目录
- 一 组件
- 1.1 组件的定义
- 1.2 特点
- 1.3 Vue-extend
- 1.4 VueCompent
- 二 脚手架
- 2.1 安装
- 2.2 结构目录
- 2.3 Render函数
- 2.4 修改默认配置
- 2.5 Ref 属性
- 2.6 Prop 属性
- 2.7 Mixin 属性
- 2.8 插件
- 2.9 Scoped
- 三 组件
- 3.1 组件的注册
- 3.1.1 局部注册
- 3.1.2 全局注册
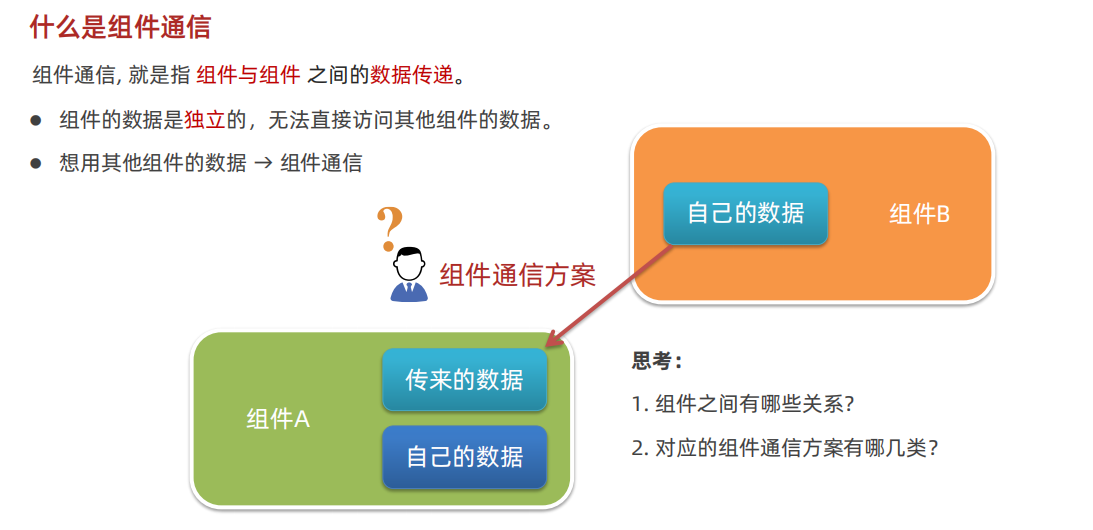
- 3.2 组件的通信
- 3.2.1 父子关系通信
- 3.2.2 Prop 详解
- 3.2.3 非父子组件通信
- 3.3 组件的其他知识
- 3.3.1 .sync 修饰符
- 3.3.2 Vue异步更新
- 3.3.3 $nextTick()
- 💌 所属专栏:【Vue2】
- 😀 作 者:长安不及十里
- 💻工作:目前从事电力行业开发
- 🌈目标:全栈开发
- 🚀 个人简介:一个正在努力学技术的Java工程师,专注基础和实战分享 ,欢迎咨询!
- 💖 欢迎大家:这里是CSDN,我总结知识的地方,喜欢的话请三连,有问题请私信 😘 😘 😘
- 📌 格言:把戏把戏要过手
- 📏 官网:https://v2.cn.vuejs.org
- ⛳ 参考教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1HV4y1a7n4
- 🔧 Vue脚手架:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh
- 🔧 VueRouter:https://router.vuejs.org/zh
- 🔧 VueX:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh
一 组件
参考官网:Vue.js
1.1 组件的定义
- 官方定义:组件(Component)是 Vue.js 最强大的功能之一,组件可以扩展 HTML 元素,封装可重用的代码。在较高层面上,组件是自定义元素, Vue.js 的编译器为它添加特殊功能。在有些情况下,组件也可以是原生 HTML 元素的形式,以 is 特性扩展。
- 组件机制的设计,可以让开发者把一个复杂的应用分割成一个个功能独立组件,降低开发的难度的同时,也提供了极好的复用性和可维护性,组件的出现,就是为了拆分Vue实例的代码量的,能够让我们以不同的组件,来划分不同的功能模块,将来我们需要什么样的功能,就可以去调用对应的组件即可。
- 组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与 new Vue 接收相同的选项,例如 data、computed、watch、methods 以及生命周期钩子等。仅有的例外是像 el 这样根实例特有的选项。
1.2 特点
- 模块化: 是从代码逻辑的角度进行划分的;方便代码分层开发,保证每个功能模块的职能单一。
- 组件化: 是从UI界面的角度进行划分的;前端的组件化,方便UI组件的重用。
1.3 Vue-extend
参考官网:API — Vue.js
使用基础 Vue 构造器,创建一个子类,数是一个包含组件选项的对象。
简单来说,就是创建一个新的组件,也就是我们说的局部注册一个组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>组件的定义</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
<my-components></my-components>
</div>
<script>
// 注册一个组件,全局注册
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<div>这是一个组件</div>',
// 注意:zai组件中,data必须是一个函数,而不能直接是一个对象
data() {
return {
name: 'shu'
}
},
// methods
methods: {
sayHi() {
console.log('hi');
}
},
// computed
computed: {
sayHello() {
return 'hello'
}
},
// 过滤器
filters: {
sayGoodbye() {
return 'goodbye'
}
},
})
// 注册一个局部组件
const MyComponent = Vue.extend({
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello, World!'
}
},
template: '<div>{{ message }}</div>'
})
// 创建一个根实例
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'my-components': MyComponent
},
})
// 原型链
Vue.prototype.$myMixin = {
created() {
console.log('Hello from $myMixin!')
}
}
// 打印原型链
console.log('@', MyComponent.prototype.__proto__);
// 打印Vue原型链
console.log('@', Vue.prototype);
// 总结:组件的定义,有两种方式,一种是全局注册,一种是局部注册,
// 全局注册:Vue.component('my-component', {template: '<div>这是一个组件</div>'})
// 局部注册:const MyComponent = Vue.extend({template: '<div>这是一个组件</div>'})
// 组件是一个独立的可复用的Vue实例,它有自己的data、methods、computed、watch、生命周期钩子等
</script>
🌈总结
- 一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数,因此每个实例可以维护一份被返回对象的独立的拷贝
- 全局注册:Vue.component(‘my-component’, {template: ‘
这是一个组件’})
- 局部注册:const MyComponent = Vue.extend({template: ‘
这是一个组件’})

1.4 VueCompent
- 组件其实是一个名为VueComponent的构造函数,且不是程序员定义的,是Vue.extend自动生成的
- 每写一个组件Vue会通过Vue.extend生成一个全新的VueComponent,写一个school组件,新生成一个VueComponent,当我们再写一个student组件时,又会重新生成一个全新的VueComponent,注意:这里只是针对于非单文件组件。
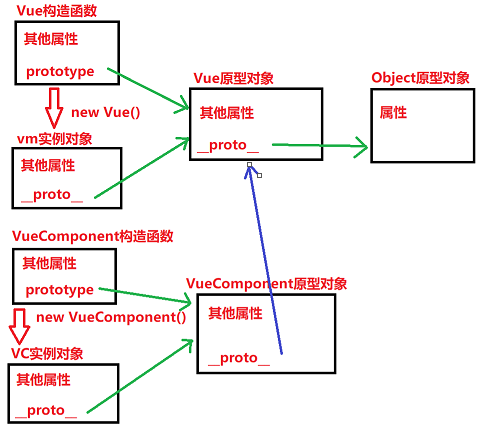
🌈Vue与VueComponent的关系
显示原型(prototype)与隐式原型(proto):
- 函数的prototype属性:在定义函数时自动添加的,默认值时一个空Object对象
- 对象的__proto__属性:创建对象时自动添加的,默认值为构造函数的prototype属性
访问一个对象属性时:
- 先在自身属性中查找,找到返回
- 如果没有,再沿着 __proto__这条链向上查找,找到返回
- 如果最终没有找到,返回undefined
Object原型对象是原型链的尽头(proto=null)
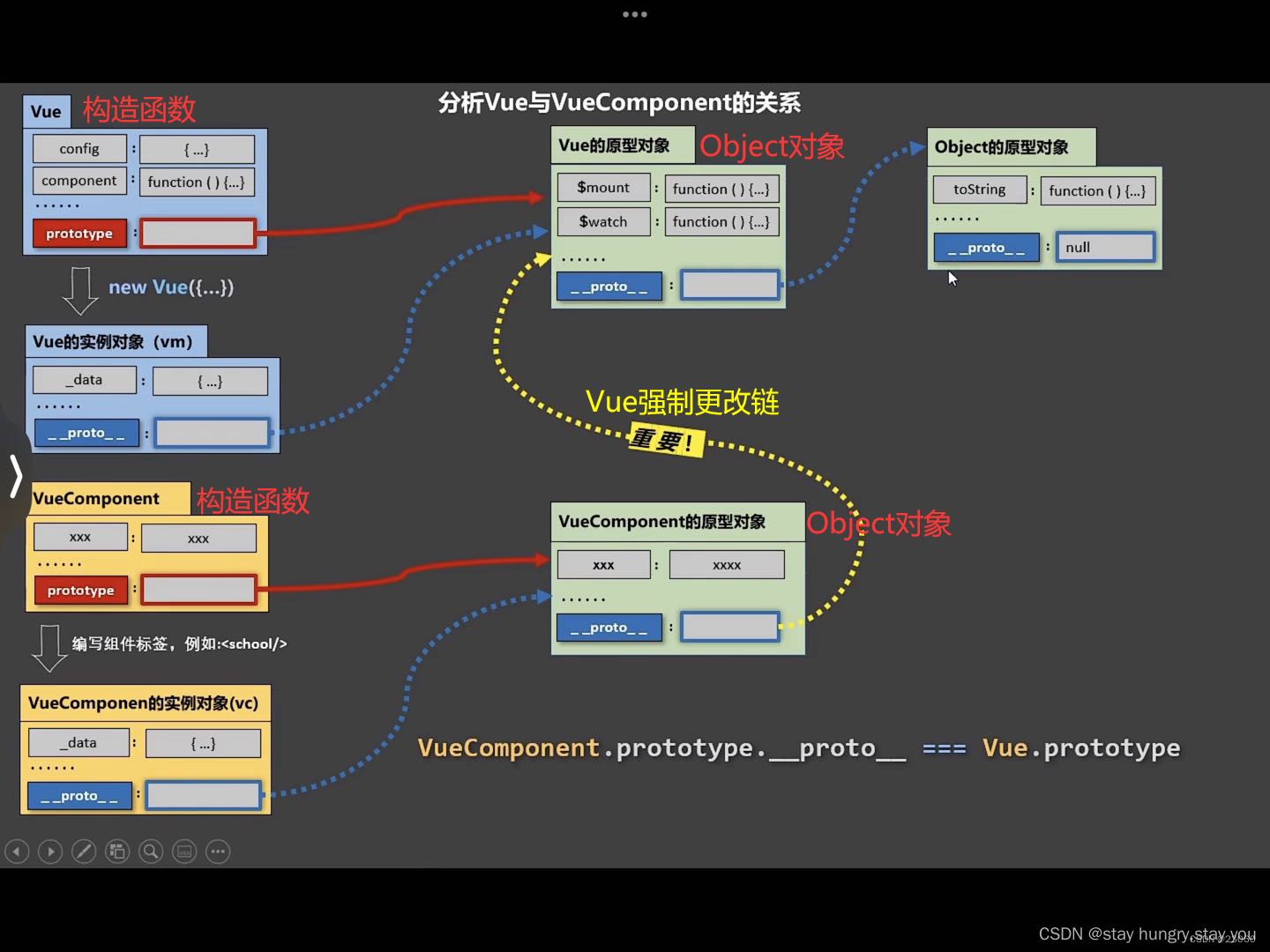
