文章目录
- 前言
- 问题
- 原理
- TagLocation流程
- 入口
- LookupIndex
- findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys
- HoodieKeyLookupHandle
- 如何优化
- 问题一 如何避免大量 IO
- 问题二 如何减少计算 Hash
- 问题三 使用什么结构优化比对结果
- 如何初始化树
- 查询
- 总结
前言
Hudi 系列文章在这个这里查看 https://github.com/leosanqing/big-data-study
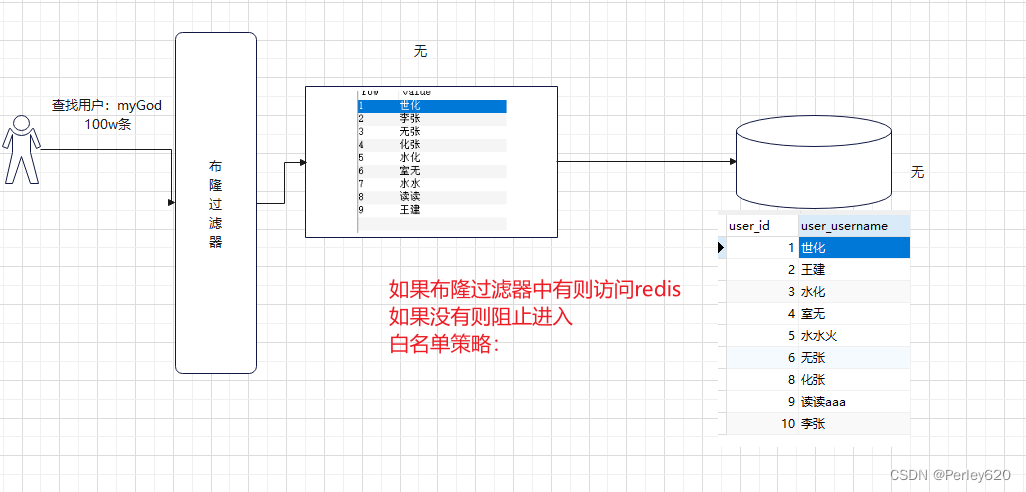
Bloom 索引是 Hudi 中非常重要的一个索引,他利用 Bloom 过滤器进行快速确认
问题
- 原理
- 优化手段有哪些
- 优缺点
- 如何消除假阳性影响
原理
bloom 索引原理就是使用 bloom 过滤器.我们都知道存储数据的三种数据结构,链表,数组,hash 表(散列表).每种 数据结构对空间复杂度,查询,删除时间复杂度是不一样的.Bloom 本质是利用 Hash 表操作
关于 Bloom 过滤器的原理可以看这篇文章
Bloom 过滤器
简单说就是用一个一定长度的BitMap,比如 M,然后准备 K 个 Hash 函数,然后一个值映分别进行 Hash 算法后得到 K 个值,这 k 个值映射到这个 BitMap 上,后续我判断这个数据存不存在,我只要再经过K个 hash 算法算一下,再查看这个 BitMap 就知道了.所以时间复杂度是O(K),空间复杂度是O(M)
但是所有散列表都会有一个问题,Hash 碰撞,HashMap上就通过链表或者红黑树存储这些值
在 Bloom 过滤器中,就没法解决这个问题,因为他本身不存储值,无法比较.所以会有假阳性问题,即如果 BitMap 不符合,那就一定不存在,但是 BitMap 符合,这个值不一定存在
TagLocation流程
刚刚说了,Bloom 实际上是利用 Bloom 过滤器判断是否要读取 parquet 文件里面的数据,再比较
所以最原始的流程应该是:
- 从 parquet 文件中的读取到 BitMap,判断是否在文件中
- 如果没命中,那就是真的不在, insert
- 如果命中 Bloom 索引,因为假阳性问题,还需要再判断是不是真的在文件里面
入口
所有索引的源码都在这个包下 org.apache.hudi.index
打标签的入口方法是这个org.apache.hudi.index.bloom.HoodieBloomIndex#tagLocation
在这个方法中,逻辑主要为这几步(重点是第三步)
-
根据配置缓存输入记录JavaRDD,避免重复加载开销。
-
提取 record 的关键信息,组成分区,主键键值对
-
根据键值对,去查找索引,获取文件 Id 等信息
-
缓存第三步结果。
-
给数据打标LeftOuterJoin,即哪些是 Insert,那些是 Update 并返回。
@Override
public <R> HoodieData<HoodieRecord<R>> tagLocation(
HoodieData<HoodieRecord<R>> records, HoodieEngineContext context,
HoodieTable hoodieTable) {
// Step 0: cache the input records if needed
if (config.getBloomIndexUseCaching()) {
records.persist(new HoodieConfig(config.getProps())
.getString(HoodieIndexConfig.BLOOM_INDEX_INPUT_STORAGE_LEVEL_VALUE));
}
// Step 1: Extract out thinner pairs of (partitionPath, recordKey)
HoodiePairData<String, String> partitionRecordKeyPairs = records.mapToPair(
record -> new ImmutablePair<>(record.getPartitionPath(), record.getRecordKey()));
// Step 2: Lookup indexes for all the partition/recordkey pair
HoodiePairData<HoodieKey, HoodieRecordLocation> keyFilenamePairs =
lookupIndex(partitionRecordKeyPairs, context, hoodieTable);
// Cache the result, for subsequent stages.
