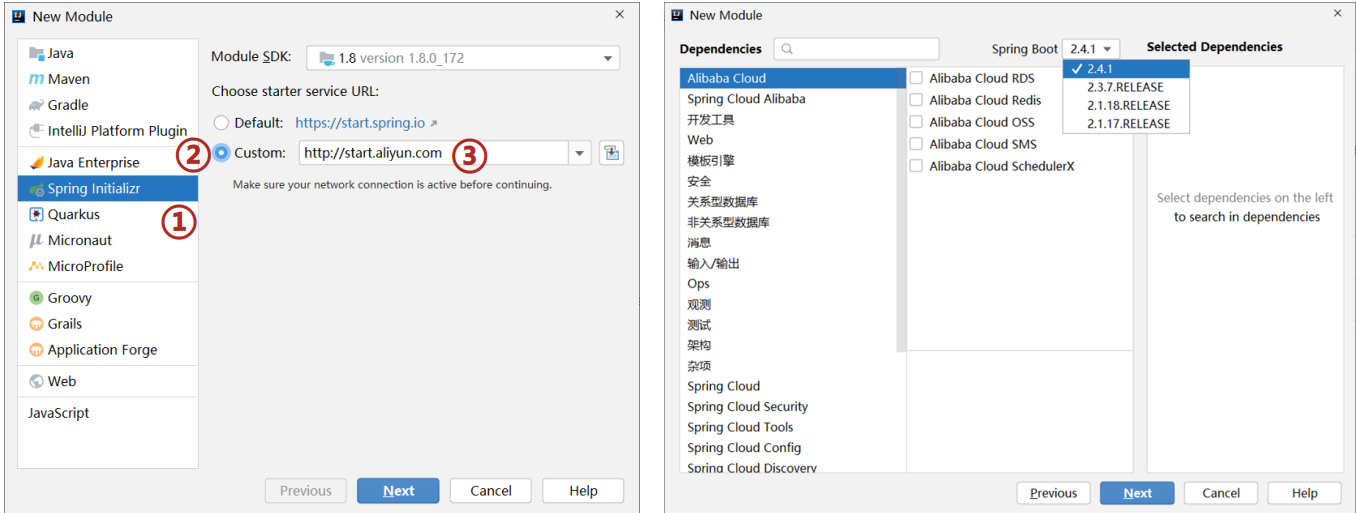
- 阿里云提供的坐标版本较低,如果需要使用高版本,进入工程后手工切换SpringBoot版本
- 阿里云提供的工程模板与Spring官网提供的工程模板略有不同
步骤:
- 选择start来源为自定义URL
- 输入阿里云start地址
- 创建项目
4.SpringBoot入门案例(手工制作版)
手工创建项目(手工导入坐标)
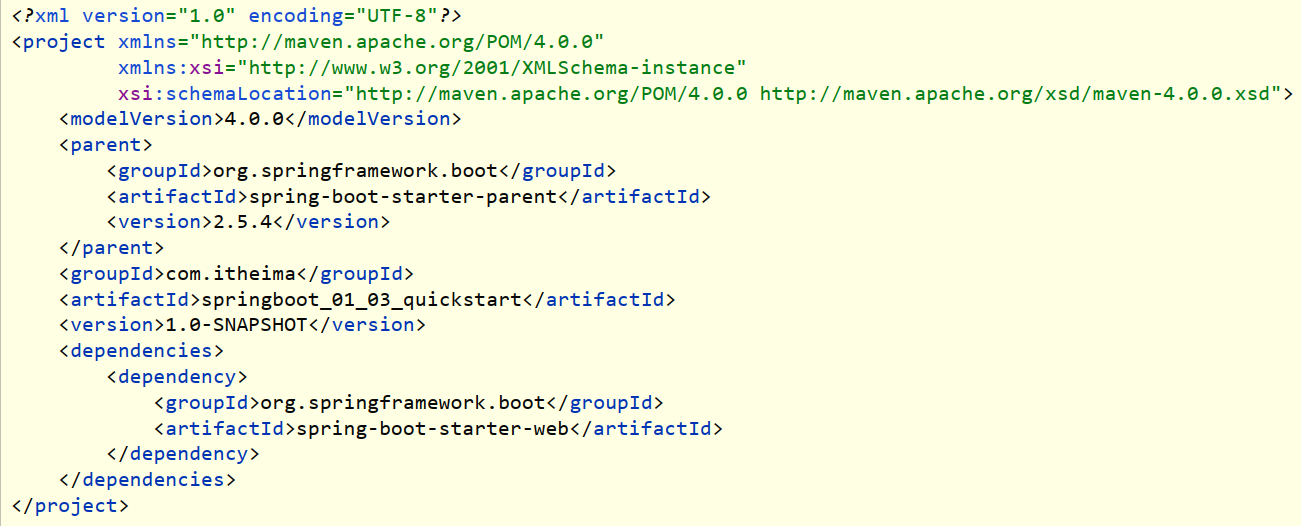
手工创建项目(手工制作引导类)
步骤:
- 创建普通Maven工程
- 继承spring-boot-starter-parent
- 添加依赖spring-boot-starter-web
- 制作引导类Application
5.教你一招,隐藏文件或文件夹

隐藏指定文件/文件夹
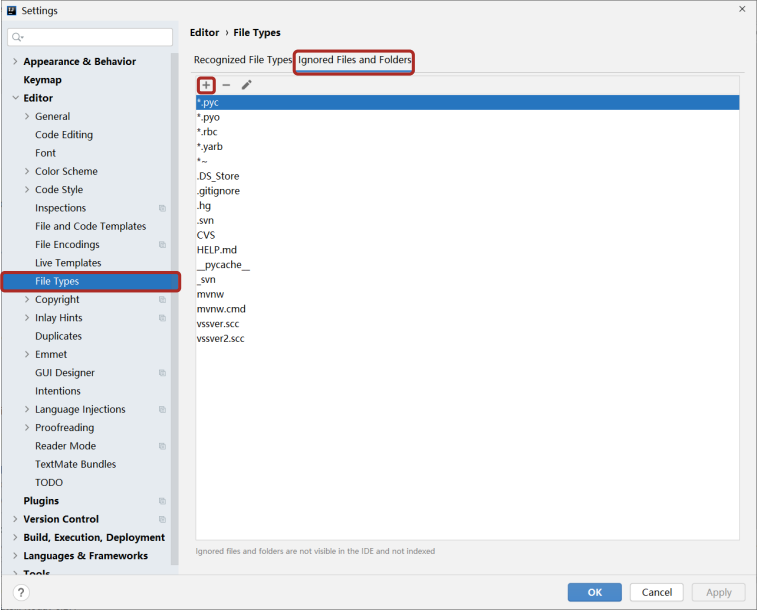
Idea中隐藏指定文件或指定类型文件 Setting → File Types → Ignored Files and Folders
- 输入要隐藏的文件名,支持*号通配符
- 回车确认添加
6.入门案例解析:parent
SpringBoot简介
- SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
- Spring程序缺点
- 依赖设置繁琐
- 配置繁琐
- SpringBoot程序优点
- 起步依赖(简化依赖配置)
- 自动配置(简化常用工程相关配置)
- 辅助功能(内置服务器, ……)
- 开发springBoot程序要继承spring-boot-starter-parent
- spring-boot-starter-parent中定义了若干个依赖管理
- 继承parent模块可以避免多个依赖使用相同技术时出现依赖版本冲突
- 继承parent的形式也可以采用引入依赖的形式实现效果
7.入门案例解析:starter
- starter
- SpringBoot中常见项目名称,定义了当前项目使用的所有依赖坐标,以达到减少依赖配置的目的
- parent
- 所有SpringBoot项目要继承的项目,定义了若干个坐标版本号(依赖管理,而非依赖), 以达到减少依赖冲突的目的
- spring-boot-starter-parent各版本间存在着诸多坐标版本不同
- 实际开发
- 使用任意坐标时,仅书写GAV中的G和A, V由SpringBoot提供,除非SpringBoot未提供对应版本V
- 如发生坐标错误,再指定Version(要小心版本冲突)
总结:
- 开发springBoot程序需要导入坐标时通常导入对应的starter
- 每个不同的starter根据功能不同,通常包含多个依赖坐标
- 使用starter可以实现快速配置的效果,达到简化配置的目的
8.入门案例解析:引导类
Application.class
package com.example._20231018;
import com.example._20231018.controller.BookController;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
BookController bean = ctx.getBean(BookController.class);
System.out.println(bean);
User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
运行结果:
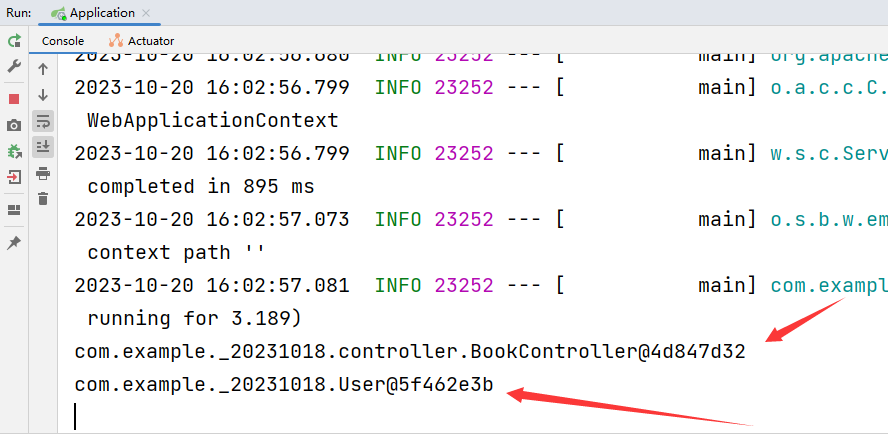
启动方式
- SpringBoot的引导类是Boot工程的执行入口,运行main方法就可以启动项目
- SpringBoot工程运行后初始化Spring容器,扫描引导类所在包加载bean
9.入门案例解析:辅助功能
内置服务器
- tomcat(默认) apache出品,粉丝多, 应用面广,负载了若干较重的组件
- jetty 更轻量级, 负载性能远不及tomcat
- undertow undertow,负载性能勉强跑赢tomcat
总结:
- 内嵌Tomcat服务器是SpringBoot辅助功能之一
- 内嵌Tomcat工作原理是将Tomcat服务器作为对象运行,并将该对象交给Spring容器管理
- 变更内嵌服务器思想是去除现有服务器,添加全新的服务器
10.REST风格简介
REST简介
- REST (Representational State Transfer),表现形式状态转换
传统风格资源描述形式
- http: / /localhost/user/getById?id=1
- http: / /localhost/user/ saveUser
REST风格描述形式
- http: / / localhost/user/1
- http: / / localhost/user
REST风格优点:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为,无法通过地址得知对资源是何种操作书写简化
按照REST风格访问资源时使用行为动作区分对资源进行了何种操作
- http: / / localhost/users 查询全部用户信息 GET(查询)
- http: / / localhost/users/1 查询指定用户信息 GET(查询)
- http: / / localhost/users 添加用户信息 POST(新增/保存)
- http: / / localhost/users 修改用户信息 PUT(修改/更新)
- http:// localhost/users/1 删除用户信息 DELETE (删除)
根据REST风格对资源进行访问称为RESTful
- 上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称REST风格,而不是REST规范
- 描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例如:users、books、account.…..