核心重点: Vue强制更改了VueComponent的原型对象指向Object的原型对象的隐式链,将其改到指向Vue的原型对象上。
二 脚手架
参考官网:Vue CLI
2.1 安装
Node 版本要求
Vue CLI 4.x 需要 Node.js v8.9 或更高版本 (推荐 v10 以上)。你可以使用 n,nvm 或 nvm-windows 在同一台电脑中管理多个 Node 版本。
- 安装
npm install -g @vue/cli
# OR
yarn global add @vue/cli
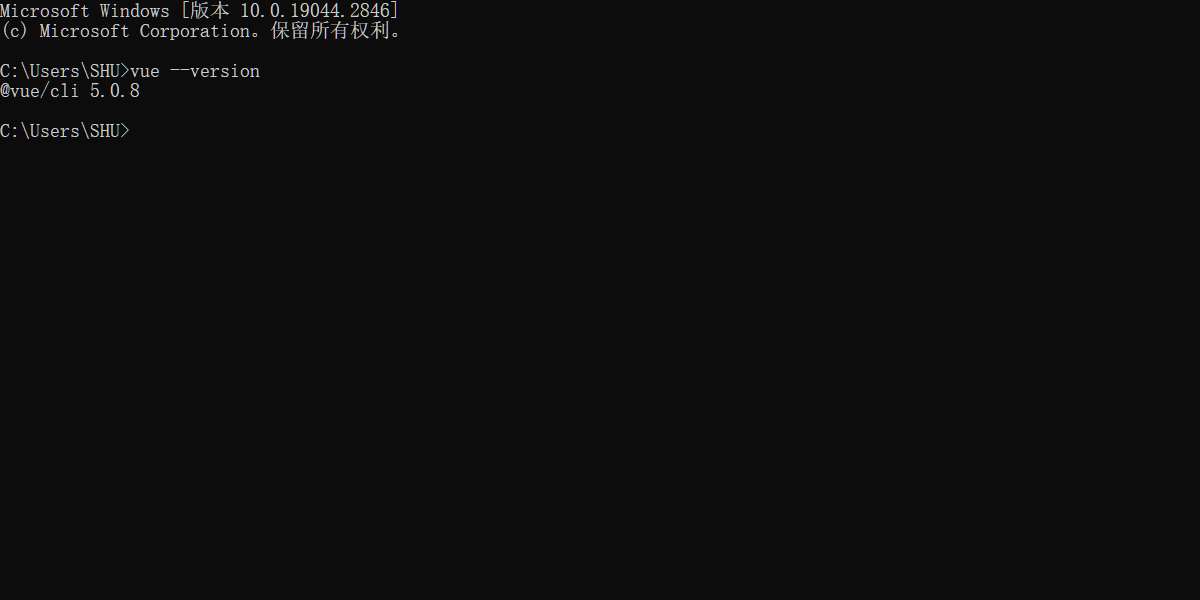
- 校验
vue --version
- 命令创建一个项目
用法:create [options] <app-name>
创建一个由 `vue-cli-service` 提供支持的新项目
选项:
-p, --preset <presetName> 忽略提示符并使用已保存的或远程的预设选项
-d, --default 忽略提示符并使用默认预设选项
-i, --inlinePreset <json> 忽略提示符并使用内联的 JSON 字符串预设选项
-m, --packageManager <command> 在安装依赖时使用指定的 npm 客户端
-r, --registry <url> 在安装依赖时使用指定的 npm registry
-g, --git [message] 强制 / 跳过 git 初始化,并可选的指定初始化提交信息
-n, --no-git 跳过 git 初始化
-f, --force 覆写目标目录可能存在的配置
-c, --clone 使用 git clone 获取远程预设选项
-x, --proxy 使用指定的代理创建项目
-b, --bare 创建项目时省略默认组件中的新手指导信息
-h, --help 输出使用帮助信息
- 图像化创建、
vue ui
上述命令会打开一个浏览器窗口,并以图形化界面将你引导至项目创建的流程。
- 案例:
2.2 结构目录
├── build --------------------------------- 项目构建(webpack)相关配置文件,配置参数什么的,一般不用动
│ ├── build.js --------------------------webpack打包配置文件
│ ├── check-versions.js ------------------------------ 检查npm,nodejs版本
│ ├── dev-client.js ---------------------------------- 设置环境
│ ├── dev-server.js ---------------------------------- 创建express服务器,配置中间件,启动可热重载的服务器,用于开发项目
│ ├── utils.js --------------------------------------- 配置资源路径,配置css加载器
│ ├── vue-loader.conf.js ----------------------------- 配置css加载器等
│ ├── webpack.base.conf.js --------------------------- webpack基本配置
│ ├── webpack.dev.conf.js ---------------------------- 用于开发的webpack设置
│ ├── webpack.prod.conf.js --------------------------- 用于打包的webpack设置
├── config ---------------------------------- 配置目录,包括端口号等。我们初学可以使用默认的。
│ ├── dev.env.js -------------------------- 开发环境变量
│ ├── index.js ---------------------------- 项目配置文件
│ ├── prod.env.js ------------------------- 生产环境变量
│ ├── test.env.js ------------------------- 测试环境变量
├── node_modules ---------------------------- npm 加载的项目依赖模块
├── src ------------------------------------- 我们要开发的目录,基本上要做的事情都在这个目录里。
│ ├── assets ------------------------------ 静态文件,放置一些图片,如logo等
│ ├── components -------------------------- 组件目录,存放组件文件,可以不用。
│ ├── main.js ----------------------------- 主js
│ ├── App.vue ----------------------------- 项目入口组件,我们也可以直接将组件写这里,而不使用 components 目录。
│ ├── router ------------------------------ 路由
├── static ---------------------------- 静态资源目录,如图片、字体等。
├── .babelrc--------------------------------- babel配置文件
├── .editorconfig---------------------------- 编辑器配置
├── .gitignore------------------------------- 配置git可忽略的文件
├── index.html ------------------------------ 首页入口文件,你可以添加一些 meta 信息或统计代码啥的。
├── package.json ---------------------------- node配置文件,记载着一些命令和依赖还有简要的项目描述信息
├── .README.md------------------------------- 项目的说明文档,markdown 格式。想怎么写怎么写,不会写就参照github上star多的项目,看人家怎么写的
2.3 Render函数
参考官网:API — Vue.js
- 简单的说,在vue中我们使用模板HTML语法组建页面的,使用render函数我们可以用js语言来构建DOM。 因为vue是虚拟DOM,所以在拿到template模板时也要转译成VNode的函数,而用render函数构建DOM,vue就免去了转译的过程。
- render 函数即渲染函数,它接收一个createElement 方法作为第一个参数用来创建 VNode。(简单的说就是 render函数的参数也是一个函数)
/*
* render: 渲染函数
* 参数: createElement
* 参数类型: Function
*/
render: function (createElement) {}
createElement也是一个函数,它接受三个参数
- 【必填】一个 HTML 标签名、组件选项对象,或者resolve 了上述任何一种的一个 async 函数。类型:{String | Object | Function}
- 【可选】一个与模板中 attribute 对应的数据对象。 类型:{Object}
- 【可选】子级虚拟节点 (VNodes) 类型:{String | Array}
示例:
//模板写法
<div id="demo" style="color: #ff0000" @click="handleClick">
Hello Vue!
