忘记过去,超越自己
- ❤️ 博客主页 单片机菜鸟哥,一个野生非专业硬件IOT爱好者 ❤️
- ❤️ 本篇创建记录 2023-10-21 ❤️
- ❤️ 本篇更新记录 2023-10-21 ❤️
- 🎉 欢迎关注 🔎点赞 👍收藏 ⭐️留言📝
- 🙏 此博客均由博主单独编写,不存在任何商业团队运营,如发现错误,请留言轰炸哦!及时修正!感谢支持!
- 🔥 Arduino ESP8266教程累计帮助过超过1W+同学入门学习硬件网络编程,入选过选修课程,刊登过无线电杂志 🔥零基础从入门到熟悉Arduino平台下开发ESP8266,同时会涉及网络编程知识。专栏文章累计超过60篇,分为基础篇、网络篇、应用篇、高级篇,涵盖ESP8266大部分开发技巧。
快速导航
单片机菜鸟的博客快速索引(快速找到你要的)
如果觉得有用,麻烦点赞收藏,您的支持是博主创作的动力。
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. 软件代码
- 2.1 TFT屏幕的配置文件
- 2.2 主工程代码
- 2.3 tft显示代码
- 2.4 睡眠模式
- 2.5 获取天气信息
1. 前言
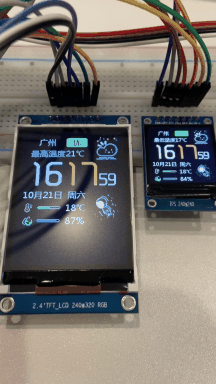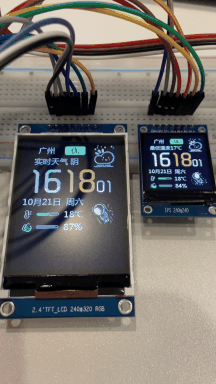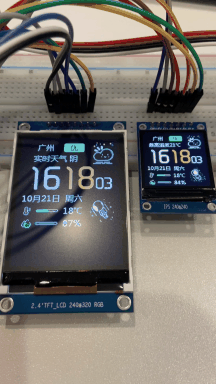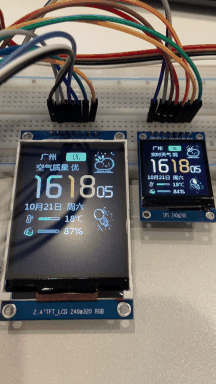
仿造网上开源的SD2 天气时钟,优化了部分代码, V1.0 最基本功能,支持夜间睡眠模式。后期会继续优化。
2. 软件代码
2.1 TFT屏幕的配置文件
// USER DEFINED SETTINGS
// Set driver type, fonts to be loaded, pins used and SPI control method etc
//
// See the User_Setup_Select.h file if you wish to be able to define multiple
// setups and then easily select which setup file is used by the compiler.
//
// If this file is edited correctly then all the library example sketches should
// run without the need to make any more changes for a particular hardware setup!
// Note that some sketches are designed for a particular TFT pixel width/height
// User defined information reported by "Read_User_Setup" test & diagnostics example
#define USER_SETUP_INFO "User_Setup"
// Define to disable all #warnings in library (can be put in User_Setup_Select.h)
//#define DISABLE_ALL_LIBRARY_WARNINGS
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 1. Call up the right driver file and any options for it
//
// ##################################################################################
// Define STM32 to invoke optimised processor support (only for STM32)
//#define STM32
// Defining the STM32 board allows the library to optimise the performance
// for UNO compatible "MCUfriend" style shields
//#define NUCLEO_64_TFT
//#define NUCLEO_144_TFT
// STM32 8 bit parallel only:
// If STN32 Port A or B pins 0-7 are used for 8 bit parallel data bus bits 0-7
// then this will improve rendering performance by a factor of ~8x
//#define STM_PORTA_DATA_BUS
//#define STM_PORTB_DATA_BUS
// Tell the library to use parallel mode (otherwise SPI is assumed)
//#define TFT_PARALLEL_8_BIT
//#defined TFT_PARALLEL_16_BIT // **** 16 bit parallel ONLY for RP2040 processor ****
// Display type - only define if RPi display
//#define RPI_DISPLAY_TYPE // 20MHz maximum SPI
// Only define one driver, the other ones must be commented out
//#define ILI9341_DRIVER // Generic driver for common displays
//#define ILI9341_2_DRIVER // Alternative ILI9341 driver, see https://github.com/Bodmer/TFT_eSPI/issues/1172
//#define ST7735_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ILI9163_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define S6D02A1_DRIVER
//#define RPI_ILI9486_DRIVER // 20MHz maximum SPI
//#define HX8357D_DRIVER
//#define ILI9481_DRIVER
//#define ILI9486_DRIVER
//#define ILI9488_DRIVER // WARNING: Do not connect ILI9488 display SDO to MISO if other devices share the SPI bus (TFT SDO does NOT tristate when CS is high)
#define ST7789_DRIVER // Full configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ST7789_2_DRIVER // Minimal configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define R61581_DRIVER
//#define RM68140_DRIVER
//#define ST7796_DRIVER
//#define SSD1351_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_480_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_800_DRIVER
//#define SSD1963_800ALT_DRIVER
//#define ILI9225_DRIVER
//#define GC9A01_DRIVER
// Some displays support SPI reads via the MISO pin, other displays have a single
// bi-directional SDA pin and the library will try to read this via the MOSI line.