11.RESTfuI入门案例
UserController.class
package com.example._20231018.controller;
import com.example._20231018.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
public class UserController {
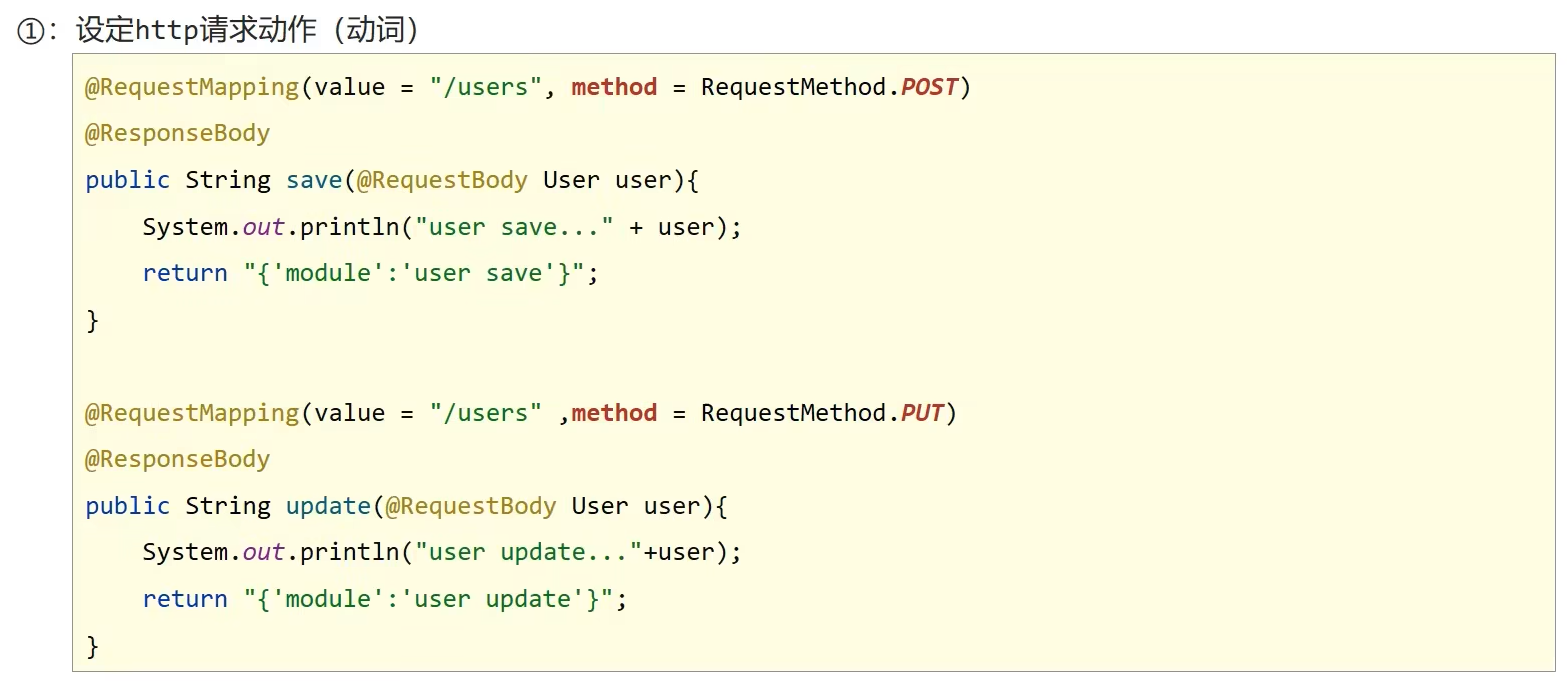
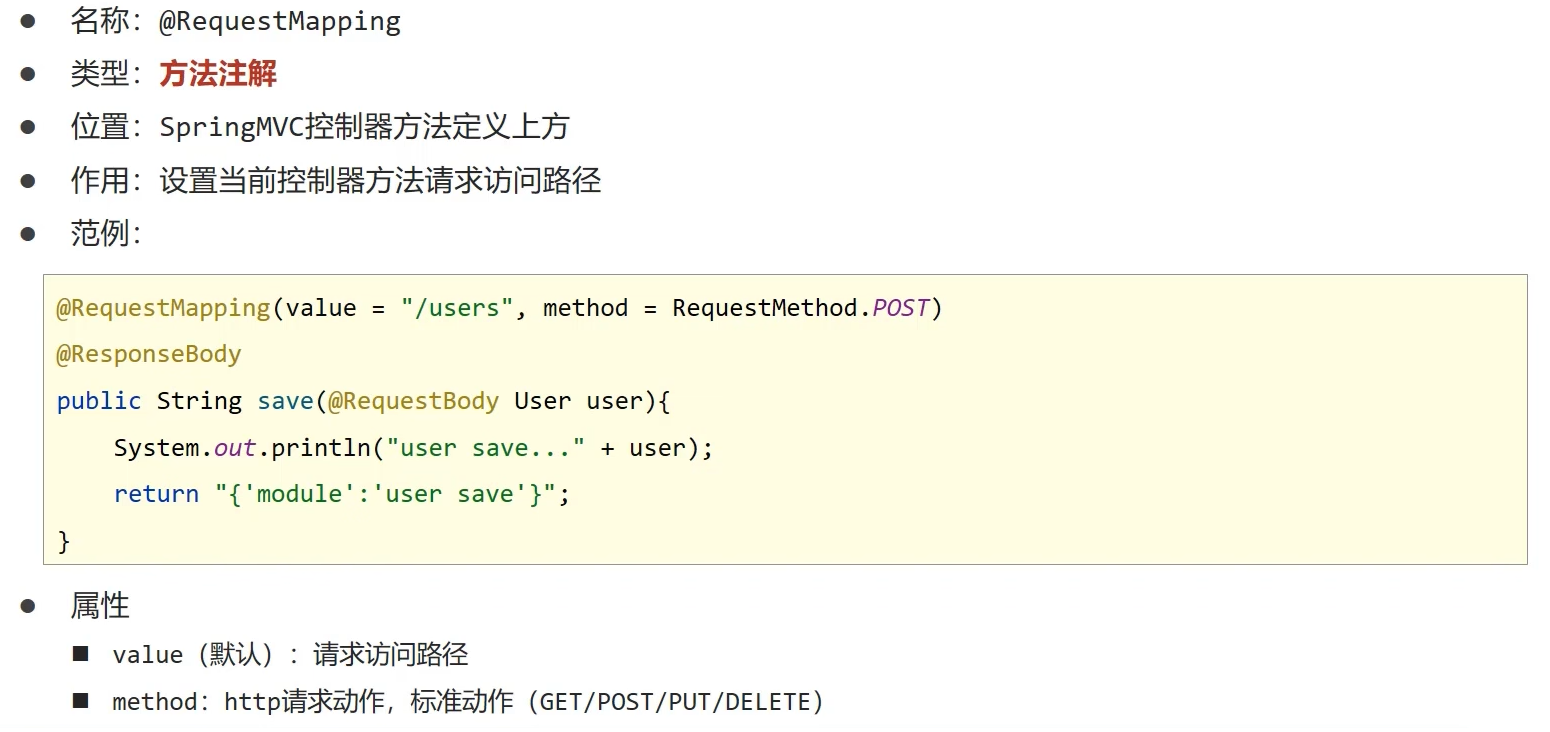
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user save..." + user);
return "{'moudle':'user save'}";
}
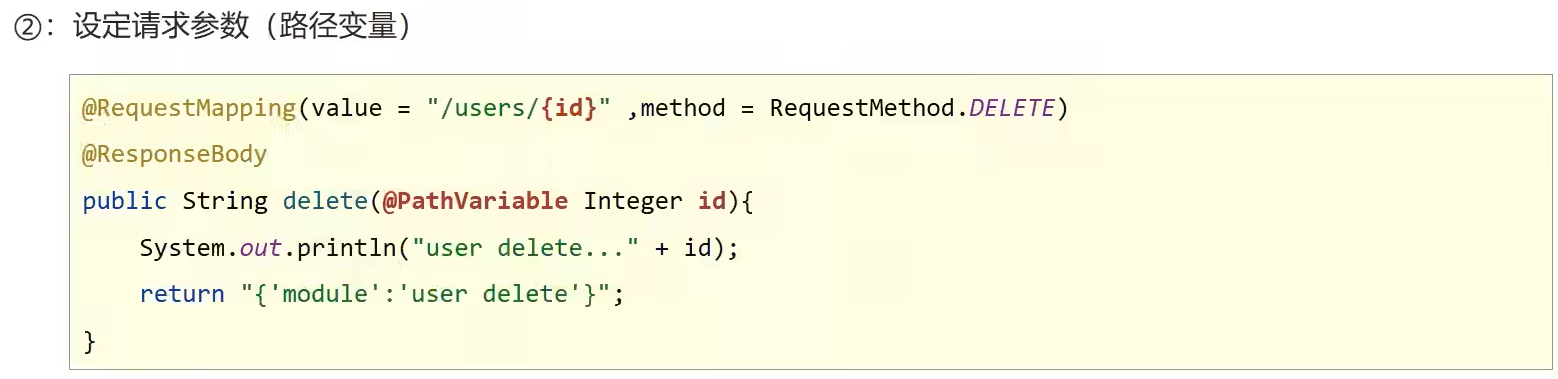
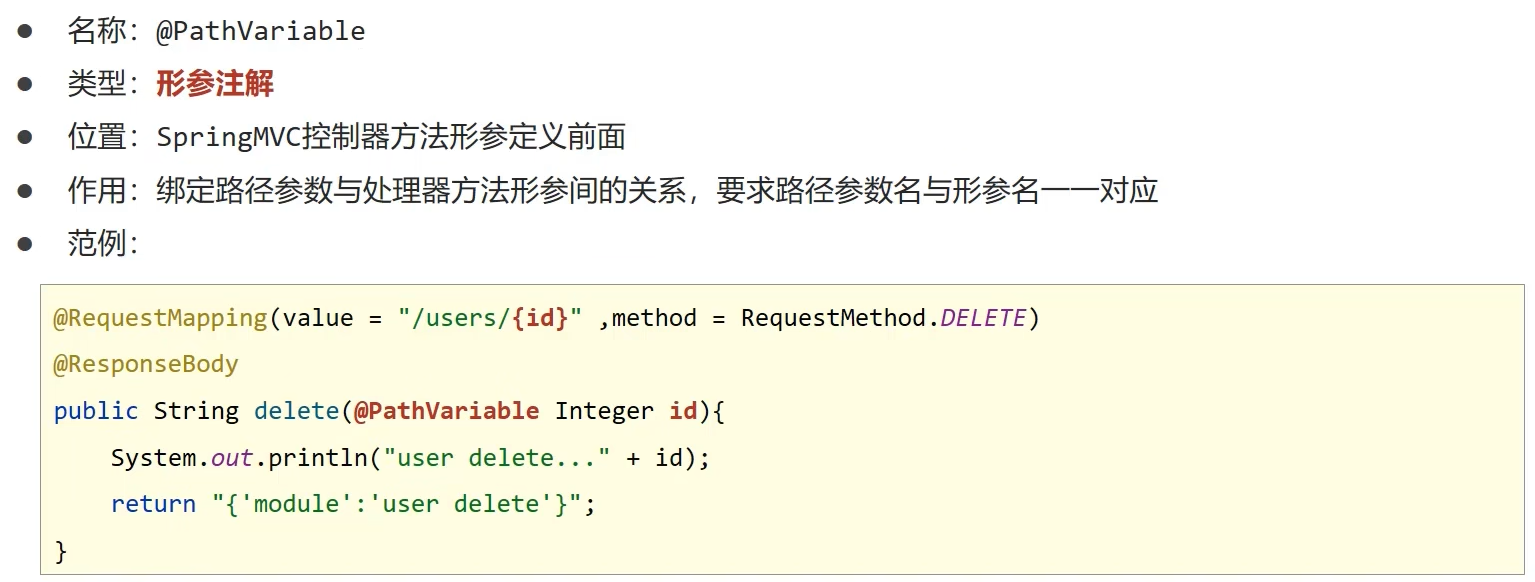
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete..." + id);
return "{'moudle':'user delete'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user update..." + user);
return "{'moudle':'user update'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("user getById..." + id);
return "{'moudle':'user getById'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'moudle':'user getAll'}";
}
}
User.class
package com.example._20231018;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
public String name;
public Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
项目结构:
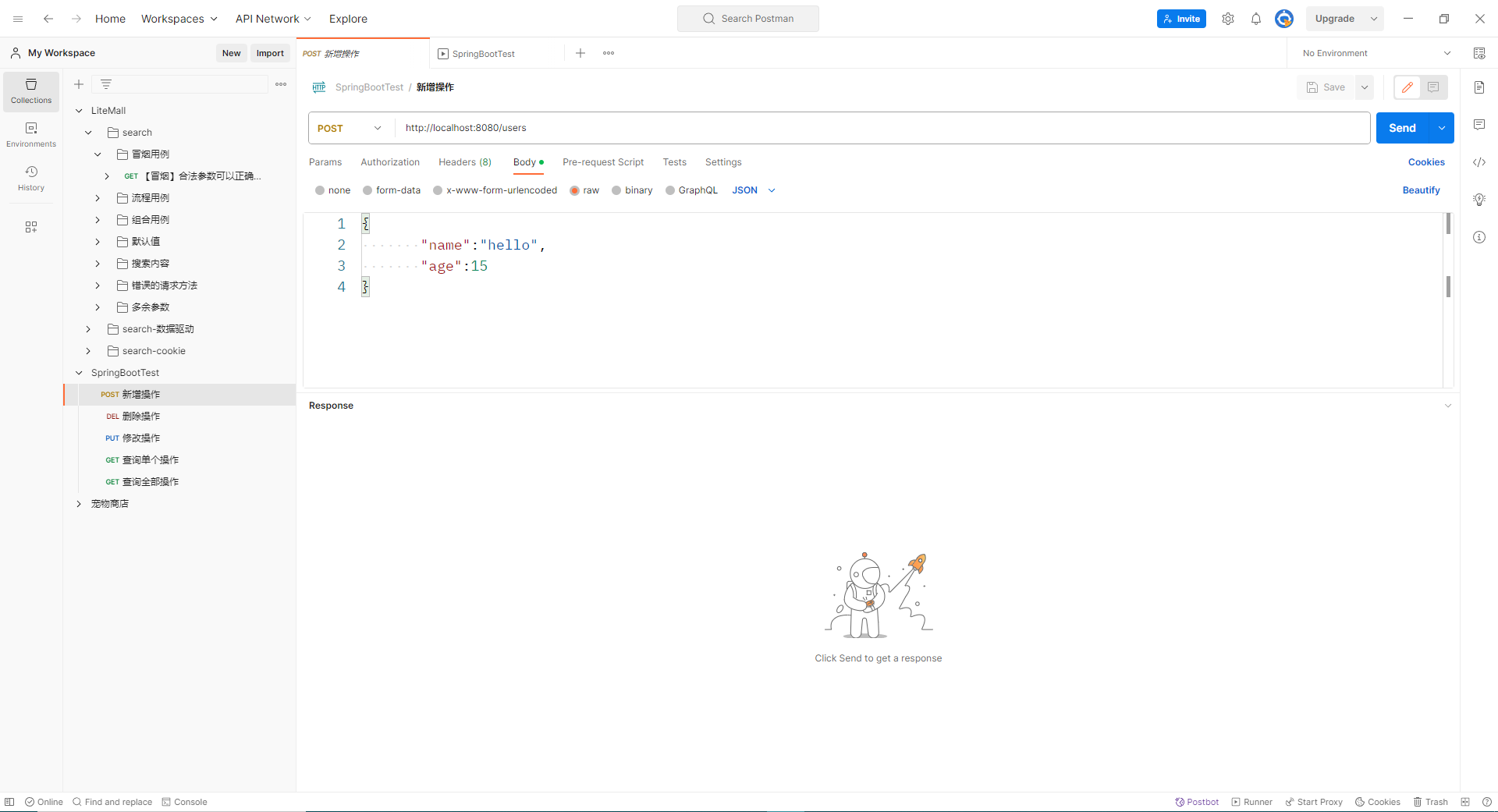
postman验证接口:
新增操作
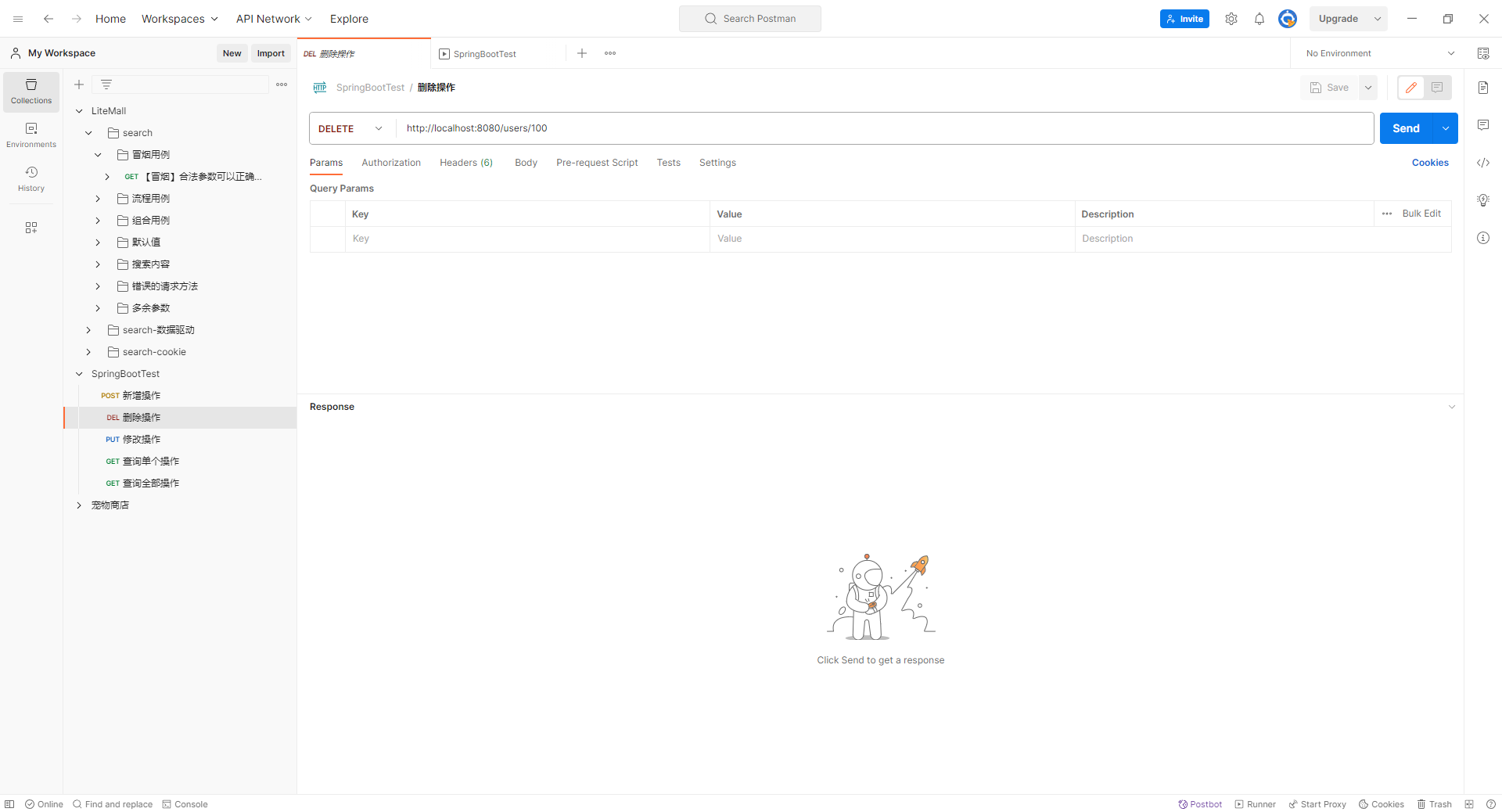
删除操作:
修改操作:
查询单个操作:
查询全部操作:
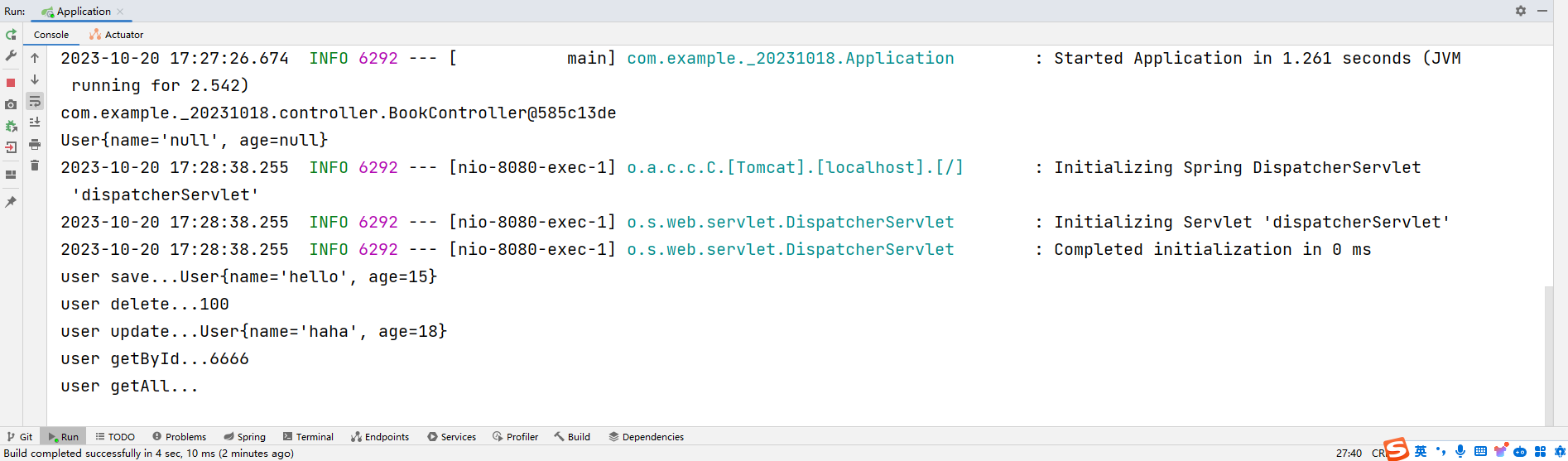
运行结果:
@RequestBody @RequestParam @PathVariable
区别
- @RequestParam用于接收url地址传参或表单传参
- @RequestBody用于接收json数据
- @PathVariable用于接收路径参数,使用{参数名称}描述路径参数
应用
- 后期开发中,发送请求参数超过1个时,以json格式为主,@RequestBody应用较广
- 如果发送非json格式数据,选用@RequestParam接收请求参数