</div>
//渲染函数写法
render: function (createElement) {
return createElement('div', {
attrs: {
id: 'demo'
},
//给div绑定样式
style:{
color: '#ff0000'
},
//给div绑定点击事件
on: {
click: this.handleClick
}
}, 'Hello Vue!')
},
将 h 作为 createElement 的别名是 Vue 生态系统中的一个通用惯例,当然我们也可以看到一个页面在组成结构:结构+逻辑+样式
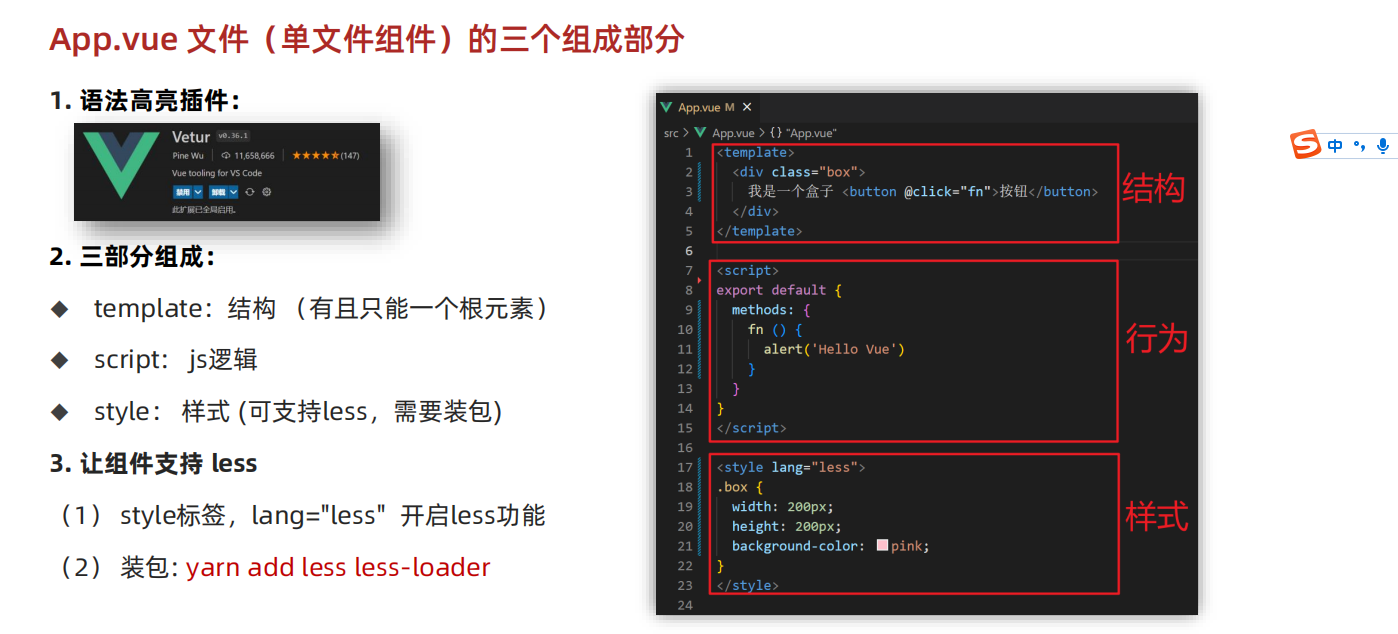
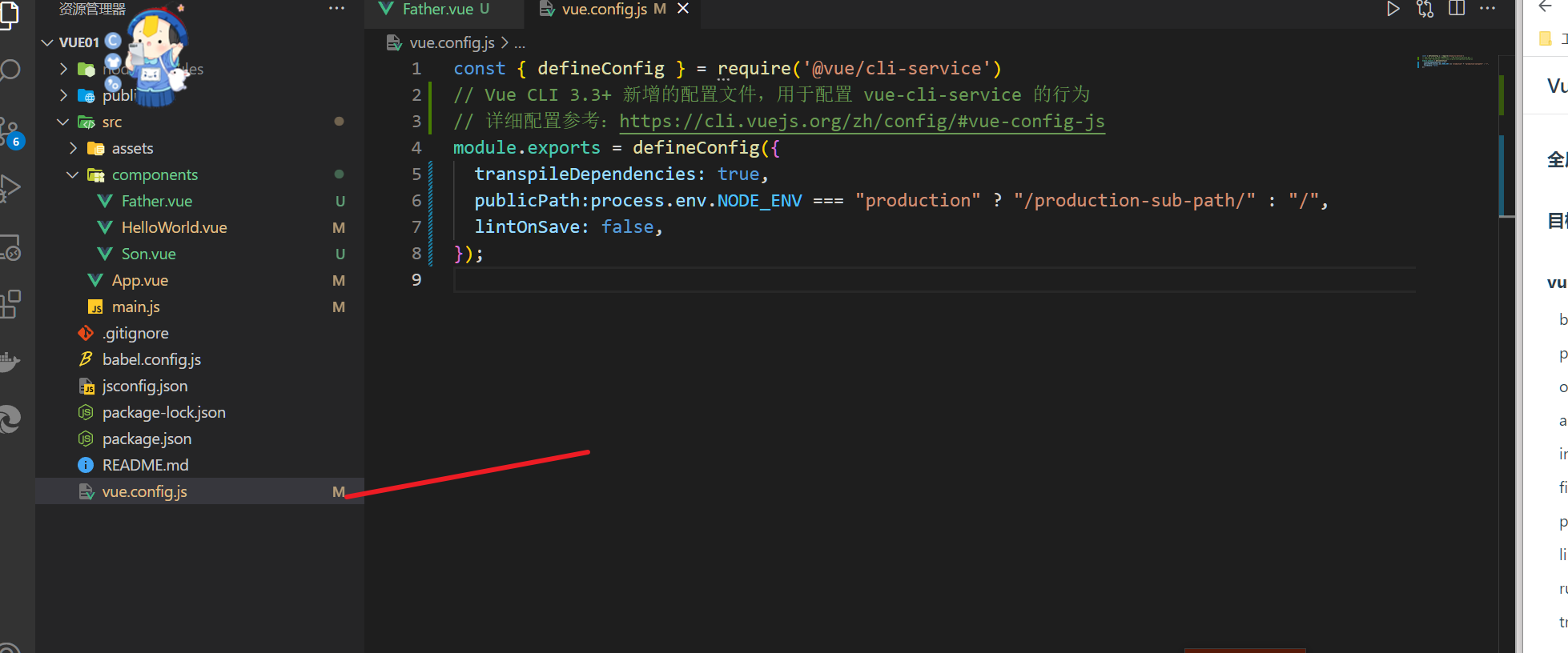
2.4 修改默认配置
参考官网:配置参考 | Vue CLI
就是Vue.config.js的配置
2.5 Ref 属性
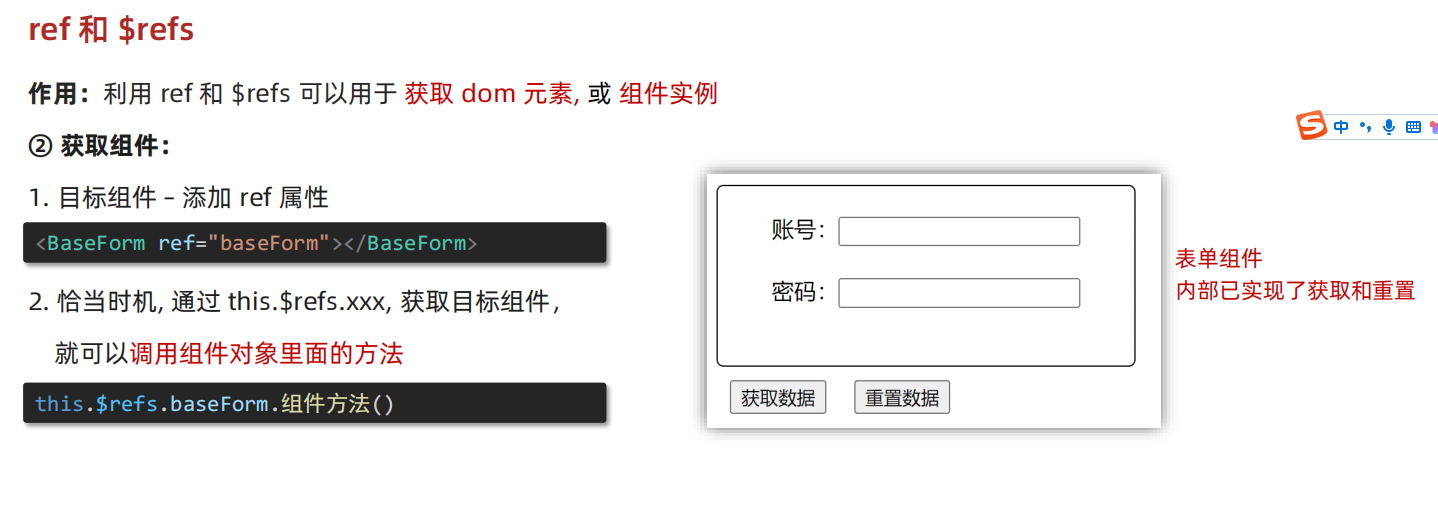
Vue中的ref属性用于在模板或组件中给某个元素或组件注册一个唯一标识符。这个标识符可以被用来访问这个元素或组件的实例或属性。ref可以绑定到DOM元素、组件或是子组件上。
<template>
<div>
<input ref="myInput" type="text">
<button @click="focusInput">Focus Input</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
focusInput() {
this.$refs.myInput.focus()
}
}
}
</script>
- 我们在input元素上使用ref属性来注册一个名为myInput的标识符,然后在focusInput方法中使用this.$refs.myInput来访问该元素的实例,并调用focus()方法聚焦该元素。
- 需要注意的是,$refs是一个特殊属性,它包含了所有通过ref注册的元素和组件的实例。这个属性只在组件渲染完成后才会被填充。
- 在组件中,ref可以绑定到子组件上,如下面的例子所示:
<template>
<div>
<my-component ref="myComponent"></my-component>
<button @click="callChildMethod">Call Child Method</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyComponent from './MyComponent.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyComponent
},
methods: {
callChildMethod() {
this.$refs.myComponent.childMethod()
}
}
}
</script>
需要注意的是,当ref用于绑定到组件上时,$refs属性将引用组件实例而不是DOM元素。
2.6 Prop 属性
参考官网:组件基础 — Vue.js
- 我的理解,在我们的实际开发过程中,我们的组件存在父子组件的关系,但是父子组件需要通信,这时就需要prop属性
- Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义 attribute,当一个值传递给一个 prop attribute 的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个 property
下面我们来看个案例
<template>
<div>
<h1 >son</h1>
<h2>来自父亲的消息{{msg}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "SonComponent",
// 通过props接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: {
msg: String
},
methods: {
click() {
this.$emit('click')
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>father</h1>
<button @click="click">给儿子发送消息</button>
<SonComponent :msg="msg"></SonComponent>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './Son.vue'
export default {
name: "FatherComponent",
data: function () {
return {
msg: '我是你爸爸'
}
},
components: {
SonComponent
},
methods: {
click() {
this.msg = '我是你爸爸,我给你发了一条消息'
}
}
}
</script>
当我们点击按钮时,子组件可以接受到父组件传递的值,具体参考官网,其中还包括类型检查,动态传递Prop,单向数据流等等
2.7 Mixin 属性
- 混入 (mixin) 提供了一种非常灵活的方式,来分发 Vue 组件中的可复用功能。一个混入对象可以包含任意组件选项。当组件使用混入对象时,所有混入对象的选项将被“混合”进入该组件本身的选项。
- 将组件的公共逻辑或者配置提取出来,哪个组件需要用到时,直接将提取的这部分混入到组件内部即可。这样既可以减少代码冗余度,也可以让后期维护起来更加容易。
- 这里需要注意的是:提取的是逻辑或配置,而不是HTML代码和CSS代码。其实大家也可以换一种想法,mixin就是组件中的组件,Vue组件化让我们的代码复用性更高,那么组件与组件之间还有重复部分,我们使用Mixin在抽离一遍。
// 定义一个混入对象
var myMixin = {
created: function () {
this.hello()
},
methods: {
hello: function () {
console.log('hello from mixin!')
}
}
}
// 定义一个使用混入对象的组件
var Component = Vue.extend({
mixins: [myMixin]
})
var component = new Component() // => "hello from mixin!"