// To use the SDA line for reading data from the TFT uncomment the following line:
// #define TFT_SDA_READ // This option is for ESP32 ONLY, tested with ST7789 and GC9A01 display only
// For ST7735, ST7789 and ILI9341 ONLY, define the colour order IF the blue and red are swapped on your display
// Try ONE option at a time to find the correct colour order for your display
// #define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_RGB // Colour order Red-Green-Blue
#define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_BGR // Colour order Blue-Green-Red
#define TFT_INVERSION_OFF
// For M5Stack ESP32 module with integrated ILI9341 display ONLY, remove // in line below
// #define M5STACK
// For ST7789, ST7735, ILI9163 and GC9A01 ONLY, define the pixel width and height in portrait orientation
// #define TFT_WIDTH 80
// #define TFT_WIDTH 128
// #define TFT_WIDTH 172 // ST7789 172 x 320
#define TFT_WIDTH 240 // ST7789 240 x 240 and 240 x 320
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 160
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 128
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 240 // ST7789 240 x 240
#define TFT_HEIGHT 320 // ST7789 240 x 320
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 240 // GC9A01 240 x 240
// For ST7735 ONLY, define the type of display, originally this was based on the
// colour of the tab on the screen protector film but this is not always true, so try
// out the different options below if the screen does not display graphics correctly,
// e.g. colours wrong, mirror images, or stray pixels at the edges.
// Comment out ALL BUT ONE of these options for a ST7735 display driver, save this
// this User_Setup file, then rebuild and upload the sketch to the board again:
// #define ST7735_INITB
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB2
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB3
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB128 // For 128 x 128 display
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display (BGR, inverted, 26 offset)
// #define ST7735_ROBOTLCD // For some RobotLCD arduino shields (128x160, BGR, https://docs.arduino.cc/retired/getting-started-guides/TFT)
// #define ST7735_REDTAB
// #define ST7735_BLACKTAB
// #define ST7735_REDTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display with 24 pixel offset
// If colours are inverted (white shows as black) then uncomment one of the next
// 2 lines try both options, one of the options should correct the inversion.
// #define TFT_INVERSION_ON
// #define TFT_INVERSION_OFF
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 2. Define the pins that are used to interface with the display here
//
// ##################################################################################
// If a backlight control signal is available then define the TFT_BL pin in Section 2
// below. The backlight will be turned ON when tft.begin() is called, but the library
// needs to know if the LEDs are ON with the pin HIGH or LOW. If the LEDs are to be
// driven with a PWM signal or turned OFF/ON then this must be handled by the user
// sketch. e.g. with digitalWrite(TFT_BL, LOW);
// #define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light control pin
// #define TFT_BACKLIGHT_ON HIGH // Level to turn ON back-light (HIGH or LOW)
// We must use hardware SPI, a minimum of 3 GPIO pins is needed.
// Typical setup for ESP8266 NodeMCU ESP-12 is :
//
// Display SDO/MISO to NodeMCU pin D6 (or leave disconnected if not reading TFT)
// Display LED to NodeMCU pin VIN (or 5V, see below)
// Display SCK to NodeMCU pin D5
// Display SDI/MOSI to NodeMCU pin D7
// Display DC (RS/AO)to NodeMCU pin D3
// Display RESET to NodeMCU pin D4 (or RST, see below)
// Display CS to NodeMCU pin D8 (or GND, see below)
// Display GND to NodeMCU pin GND (0V)
// Display VCC to NodeMCU 5V or 3.3V
//
// The TFT RESET pin can be connected to the NodeMCU RST pin or 3.3V to free up a control pin
//
// The DC (Data Command) pin may be labelled AO or RS (Register Select)
//
// With some displays such as the ILI9341 the TFT CS pin can be connected to GND if no more
// SPI devices (e.g. an SD Card) are connected, in this case comment out the #define TFT_CS
// line below so it is NOT defined. Other displays such at the ST7735 require the TFT CS pin
// to be toggled during setup, so in these cases the TFT_CS line must be defined and connected.
//
// The NodeMCU D0 pin can be used for RST
//
//
// Note: only some versions of the NodeMCU provide the USB 5V on the VIN pin
// If 5V is not available at a pin you can use 3.3V but backlight brightness
// will be lower.
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP8266 SETUP ######
// // For NodeMCU - use pin numbers in the form PIN_Dx where Dx is the NodeMCU pin designation
// #define TFT_CS PIN_D8 // Chip select control pin D8
// #define TFT_DC PIN_D3 // Data Command control pin
// #define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
// //#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
//#define TFT_BL PIN_D1 // LED back-light (only for ST7789 with backlight control pin)
//#define TOUCH_CS PIN_D2 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR PIN_D2 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// ###### FOR ESP8266 OVERLAP MODE EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE FOLLOWING LINES ######
// Overlap mode shares the ESP8266 FLASH SPI bus with the TFT so has a performance impact
// but saves pins for other functions. It is best not to connect MISO as some displays
// do not tristate that line when chip select is high!
// Note: Only one SPI device can share the FLASH SPI lines, so a SPI touch controller
// cannot be connected as well to the same SPI signals.