- 采用RESTful进行开发,当参数数量较少时,例如1个,可以采用@PathVariable接收请求路径变量,通常用于传递id值
12.RESTful快速开发
BookController.class
package com.example._20231018.controller;
import com.example._20231018.Book;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
//@Controller
//@ResponseBody
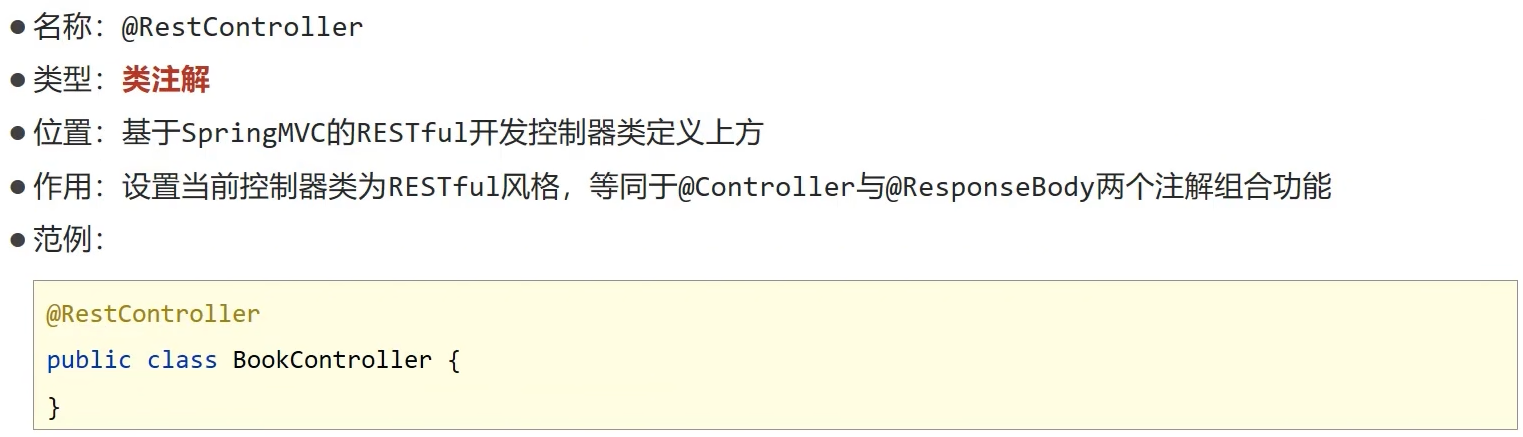
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
// @ResponseBody
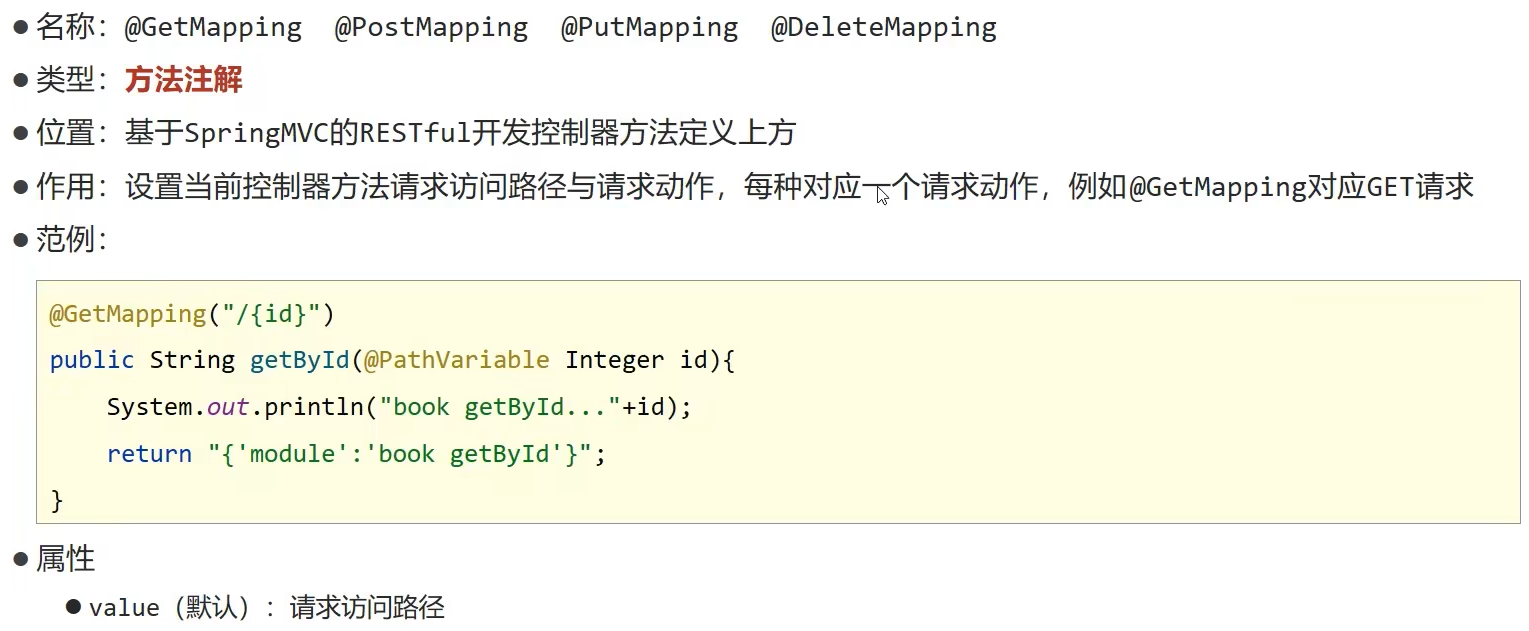
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("book save..." + book);
return "{'moudle':'book save'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
// @ResponseBody
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("book delete..." + id);
return "{'moudle':'book delete'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
// @ResponseBody
@PutMapping
public String update(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("book update..." + book);
return "{'moudle':'book update'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
// @ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("book getById..." + id);
return "{'moudle':'book getById'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
// @ResponseBody
@GetMapping
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("book getAll...");
return "{'moudle':'book getAll'}";
}
}
Book.class
package com.example._20231018;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Book {
public String name;
public int price;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