2.8 插件
参考官网:API — Vue.js
安装 Vue.js 插件。如果插件是一个对象,必须提供 install 方法。如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为 install 方法。install 方法调用时,会将 Vue 作为参数传入,该方法需要在调用 new Vue() 之前被调用,当 install 方法被同一个插件多次调用,插件将只会被安装一次。
来个案例:
// myPlugin.js
const MyPlugin = {}
MyPlugin.install = function (Vue, options) {
// 添加全局方法或属性
Vue.myGlobalMethod = function () {
console.log('myGlobalMethod is called')
}
// 添加全局资源(指令、过滤器、组件)
Vue.directive('my-directive', {
bind (el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) {
// 绑定时的逻辑
},
// ...其他生命周期钩子
})
Vue.filter('my-filter', function (value) {
// 过滤器的实现逻辑
})
Vue.component('my-component', {
// 组件选项
})
}
export default MyPlugin
我们首先定义了一个名为 MyPlugin 的对象,并向其添加了一个名为 install 的方法。然后,在 install 方法中,我们可以添加全局方法或属性、全局资源(指令、过滤器、组件)等,这些添加的全局内容可以在 Vue 实例中直接使用。
使用:
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import MyPlugin from './myPlugin.js'
Vue.use(MyPlugin)
// 现在可以在应用程序中使用 Vue.myGlobalMethod、<my-component> 等全局内容了
需要注意的是,我们在自定义插件时,应该尽可能保持插件的功能单一性,将不同的功能分散在不同的插件中。这样可以提高插件的可复用性,并方便我们管理和维护应用程序的功能。
2.9 Scoped

Vue中的style标签上有一个特殊的属性scoped,当style标签拥有scoped属性时候,它的css样式只能作用于当前的Vue组件,防止组件之间污染。
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<style scoped>h3 {
margin: 40px 0 0;
}
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
}
a {
color: #42b983;
}</style>
三 组件
3.1 组件的注册
我们的组件必须先注册才能使用,分为局部注册于全局注册
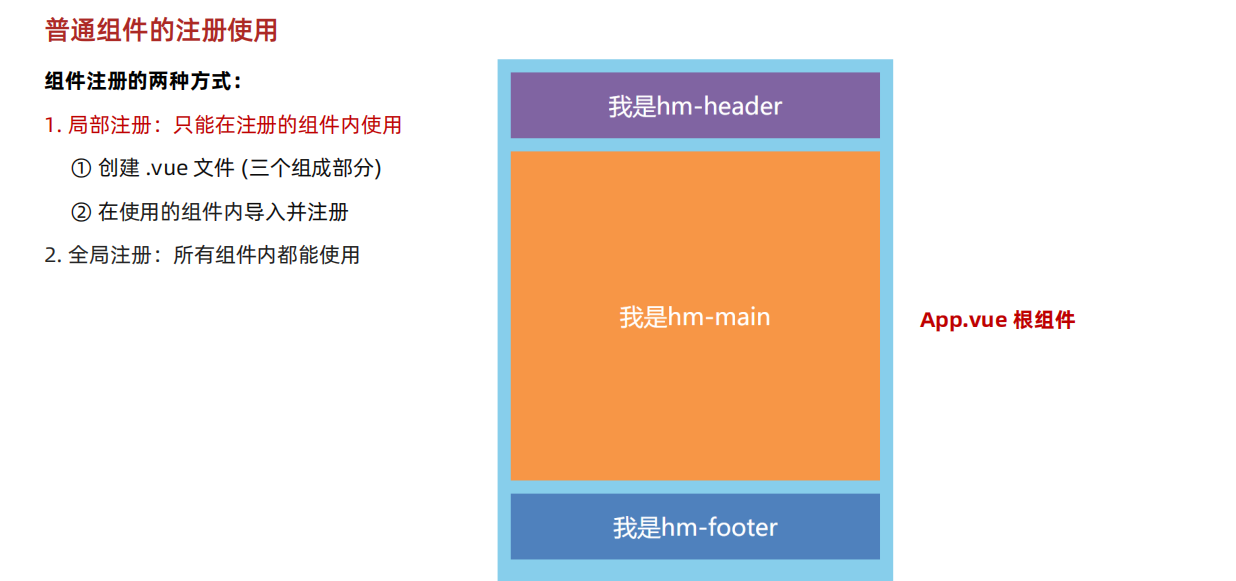
3.1.1 局部注册

- 首先我们定义一个组件:PartialRegistration
<template>
<div class="part">我是局部注册组件</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'PartialRegistration',
// 组件数据
data() {
return {
// ...
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.part {
color: red;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
- 在需要使用的组件中注册该组件
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 16:49:48
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 17:30:38
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\App.vue
-->
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<PartialRegistration/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import PartialRegistration from './components/PartialRegistration.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
// 简写形式
PartialRegistration
// 完整形式
// PartialRegistration: PartialRegistration
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
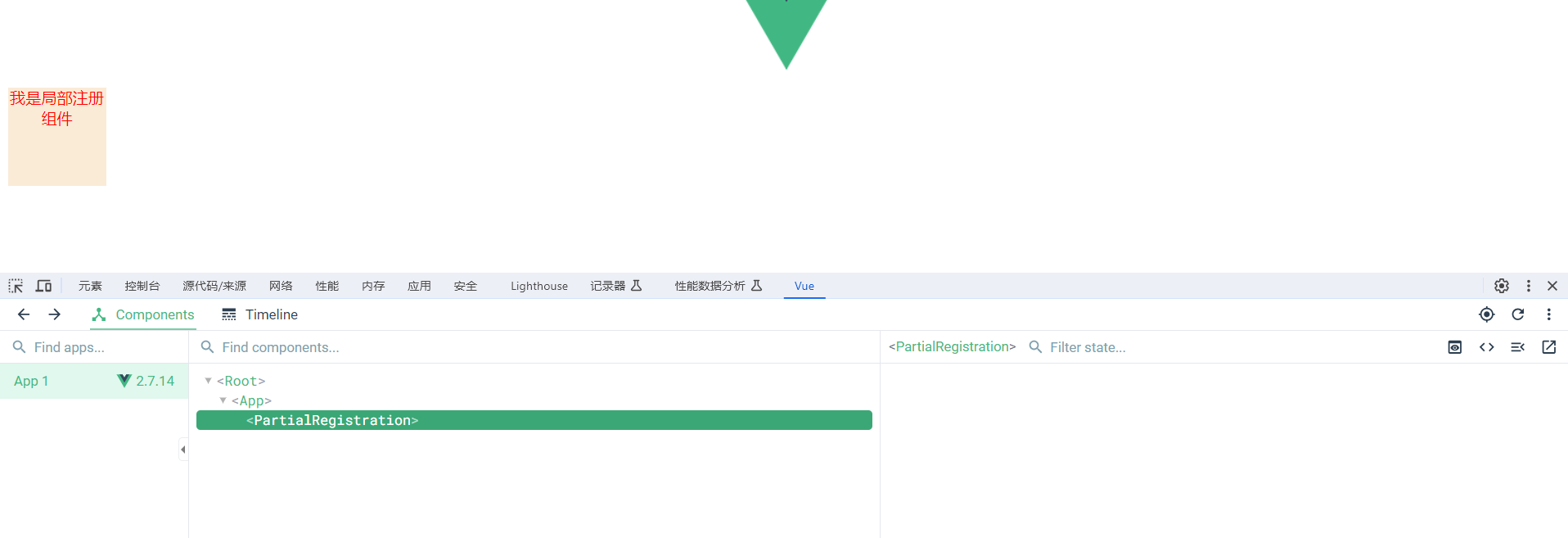
我们可以通过浏览器的Vue工具进行查看
3.1.2 全局注册

- 全局注册组件一般是我们需要常用的组件进行封装,供组件的其他地方进行使用
- 首先我们定义一个全局组件:GlobalRegistration
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 17:38:59
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 17:41:19
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\components\GlobalRegistration.vue
-->
<template>
<div class="global">我是全局注册组件</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'GlobalRegistration',
// 组件数据
data() {
return {
// ...