// On NodeMCU 1.0 SD0=MISO, SD1=MOSI, CLK=SCLK to connect to TFT in overlap mode
// On NodeMCU V3 S0 =MISO, S1 =MOSI, S2 =SCLK
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the following must be defined
//#define TFT_SPI_OVERLAP
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the TFT chip select MUST connect to pin D3
//#define TFT_CS PIN_D3
//#define TFT_DC PIN_D5 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 SETUP ######
// For ESP32 Dev board (only tested with ILI9341 display)
// The hardware SPI can be mapped to any pins
// #define TFT_MISO 19
// #define TFT_MOSI 23
// #define TFT_SCLK 18
// #define TFT_CS 15 // Chip select control pin
// #define TFT_DC 2 // Data Command control pin
// #define TFT_RST 4 // Reset pin (could connect to RST pin)
// #define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if display RESET is connected to ESP32 board RST
// For ESP32 Dev board (only tested with GC9A01 display)
// The hardware SPI can be mapped to any pins
//#define TFT_MOSI 15 // In some display driver board, it might be written as "SDA" and so on.
//#define TFT_SCLK 14
//#define TFT_CS 5 // Chip select control pin
//#define TFT_DC 27 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST 33 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
//#define TFT_BL 22 // LED back-light
//#define TOUCH_CS 21 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR 22 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// For the M5Stack module use these #define lines
//#define TFT_MISO 19
//#define TFT_MOSI 23
//#define TFT_SCLK 18
//#define TFT_CS 14 // Chip select control pin
//#define TFT_DC 27 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST 33 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
//#define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light (required for M5Stack)
// ###### EDIT THE PINs BELOW TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 PARALLEL TFT SETUP ######
// The library supports 8 bit parallel TFTs with the ESP32, the pin
// selection below is compatible with ESP32 boards in UNO format.
// Wemos D32 boards need to be modified, see diagram in Tools folder.
// Only ILI9481 and ILI9341 based displays have been tested!
// Parallel bus is only supported for the STM32 and ESP32
// Example below is for ESP32 Parallel interface with UNO displays
// Tell the library to use 8 bit parallel mode (otherwise SPI is assumed)
//#define TFT_PARALLEL_8_BIT
// The ESP32 and TFT the pins used for testing are:
//#define TFT_CS 33 // Chip select control pin (library pulls permanently low
//#define TFT_DC 15 // Data Command control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RST 32 // Reset pin, toggles on startup
//#define TFT_WR 4 // Write strobe control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RD 2 // Read strobe control pin
//#define TFT_D0 12 // Must use pins in the range 0-31 for the data bus
//#define TFT_D1 13 // so a single register write sets/clears all bits.
//#define TFT_D2 26 // Pins can be randomly assigned, this does not affect
//#define TFT_D3 25 // TFT screen update performance.
//#define TFT_D4 17
//#define TFT_D5 16
//#define TFT_D6 27
//#define TFT_D7 14
// ###### EDIT THE PINs BELOW TO SUIT YOUR STM32 SPI TFT SETUP ######
// The TFT can be connected to SPI port 1 or 2
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 1 // SPI port 1 maximum clock rate is 55MHz
//#define TFT_MOSI PA7
//#define TFT_MISO PA6
//#define TFT_SCLK PA5
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 2 // SPI port 2 maximum clock rate is 27MHz
//#define TFT_MOSI PB15
//#define TFT_MISO PB14
//#define TFT_SCLK PB13
// Can use Ardiuno pin references, arbitrary allocation, TFT_eSPI controls chip select
//#define TFT_CS D5 // Chip select control pin to TFT CS
//#define TFT_DC D6 // Data Command control pin to TFT DC (may be labelled RS = Register Select)
//#define TFT_RST D7 // Reset pin to TFT RST (or RESET)
// OR alternatively, we can use STM32 port reference names PXnn
//#define TFT_CS PE11 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D5
//#define TFT_DC PE9 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D6
//#define TFT_RST PF13 // Nucleo-F767ZI equivalent of D7
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to processor reset
// Use an Arduino pin for initial testing as connecting to processor reset
// may not work (pulse too short at power up?)
// #define TFT_MISO 19
#define TFT_MOSI 23 // In some display driver board, it might be written as "SDA" and so on.
#define TFT_SCLK 18
#define TFT_CS -1 // Chip select control pin
#define TFT_DC 16 // Data Command control pin
#define TFT_RST 17 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
#define TFT_BL 4 // LED back-light
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 3. Define the fonts that are to be used here
//
// ##################################################################################
// Comment out the #defines below with // to stop that font being loaded
// The ESP8366 and ESP32 have plenty of memory so commenting out fonts is not
// normally necessary. If all fonts are loaded the extra FLASH space required is
// about 17Kbytes. To save FLASH space only enable the fonts you need!
#define LOAD_GLCD // Font 1. Original Adafruit 8 pixel font needs ~1820 bytes in FLASH
#define LOAD_FONT2 // Font 2. Small 16 pixel high font, needs ~3534 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT4 // Font 4. Medium 26 pixel high font, needs ~5848 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT6 // Font 6. Large 48 pixel font, needs ~2666 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.apm
#define LOAD_FONT7 // Font 7. 7 segment 48 pixel font, needs ~2438 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
#define LOAD_FONT8 // Font 8. Large 75 pixel font needs ~3256 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
//#define LOAD_FONT8N // Font 8. Alternative to Font 8 above, slightly narrower, so 3 digits fit a 160 pixel TFT
#define LOAD_GFXFF // FreeFonts. Include access to the 48 Adafruit_GFX free fonts FF1 to FF48 and custom fonts
// Comment out the #define below to stop the SPIFFS filing system and smooth font code being loaded
// this will save ~20kbytes of FLASH
#define SMOOTH_FONT
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 4. Other options
//
// ##################################################################################
// For RP2040 processor and SPI displays, uncomment the following line to use the PIO interface.