if (config.getBloomIndexUseCaching()) {
keyFilenamePairs.persist(new HoodieConfig(config.getProps())
.getString(HoodieIndexConfig.BLOOM_INDEX_INPUT_STORAGE_LEVEL_VALUE));
}
// Step 3: Tag the incoming records, as inserts or updates, by joining with existing record keys
HoodieData<HoodieRecord<R>> taggedRecords = tagLocationBacktoRecords(keyFilenamePairs, records, hoodieTable);
if (config.getBloomIndexUseCaching()) {
records.unpersist();
keyFilenamePairs.unpersist();
}
return taggedRecords;
}
LookupIndex
步骤为:(最重要的是第三步,即怎么 根据主键确定数据存不存在)
-
将传入的 records,根据分区进行分组,并统计每个分区下record的数量
-
去每个分区下面找到相应的parquet文件(主要是符合 InstantTime的 parquet),
getBloomIndexFileInfoForPartitions方法 -
过滤掉文件中没有的数据(即新增的数据)返回(step3 和findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys)
/**
* Lookup the location for each record key and return the pair<record_key,location> for all record keys already
* present and drop the record keys if not present.
*/
private HoodiePairData<HoodieKey, HoodieRecordLocation> lookupIndex(
HoodiePairData<String, String> partitionRecordKeyPairs, final HoodieEngineContext context,
final HoodieTable hoodieTable) {
// Step 1: Obtain records per partition, in the incoming records
Map<String, Long> recordsPerPartition = partitionRecordKeyPairs.countByKey();
List<String> affectedPartitionPathList = new ArrayList<>(recordsPerPartition.keySet());
// Step 2: Load all involved files as <Partition, filename> pairs
List<Pair<String, BloomIndexFileInfo>> fileInfoList = getBloomIndexFileInfoForPartitions(context, hoodieTable, affectedPartitionPathList);
final Map<String, List<BloomIndexFileInfo>> partitionToFileInfo =
fileInfoList.stream().collect(groupingBy(Pair::getLeft, mapping(Pair::getRight, toList())));
// Step 3: Obtain a HoodieData, for each incoming record, that already exists, with the file id,
// that contains it.
HoodiePairData<HoodieFileGroupId, String> fileComparisonPairs =
explodeRecordsWithFileComparisons(partitionToFileInfo, partitionRecordKeyPairs);
return bloomIndexHelper.findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys(config, context, hoodieTable,
partitionRecordKeyPairs, fileComparisonPairs, partitionToFileInfo, recordsPerPartition);
}
/** 重点是这个方法 getFileInfoForLatestBaseFiles, 其他都是优化 */
private List<Pair<String, BloomIndexFileInfo>> getBloomIndexFileInfoForPartitions(HoodieEngineContext context,
HoodieTable hoodieTable,
List<String> affectedPartitionPathList) {
List<Pair<String, BloomIndexFileInfo>> fileInfoList = new ArrayList<>();
...