postman测试接口:
新增操作:
删除操作:
修改操作:
查询单个操作:
查询全部操作:
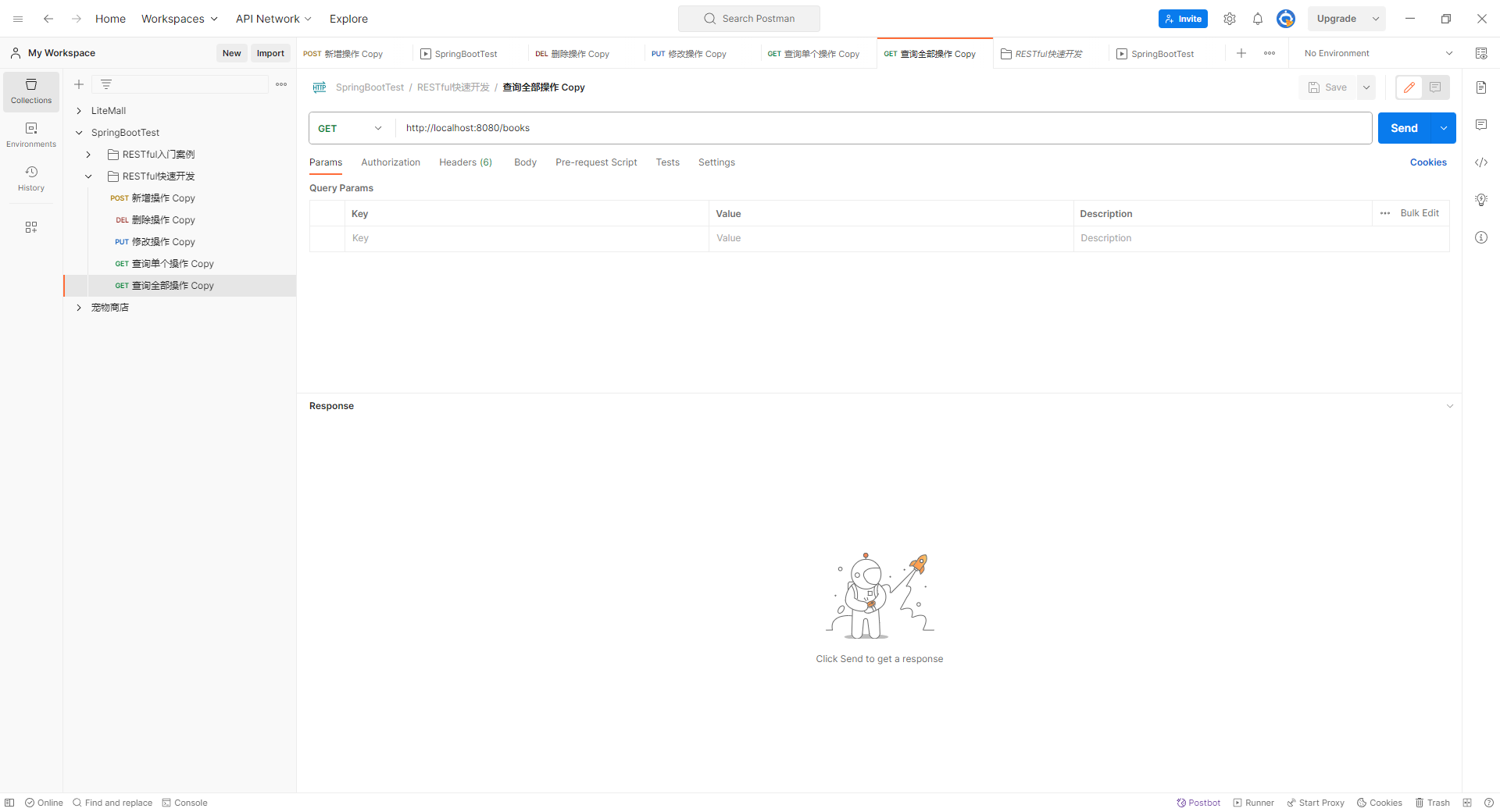
运行结果:
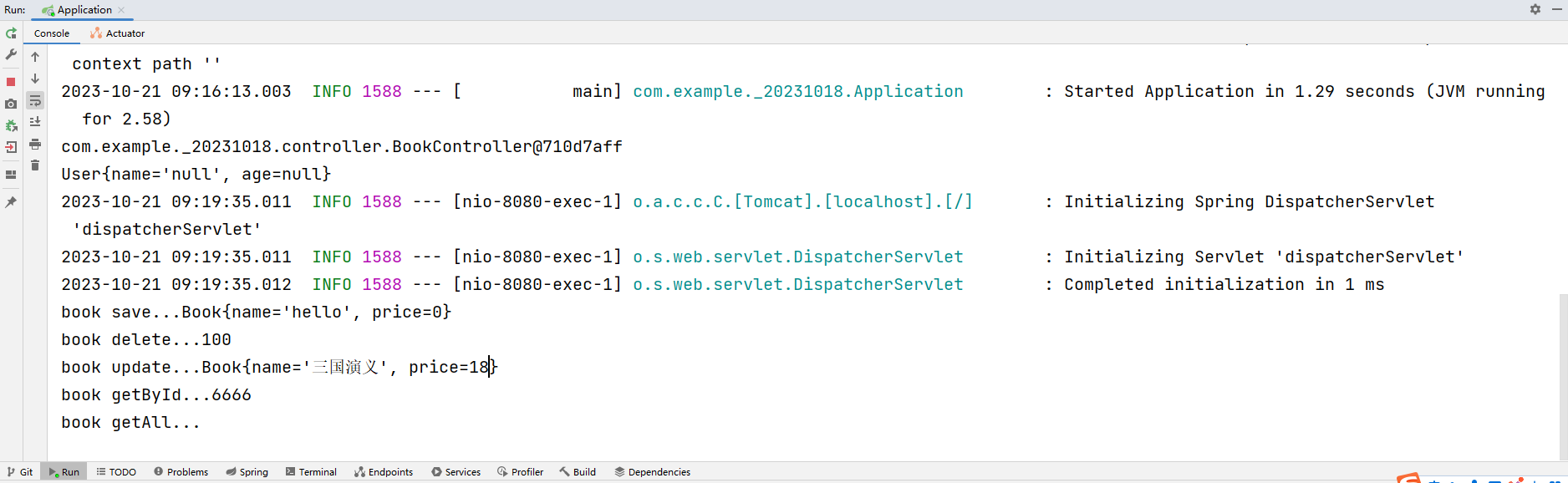
总结:
13.复制模块
原则
- 保留工程基础结构
- 抹掉原始工程痕迹
总结:
- 在工作空间中复制对应工程,并修改工程名称
- 删除与Idea相关配置文件,仅保留src目录与pom.xml文件
- 修改pom.xml文件中的artifactId与新工程/模块名相同
- 删除name标签(可选)
- 保留备份工程供后期使用
14.属性配置方式
修改配置
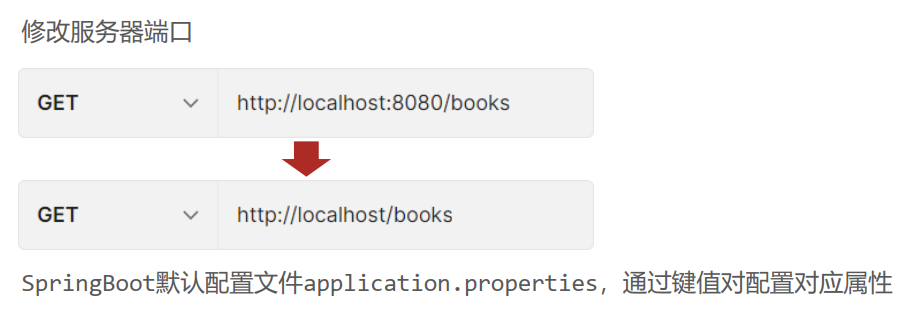
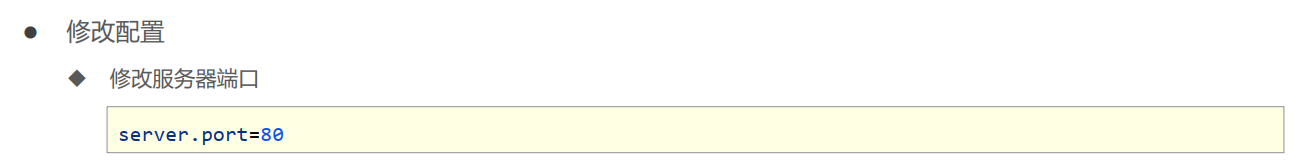
- 修改服务器端口
- server.prot=80
- 关闭运行日志图标(banner)
- spring.main.banner-mode=off
- 设置日志相关
- logging.level.root=debug
springbooot内置属性查询
15.基础配置
- SpringBoot中导入对应starter后,提供对应配置属性
- 书写SpringBoot配置采用关键字+提示形式书写
16.3种配置文件类型
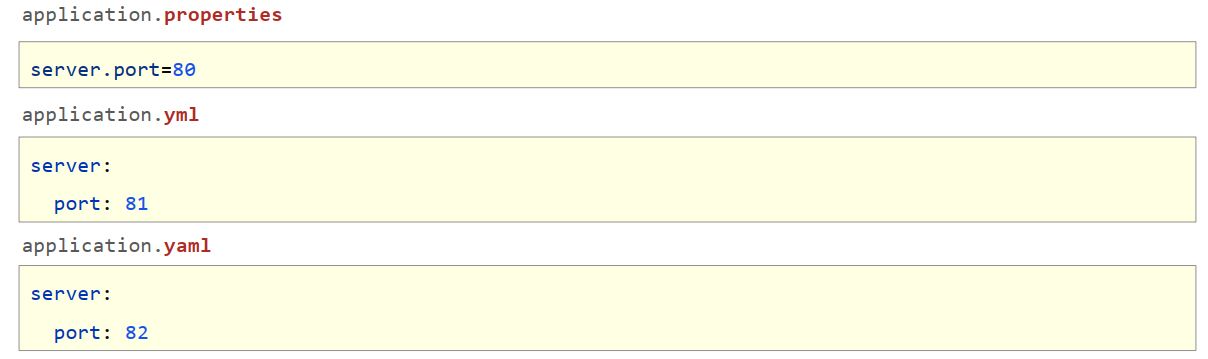
- 配置文件格式

- SpringBoot提供了多种属性配置方式
总结:
- SpringBoot提供了3种配置文件的格式
- properties (传统格式 /默认格式)
- yml(主流格式)
- yaml
17.配置文件加载优先级

- SpringBoot配置文件加载顺序
- application.properties > application.yml > application.yaml
- 常用配置文件种类
- application.yml
小结:
1.配置文件间的加载优先级
- properties(最高)
- yml
- yaml(最低)
2. 不同配置文件中相同配置按照加载优先级相互覆盖,不同配置文件中不同配置全部保留
18.属性提示消失解决方案

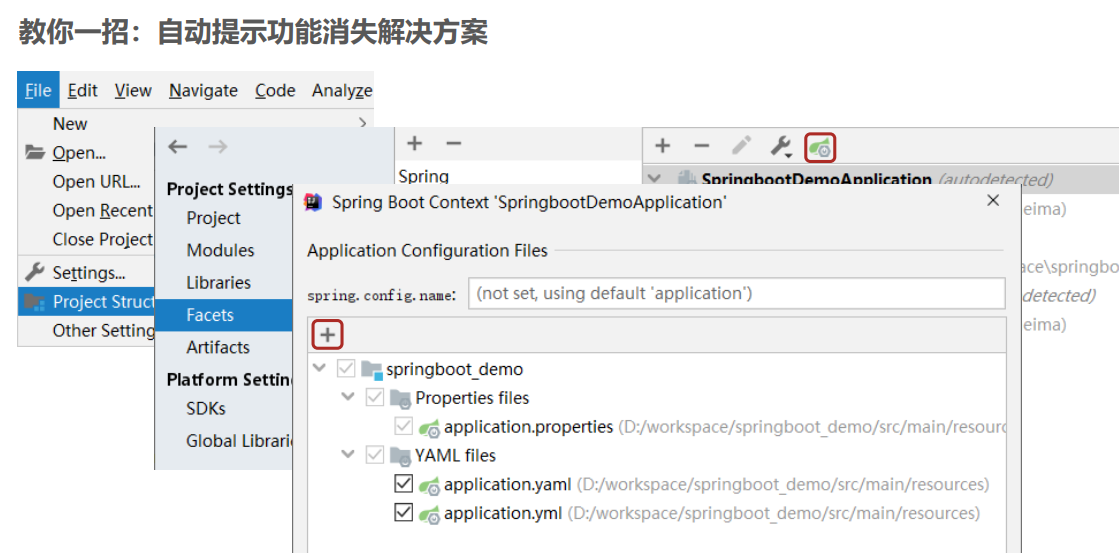
小结:
- 指定SpringBoot配置文件
- setting →Project Structure Facets
- 选中对应项目/工程·
- customize Spring Boot
- 选择配置文件
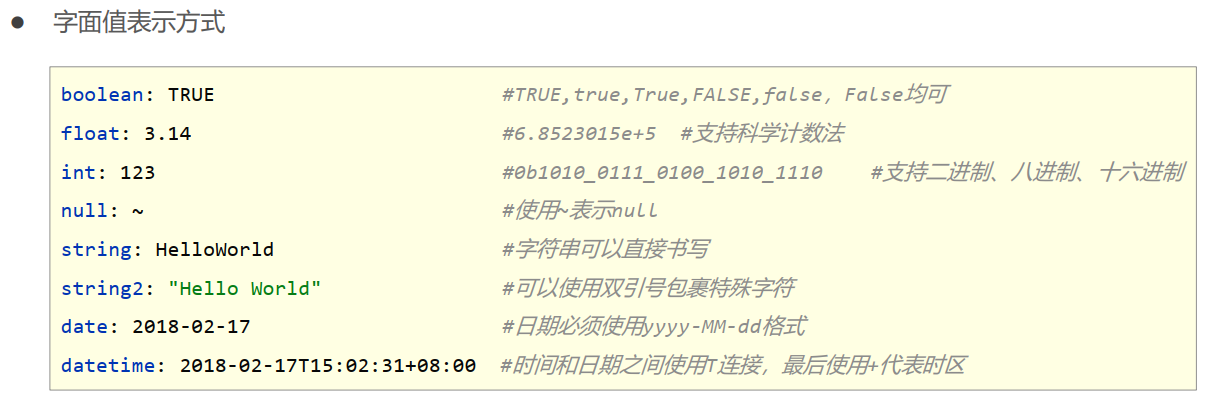
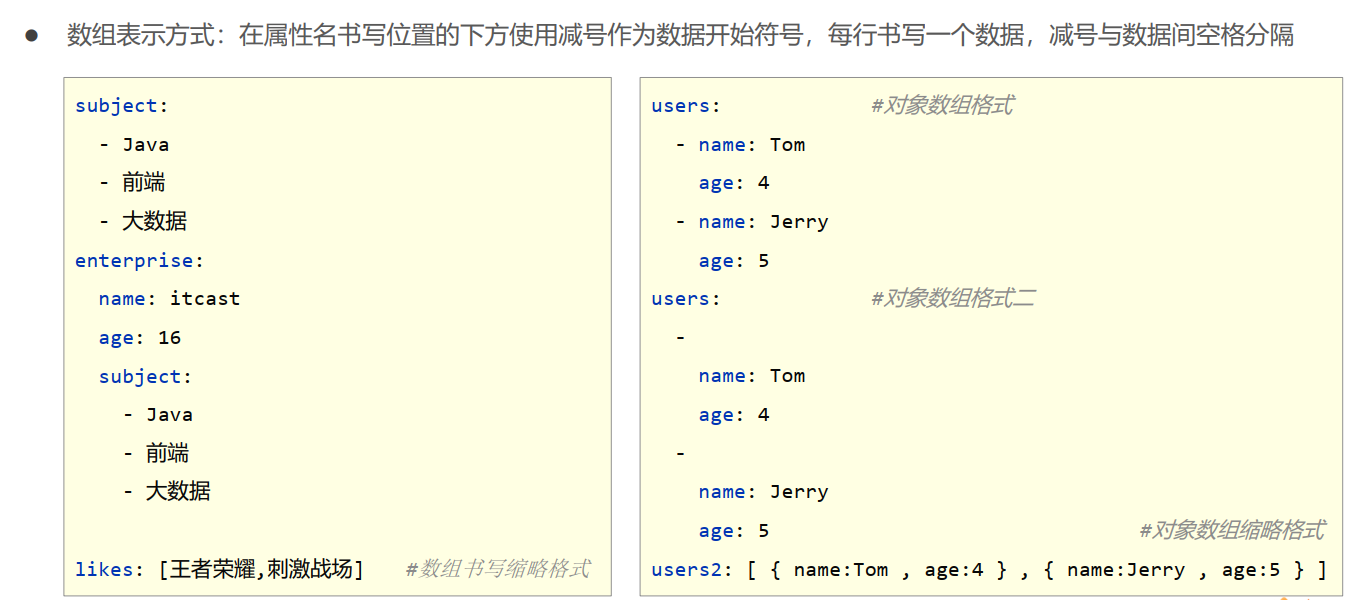
19.yaml数据格式


小结:
1. yaml语法规则
- 大小写敏感
- 属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
- 属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
- #表示注释
2.注意属性名冒号后面与数据之间有一个空格
3.字面值、对象数据格式、数组数据格式
20.读取yaml单一属性数据
yaml与yml文件有啥不同?
- YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)和YML(YAML)没有区别,它们是同一种文件格式的不同文件扩展名。
- YAML 是一种可读性高、用途广泛的数据序列化格式。它参考了其他多种语言,包括C语言、Python、Perl,并从XML、电子邮件的数据格式(RFC 2822)中获得灵感。YAML 文件使用缩进和换行等符号来表示层次结构和序列关系,从而达到编写简单易读的数据文档的目的。
- 由于历史原因,许多 Windows 程序员仍然不敢使用具有三个以上字符的扩展名,因此选择使用 yml 代替。但这只是一种习惯,并不影响文件的解析或者使用。
- 因此,YAML 和 YML 是同一个文件格式的不同文件扩展名,只是习惯上大家更常使用 YAML 这个名称。
示例:读取application.yml文件
country: china
user:
name_1: itcast
age: 16
a:
b:
c:
d:
e: 123
likes:
- game
- music
- sleep
likes2: [ game,music,sleep ]
users3:
- name: zhangsan
age: 45
- name: lisi
age: 23ReadYmlController.class
package com.example.demo_01.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/read")
public class ReadYmlController {
@Value("${country}")
private String country_variable;
@Value("${user.name_1}")
private String name_variable;
@Value("${user.age}")
private Integer age_variable;
@Value("${a.b.c.d.e}")
private Integer e_variable;
@Value("${likes[1]}")
private String music_variable;
@Value("${likes2[0]}")
private String game_variable;
@Value("${users3[0].name}")
private String name111_variable;
@GetMapping
public String showVariable() {
System.out.println(country_variable);
System.out.println(name_variable);
System.out.println(age_variable);
System.out.println(e_variable);
System.out.println(music_variable);
System.out.println(game_variable);
System.out.println(name111_variable);
return country_variable + name_variable + age_variable + e_variable + music_variable + game_variable + name111_variable;
}
}
运行结果:
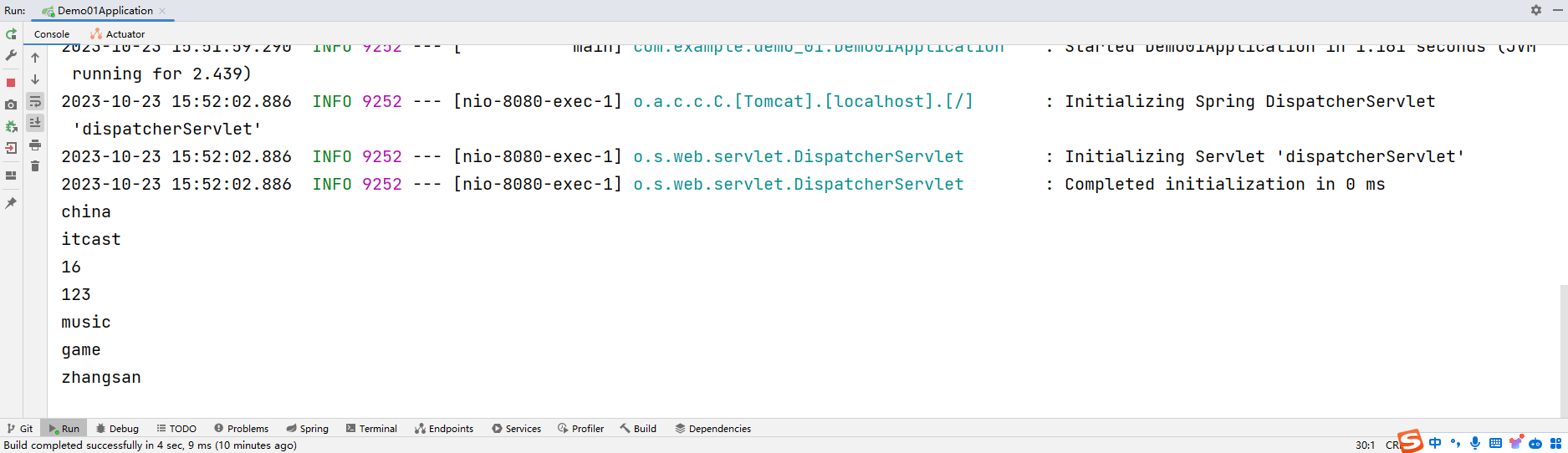
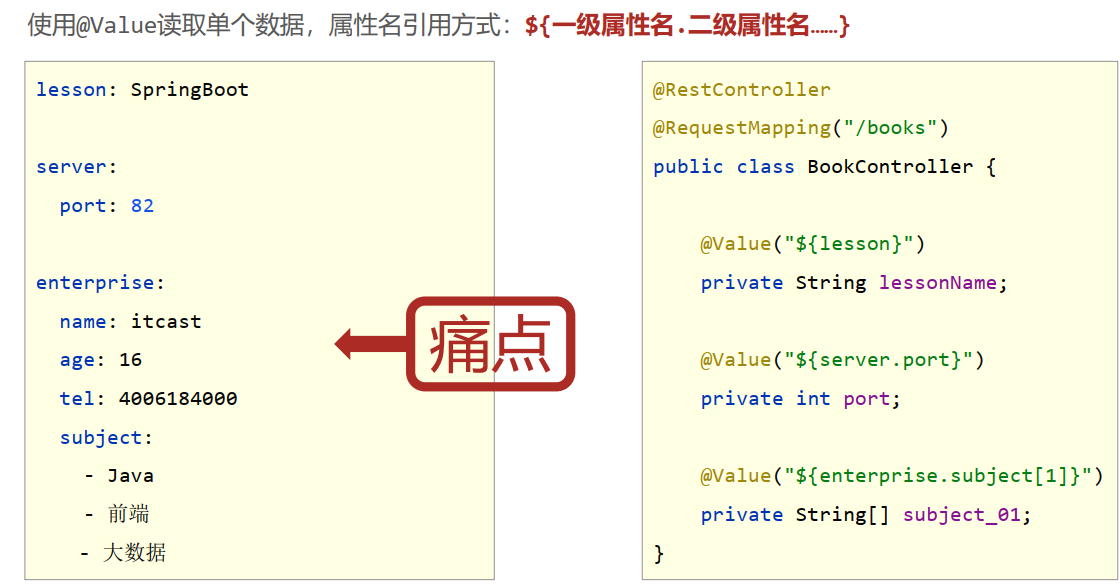
- 使用@Value配合SpEL读取单个数据
- 如果数据存在多层级,依次书写层级名称即可
21.yaml文件中的变量引用
application.yml
country: china
user:
name_1: itcast
age: 16
a:
b:
c:
d:
e: 123
likes:
- game
- music
- sleep
likes2: [ game,music,sleep ]
users3:
- name: zhangsan
age: 45
- name: lisi
age: 23
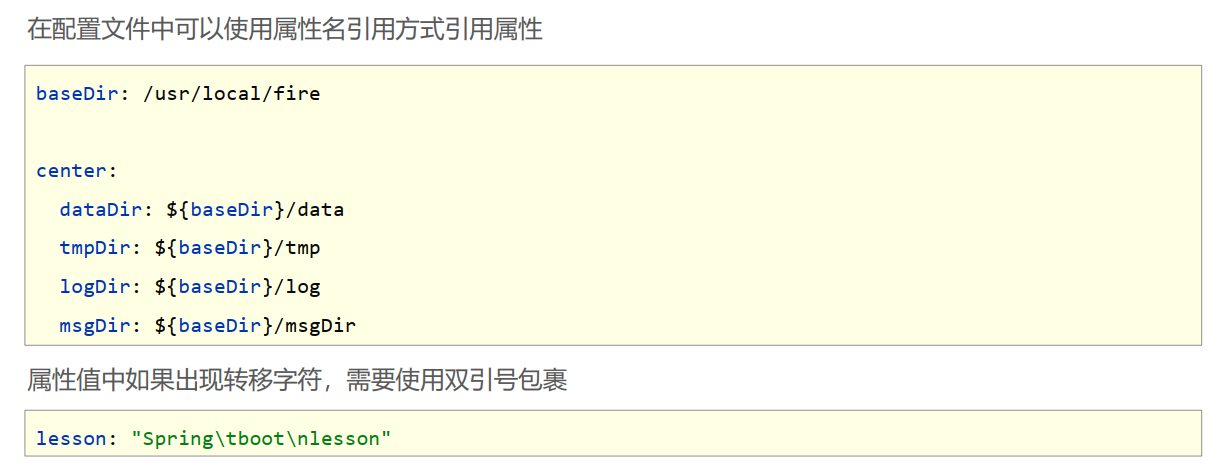
baseDir: c\windows
#tempDir: c\windows\temp
tempDir: ${baseDir}\temp
#使用引号包裹的字符串,其中的转义字符可以生效
tempDir1: "${baseDir}\temp \t1 \t2 \t3"ReadYmlController.class
package com.example.demo_01.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/read")
public class ReadYmlController {
@Value("${country}")
private String country_variable;
@Value("${user.name_1}")
private String name_variable;
@Value("${user.age}")
private Integer age_variable;
@Value("${a.b.c.d.e}")
private Integer e_variable;
@Value("${likes[1]}")
private String music_variable;
@Value("${likes2[0]}")
private String game_variable;
@Value("${users3[0].name}")
private String name111_variable;
@Value("${tempDir}")
private String temp_dir_variable;
@Value("${tempDir1}")
private String temp_dir1_variable;
@GetMapping
public String showVariable() {
System.out.println(country_variable);
System.out.println(name_variable);
System.out.println(age_variable);
System.out.println(e_variable);
System.out.println(music_variable);
System.out.println(game_variable);
System.out.println(name111_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir1_variable);