//#define RP2040_PIO_SPI // Leave commented out to use standard RP2040 SPI port interface
// For RP2040 processor and 8 or 16 bit parallel displays:
// The parallel interface write cycle period is derived from a division of the CPU clock
// speed so scales with the processor clock. This means that the divider ratio may need
// to be increased when overclocking. I may also need to be adjusted dependant on the
// display controller type (ILI94341, HX8357C etc). If RP2040_PIO_CLK_DIV is not defined
// the library will set default values which may not suit your display.
// The display controller data sheet will specify the minimum write cycle period. The
// controllers often work reliably for shorter periods, however if the period is too short
// the display may not initialise or graphics will become corrupted.
// PIO write cycle frequency = (CPU clock/(4 * RP2040_PIO_CLK_DIV))
//#define RP2040_PIO_CLK_DIV 1 // 32ns write cycle at 125MHz CPU clock
//#define RP2040_PIO_CLK_DIV 2 // 64ns write cycle at 125MHz CPU clock
//#define RP2040_PIO_CLK_DIV 3 // 96ns write cycle at 125MHz CPU clock
// For the RP2040 processor define the SPI port channel used (default 0 if undefined)
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 1 // Set to 0 if SPI0 pins are used, or 1 if spi1 pins used
// For the STM32 processor define the SPI port channel used (default 1 if undefined)
//#define TFT_SPI_PORT 2 // Set to 1 for SPI port 1, or 2 for SPI port 2
// Define the SPI clock frequency, this affects the graphics rendering speed. Too
// fast and the TFT driver will not keep up and display corruption appears.
// With an ILI9341 display 40MHz works OK, 80MHz sometimes fails
// With a ST7735 display more than 27MHz may not work (spurious pixels and lines)
// With an ILI9163 display 27 MHz works OK.
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 1000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 5000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 10000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 20000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 27000000
#define SPI_FREQUENCY 27000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 40000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 55000000 // STM32 SPI1 only (SPI2 maximum is 27MHz)
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 80000000
// Optional reduced SPI frequency for reading TFT
#define SPI_READ_FREQUENCY 20000000
// The XPT2046 requires a lower SPI clock rate of 2.5MHz so we define that here:
#define SPI_TOUCH_FREQUENCY 2500000
// The ESP32 has 2 free SPI ports i.e. VSPI and HSPI, the VSPI is the default.
// If the VSPI port is in use and pins are not accessible (e.g. TTGO T-Beam)
// then uncomment the following line:
//#define USE_HSPI_PORT
// Comment out the following #define if "SPI Transactions" do not need to be
// supported. When commented out the code size will be smaller and sketches will
// run slightly faster, so leave it commented out unless you need it!
// Transaction support is needed to work with SD library but not needed with TFT_SdFat
// Transaction support is required if other SPI devices are connected.
// Transactions are automatically enabled by the library for an ESP32 (to use HAL mutex)
// so changing it here has no effect
// #define SUPPORT_TRANSACTIONS
2.2 主工程代码
/* *****************************************************************
*
* 参考 SmallDesktopDisplay 做的wifi天气时钟
* 创 建 日 期:2023.10.20
* 最后更改日期:2023.10.20
* 更 改 说 明:
* V1.0 最基本功能,支持夜间睡眠模式
*
* 引 脚 分 配:
* SCK GPIO18
* MOSI GPIO23
* RES GPIO17
* DC GPIO16
* LCDBL GPIO4
*
* *****************************************************************/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
#include <HTTPClient.h>
#include <TFT_eSPI.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <TJpg_Decoder.h>
#include <esp_sleep.h>
#include "number.h"
#include "weathernum.h"
#define Version "CL V1.0"
/* *****************************************************************
* 字库、图片库
* *****************************************************************/
#include "font/ZdyLwFont_20.h"