fileInfoList = getFileInfoForLatestBaseFiles(affectedPartitionPathList, context, hoodieTable);
...
return fileInfoList;
}
findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys
主要做几件事情(重点是第三和第四步)
- 算查找索引的时候的并行度
- 根据配置是否使用缓存
- 读取 parquet 文件 Footer 数据,找出索引策略,反序列化出 BitMap
HoodieSparkBloomIndexCheckFunctionHoodieKeyLookupHandle - 挨个比较parquet 文件中的数据
/// 主要应该看这个方法,其他分支的都是优化手段
keyLookupResultRDD = fileComparisonsRDD.sortByKey(true, targetParallelism)
.mapPartitions(new HoodieSparkBloomIndexCheckFunction(hoodieTable, config), true);
// 重点应该关注这个类 HoodieSparkBloomIndexCheckFunction
// 根据主键查找索引这个方法在 org.apache.hudi.index.bloom.HoodieBloomIndexCheckFunction.LazyKeyCheckIterator#computeNext
HoodieKeyLookupHandle
HoodieKeyLookupHandle 初始化这个类的时候,会真正去 Parquet 文件的 footer 中找到 bitMap
public HoodieKeyLookupHandle(HoodieWriteConfig config, HoodieTable<T, I, K, O> hoodieTable,
Pair<String, String> partitionPathFileIDPair) {
super(config, hoodieTable, partitionPathFileIDPair);
this.candidateRecordKeys = new ArrayList<>();
this.totalKeysChecked = 0;
// 初始化 BloomFilter
this.bloomFilter = getBloomFilter();
}
private BloomFilter getBloomFilter() {
try (HoodieFileReader reader = createNewFileReader()) {
bloomFilter = reader.readBloomFilter();
}
return bloomFilter;
}
/**
* Read the bloom filter from the metadata of the given data file.
* @param configuration Configuration
* @param filePath The data file path
* @return a BloomFilter object
*/
public BloomFilter readBloomFilterFromMetadata(Configuration configuration, Path filePath) {
Map<String, String> footerVals =
readFooter(configuration, false, filePath,
HoodieAvroWriteSupport.HOODIE_AVRO_BLOOM_FILTER_METADATA_KEY,
HoodieAvroWriteSupport.OLD_HOODIE_AVRO_BLOOM_FILTER_METADATA_KEY,
HoodieBloomFilterWriteSupport.HOODIE_BLOOM_FILTER_TYPE_CODE);
String footerVal = footerVals.get(HoodieAvroWriteSupport.HOODIE_AVRO_BLOOM_FILTER_METADATA_KEY);
if (null == footerVal) {
// We use old style key "com.uber.hoodie.bloomfilter"
footerVal = footerVals.get(HoodieAvroWriteSupport.OLD_HOODIE_AVRO_BLOOM_FILTER_METADATA_KEY);
}
BloomFilter toReturn = null;
if (footerVal != null) {
if (footerVals.containsKey(HoodieBloomFilterWriteSupport.HOODIE_BLOOM_FILTER_TYPE_CODE)) {
toReturn = BloomFilterFactory.fromString(footerVal,
footerVals.get(HoodieBloomFilterWriteSupport.HOODIE_BLOOM_FILTER_TYPE_CODE));
} else {
toReturn = BloomFilterFactory.fromString(footerVal, BloomFilterTypeCode.SIMPLE.name());
}
}
return toReturn;
}
public HoodieKeyLookupResult getLookupResult() {
HoodieBaseFile baseFile = getLatestBaseFile();
List<String> matchingKeys = HoodieIndexUtils.filterKeysFromFile(new Path(baseFile.getPath()), candidateRecordKeys,
hoodieTable.getHadoopConf());
return new HoodieKeyLookupResult(partitionPathFileIDPair.getRight(), partitionPathFileIDPair.getLeft(),
baseFile.getCommitTime(), matchingKeys);
}
public static List<String> filterKeysFromFile(Path filePath, List<String> candidateRecordKeys,
Configuration configuration) throws HoodieIndexException {
...