return country_variable +
name_variable +
age_variable +
e_variable +
music_variable +
game_variable +
name111_variable +
temp_dir_variable +
temp_dir1_variable
;
}
}
运行结果:
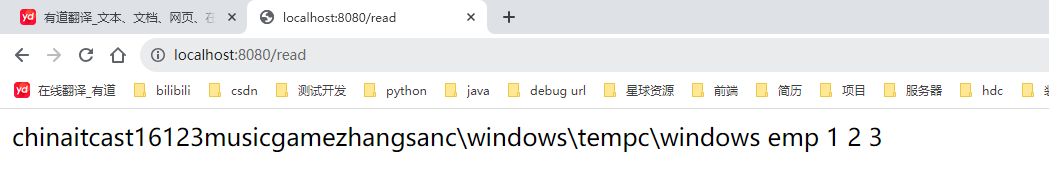

小结:
- 在配置文件中可以使用${属性名}方式引用属性值
- 如果属性中出现特殊字符,可以使用双引号包裹起来作为字符解析
22.读取yaml全部属性数据
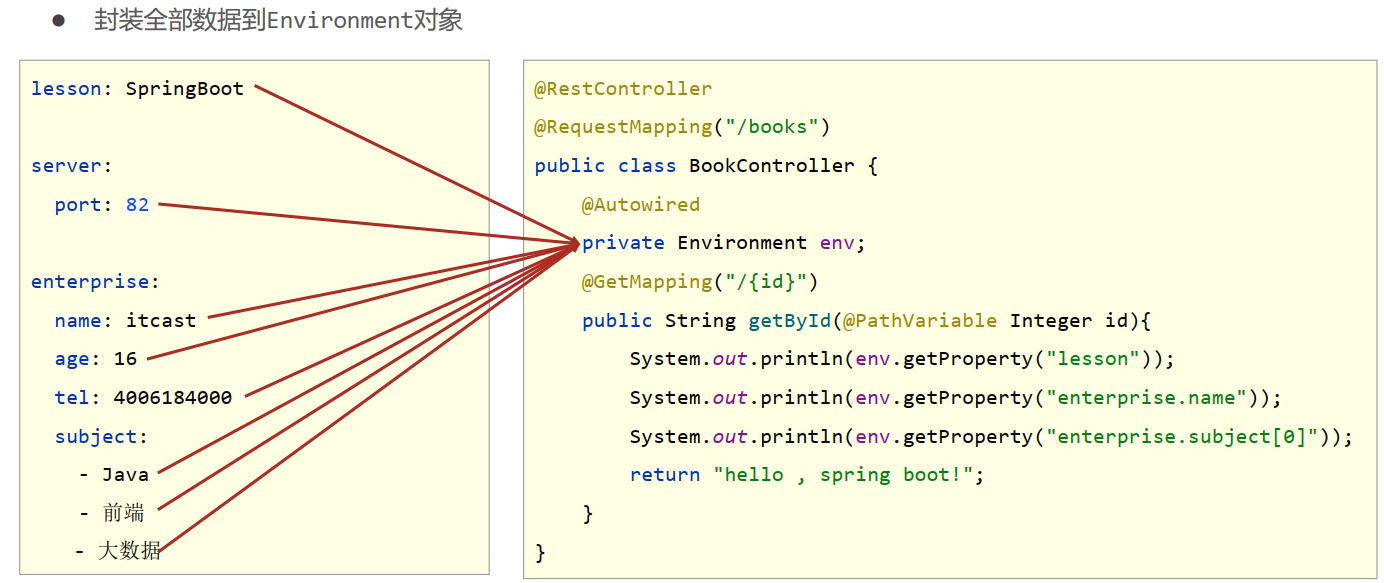
- 使用Environment对象封装全部配置信息
- 使用@Autowired自动装配数据到Environment对象中
示例:
ReadYmlController.class
package com.example.demo_01.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/read")
public class ReadYmlController {
@Value("${country}")
private String country_variable;
@Value("${user.name_1}")
private String name_variable;
@Value("${user.age}")
private Integer age_variable;
@Value("${a.b.c.d.e}")
private Integer e_variable;
@Value("${likes[1]}")
private String music_variable;
@Value("${likes2[0]}")
private String game_variable;
@Value("${users3[0].name}")
private String name111_variable;
@Value("${tempDir}")
private String temp_dir_variable;
@Value("${tempDir1}")
private String temp_dir1_variable;
//使用自动装配将所有的数据封装到一个对象Environment中
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@GetMapping
public String showVariable() {
System.out.println(country_variable);
System.out.println(name_variable);
System.out.println(age_variable);
System.out.println(e_variable);
System.out.println(music_variable);
System.out.println(game_variable);
System.out.println(name111_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir1_variable);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("country"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("user.age"));
return country_variable +
name_variable +
age_variable +
e_variable +
music_variable +
game_variable +
name111_variable +
temp_dir_variable +
temp_dir1_variable
;
}
}
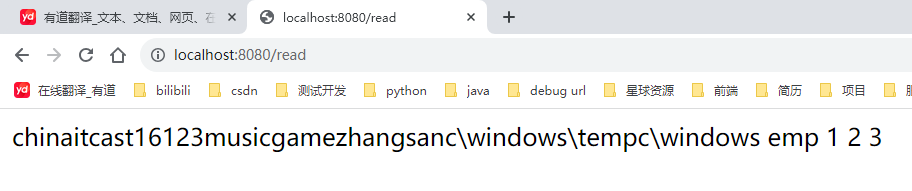
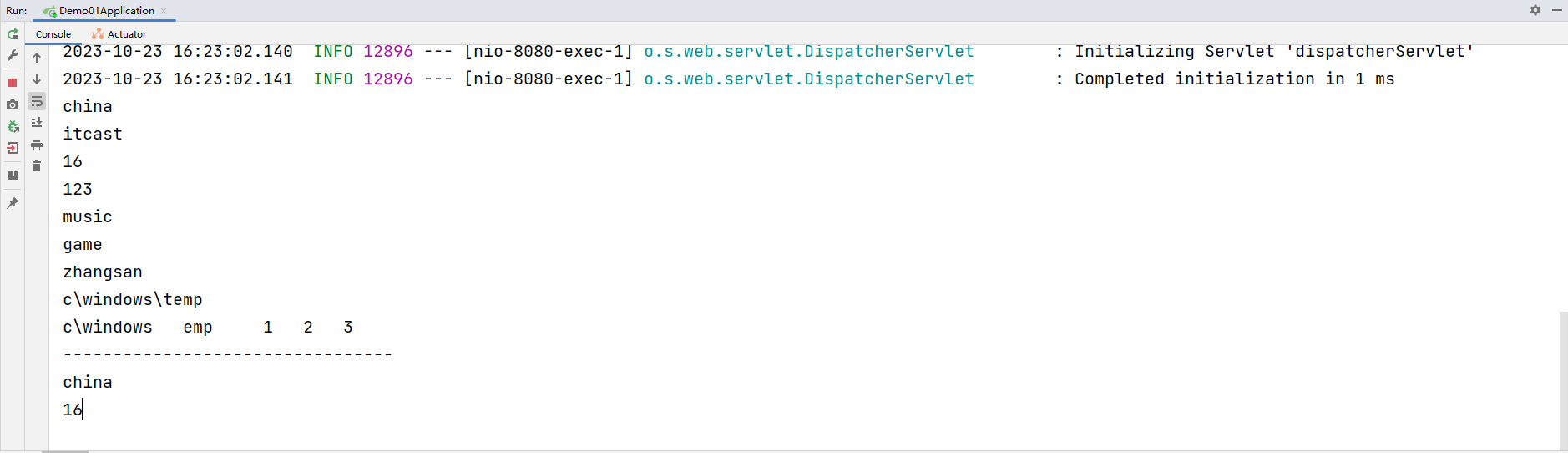
运行结果:
23.读取yaml引用类型属性数据
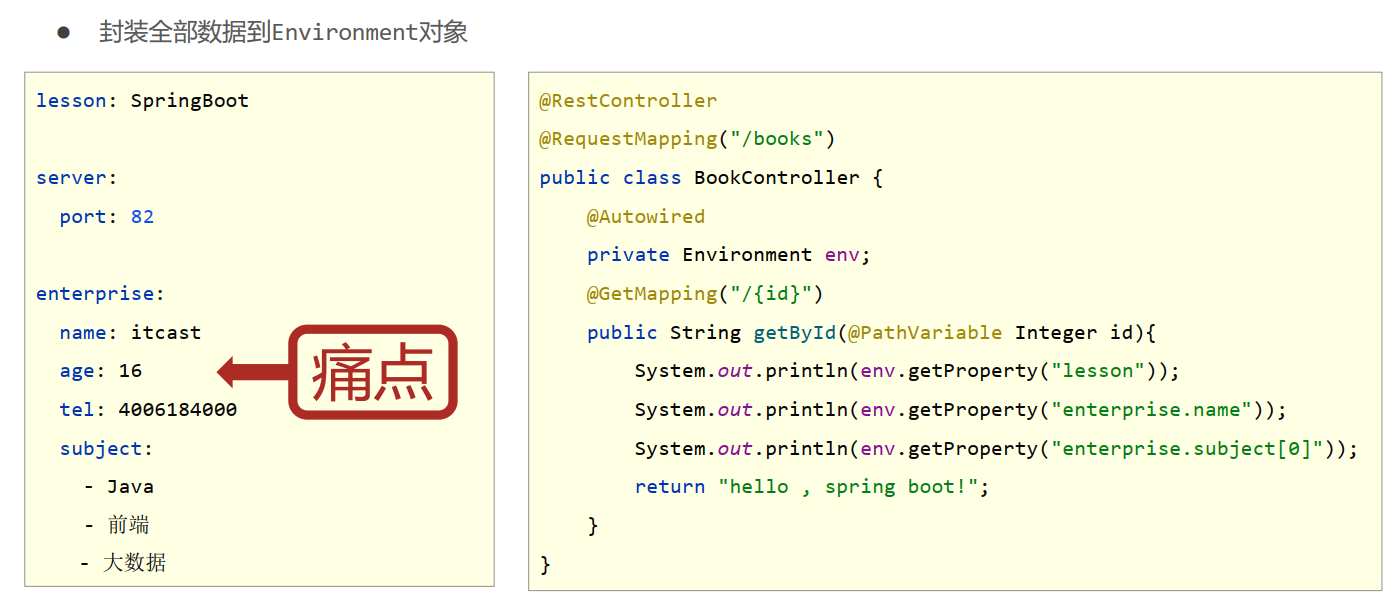

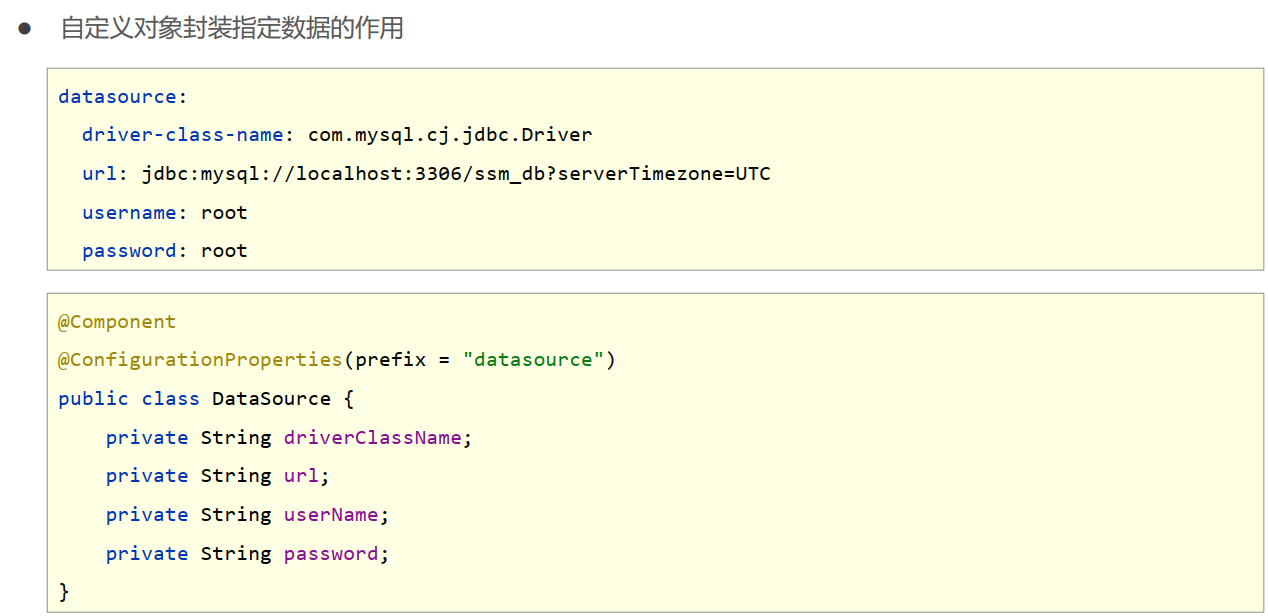
- 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定配置信息到封装类中
- 封装类需要定义为Spring管理的bean,否则无法进行属性注入
代码示例:
application.yml
country: china
user:
name_1: itcast
age: 16
a:
b:
c:
d:
e: 123
likes:
- game
- music
- sleep
likes2: [ game,music,sleep ]
users3:
- name: zhangsan
age: 45
- name: lisi
age: 23
baseDir: c\windows
#tempDir: c\windows\temp
tempDir: ${baseDir}\temp
#使用引号包裹的字符串,其中的转义字符可以生效
tempDir1: "${baseDir}\temp \t1 \t2 \t3"
datasource:
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/springboot_db
username: root
password: 666666MyDataSource.class
package com.example.demo_01.entity;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//1.定义数据模型封装yamL文件中对应的数据
//2.定义为spring管控的bean
//3.指定加载的数据
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("datasource")
public class MyDataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
ReadYmlController.class
package com.example.demo_01.controller;
import com.example.demo_01.entity.MyDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/read")