#include "img/misaka.h"
#include "img/temperature.h"
#include "img/humidity.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i0.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i1.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i2.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i3.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i4.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i5.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i6.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i7.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i8.h"
#include "img/pangzi/i9.h"
/* *****************************************************************
* 字库、图片库
* *****************************************************************/
const char ssid[] = "CMCC-pm3h"; // WIFI名称
const char password[] = "hw2htwv4"; // WIFI密码
String cityCode = "101280101"; // 天气城市代码,广州
// 睡眠
#define ENABLE_SLEEP 0 // 是否启用夜间睡眠模式
#define SLEEP_COUNT_NIGHT_MAX 12 // 需要跳过几次,20-8点不更新
#define SLEEP_TIME_START 20 // 20点开始休眠
#define SLEEP_TIME_END 7 // 8点结束休眠
#define SLEEP_TIME_NIGHT 60 // 夜间休眠60min
#define SLEEP_TIME_DAY 10 // 白天休眠10min
TFT_eSPI tft = TFT_eSPI(); // 引脚请自行配置tft_espi库中的 User_Setup.h文件
TFT_eSprite clk = TFT_eSprite(&tft);
time_t time_old = 0; //上次时间刷新时间
time_t weather_old = 0; //上次天气获取时间
time_t banner_old = 0; //上次banner刷新时间
time_t time_now = 0; //当前秒
time_t hour_old = 0;
time_t hour_now = 0;
bool isChangeMode = false; // 定义是否切换动图样式
Number dig;
WeatherNum wrat;
uint32_t targetTime = 0;
int tempNum = 0; //温度百分比
int humiNum = 0; //湿度百分比
int tempCol =0xffff; //温度显示颜色
int humiCol =0xffff; //湿度显示颜色
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// #if ENABLE_SLEEP //不休眠
// sleep_at_night(0); //自动休眠检查
// #endif
print_wakeup_reason();
tft_init(); //屏幕初始化
//连接wifi,并刷新进度条
if(!wifi_connect()) {
// wifi连接失败进入休眠,休眠时长 SLEEP_TIME_DAY
esp_sleep(SLEEP_TIME_DAY);
}
ntp_init(); //ntp服务初始化
//getCityCode(); //根据IP自动获取城市代码,用于后续天气显示
tft_display_loading_complete(); // 将进度条刷到100%
tft_display_layout(); // 绘制屏幕布局
}
void loop(){
time_now = now();
hour_now = hour();
//刷新时间信息,每秒刷新
if (time_now != time_old)
{
time_old = time_now;
tft_display_time();
//整点报时
if(hour_now != hour_old)
{
hour_old = hour_now;
isChangeMode = true;
#if ENABLE_SLEEP //不休眠
//夜间休眠
if(hour_now >= SLEEP_TIME_START || hour_now <= SLEEP_TIME_END){
sleep_at_night(1); // 立即休眠
}
#endif
}
}
// 刷新天气信息,每30分钟刷新
if (time_now - weather_old > 30 * 60){
weather_old = time_now;
getCityWeather();
}
// 刷新banner,每3秒刷新
if (time_now - banner_old > 2){
banner_old = time_now;
tft_display_banner();
}
// 刷新gif
tft_display_gif(isChangeMode);
if(isChangeMode) isChangeMode= false;
}
2.3 tft显示代码
uint16_t bgColor = TFT_BLACK; // 黑色背景色
int Anim = 0; //太空人图标显示指针记录
int AprevTime = 0; //太空人更新时间记录
//初始化屏幕
extern void tft_init(void){
tft.begin(); // TFT初始化
tft.setRotation(0); // 旋转角度0-3
tft.setTextColor(TFT_BLACK, TFT_WHITE); //设置字体颜色
tft.fillScreen(TFT_BLACK); // 清屏
TJpgDec.setJpgScale(1); // 设置放大倍数
TJpgDec.setSwapBytes(true); // 它的作用是设置TFT液晶屏的像素字节序。在某些情况下,像素字节序可能需要被交换,以确保图像正确显示。这段代码中的true表示需要交换字节序,而false则表示不需要交换字节序。
TJpgDec.setCallback(tft_output); // 回调函数
}
extern bool tft_output(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint16_t w, uint16_t h, uint16_t *bitmap) {
if (y >= tft.height())
return 0;
// 这句代码是将一个位图(bitmap)显示在TFT屏幕上,其中x和y是位图左上角的坐标,w和h是位图的宽度和高度。具体来说,它将位图的像素数据推送到TFT屏幕上,从而在指定的位置显示出来。
tft.pushImage(x, y, w, h, bitmap);
return 1;
}
// 进度条
byte loadNum = 6;
extern void tft_display_loading(byte delayTime){
clk.setColorDepth(8); // 设置TFT屏幕的颜色深度为8位。TFT屏幕的颜色深度指的是每个像素点可以显示的颜色数量,8位颜色深度可以显示256种颜色。
clk.createSprite(200, 50); // 创建Sprite
clk.fillSprite(TFT_BLACK); // 填充颜色:黑色
clk.drawRoundRect(0, 0, 200, 16, 8, TFT_WHITE); // 画一个圆角矩形框,白色
clk.fillRoundRect(3, 3, loadNum, 10, 5, TFT_WHITE); // 画一个填充的圆角矩形,白色
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM); // 设置文本显示基准为居中对齐
clk.setTextColor(TFT_GREEN, TFT_BLACK); // 设置文本的前景色和背景色
clk.drawString("Connecting to WiFi", 100, 40, 2); // 显示“Connecting to WiFi”这个字符串,位置为(100,40),字体大小为2。
clk.pushSprite(20, 110); // Sprite中内容一次推向屏幕
clk.deleteSprite(); // 删除Sprite
loadNum += 1;
