文章目录
- 1. 使用 ActionQueryKnowledgeBase
- 创建知识库
- NLU数据
- 2. 音乐机器人
- nlu.yml
- stories.yml
- rules.yml
- domain.yml
- config.yml
- endpoints.yml
- data.json
- 自定义动作 actions.py
- 测试
- 使用Neo4j
learn from https://github.com/Chinese-NLP-book/rasa_chinese_book_code
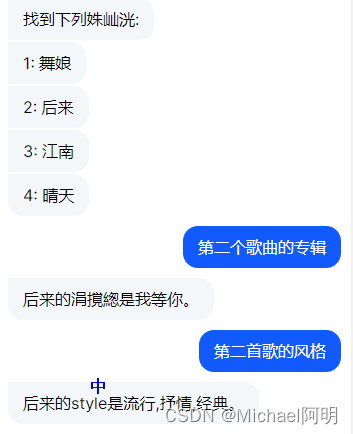
机器人返回了一个列表,用户说第X个,你得知道他说的是啥
1. 使用 ActionQueryKnowledgeBase
创建知识库
最简单的知识库 json 文件
{
"song": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "晴天",
"singer": "周杰伦",
"album": "叶惠美",
"style": "流行,英伦摇滚"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "江南",
"singer": "林俊杰",
"album": "第二天堂",
"style": "流行,中国风"
},
],
"singer": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "周杰伦",
"gender": "male",
"birthday": "1979/01/18"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "林俊杰",
"gender": "male",
"birthday": "1979/03/27"
},
]
}
格式 key : [object1,object2...]
InMemoryKnowledgeBase 实现中,每个 obj 都有至少有 name,id 属性
NLU数据
意图想要进行知识库信息查询
version: "3.0"
nlu:
- intent: query_knowledge_base
examples: |
- 有什么好听的[歌曲](object_type)?
- 有什么唱歌好听的[歌手](object_type)?
- 给我列一些[男](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列出一些[周杰伦](singer)的[歌曲](object_type)
- [刚才那首](mention)属于什么[专辑](attribute)
- [刚才那首](mention)是[谁](attribute)唱的
- [刚才那首](mention)的[歌手](attribute)是谁
- [那首歌](mention)属于什么[风格](attribute)?
- [晴天](song)这首歌属于什么[专辑](attribute)?
- [晴天](song)的[专辑](attribute)?
- [江南](song)属于什么[专辑](attribute)?
- [江南](song)在什么[专辑](attribute)里面?
- [第一个](mention)人的[生日](attribute)
- [周杰伦](singer)的[生日](attribute)
object_type将歌曲映射为songmention将第一个,最后一个的表述标注化为1,LASTattribute'知识库中 obj 的属性,在 nlu 训练数据中都要标注为attribute
同时 domain.yml 文件需要加入
entities:
- object_type
- mention
- attribute
- object-type
- song
- singer
- gender
slots:
attribute:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: attribute
gender:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: gender
knowledge_base_last_object:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_last_object_type:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_listed_objects:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_objects:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
mention:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: mention
object_type:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: object_type
singer:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: singer
song:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: song
2. 音乐机器人
tree
.
├── actions.py
├── config.yml
├── credentials.yml
├── data
│ ├── nlu.yml
│ ├── rules.yml
│ └── stories.yml
├── data.json
├── data_to_neo4j.py
├── dicts
│ ├── ordinal.txt
│ └── songs.txt
├── domain.yml
├── endpoints.yml
├── en_to_zh.json
├── index.html
├── index.js
├── __init__.py
├── Makefile
├── media
│ ├── demo2.png
│ └── demo.png
├── neo4j_knowledge_base.py
├── README.md
├── run_neo4j_in_docker.bash
└── tests
└── basic.md
nlu.yml
version: "3.0"
nlu:
- intent: goodbye
examples: |
- 拜拜
- 再见
- 拜
- 退出
- 结束
- intent: greet
examples: |
- 你好
- 您好
- Hello
- hello
- Hi
- hi
- 喂
- 在么
- intent: query_knowledge_base
examples: |
- 有什么好听的[歌曲](object_type)?
- 有什么唱歌好听的[歌手](object_type)?
