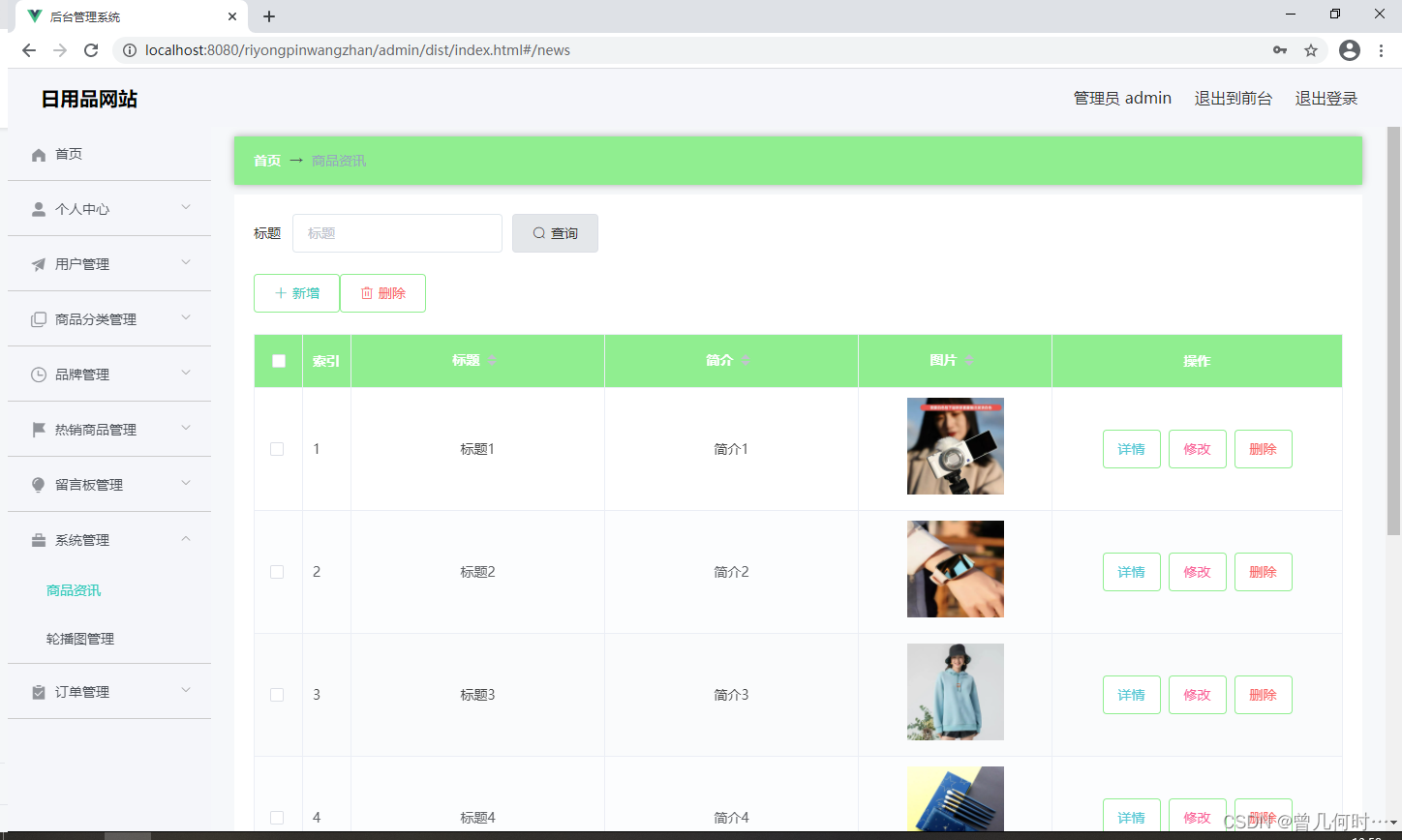
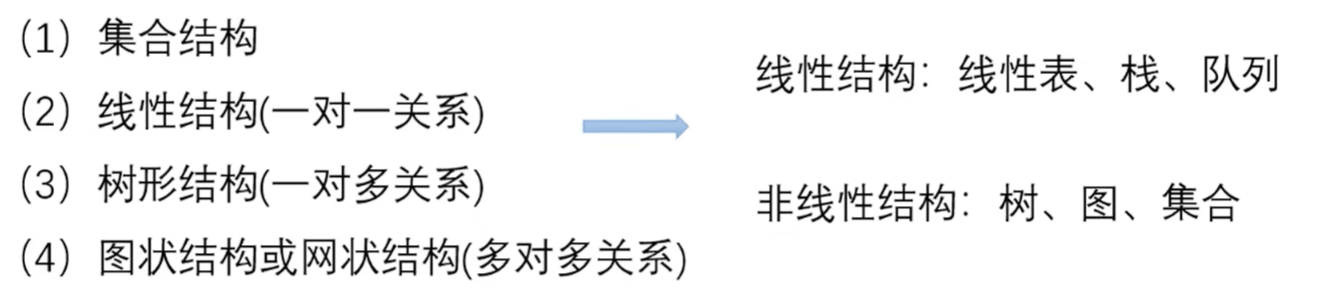
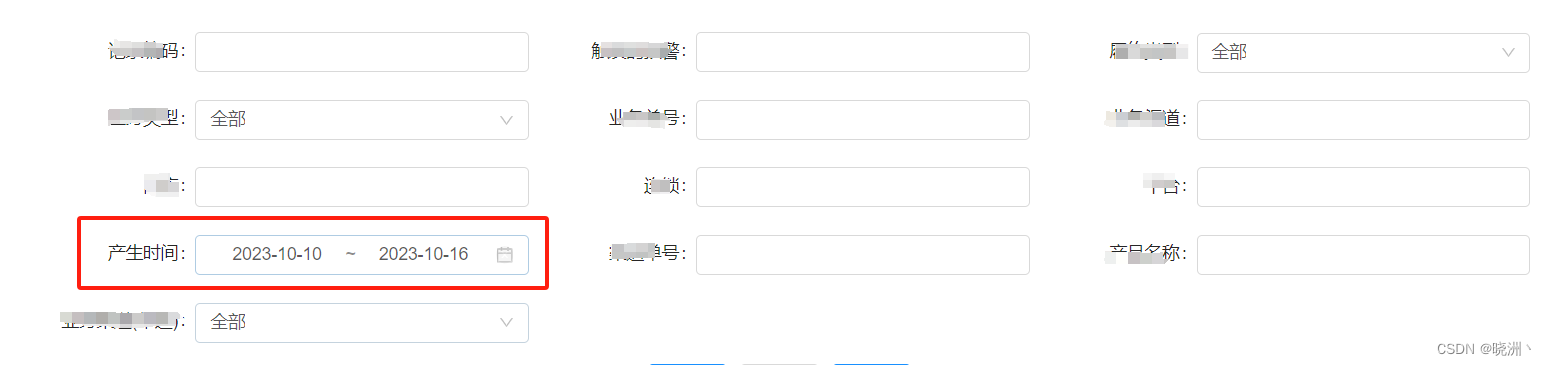
import optimtool as oo
from optimtool.base import np, sp, plt
pip install optimtool # any version with accessible L_BFGS
加载L_BFGS方法
import optimtool.unconstrain as ou
lbfgs = ou.newton_quasi.L_BFGS
f ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n − 1 ( x i + x i + 1 − 3 ) 2 + ( x i − x i + 1 + 1 ) 4 , x 0 = [ 2 , 2 , . . . , 2 ] . f(x)=\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}(x_i+x_{i+1}-3)^2+(x_i-x_{i+1}+1)^4, x_0=[2,2,...,2]. f(x)=i=1∑n−1(xi+xi+1−3)2+(xi−xi+1+1)4,x0=[2,2,...,2].
初始化输入数据
# make data(3 dimension)
x = sp.symbols("x1:4")
f = (x[0] + x[1] - 3)**2 + (x[0] - x[1] + 1)**4 + \
(x[1] + x[2] - 3)**2 + (x[1] - x[2] + 1)**4
x_0 = (2, 2, 2) # Random given
查看L_BFGS超参数
L_BFGS(funcs: FuncArray, args: ArgArray, x_0: PointArray, verbose: bool=False, draw: bool=True, output_f: bool=False, method: str=“wolfe”, m: float=6, epsilon: float=1e-10, k: int=0) -> OutputType
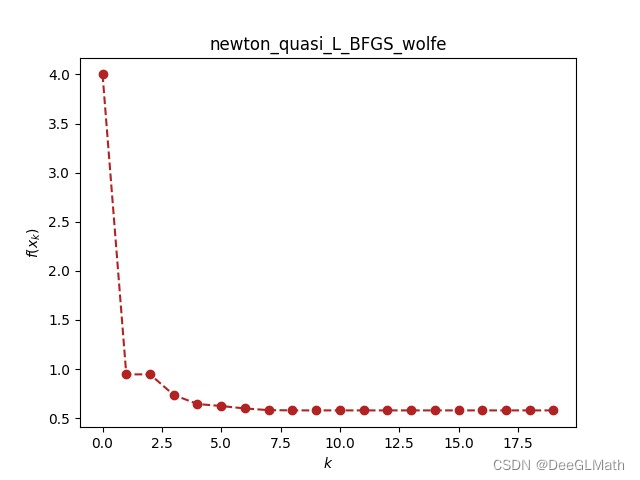