if (loadNum >= 194)
{
loadNum = 194;
}
delay(delayTime);
}
// 将进度条刷到100%
extern void tft_display_loading_complete(void){
while (loadNum < 194) { //让动画走完
tft_display_loading(1);
}
}
// 绘制屏幕布局
extern void tft_display_layout(void){
tft.fillScreen(bgColor); //清屏
TJpgDec.drawJpg(15,183,temperature, sizeof(temperature)); //温度图标
TJpgDec.drawJpg(15,213,humidity, sizeof(humidity)); //湿度图标
}
// 刷新时间显示
extern void tft_display_time(void){
int timeY = 82;
// 记录上一次时间
static String hourMinute_old = "";
static String second_old = "";
static String week_old = "";
static String monthDay_old = "";
static unsigned char Hour_old = 60;
static unsigned char Minute_old = 60;
static unsigned char Second_old = 60;
String hourMinute_now = hourMinute();
String week_now = week();
String monthDay_now = monthDay();
//--------------------中间时间区显示开始--------------------
// 时分
if(hourMinute_now != hourMinute_old){
hourMinute_old = hourMinute_now;
// 小时刷新
if(hour()!= Hour_old){
dig.printfW3660(20, timeY, hour()/10);
dig.printfW3660(60, timeY, hour()%10);
Hour_old = hour();
}
// 分钟刷新
if(minute()!= Minute_old ){
dig.printfO3660(101, timeY, minute()/10);
dig.printfO3660(141, timeY, minute()%10);
Minute_old = minute();
}
}
// 秒
if(second()!= Second_old){
dig.printfW1830(182, timeY + 30, second()/10);
dig.printfW1830(202, timeY + 30, second()%10);
Second_old = second();
}
//--------------------中间时间区显示结束--------------------
clk.setColorDepth(8);
clk.loadFont(ZdyLwFont_20); // 加载汉字字体
// 星期
if(week_now != week_old){
week_old = week_now;
clk.createSprite(58, 30);
clk.fillSprite(bgColor);
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clk.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor);
clk.drawString(week(),29,16);
clk.pushSprite(102,150);
clk.deleteSprite();;
}
// 月日
if(monthDay_now != monthDay_old) {
monthDay_old = monthDay_now;
clk.createSprite(95, 30);
clk.fillSprite(bgColor);
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clk.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor);
clk.drawString(monthDay(),49,16);
clk.pushSprite(5,150);
clk.deleteSprite();
}
clk.unloadFont(); // 卸载字体
}
//湿度图标显示函数
void humidityWin()
{
clk.setColorDepth(8);
humiNum = humiNum/2;
clk.createSprite(52, 6); //创建窗口
clk.fillSprite(0x0000); //填充率
clk.drawRoundRect(0,0,52,6,3,0xFFFF); //空心圆角矩形 起始位x,y,长度,宽度,圆弧半径,颜色
clk.fillRoundRect(1,1,humiNum,4,2,humiCol); //实心圆角矩形
clk.pushSprite(45,222); //窗口位置
clk.deleteSprite();
}
//温度图标显示函数
extern void tempWin()
{
clk.setColorDepth(8);
clk.createSprite(52, 6); //创建窗口
clk.fillSprite(0x0000); //填充率
clk.drawRoundRect(0,0,52,6,3,0xFFFF); //空心圆角矩形 起始位x,y,长度,宽度,圆弧半径,颜色
clk.fillRoundRect(1,1,tempNum,4,2,tempCol); //实心圆角矩形
clk.pushSprite(45,192); //窗口位置
clk.deleteSprite();
}
String scrollText[6];
// 天气信息写到屏幕上
extern void tft_display_weather(String *cityDZ, String *dataSK, String *dataFC)
{
DynamicJsonDocument doc(1024);
deserializeJson(doc, *dataSK);
JsonObject sk = doc.as<JsonObject>();
/***绘制相关文字***/
clk.setColorDepth(8);
clk.loadFont(ZdyLwFont_20); // 加载汉字字体
// 温度
clk.createSprite(58, 24); // 创建Sprite
clk.fillSprite(bgColor); // 填充颜色
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM); // 显示对齐方式
clk.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor); // 文本的前景色和背景色
clk.drawString(sk["temp"].as<String>() + "℃", 28, 13); // 显示文本
clk.pushSprite(100, 184); // Sprite中内容一次推向屏幕
clk.deleteSprite(); // 删除Sprite
tempNum = sk["temp"].as<int>();
tempNum = tempNum+10;
if(tempNum<10)
tempCol=0x00FF;
else if(tempNum<28)
tempCol=0x0AFF;
else if(tempNum<34)
tempCol=0x0F0F;
else if(tempNum<41)
tempCol=0xFF0F;
else if(tempNum<49)
tempCol=0xF00F;
else
{
tempCol=0xF00F;
tempNum=50;
}
tempWin();
// 湿度
clk.createSprite(58, 24);
clk.fillSprite(bgColor);
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clk.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor);
clk.drawString(sk["SD"].as<String>(), 28, 13);
clk.pushSprite(100, 214);
clk.deleteSprite();
humiNum = atoi((sk["SD"].as<String>()).substring(0,2).c_str());
if(humiNum>90)
humiCol=0x00FF;
else if(humiNum>70)
humiCol=0x0AFF;
else if(humiNum>40)
humiCol=0x0F0F;
else if(humiNum>20)
humiCol=0xFF0F;
else