List<String> foundRecordKeys = new ArrayList<>();
try (HoodieFileReader fileReader = HoodieFileReaderFactory.getReaderFactory(HoodieRecordType.AVRO)
.getFileReader(configuration, filePath)) {
// Load all rowKeys from the file, to double-confirm
Set<String> fileRowKeys = fileReader.filterRowKeys(new TreeSet<>(candidateRecordKeys));
foundRecordKeys.addAll(fileRowKeys);
return foundRecordKeys;
}
// 去 parquet 文件中,挨个查找 recordKey
/**
* Read the rowKey list matching the given filter, from the given parquet file. If the filter is empty, then this will
* return all the rowkeys.
*
* @param filePath The parquet file path.
* @param configuration configuration to build fs object
* @param filter record keys filter
* @param readSchema schema of columns to be read
* @return Set Set of row keys matching candidateRecordKeys
*/
private static Set<String> filterParquetRowKeys(Configuration configuration, Path filePath, Set<String> filter,
Schema readSchema) {
Set<String> rowKeys = new HashSet<>();
try (ParquetReader reader = AvroParquetReader.builder(filePath).withConf(conf).build()) {
Object obj = reader.read();
while (obj != null) {
if (obj instanceof GenericRecord) {
String recordKey = ((GenericRecord) obj).get(HoodieRecord.RECORD_KEY_METADATA_FIELD).toString();
// 挨个比较数据
if (!filterFunction.isPresent() || filterFunction.get().apply(recordKey)) {
rowKeys.add(recordKey);
}
}
obj = reader.read();
}
return rowKeys;
}
如何优化
问题一 如何避免大量 IO
我们看到Bloom 索引的原理看上去非常简单,但是执行起来会非常繁琐
BloomFilter 的 BitMap 存在 Parquet Footer 中, 光遍历 BitMap,放到 Map 中都需要大量 IO 操作,如何避免大量 IO 操作
把数据缓存起来
假如我把这些数据放到 MetaData 中,从这里获取,这样就不用涉及大量 IO 操作了
来看看 Hudi 怎么做的,还记得我们之前的这步findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys,提到其他都是优化手段,主分支逻辑就是最后的 else,其中一个优化手段就是把 BloomFilter 缓存起来,减少真正去读取 Parquet 的 IO 操作
// org.apache.hudi.index.bloom.SparkHoodieBloomIndexHelper#findMatchingFilesForRecordKeys
// 参数为 hoodie.bloom.index.use.metadata = true
if (config.getBloomIndexUseMetadata()
&& hoodieTable.getMetaClient().getTableConfig().getMetadataPartitions()
.contains(BLOOM_FILTERS.getPartitionPath())) {
XXXX
} else {
keyLookupResultRDD = fileComparisonsRDD.sortByKey(true, targetParallelism)
.mapPartitions(new HoodieSparkBloomIndexCheckFunction(hoodieTable, config), true);
}
问题二 如何减少计算 Hash
虽然我们缓存了 BloomFilter 的 BitMap,但是我们还是要挨个算一下,需要消耗 O(K),那能不能减少这步的操作.
当然可以,我们只需要在记录一下这个文件的 RowKey 的最大值,最小值,就可以根据比较这两个值来过滤,不用再计算了
这个就在LookupIndex 的第二步,之前提到的主要逻辑都是 else 中的,if 中的就是优化手段
从下面代码可以看出来,这个方式和上面的缓存方式是解耦的,如果没缓存,就从 parquet 文件 Footer 中获取
// 参数为 hoodie.bloom.index.prune.by.ranges
if (config.getBloomIndexPruneByRanges()) {
// load column ranges from metadata index if column stats index is enabled and column_stats metadata partition is available
if (config.getBloomIndexUseMetadata()