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.global {
color: rgb(0, 38, 255);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-left: 200px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
- 由于是全局使用组件,所以我们需要在main.js中来注册他
/*
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 16:49:48
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 17:42:25
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\main.js
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 注册全局组件
import GlobalRegistration from './components/GlobalRegistration.vue'
Vue.component('GlobalRegistration', GlobalRegistration)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
- 使用
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 16:49:48
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 17:30:38
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\App.vue
-->
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<PartialRegistration/>
<GlobalRegistration />
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 局部注册组件
import PartialRegistration from './components/PartialRegistration.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
// 简写形式
PartialRegistration
// 完整形式
// PartialRegistration: PartialRegistration
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>

3.2 组件的通信
3.2.1 父子关系通信
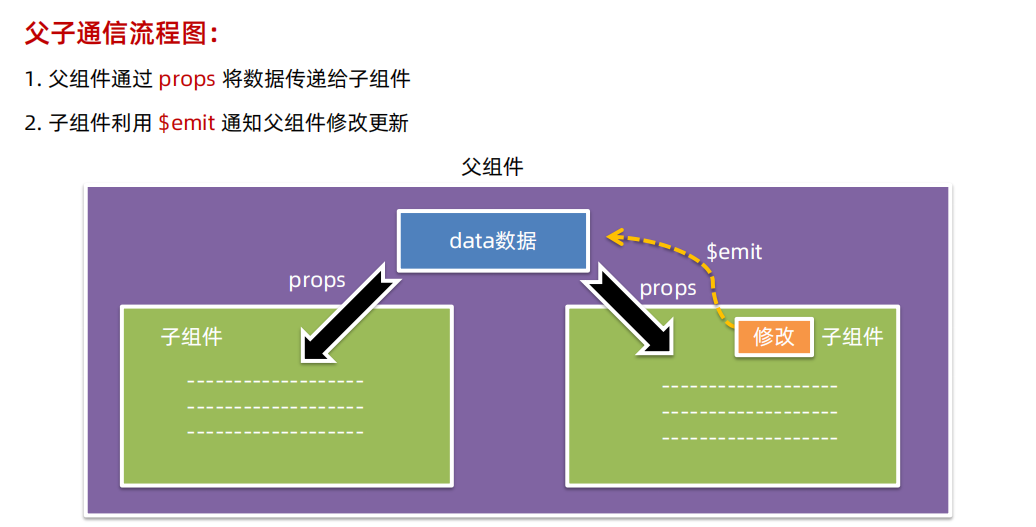
父->子
父组件通过 props 将数据传递给子组件
- 我们首先定义一个父组件:FatherComponent,首先介绍将父组件消息传递给子组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="father">我是父组件</h1>
<hr>
<SonComponent :msg="msg"></SonComponent>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './SonComponent.vue'
export default {
// father组件中注册了son组件
name: 'FatherComponent',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
SonComponent
},
data() {
return {
msg: '我是父组件的数据,我会传给子组件'
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.father {
color: blue;
}
</style>
- 子组件需要用prop属性来接受父组件的值
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="son">我是子组件</h1>
<hr>
<p class="son">我是父组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'SonComponent',
// 接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: ['msg'],
data() {
return {
}
},
// 父组件传递过来的数据
mounted() {
console.log("xxxxx"+this.msg)
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
color: red;
}
</style>
子->父
子组件利用 $emit 通知父组件,进行修改更新
父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="father">我是父组件</h1>
<hr>
<SonComponent :msg="msg" @son-change="handleChanges"></SonComponent>
<hr>
<p class="father">我是子组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './SonComponent.vue'
export default {
// father组件中注册了son组件
name: 'FatherComponent',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
SonComponent
},
data() {
return {
msg: '我是父组件的数据,我会传给子组件'
}
},
methods: {
// 监听子组件传递过来的数据
handleChanges(val) {
console.log("xxxxxx"+val)
this.msg = val
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.father {
color: blue;
}
</style>
子组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="son">我是子组件</h1>
<hr>
<p class="son">我是父组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<button @click="handleClick">点击我向父组件传递数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'SonComponent',
// 接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: ['msg'],
data() {
return {
}
},
// 父组件传递过来的数据
mounted() {
console.log("xxxxx"+this.msg)
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// 向父组件传递数据
this.$emit('son-change', '哈哈哈,我是子组件传递过来的数据')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
color: red;
}
</style>

3.2.2 Prop 详解
props主要用于组件的传值,他的工作就是为了接收外面传过来的数据,与data、el、ref是一个级别的配置项,基本的使用上面都讲了下面我们来看看具体的配置信息,props 校验

- 父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="father">我是父组件</h1>
<hr>
<SonComponent :msg="msg" @son-change="handleChanges" :person="person"></SonComponent>
<hr>
<p class="father">我是子组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './SonComponent.vue'
export default {
// father组件中注册了son组件
name: 'FatherComponent',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
SonComponent
},
data() {
return {
msg: '我是父组件的数据,我会传给子组件',
person: {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
}
}
},
methods: {
// 监听子组件传递过来的数据
handleChanges(val) {
console.log("xxxxxx"+val)
this.msg = val
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.father {
color: blue;
}
</style>
子组件:
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="son">我是子组件</h1>
<hr>
<p class="son">我是父组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<button @click="handleClick">点击我向父组件传递数据</button>