humiCol=0xF00F;
humidityWin();
//城市名称
clk.createSprite(94, 30);
clk.fillSprite(bgColor);
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clk.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor);
clk.drawString(sk["cityname"].as<String>(),44,16);
clk.pushSprite(15,15);
clk.deleteSprite();
// PM2.5空气指数
uint16_t pm25BgColor = tft.color565(156, 202, 127); // 优
String aqiTxt = "优";
int pm25V = sk["aqi"];
if (pm25V > 200){
pm25BgColor = tft.color565(136, 11, 32); // 重度
aqiTxt = "重度";
}else if (pm25V > 150){
pm25BgColor = tft.color565(186, 55, 121); // 中度
aqiTxt = "中度";
}else if (pm25V > 100){
pm25BgColor = tft.color565(242, 159, 57); // 轻
aqiTxt = "轻度";
}else if (pm25V > 50){
pm25BgColor = tft.color565(247, 219, 100); // 良
aqiTxt = "良";
}
// 先绘制背景颜色
clk.createSprite(56, 24);
clk.fillSprite(bgColor);
clk.fillRoundRect(0,0,50,24,4,pm25BgColor);
// 再绘制文本
clk.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clk.setTextColor(0x0000);
clk.drawString(aqiTxt,25,13);
clk.pushSprite(104,18);
clk.deleteSprite();
scrollText[0] = "实时天气 " + sk["weather"].as<String>();
scrollText[1] = "空气质量 " + aqiTxt;
scrollText[2] = "风向 " + sk["WD"].as<String>() + sk["WS"].as<String>();
//天气图标
wrat.printfWeather(170,15,atoi((sk["weathercode"].as<String>()).substring(1,3).c_str()));
// 左上角滚动字幕
// 解析第二段JSON
deserializeJson(doc, *cityDZ);
JsonObject dz = doc.as<JsonObject>();
//Serial.println(sk["ws"].as<String>());
//横向滚动方式
//String aa = "今日天气:" + dz["weather"].as<String>() + ",温度:最低" + dz["tempn"].as<String>() + ",最高" + dz["temp"].as<String>() + " 空气质量:" + aqiTxt + ",风向:" + dz["wd"].as<String>() + dz["ws"].as<String>();
//scrollTextWidth = clk.textWidth(scrollText);
//Serial.println(aa);
scrollText[3] = "今日" + dz["weather"].as<String>();
deserializeJson(doc, *dataFC);
JsonObject fc = doc.as<JsonObject>();
scrollText[4] = "最低温度" + fc["fd"].as<String>() + "℃";
scrollText[5] = "最高温度" + fc["fc"].as<String>() + "℃";
//Serial.println(scrollText[0]);
clk.unloadFont();
}
int currentIndex = 0;
int prevTime = 0;
TFT_eSprite clkb = TFT_eSprite(&tft);
// 天气滚动条显示
extern void tft_display_banner(void){
if(scrollText[currentIndex])
{
clkb.setColorDepth(8);
clkb.loadFont(ZdyLwFont_20);
clkb.createSprite(150, 30);
clkb.fillSprite(bgColor);
clkb.setTextWrap(false);
clkb.setTextDatum(CC_DATUM);
clkb.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, bgColor);
clkb.drawString(scrollText[currentIndex],74, 16);
clkb.pushSprite(10,45);
clkb.deleteSprite();
clkb.unloadFont();
if(currentIndex>=5)
currentIndex = 0; //回第一个
else
currentIndex += 1; //准备切换到下一个
}
prevTime = 1;
}
// 刷新gif
extern void tft_display_gif(bool isChangeMode)
{
int x = 160, y = 160;
//x ms切换一次
if(millis() - AprevTime > 37) {
Anim++;
AprevTime = millis();
}
if(Anim==10)
Anim=0;
switch(Anim)
{
case 0:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i0, sizeof(i0));
break;
case 1:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i1, sizeof(i1));
break;
case 2:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i2, sizeof(i2));
break;
case 3:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i3, sizeof(i3));
break;
case 4:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i4, sizeof(i4));
break;
case 5:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i5, sizeof(i5));
break;
case 6:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i6, sizeof(i6));
break;
case 7:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i7, sizeof(i7));
break;
case 8:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i8, sizeof(i8));
break;
case 9:
TJpgDec.drawJpg(x,y,i9, sizeof(i9));
break;
default:
Serial.println("显示Anim错误");
break;
}
}
2.4 睡眠模式
#define TFT_COMMAND_HWRESET 0x61 //tft command: HWRESET(61h): Hardeware Reset
#define TFT_COMMAND_SWRESET 0x01 //tft command: SWRESET(01h): Software Reset
#define TFT_COMMAND_SLPIN 0x10 //tft command: SLPIN(10h): Sleep In mode
#define TFT_COMMAND_DLPOFFSAVE 0xBD //tft command: DLPOFFSAVE (BDh): Display off power save
#define TFT_COMMANDDATA_DOFSAVE 0x00 //tft command data: Power save for display off mode. When DOFSAVE=0, power consumption in display off mode will be saved.