&& hoodieTable.getMetaClient().getTableConfig().getMetadataPartitions().contains(COLUMN_STATS.getPartitionPath())) {
fileInfoList = loadColumnRangesFromMetaIndex(affectedPartitionPathList, context, hoodieTable);
}
// fallback to loading column ranges from files
if (isNullOrEmpty(fileInfoList)) {
fileInfoList = loadColumnRangesFromFiles(affectedPartitionPathList, context, hoodieTable);
}
} else {
fileInfoList = getFileInfoForLatestBaseFiles(affectedPartitionPathList, context, hoodieTable);
}
问题三 使用什么结构优化比对结果
如果我们开启了rowKey 的裁剪(即最大值最小值),把所有parquet 的中的最大值,最小值也拿到了,那我应该用什么数据结构优化查询速度呢
- 链表
- 树
答案是用树,因为树的查询效率是 LogN,链表为O(N),但是树在一开始初始化的时候效率就没有链表高,O(LogN),链表为 O(1)
/// org.apache.hudi.index.bloom.HoodieBloomIndex#explodeRecordsWithFileComparisons
// 参数为 hoodie.bloom.index.use.treebased.filter
HoodiePairData<HoodieFileGroupId, String> explodeRecordsWithFileComparisons(
final Map<String, List<BloomIndexFileInfo>> partitionToFileIndexInfo,
HoodiePairData<String, String> partitionRecordKeyPairs) {
IndexFileFilter indexFileFilter =
config.useBloomIndexTreebasedFilter() ? new IntervalTreeBasedIndexFileFilter(partitionToFileIndexInfo)
: new ListBasedIndexFileFilter(partitionToFileIndexInfo);
return partitionRecordKeyPairs.map(partitionRecordKeyPair -> {
String recordKey = partitionRecordKeyPair.getRight();
String partitionPath = partitionRecordKeyPair.getLeft();
return indexFileFilter.getMatchingFilesAndPartition(partitionPath, recordKey)
.stream()
.map(partitionFileIdPair ->
new ImmutablePair<>(
new HoodieFileGroupId(partitionFileIdPair.getLeft(), partitionFileIdPair.getRight()), recordKey));
})
.flatMapToPair(Stream::iterator);
}
// 如果没有开启 rowKey 修剪(最大/最小值),因为没法比较,所以两个都做了特殊处理
// 没开启,树就把他分区下的所有文件直接放到一个 Map 中,不是树了
if (partitionToFilesWithNoRanges.containsKey(partitionPath)) {
partitionToFilesWithNoRanges.get(partitionPath).forEach(file ->
toReturn.add(Pair.of(partitionPath, file)));
}
// 链表的话,也是直接把分区下的文件全部放进去
// org.apache.hudi.index.bloom.ListBasedIndexFileFilter#shouldCompareWithFile
if (shouldCompareWithFile(indexInfo, recordKey)) {
toReturn.add(Pair.of(partitionPath, indexInfo.getFileId()));
}
protected boolean shouldCompareWithFile(BloomIndexFileInfo indexInfo, String recordKey) {
return !indexInfo.hasKeyRanges() || indexInfo.isKeyInRange(recordKey);
}
开启的话,链表就不说了,比较简单,他会挨个去遍历.这里重点说在树的情况下,怎么加快查询
如何初始化树
IntervalTreeBasedIndexFileFilter(final Map<String, List<BloomIndexFileInfo>> partitionToFileIndexInfo) {
partitionToFileIndexInfo.forEach((partition, bloomIndexFiles) -> {
// Note that the interval tree implementation doesn't have auto-balancing to ensure logN search time.
// So, we are shuffling the input here hoping the tree will not have any skewness. If not, the tree could be
// skewed which could result in N search time instead of logN.