public class ReadYmlController {
@Value("${country}")
private String country_variable;
@Value("${user.name_1}")
private String name_variable;
@Value("${user.age}")
private Integer age_variable;
@Value("${a.b.c.d.e}")
private Integer e_variable;
@Value("${likes[1]}")
private String music_variable;
@Value("${likes2[0]}")
private String game_variable;
@Value("${users3[0].name}")
private String name111_variable;
@Value("${tempDir}")
private String temp_dir_variable;
@Value("${tempDir1}")
private String temp_dir1_variable;
//使用自动装配将所有的数据封装到一个对象Environment中
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Autowired
private MyDataSource myDataSource;
@GetMapping
public String showVariable() {
System.out.println(country_variable);
System.out.println(name_variable);
System.out.println(age_variable);
System.out.println(e_variable);
System.out.println(music_variable);
System.out.println(game_variable);
System.out.println(name111_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir_variable);
System.out.println(temp_dir1_variable);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("country"));
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("user.age"));
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println(myDataSource);
return country_variable +
name_variable +
age_variable +
e_variable +
music_variable +
game_variable +
name111_variable +
temp_dir_variable +
temp_dir1_variable
;
}
}
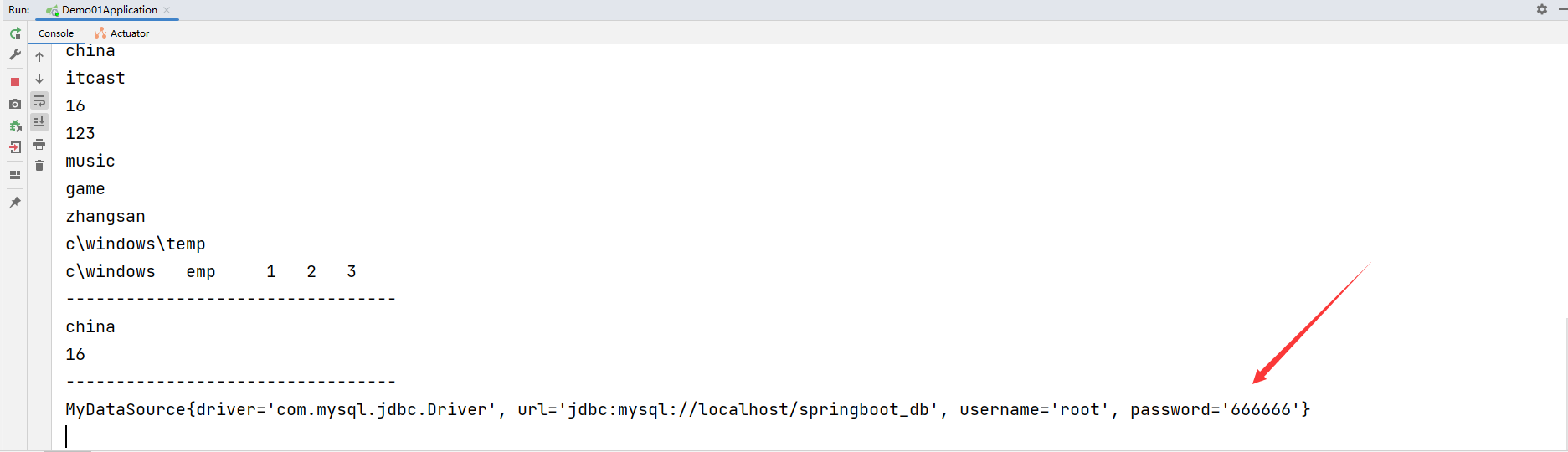
运行结果:
24.SpringBoot整合JUnit
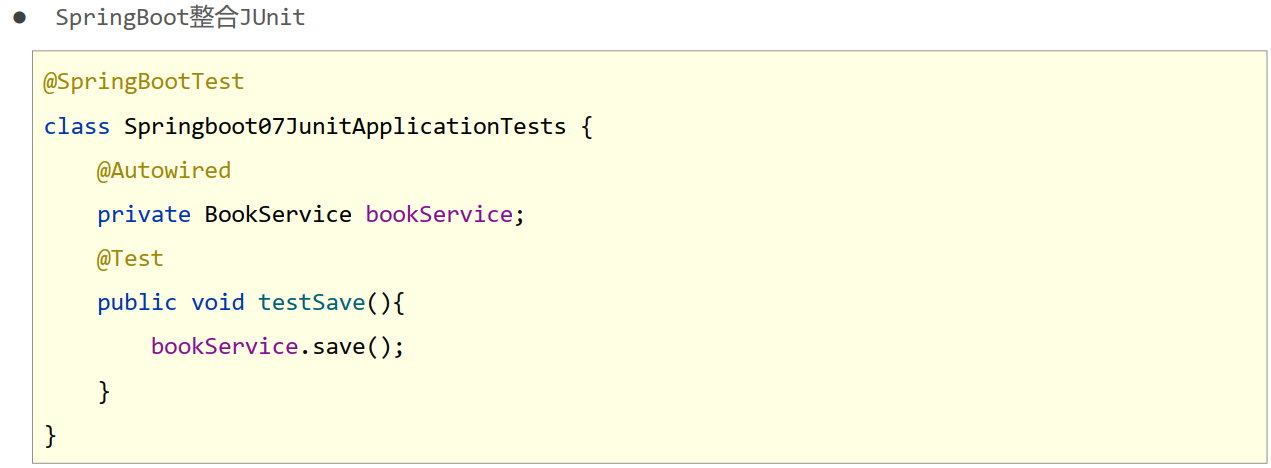
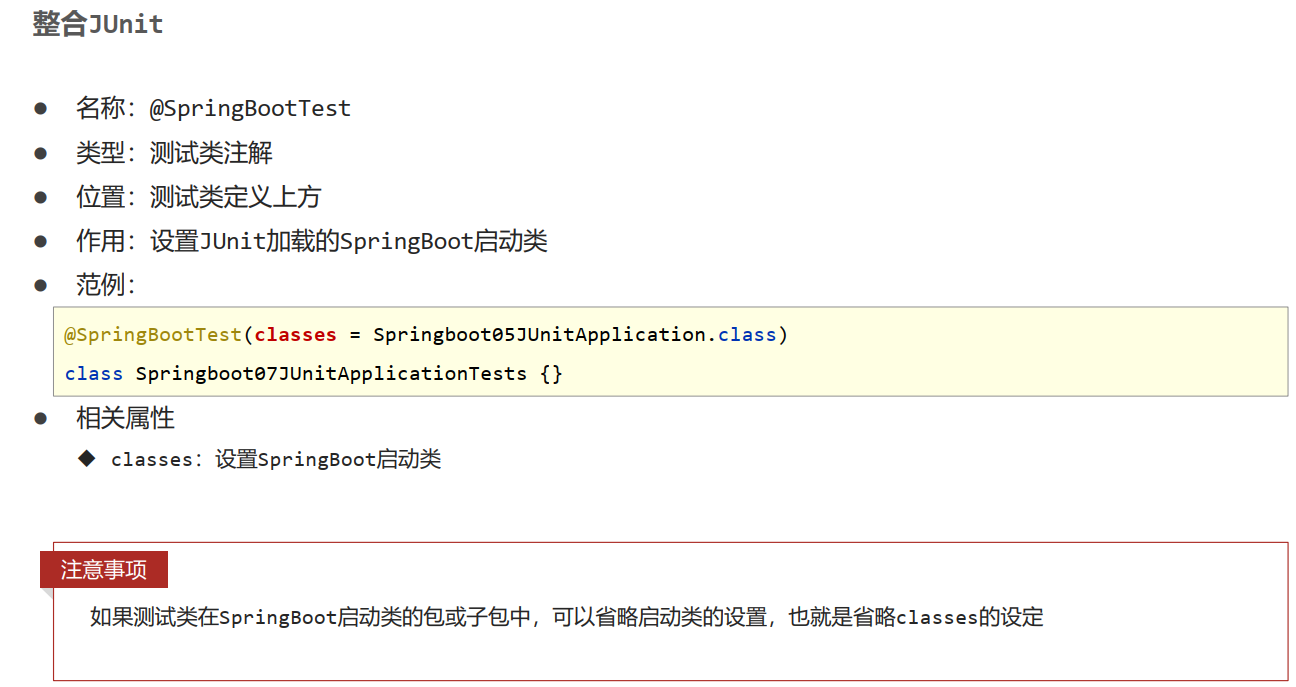
- 名称: @SpringBootTest
- 类型:测试类注解
- 位置:测试类定义上方
- 作用:设置JUnit加载的SpringBoot启动类
- 范例:
代码示例:
BookDao.interface
package com.example.junit.Dao;
public interface BookDao {
public void save();
}
BookDaoImpl.class
package com.example.junit.Dao.impl;
import com.example.junit.Dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao is running ...");
}
}
JunitApplicationTests.class
package com.example.junit;
import com.example.junit.Dao.BookDao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class JunitApplicationTests {
//1.注入你要测试的对象
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//2.执行要测试的对象对应的方法
bookDao.save();
}
}
项目结构:
运行结果:
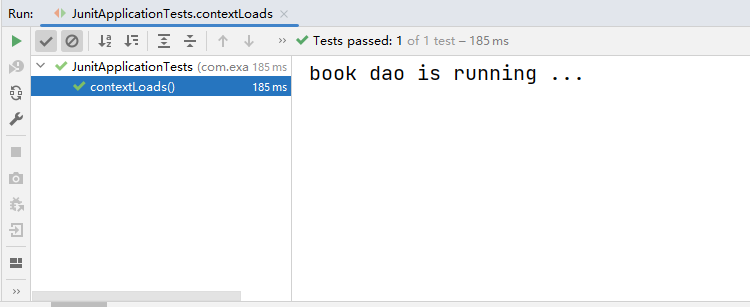
小结:
- 导入测试对应的starter
- 测试类使用@SpringBootTest修饰
- 使用自动装配的形式添加要测试的对象
25.整合JUnit--classes属性
小结:
- 测试类如果存在于引导类所在包或子包中无需指定引导类
- 测试类如果不存在于引导类所在的包或子包中需要通过classes属性指定引导类
26.SpringBoot整合MyBatis
整合MyBatis
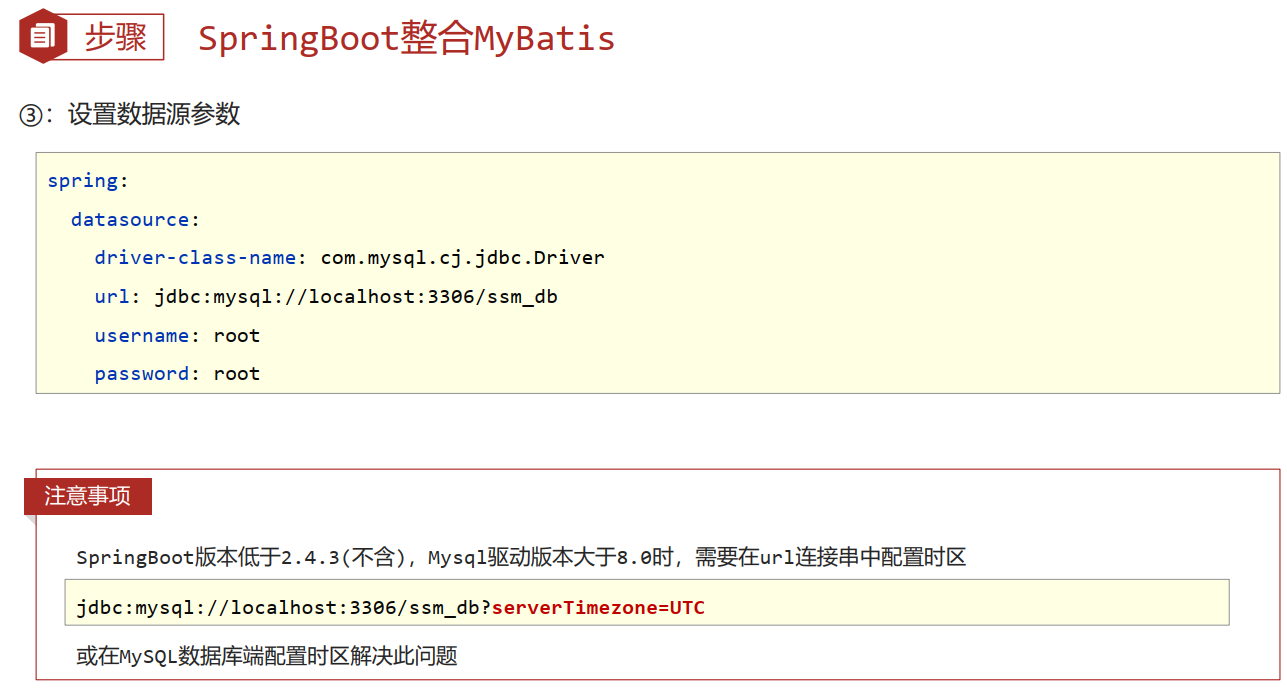
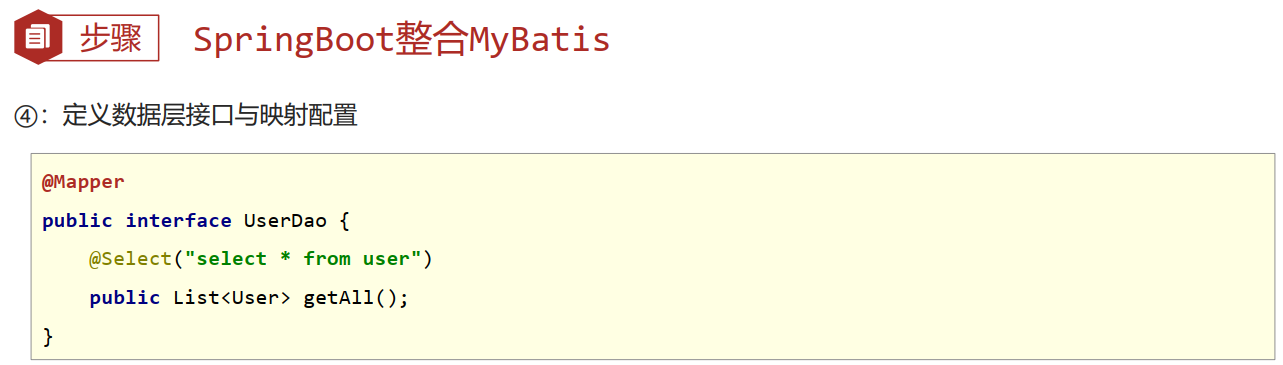
- 核心配置:数据库连接相关信息(连什么?连谁?什么权限)
- 映射配置:SQL映射(XML/注解)

代码示例:
BookDao.interface
package com.example._20231023.dao;
import com.example._20231023.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface BookDao {
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id = #{id}")
public Book getById(Integer id);
}
Book.class
package com.example._20231023.domain;
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
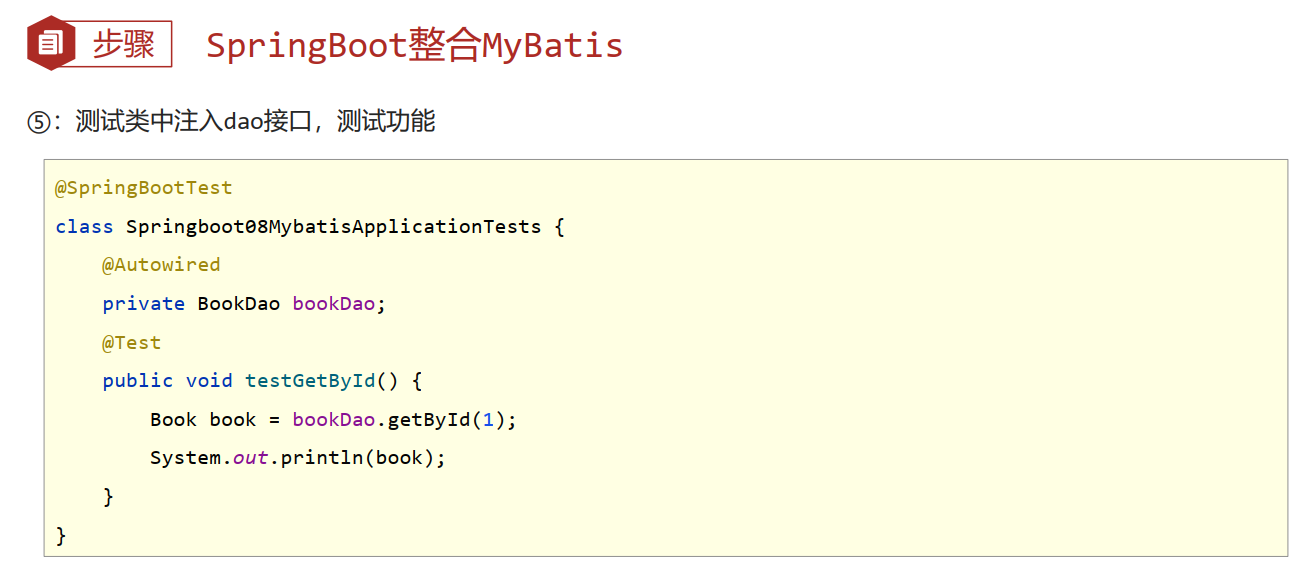