<hr>
<h1 class="son">我是父组件传递过来的对象数据</h1>
<p class="son">姓名: {{person.name}}</p>
<p class="son">年龄: {{person.age}}</p>
<p class="son">学校: {{person.school}}</p>
<p class="son">城市: {{person.city}}</p>
<p class="son">是否结婚: {{person.isMarry}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'SonComponent',
// 接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: {
msg: {
type: String, // 数据类型
default: '我是子组件的默认数据' ,// 默认值
required: true ,// 是否必须传递
validator: (value) => {
// value是父组件传递过来的数据
// 如果返回true,表示验证通过,如果返回false,表示验证不通过
return value.length > 5
}
},
person: {
type: Object,
default: () => {
return {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
}
}
}
},
data() {
return {
}
},
// 父组件传递过来的数据
mounted() {
console.log("xxxxx"+this.msg)
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// 向父组件传递数据
this.$emit('son-change', '哈哈哈,我是子组件传递过来的数据')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
color: red;
}
</style>

注意:
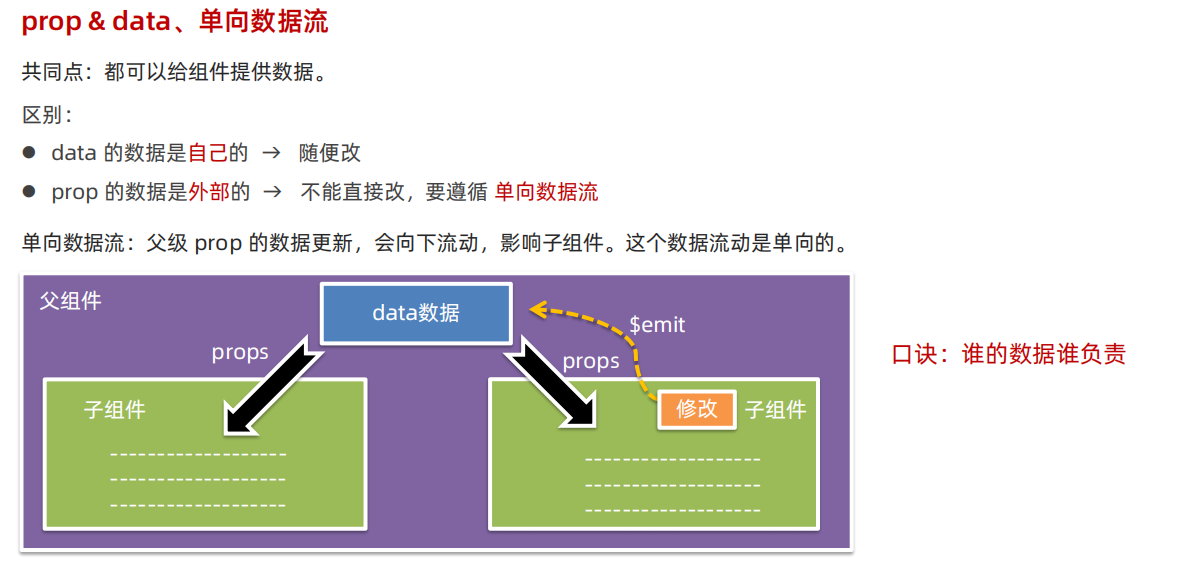
- 所有 prop 都使得其父子 prop 之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来不行。这样会防止子组件意外变更父组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。
- 每次父级组件发生变更时,子组件中所有的 prop 都将会刷新为最新的值。如果你在一个子组件内部改变 prop,Vue 会在浏览器的控制台中发出警告
- 点击按钮子组件会修改父组件传递过来的 prop,浏览器会报错
3.2.3 非父子组件通信
event bus 事件总线
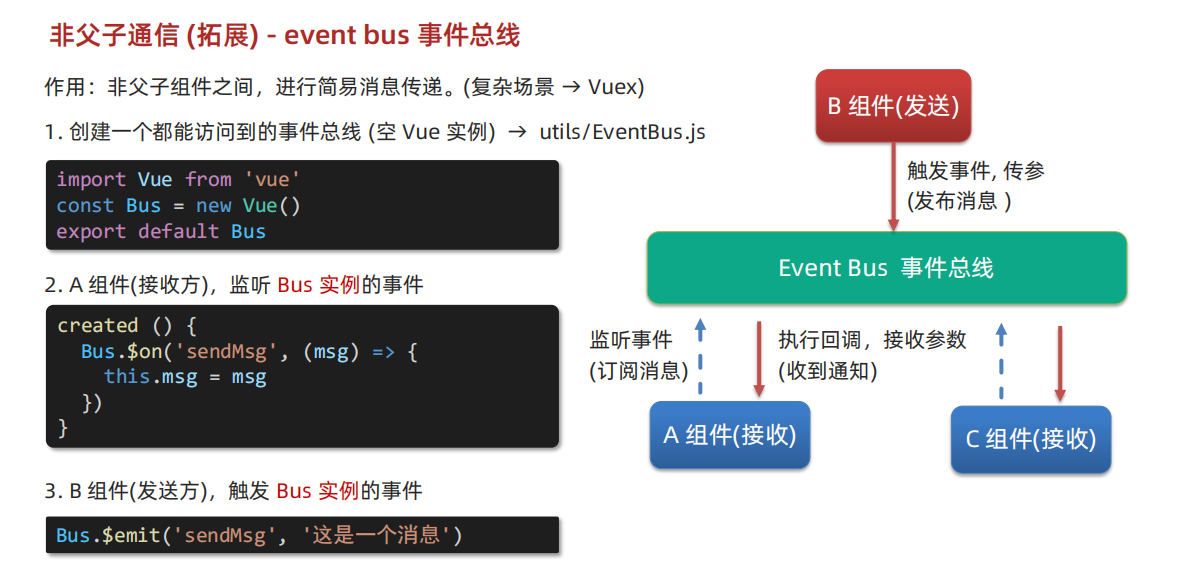
- 写一个工具类
/*
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 18:23:38
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 18:23:42
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\utils\EventBus.js
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
const EventBus = new Vue()
export default EventBus
- 将这个方法全局注册
/*
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 16:49:48
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 18:26:18
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\main.js
*/
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 注册全局组件
import GlobalRegistration from './components/GlobalRegistration.vue'
Vue.component('GlobalRegistration', GlobalRegistration)
// 注册EventBus
import EventBus from './utils/EventBus.js'
Vue.prototype.$bus = EventBus
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
- 父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="father">我是父组件</h1>
<hr>
<SonComponent :msg="msg" @son-change="handleChanges" :person="person"></SonComponent>
<hr>
<p class="father">我是子组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<!-- 利用EventBus 传递消息 -->
<button @click="handleClick">利用EventBus 传递消息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './SonComponent.vue'
export default {
// father组件中注册了son组件
name: 'FatherComponent',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
SonComponent
},
data() {
return {
msg: '我是父组件的数据,我会传给子组件',
person: {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
}
}
},
methods: {
// 监听子组件传递过来的数据
handleChanges(val) {
console.log("xxxxxx"+val)
this.msg = val
},
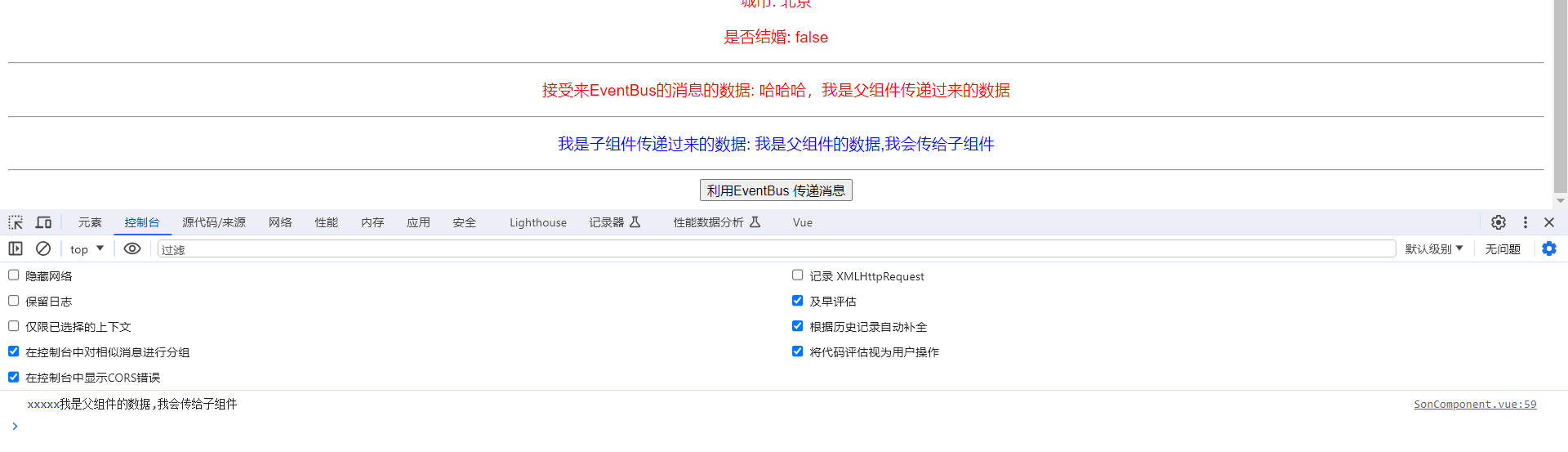
handleClick() {
// 利用EventBus 传递消息
this.$bus.$emit('father-change', '哈哈哈,我是父组件传递过来的数据')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.father {
color: blue;
}
</style>
- 子组件
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="son">我是子组件</h1>
<hr>
<p class="son">我是父组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<button @click="handleClick">点击我向父组件传递数据</button>
<hr>
<h1 class="son">我是父组件传递过来的对象数据</h1>
<p class="son">姓名: {{person.name}}</p>
<p class="son">年龄: {{person.age}}</p>
<p class="son">学校: {{person.school}}</p>
<p class="son">城市: {{person.city}}</p>
<p class="son">是否结婚: {{person.isMarry}}</p>
<hr>
<!-- 接受来EventBus的消息 -->
<p class="son">接受来EventBus的消息的数据: {{events}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'SonComponent',
// 接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: {
msg: {
type: String, // 数据类型
default: '我是子组件的默认数据' ,// 默认值
required: true ,// 是否必须传递
validator: (value) => {
// value是父组件传递过来的数据
// 如果返回true,表示验证通过,如果返回false,表示验证不通过
return value.length > 5
}
},
person: {
type: Object,
default: () => {
return {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
}
}
}
},
data() {
return {
events: ''
}
},
// 父组件传递过来的数据
mounted() {
console.log("xxxxx"+this.msg)
// 接受来EventBus的消息
this.$bus.$on('father-change', (val) => {
this.events = val
})
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// 向父组件传递数据
this.$emit('son-change', '哈哈哈,我是子组件传递过来的数据')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