// 上来先 shuffle,因为如果读到的文件是这样的,那就会严重倾斜,退化成链表了.原理等下讲构建步骤就知道了,其他也一样,所以随机打乱
// file1[1,50], f2[2,51], f3[3,52], f4[4,53]
Collections.shuffle(bloomIndexFiles);
KeyRangeLookupTree lookUpTree = new KeyRangeLookupTree();
bloomIndexFiles.forEach(indexFileInfo -> {
if (indexFileInfo.hasKeyRanges()) {
lookUpTree.insert(new KeyRangeNode(indexFileInfo.getMinRecordKey(), indexFileInfo.getMaxRecordKey(),
indexFileInfo.getFileId()));
} else {
// 不用看了 这个是不开启修剪的,上面提过了
}
});
partitionToFileIndexLookUpTree.put(partition, lookUpTree);
});
}
// 重点看 insert 方法
// 介绍 insert 前,先讲下如何比较的
public int compareTo(KeyRangeNode that) {
// 如果当前节点的最小值,比要插入的小,就返回 负数
// 最小值相等,就比较最大值.最大值比要插入的小,也返回负数
// 最大值最小值相等,返回 0
int compareValue = minRecordKey.compareTo(that.minRecordKey);
if (compareValue == 0) {
return maxRecordKey.compareTo(that.maxRecordKey);
} else {
return compareValue;
}
}
// insert 比插入值小,插入值就放到右子树,否则放到左子树,相等就直接插入文件就好,用 List 维护
// 在插入的时候还会维护四个值, 左/右子树的最大/最小值.每比较一次就会更新一次
// 所以如果不做 shuffle,按照上面的写法,他就会一直往右子树插入,然后变成一个链表
private KeyRangeNode insert(KeyRangeNode root, KeyRangeNode newNode) {
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
return root;
}
if (root.compareTo(newNode) == 0) {
root.addFiles(newNode.getFileNameList());
return root;
}
if (root.compareTo(newNode) < 0) {
if (root.getRight() == null) {
root.setRightSubTreeMax(newNode.getMaxRecordKey());
root.setRightSubTreeMin(newNode.getMinRecordKey());
root.setRight(newNode);
} else {
if (root.getRightSubTreeMax().compareTo(newNode.getMaxRecordKey()) < 0) {
root.setRightSubTreeMax(newNode.getMaxRecordKey());
}
if (root.getRightSubTreeMin().compareTo(newNode.getMinRecordKey()) > 0) {
root.setRightSubTreeMin(newNode.getMinRecordKey());
}
insert(root.getRight(), newNode);
}
} else {
if (root.getLeft() == null) {
root.setLeftSubTreeMax(newNode.getMaxRecordKey());
root.setLeftSubTreeMin(newNode.getMinRecordKey());
root.setLeft(newNode);
} else {
if (root.getLeftSubTreeMax().compareTo(newNode.getMaxRecordKey()) < 0) {
root.setLeftSubTreeMax(newNode.getMaxRecordKey());
}
if (root.getLeftSubTreeMin().compareTo(newNode.getMinRecordKey()) > 0) {
root.setLeftSubTreeMin(newNode.getMinRecordKey());
}
insert(root.getLeft(), newNode);
}
}
return root;
}
查询
当一个 RowKey 进来,我只要在树上比较就行
在我这个节点最大值最小值范围里,就把这个节点上的所有文件列为待比较项
然后看在不在我左右子树的区间中,在就去相应子树,不在就返回添加的待比较项,本次遍历就完成了
/**
* Fetches all the matching index files where the key could possibly be present.
*
* @param root refers to the current root of the look up tree
* @param lookupKey the key to be searched for
*/
private void getMatchingIndexFiles(KeyRangeNode root, String lookupKey, Set<String> matchingFileNameSet) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 在我这个节点最大值最小值范围里,就把这个节点上的所有文件列为待比较项
if (root.getMinRecordKey().compareTo(lookupKey) <= 0 && lookupKey.compareTo(root.getMaxRecordKey()) <= 0) {
matchingFileNameSet.addAll(root.getFileNameList());
}
// 然后看在不在我左右子树的区间中,在就去相应子树,不在就返回添加的待比较项,本次遍历就完成了
if (root.getLeftSubTreeMax() != null && root.getLeftSubTreeMin().compareTo(lookupKey) <= 0
&& lookupKey.compareTo(root.getLeftSubTreeMax()) <= 0) {
getMatchingIndexFiles(root.getLeft(), lookupKey, matchingFileNameSet);
}
if (root.getRightSubTreeMax() != null && root.getRightSubTreeMin().compareTo(lookupKey) <= 0
&& lookupKey.compareTo(root.getRightSubTreeMax()) <= 0) {
getMatchingIndexFiles(root.getRight(), lookupKey, matchingFileNameSet);
}
}
总结
- 原理: 利用存在 parquet 文件 Footer 的Bloom 过滤器过滤,然后挨个遍历符合的文件
- 优化手段有哪些
- 缓存
- range 修剪
- 树化
- 优缺点
- 优点
- 存储空间少
- 简单
- 缺点
- 假阳性问题
- Flink 无法使用
- 优点
- 如何消除假阳性影响
- 把所有阳性(符合条件)的文件全部打开都真正遍历一遍, 查看RecordKey 是否真的在文件中