- 给我列一些[歌曲](object_type)
- 给我列一些[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[男](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[男](gender)的[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[女](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[女](gender)的[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[男性](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列一些[女性](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我[男性](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我[女性](gender)[歌手](object_type)
- 给我列出一些[周杰伦](singer)的[歌曲](object_type)
- 给我列出[周杰伦](singer)的[歌曲](object_type)
- 给我列出[周杰伦](singer)唱的[歌曲](object_type)
- 列出[周杰伦](singer)的[歌曲](object_type)
- 给我列[周杰伦](singer)的[歌曲](object_type)
- [林俊杰](singer)都有什么[歌曲](object_type)
- [林俊杰](singer)有什么[歌曲](object_type)
- [刚才那首](mention)属于什么[专辑](attribute)
- [刚才那首](mention)是[谁](attribute)唱的
- [刚才那首](mention)的[歌手](attribute)是谁
- [那首歌](mention)属于什么[风格](attribute)?
- [最后一个](mention)属于什么[风格](attribute)?
- [第一个](mention)属于什么[专辑](attribute)?
- [第一个](mention)的[专辑](attribute)
- [第一个](mention)是[谁](attribute)唱的?
- [最后一个](mention)是[哪个](attribute)唱的?
- [舞娘](song)是[哪个歌手](attribute)唱的?
- [晴天](song)这首歌属于什么[专辑](attribute)?
- [晴天](song)的[专辑](attribute)?
- [江南](song)属于什么[专辑](attribute)?
- [江南](song)在什么[专辑](attribute)里面?
- [第一个](mention)人的[生日](attribute)
- [周杰伦](singer)的[生日](attribute)
- intent: play_song
examples: |
- 播放这首歌
- 播这首歌
- intent: play_album
examples: |
- 播放这个专辑
- 播这个专辑
- synonym: "1" # 同义词,第一个 -> 1
examples: |
- 第一个
- 首个
- 第一首
- synonym: "2"
examples: |
- 第二个
- 第二首
- synonym: "3"
examples: |
- 第三个
- 第三首
- synonym: LAST
examples: |
- 最后一个
- 最后那个
- 最后的
- synonym: birthday
examples: |
- 生日
- synonym: song
examples: |
- 歌曲
- synonym: singer
examples: |
- 歌手
- 谁
- 哪个
- 哪个歌手
- synonym: album
examples: |
- 专辑
- synonym: "4"
examples: |
- 第四个
- 第四首
- synonym: style
examples: |
- 风格
- 类型
- 流派
- synonym: male
examples: |
- 男
- 男性
- synonym: famale
examples: |
- 女
- 女性
stories.yml
version: "3.0"
stories:
- story: greet
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- story: knowledge query
steps:
- intent: query_knowledge_base
- action: action_response_query
- intent: query_knowledge_base
- action: action_response_query
- story: say goodbye
steps:
- intent: goodbye
- action: utter_goodbye
rules.yml
version: "3.0"
rules:
- rule: 处理NLU低置信度时的规则
steps:
- intent: nlu_fallback
- action: action_default_fallback
- rule: 处理知识图谱查询
steps:
- intent: query_knowledge_base
- action: action_response_query
domain.yml
version: "3.0"
session_config:
session_expiration_time: 60
carry_over_slots_to_new_session: true
intents:
- goodbye
- greet
- query_knowledge_base:
use_entities: []
- play_song
- play_album
entities:
- object_type
- mention
- attribute
- object-type
- song
- singer
- gender
slots:
attribute:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: attribute
gender:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: gender
knowledge_base_last_object:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_last_object_type:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_listed_objects:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
knowledge_base_objects:
type: any
mappings:
- type: custom
mention:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: mention
object_type:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: object_type
singer:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: singer
song:
type: any
mappings:
- type: from_entity
entity: song
responses:
utter_greet:
- text: 你好,我是 Silly, 一个可以利用知识图谱帮你查询歌手、音乐和专辑的机器人。
utter_goodbye:
- text: 再见!