#define TFT_COMMAND_DELAY 10 //delay 10ms for next command
//打开显示
static void tft_display_reset(void){
tft.writecommand(TFT_COMMAND_HWRESET);//Hardeware Reset
delayMicroseconds(TFT_COMMAND_DELAY);
tft.writecommand(TFT_COMMAND_SWRESET);//Software Reset
delayMicroseconds(TFT_COMMAND_DELAY);
}
//关闭显示
static void tft_display_off(void){
tft.writecommand(TFT_COMMAND_SLPIN); //tft 设置为 Sleep In mode
delayMicroseconds(TFT_COMMAND_DELAY);
tft.writecommand(TFT_COMMAND_DLPOFFSAVE); //tft 设置为 Display off power save
delayMicroseconds(TFT_COMMAND_DELAY);
tft.writedata(TFT_COMMANDDATA_DOFSAVE);
delayMicroseconds(TFT_COMMAND_DELAY);
}
#define uS_TO_S_FACTOR 1000000 /* Conversion factor for micro seconds to seconds */
#define TIME_TO_SLEEP 5 /* Time ESP32 will go to sleep (in seconds) */
extern void print_wakeup_reason(){
esp_sleep_wakeup_cause_t wakeup_reason;
wakeup_reason = esp_sleep_get_wakeup_cause();
switch(wakeup_reason)
{
case ESP_SLEEP_WAKEUP_EXT0 : Serial.println("Wakeup caused by external signal using RTC_IO"); break;
case ESP_SLEEP_WAKEUP_EXT1 : Serial.println("Wakeup caused by external signal using RTC_CNTL"); break;
case ESP_SLEEP_WAKEUP_TIMER : Serial.println("Wakeup caused by timer"); break;
case ESP_SLEEP_WAKEUP_TOUCHPAD : Serial.println("Wakeup caused by touchpad"); break;
case ESP_SLEEP_WAKEUP_ULP : Serial.println("Wakeup caused by ULP program"); break;
default : Serial.printf("Wakeup was not caused by deep sleep: %d\n",wakeup_reason); break;
}
}
// 系统休眠
extern void esp_sleep(unsigned int minutes){
tft_display_off(); //关闭显示
if (minutes > 70) minutes = 70;
uint32_t timeOut = minutes * 60 * 1000000;
Serial.println(timeOut);
esp_sleep_enable_timer_wakeup(timeOut);// 定时时间,单位μ秒, 类型uint64_t, 所以定时时间要在584942年以内
Serial.println("进入睡眠模式");
Serial.print("时间睡眠(分钟):");
Serial.println(minutes);
esp_deep_sleep_start();
}
RTC_DATA_ATTR int RTC_sleep_count_night = 0; // 20-8点不更新
//夜间休眠, 0-自动,1-立即
extern void sleep_at_night(unsigned int type){
//立即休眠
if (type == 1){
Serial.println("need sleep");
RTC_sleep_count_night = 1;
esp_sleep(SLEEP_TIME_NIGHT);
return;
}
//自动判断是否休眠
Serial.printf("RTC_sleep_count_night: %d\n", RTC_sleep_count_night);
// 继续休眠
if (RTC_sleep_count_night < SLEEP_COUNT_NIGHT_MAX){
Serial.println("auto sleep");
++RTC_sleep_count_night;
esp_sleep(SLEEP_TIME_NIGHT);
return;
}
Serial.println("weak up");
//不休眠则点亮屏幕
tft_display_reset();
}
2.5 获取天气信息
//获取城市代码
extern void getCityCode(void)
{
String URL = "http://wgeo.weather.com.cn/ip/?_=" + String(now());
//创建 HTTPClient 对象
HTTPClient httpClient;
//配置请求地址。此处也可以不使用端口号和PATH而单纯的
httpClient.begin(URL);
//设置请求头中的User-Agent
httpClient.setUserAgent("Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 11_0 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/604.1.38 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/11.0 Mobile/15A372 Safari/604.1");
// 不加这一句拿不到对应编号 感觉这里是特意处理了 不建议一直调用
httpClient.addHeader("Referer", "http://www.weather.com.cn/");
//启动连接并发送HTTP请求
int httpCode = httpClient.GET();
Serial.print("Send GET request to URL: ");
Serial.println(URL);
//如果服务器响应OK则从服务器获取响应体信息并通过串口输出
if (httpCode == HTTP_CODE_OK){
String str = httpClient.getString();
Serial.print("Get Response: ");
Serial.println(str);
int aa = str.indexOf("id=");
if (aa > -1){
//cityCode = str.substring(aa+4,aa+4+9).toInt();
cityCode = str.substring(aa + 4, aa + 4 + 9);
Serial.println(cityCode);
}else{
Serial.println("获取城市代码失败");
}
} else {
Serial.println("请求城市代码错误:");
Serial.println(httpCode);
}
//关闭与服务器连接
httpClient.end();
}
// 获取城市天气
extern void getCityWeather(void){
String URL = "http://d1.weather.com.cn/weather_index/" + cityCode + ".html?_=" + String(now());
//创建 HTTPClient 对象
HTTPClient httpClient;
httpClient.begin(URL);
//设置请求头中的User-Agent
httpClient.setUserAgent("Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 11_0 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/604.1.38 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/11.0 Mobile/15A372 Safari/604.1");
httpClient.addHeader("Referer", "http://www.weather.com.cn/");
//启动连接并发送HTTP请求
int httpCode = httpClient.GET();
Serial.println("正在获取天气数据");
Serial.println(URL);
//如果服务器响应OK则从服务器获取响应体信息并通过串口输出
if (httpCode == HTTP_CODE_OK){
String str = httpClient.getString();
int indexStart = str.indexOf("weatherinfo\":");
int indexEnd = str.indexOf("};var alarmDZ");
String jsonCityDZ = str.substring(indexStart + 13, indexEnd);
Serial.println(jsonCityDZ);
indexStart = str.indexOf("dataSK =");
indexEnd = str.indexOf(";var dataZS");
String jsonDataSK = str.substring(indexStart + 8, indexEnd);
Serial.println(jsonDataSK);
indexStart = str.indexOf("\"f\":[");
indexEnd = str.indexOf(",{\"fa");
String jsonFC = str.substring(indexStart + 5, indexEnd);
Serial.println(jsonFC);
tft_display_weather(&jsonCityDZ, &jsonDataSK, &jsonFC);
Serial.println("获取成功");
}else{
Serial.println("请求城市天气错误:");
Serial.print(httpCode);
}
//关闭与服务器连接
httpClient.end();
}


![2023年中国自动排气阀产业链、市场规模及存在问题分析]图[](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9cc8e72252ce081b74d8f2af16c45015.png)