color: red;
}
</style>
后面我们还会介绍Vuex
3.3 组件的其他知识
3.3.1 .sync 修饰符
- .sync修饰符可以实现子组件与父组件的双向绑定,并且可以实现子组件同步修改父组件的值。
- 一般情况下,想要实现父子组件间值的传递,通常使用的是 props 和自定义事件 $emit 。
- 其中,父组件通过 props 将值传给子组件,子组件再通过 $emit 将值传给父组件,父组件通过事件j监听获取子组件传过来的值。
- 如果想要简化这里的代码,可以使用.sync修饰符,实际上就是一个语法糖。
父组件
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 17:50:39
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 18:46:16
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\components\FatherComponent.vue
-->
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="father">我是父组件</h1>
<hr>
<SonComponent :msg="msg" @son-change="handleChanges" :isShow.sync="isShow" :person="person"></SonComponent>
<hr>
<p class="father">我是子组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<!-- 利用EventBus 传递消息 -->
<button @click="handleClick">利用EventBus 传递消息</button>
<hr>
<!-- 监听子组件按钮的显示状态 -->
<p>子组件按钮状态:{{ isShow }} </p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SonComponent from './SonComponent.vue'
export default {
// father组件中注册了son组件
name: 'FatherComponent',
// 局部注册组件
components: {
SonComponent
},
data() {
return {
msg: '我是父组件的数据,我会传给子组件',
person: {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
},
isShow: true
}
},
methods: {
// 监听子组件传递过来的数据
handleChanges(val) {
console.log("xxxxxx"+val)
this.msg = val
},
handleClick() {
// 利用EventBus 传递消息
this.$bus.$emit('father-change', '哈哈哈,我是父组件传递过来的数据')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.father {
color: blue;
}
</style>
- 子组件
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 17:51:40
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 18:48:38
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\components\SonComponent.vue
-->
<template>
<div>
<h1 class="son">我是子组件</h1>
<hr>
<p class="son">我是父组件传递过来的数据: {{msg}}</p>
<hr>
<button @click="handleClick">点击我向父组件传递数据</button>
<hr>
<h1 class="son">我是父组件传递过来的对象数据</h1>
<p class="son">姓名: {{person.name}}</p>
<p class="son">年龄: {{person.age}}</p>
<p class="son">学校: {{person.school}}</p>
<p class="son">城市: {{person.city}}</p>
<p class="son">是否结婚: {{person.isMarry}}</p>
<hr>
<!-- 接受来EventBus的消息 -->
<p class="son">接受来EventBus的消息的数据: {{events}}</p>
<!-- 按钮的可用状态 -->
<button :disabled="isShow">我是按钮</button>
<!-- 改变按钮的状态 -->
<button @click="changeStatus">改变按钮的状态</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 组件名称
name: 'SonComponent',
// 接收父组件传递过来的数据
props: {
msg: {
type: String, // 数据类型
default: '我是子组件的默认数据' ,// 默认值
required: true ,// 是否必须传递
validator: (value) => {
// value是父组件传递过来的数据
// 如果返回true,表示验证通过,如果返回false,表示验证不通过
return value.length > 5
}
},
person: {
type: Object,
default: () => {
return {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
school: '清华大学',
city: '北京',
isMarry: false
}
}
},
isShow: {
type: Boolean,
default: true
}
},
data() {
return {
events: '',
isShows: true
}
},
// 父组件传递过来的数据
mounted() {
console.log("xxxxx"+this.msg)
// 接受来EventBus的消息
this.$bus.$on('father-change', (val) => {
this.events = val
})
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// 向父组件传递数据
this.$emit('son-change', '哈哈哈,我是子组件传递过来的数据')
},
changeStatus() {
// 向父组件传递数据
this.$emit('update:isShow', !this.isShow)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
color: red;
}
</style>
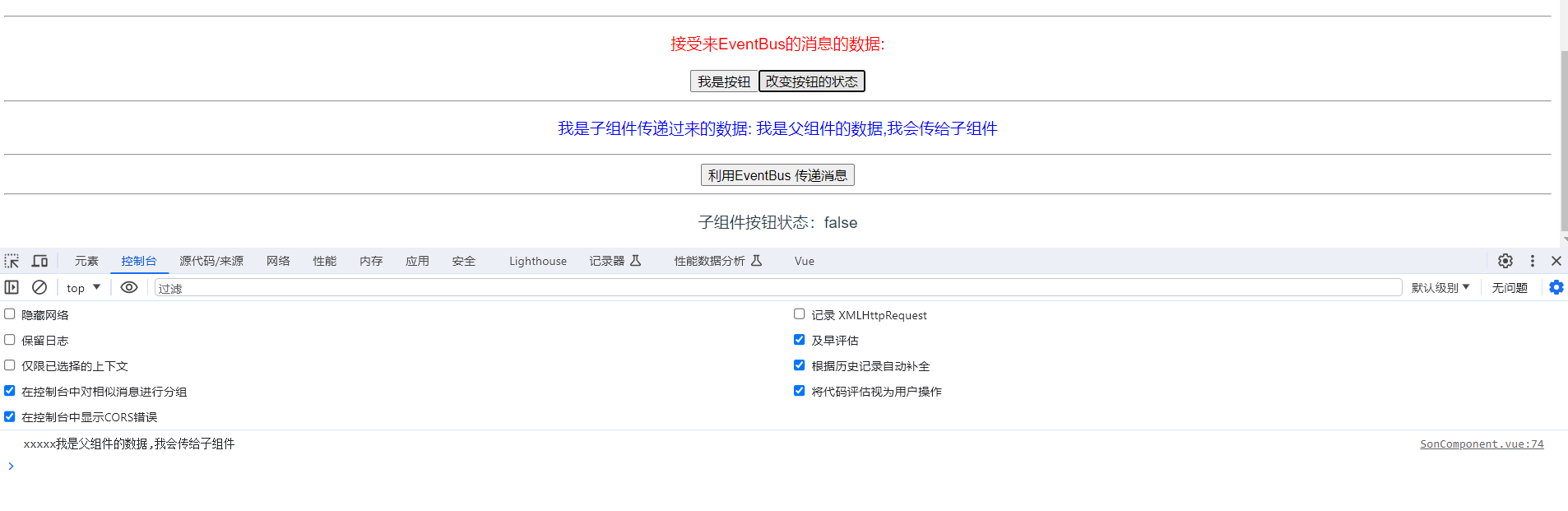
3.3.2 Vue异步更新
Vue的异步更新
- Vue.js是一种用于构建用户界面的渐进式 JavaScript 框架。
- 其中一个非常重要的特性是异步更新。
- 异步更新是指当数据发生变化时,Vue不会立即更新DOM。
- 相反,它会在下一个“tick”或渲染循环中异步执行DOM更新。这种机制可以提高性能,减少不必要的操作
- 当我们直接修改 Vue 实例的数据时,Vue 会在内部将数据更新操作放入一个异步队列中,而不是立即进行更新。
3.3.3 $nextTick()
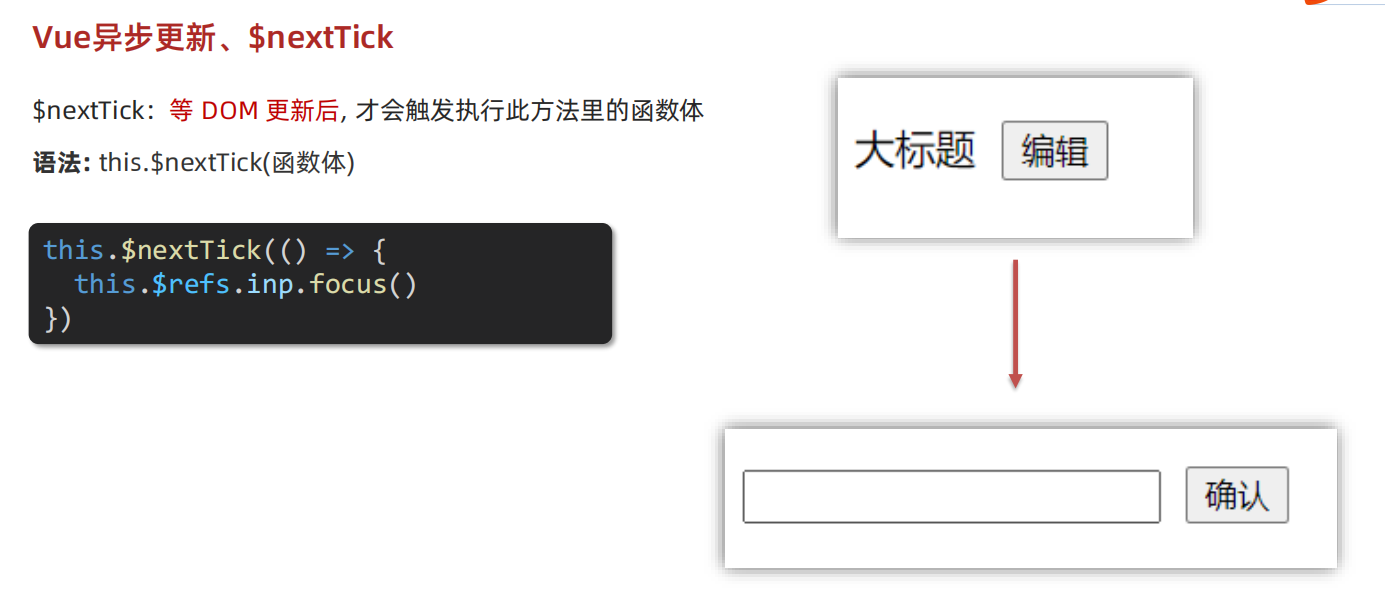
- $nextTick() 是 Vue.js 框架中的一个方法,它主要用于 DOM 操作。当我们修改 Vue 组件中的数据时,Vue.js 会在下次事件循环前自动更新视图,并异步执行 $nextTick() 中的回调函数。这个过程可以确保 DOM 已经被更新,以及可以操作到最新的 DOM。
- 具体来说,当修改了 Vue 组件中的数据时,Vue.js 并不会立即进行视图更新。Vue.js 会将修改的数据记录下来,并在下一次事件循环时才更新视图。而 $nextTick() 方法则是用于等待这个事件循环结束后再执行回调函数。这样可以确保我们操作 DOM 的时候,DOM 已经被 Vue 更新过了。
案例:
<!--
* @Author: EasonShu
* @Date: 2023-10-21 19:50:08
* @LastEditors: Do not edit
* @LastEditTime: 2023-10-21 19:51:18
* @FilePath: \vue-demo01\src\components\NextTickComponent.vue
-->
<template>
<div>
<div>{{message}}</div>
<!-- 更新消息 -->
<button @click="updateMessage">Update Message</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'NextTickComponent',
data () {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue'
}
},
methods: {
updateMessage () {
this.message = 'Updated Message'
// 在 DOM 更新后操作 DOM
this.$nextTick(() => {
// 通过 DOM API 更新文本
this.$el.textContent = 'DOM Updated!'
})
}
}
}
</script>