utter_default:
- text: 系统不明白您说的话
utter_ask_rephrase:
- text: 抱歉系统没能明白您的话,请您重新表述一次
actions:
- action_response_query
- utter_goodbye
- utter_greet
- utter_default
- utter_ask_rephrase
config.yml
recipe: default.v1
language: zh
pipeline:
- name: JiebaTokenizer
- name: LanguageModelFeaturizer
model_name: bert
model_weights: bert-base-chinese
- name: RegexFeaturizer
- name: DIETClassifier
epochs: 1000
learning_rate: 0.001
- name: FallbackClassifier
threshold: 0.4
ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
- name: EntitySynonymMapper
policies:
- name: MemoizationPolicy
- name: TEDPolicy
- name: RulePolicy
core_fallback_threshold: 0.3
core_fallback_action_name: "action_default_fallback"
endpoints.yml
action_endpoint:
url: "http://localhost:5055/webhook"
data.json
{
"song": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "晴天",
"singer": "周杰伦",
"album": "叶惠美",
"style": "流行,英伦摇滚"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "江南",
"singer": "林俊杰",
"album": "第二天堂",
"style": "流行,中国风"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "舞娘",
"singer": "蔡依林",
"album": "舞娘",
"style": "流行"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "后来",
"singer": "刘若英",
"album": "我等你",
"style": "流行,抒情,经典"
}
],
"singer": [
{
"id": 0,
"name": "周杰伦",
"gender": "male",
"birthday": "1979/01/18"
},
{
"id": 1,
"name": "林俊杰",
"gender": "male",
"birthday": "1979/03/27"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "蔡依林",
"gender": "female",
"birthday": "1980/09/15"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "刘若英",
"gender": "female",
"birthday": "1969/06/01"
}
]
}
自定义动作 actions.py
import os
import json
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Text
from rasa_sdk import utils
from rasa_sdk.executor import CollectingDispatcher
from rasa_sdk.knowledge_base.actions import ActionQueryKnowledgeBase
from rasa_sdk.knowledge_base.storage import InMemoryKnowledgeBase
USE_NEO4J = bool(os.getenv("USE_NEO4J", False))
if USE_NEO4J:
from neo4j_knowledge_base import Neo4jKnowledgeBase
class EnToZh:
def __init__(self, data_file):
with open(data_file) as fd:
self.data = json.load(fd)
def __call__(self, key):
return self.data.get(key, key)
class MyKnowledgeBaseAction(ActionQueryKnowledgeBase):
def name(self) -> Text:
return "action_response_query"
def __init__(self):
if USE_NEO4J:
print("using Neo4jKnowledgeBase")
knowledge_base = Neo4jKnowledgeBase(
"bolt://localhost:7687", "neo4j", "43215678"
)
else:
print("using InMemoryKnowledgeBase")
knowledge_base = InMemoryKnowledgeBase("data.json")
super().__init__(knowledge_base)
self.en_to_zh = EnToZh("en_to_zh.json")
async def utter_objects(
self,
dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher,
object_type: Text,
objects: List[Dict[Text, Any]],
) -> None:
"""
Utters a response to the user that lists all found objects.
Args:
dispatcher: the dispatcher
object_type: the object type
objects: the list of objects
"""
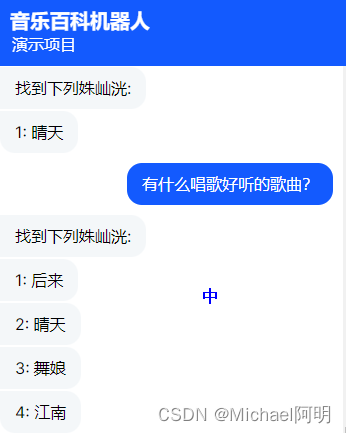
if objects:
dispatcher.utter_message(text="找到下列{}:".format(self.en_to_zh(object_type)))
repr_function = await self.knowledge_base.get_representation_function_of_object(
object_type
)
for i, obj in enumerate(objects, 1):
dispatcher.utter_message(text=f"{i}: {repr_function(obj)}")
else:
dispatcher.utter_message(
text="我没找到任何{}.".format(self.en_to_zh(object_type))
)
def utter_attribute_value(
self,
dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher,
object_name: Text,
attribute_name: Text,
attribute_value: Text,
) -> None:
"""
Utters a response that informs the user about the attribute value of the
attribute of interest.
Args:
dispatcher: the dispatcher
object_name: the name of the object
attribute_name: the name of the attribute
attribute_value: the value of the attribute
"""
if attribute_value:
dispatcher.utter_message(
text="{}的{}是{}。".format(
self.en_to_zh(object_name),
self.en_to_zh(attribute_name),
self.en_to_zh(attribute_value),
)
)
else:
dispatcher.utter_message(
text="没有找到{}的{}。".format(
self.en_to_zh(object_name), self.en_to_zh(attribute_name)
)
)
测试
rasa train
rasa run --cors "*"
rasa run actions
python -m http.server

使用Neo4j
图数据库
docker 安装 docker run --env=NEO4J_AUTH=none --publish=7474:7474 --publish=7687:7687 neo4j
pip install neo4j
导入数据
python data_to_neo4j.py
windows
set USE_NEO4J=1
rasa run actions