调用并绘制迭代图
print(lbfgs(f, x, x_0, verbose=True))
(2, 2, 2) 4.0 0
[1.25 1.5 2.25] 0.9453125000000002 1
[1.2508132 1.50055287 2.24971504] 0.9455254266849167 2
[1.14857133 1.53464418 2.15242661] 0.7358195964077977 3
[1.08514444 1.59724704 2.00578909] 0.6435684144202295 4
[1.04712651 1.55941861 2.00256007] 0.6233603758928477 5
[1.02980813 1.5177135 1.95872827] 0.5981377885052529 6
[1.06143634 1.49410798 1.92206387] 0.5814170599663506 7
[1.08729744 1.49657415 1.90815247] 0.5786175770124571 8
[1.08940649 1.4996921 1.9096457 ] 0.5785482832298223 9
[1.08979309 1.49998871 1.91028685] 0.5785468604986556 10
[1.08975568 1.49999224 1.91024822] 0.5785468483400542 11
[1.08975376 1.49999833 1.9102448 ] 0.578546847890699 12
[1.08975434 1.49999989 1.91024533] 0.5785468478757178 13
[1.0897545 1.5 1.91024548] 0.5785468478755569 14
[1.08975451 1.5 1.91024549] 0.5785468478755555 15
[1.08975451 1.5 1.91024549] 0.578546847875556 16
[1.08975451 1.5 1.91024549] 0.5785468478755558 17
[1.08975451 1.5 1.91024549] 0.5785468478755561 18
[1.08975451 1.5 1.91024549] 0.5785468478755559 19