Application.Tests
package com.example._20231023;
import com.example._20231023.dao.BookDao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(bookDao.getById(11));
}
}
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/test_db
username: root
password: 666666
运行结果:

小结:
- 勾选MyBatis技术,也就是导入MyBatis对应的starter
- 数据库连接相关信息转换成配置
- 数据库SQL映射需要添加@Mapper被容器识别到
27.SpringBoot整合MyBatis常见问题处理
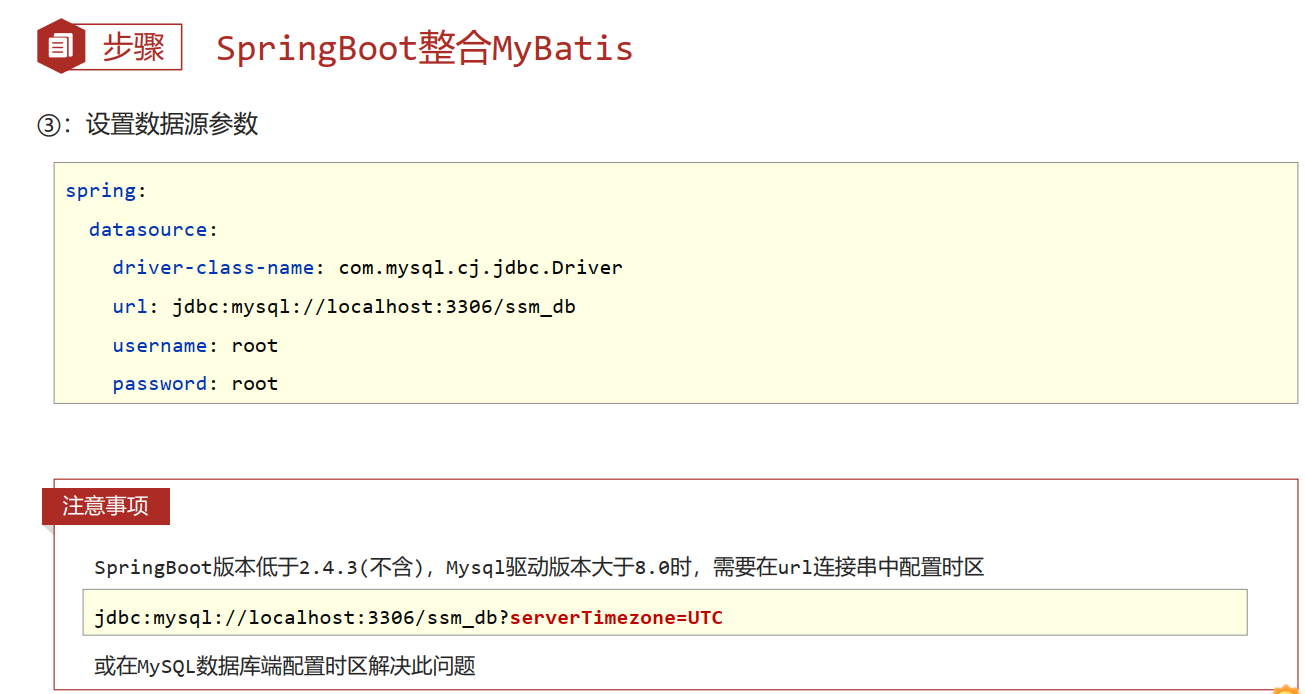
- MySQL 8.X驱动强制要求设置时区
- 修改url,添加serverTimezone设定
- 修改MySQL数据库配置(略)
- 驱动类过时,提醒更换为com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
28.SpringBoot整合MyBatisPlus
BookDao.interface
package com.example._20231024.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example._20231024.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
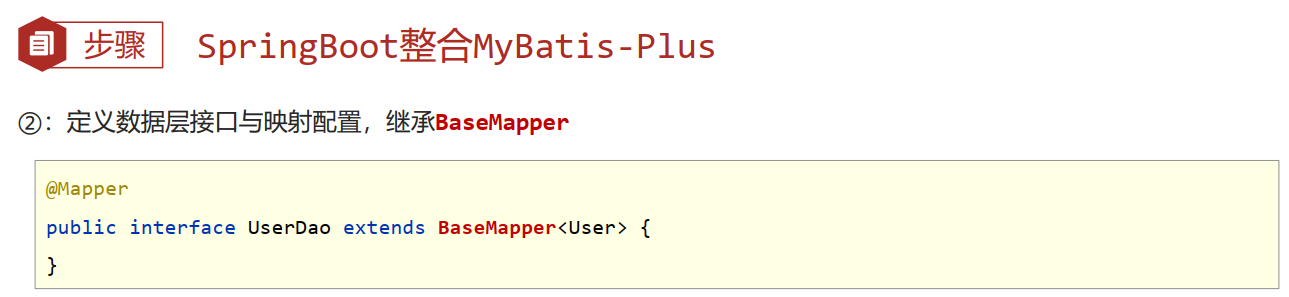
@Mapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper<Book> {
}
Book.class
package com.example._20231024.domain;
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/test_db
username: root
password: 666666
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
ApplicationTests
package com.example._20231024;
import com.example._20231024.dao.BookDao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
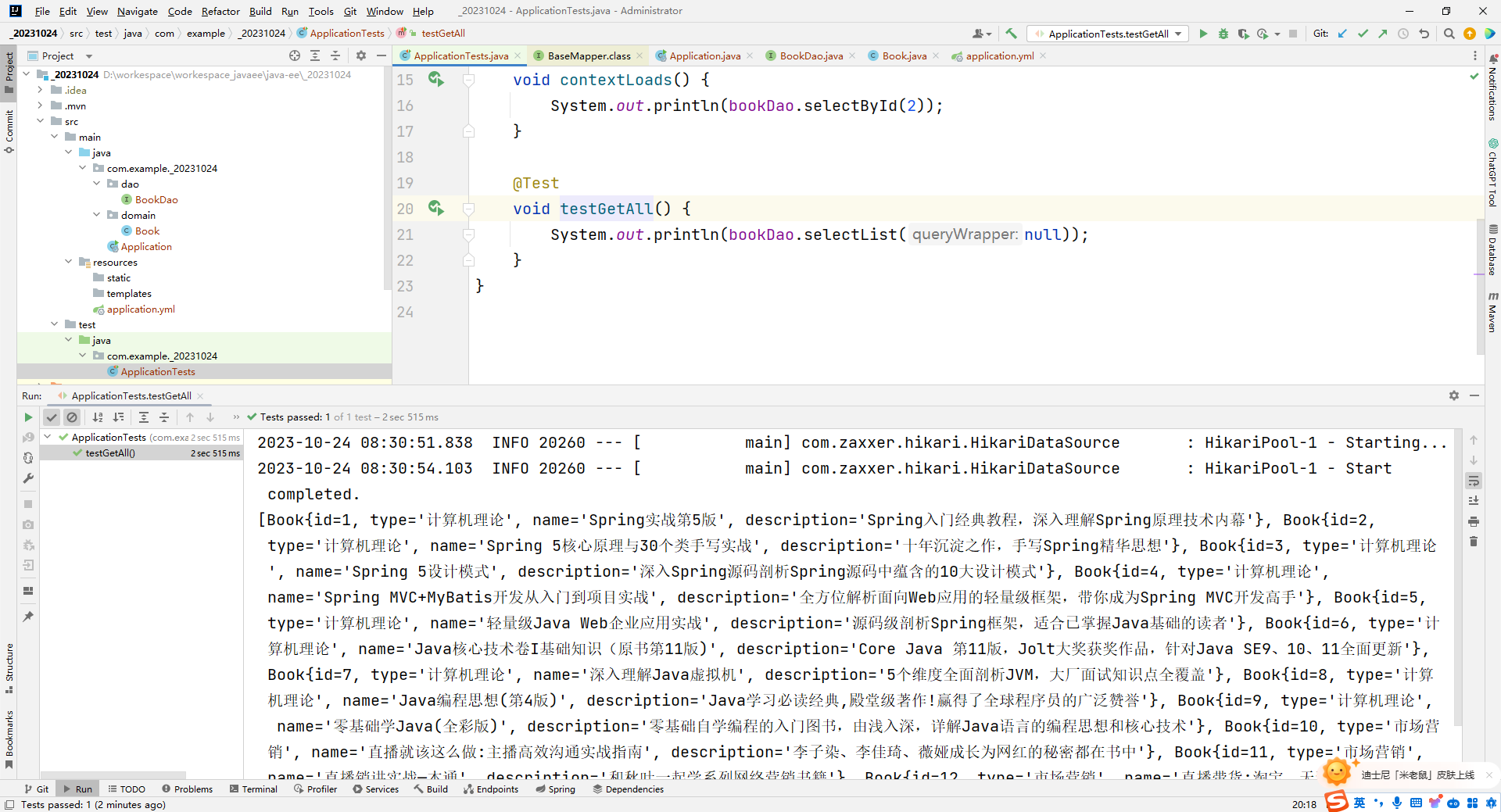
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(bookDao.selectById(2));
}
@Test
void testGetAll() {
System.out.println(bookDao.selectList(null));
}
}
运行结果:
MyBatis-Plus与MyBatis区别
- 导入坐标不同
- 数据层实现简化
小结:
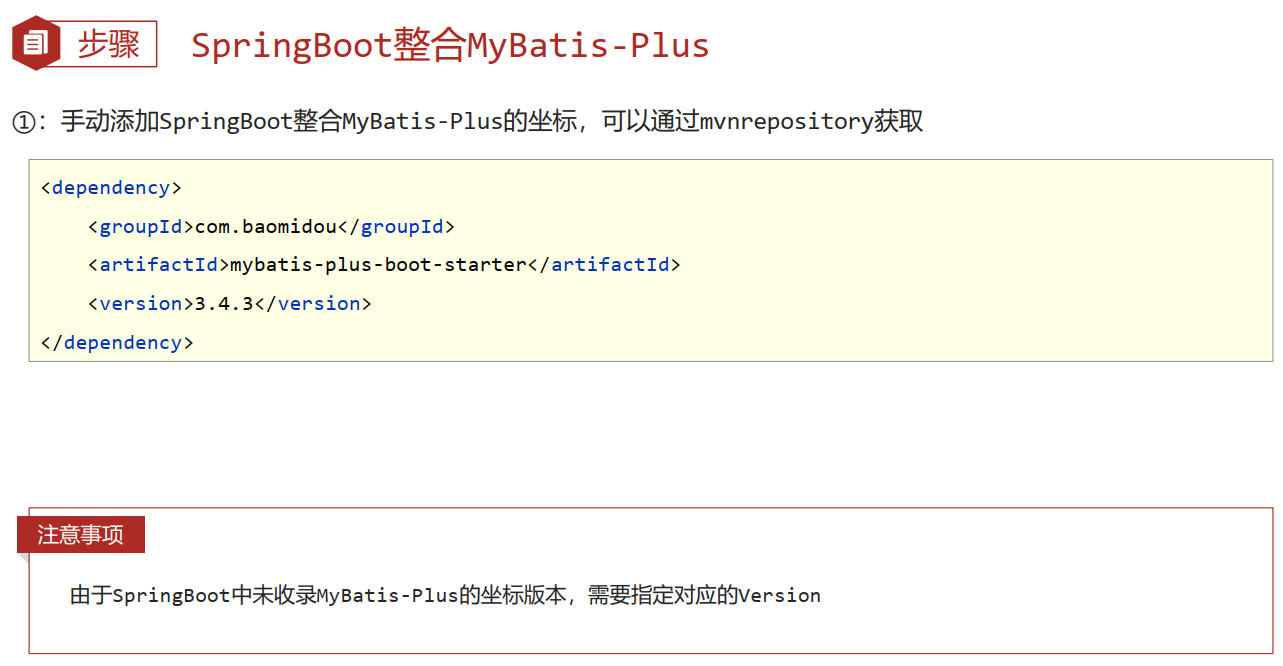
- 手工添加MyBatis-Plus对应的starter
- 数据层接口使用BaseMapper简化开发
- 需要使用的第三方技术无法通过勾选确定时,需要手工添加坐标
29.SpringBoot整合Druid
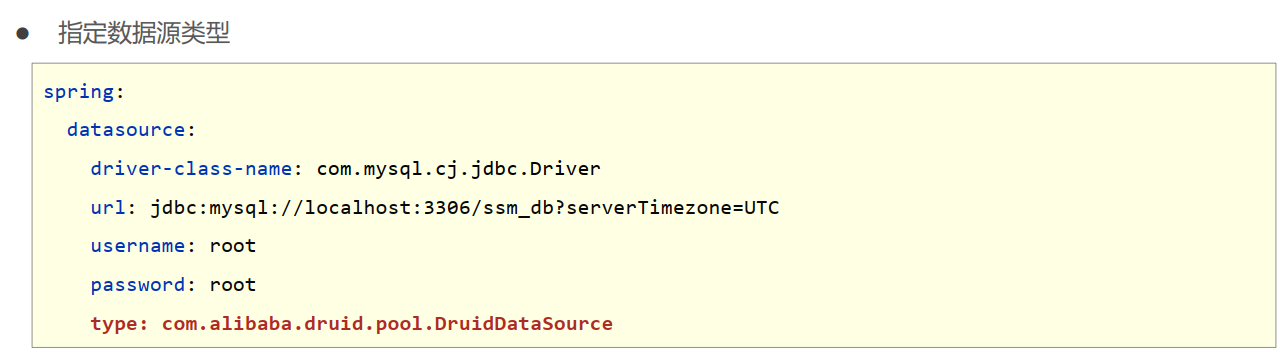
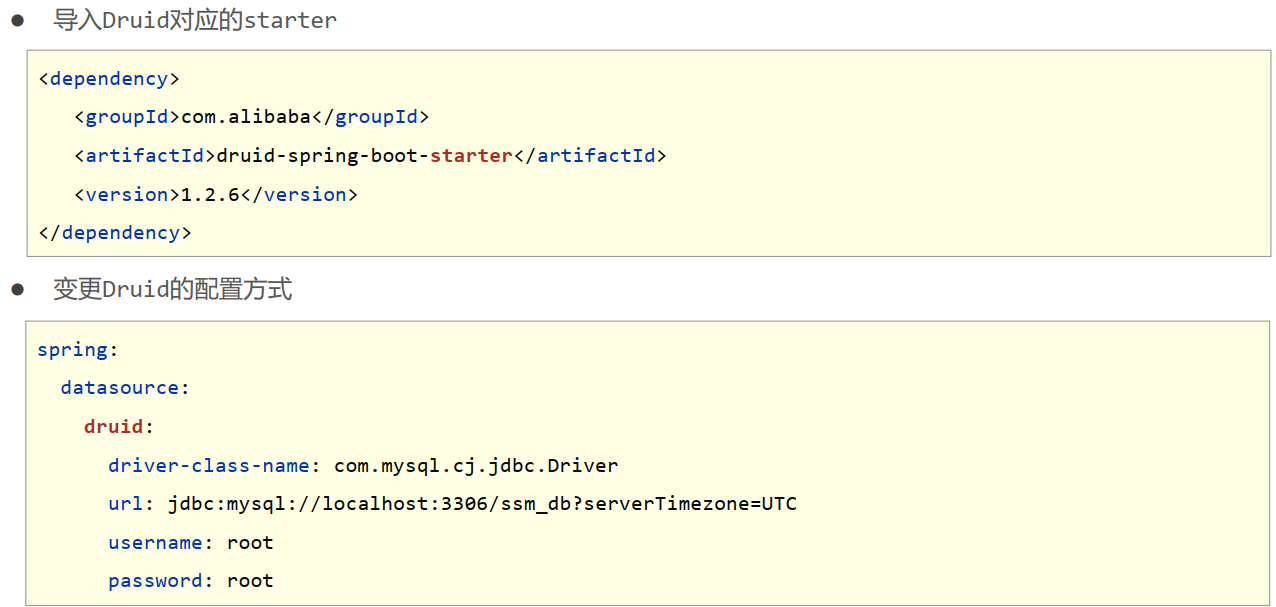
整合任意第三方技术
- 导入对应的starter
- 配置对应的设置或采用默认配置
代码示例:
BookDao.interface
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface BookDao {
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id = #{id}")
public Book getById(Integer id);
}
Book.class
package com.example.domain;
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
application.yml
#spring:
# datasource:
# driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/test_db
# username: root
# password: 666666
# type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/test_db
username: root
password: 666666ApplicationTests
package com.example;
import com.example.dao.BookDao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(bookDao.getById(3));
}
}
运行结果:
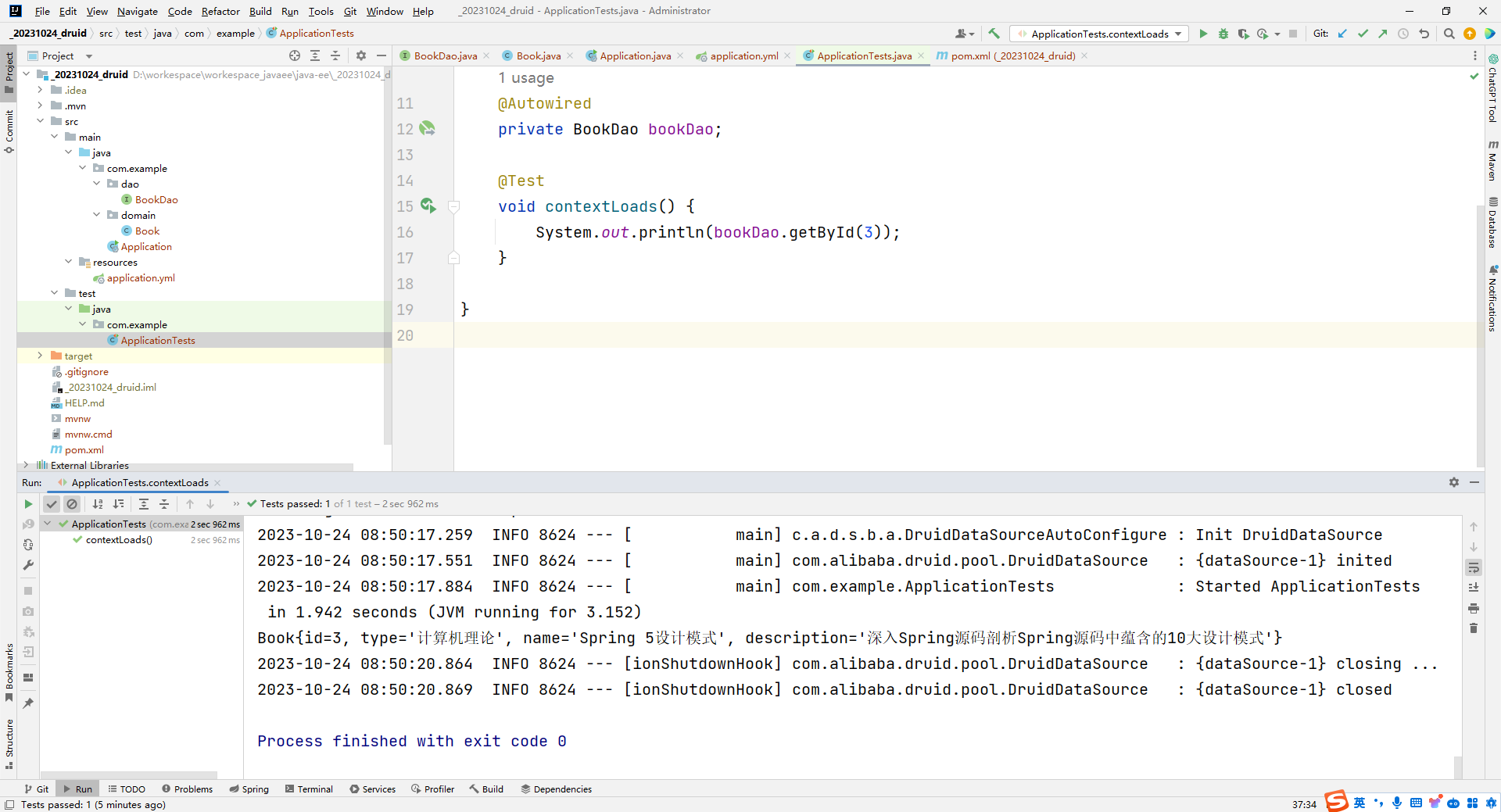
小结:
- 整合Druid需要导入Druid对应的starter
- 根据Druid提供的配置方式进行配置
- 整合第三方技术通用方式
- 导入对应的starter
- 根据提供的配置格式,配置非默认值对应的配置项
30.SSMP整合案例制作分析
SSMP整合案例
- 案例效果演示
- 案例实现方案分析
- 实体类开发---使用Lombok快速制作实体类
- Dao开发----整合MyBatisPlus,制作数据层测试类
- Service开发----基于MyBatisPlus进行增量开发,制作业务层测试类
- Controller开发----基于Restful开发,使用PostMan测试接口功能
- Controller开发----前后端开发协议制作
- 页面开发--基于VUE+ElementuI制作,前后端联调,页面数据处理,页面消息处理
- 列表、新增、修改、删除、分页、查询
- 项目异常处理
- 按条件查询--—页面功能调整、controller修正功能、Service修正功能
小结:
- SSMP案例效果演示
- SSMP案例制作流程解析
- 先开发基础CRUD功能,做一层测一层
- 调通页面,确认异步提交成功后,制作所有功能
- 添加分页功能与查询功能