素数
质数/素数定义
在大于1的整数中,如果只包含1和本身这两个约数,就被称为质数,或者叫素数
判断素数(试除法)
约数有一个重要的性质:
假设n代表数字,d代表n的一个约数
即d能整除n(d|n)
那么n/d为n的另外一个约数
即n/d能整除d(n/d | n)
简单思路:

模板:
bool is_prime(int n)
{
if (n <= 1) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
if (n % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}866. 试除法判定质数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
bool is_prime(int n)
{
if (n <= 1) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
if (n % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a;
cin >> a;
if (is_prime(a)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
分解质因数(试除法)
从小到大枚举所有的数
为什么不需要判断是否为质因子?
因为i是n的因子,即n是i的倍数,当枚举的到i时,n中已经不包含有2~i-1的因子,即i中也不包含,2~i-1的因子,所以i是质数
n中最多只包括一个大于sqrt(n)的质因子
如果最后剩下一个大于1的数,那就是大于sqrt(n)的质因子
模板:
void divide(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (n % i == 0)
{
cnt ++;
n /= i;
}
printf("%d %d\n", i, cnt);
}
}
if (n > 1) printf("%d %d\n", n, 1);
printf("\n");
}
acwing 867. 分解质因数

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void divide(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (n % i == 0)
{
cnt ++;
n /= i;
}
printf("%d %d\n", i, cnt);
}
}
if (n > 1) printf("%d %d\n", n, 1);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n --)
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
divide(a);
}
return 0;
}
埃氏筛法
算法思路:

模板:
void gets_prime(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i])
{
cnt ++;
for (int j = i * 2; j <= n; j += i) st[j] = true;
}
}
}868. 筛质数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
bool st[N];
int cnt;
void gets_prime(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i])
{
cnt ++;
for (int j = i * 2; j <= n; j += i) st[j] = true;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
gets_prime(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
}
线性筛(欧拉筛法)
算法思路:

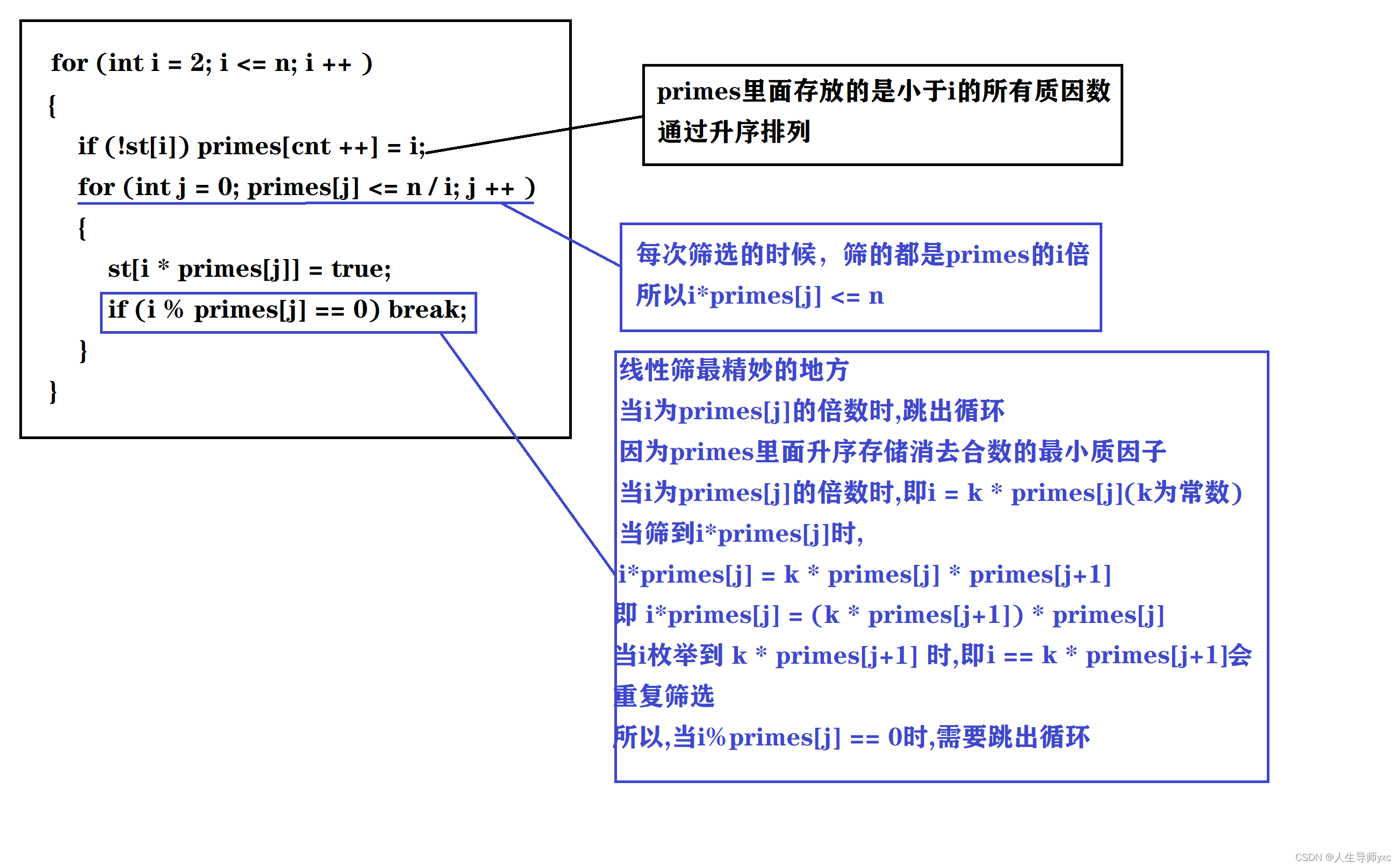
模板:
void oula(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i;
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
{
st[i * primes[j]] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}868. 筛质数
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int primes[N];
bool st[N];
int cnt;
void oula(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i;
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
{
st[i * primes[j]] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
oula(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
}
约数
试除法
思路:
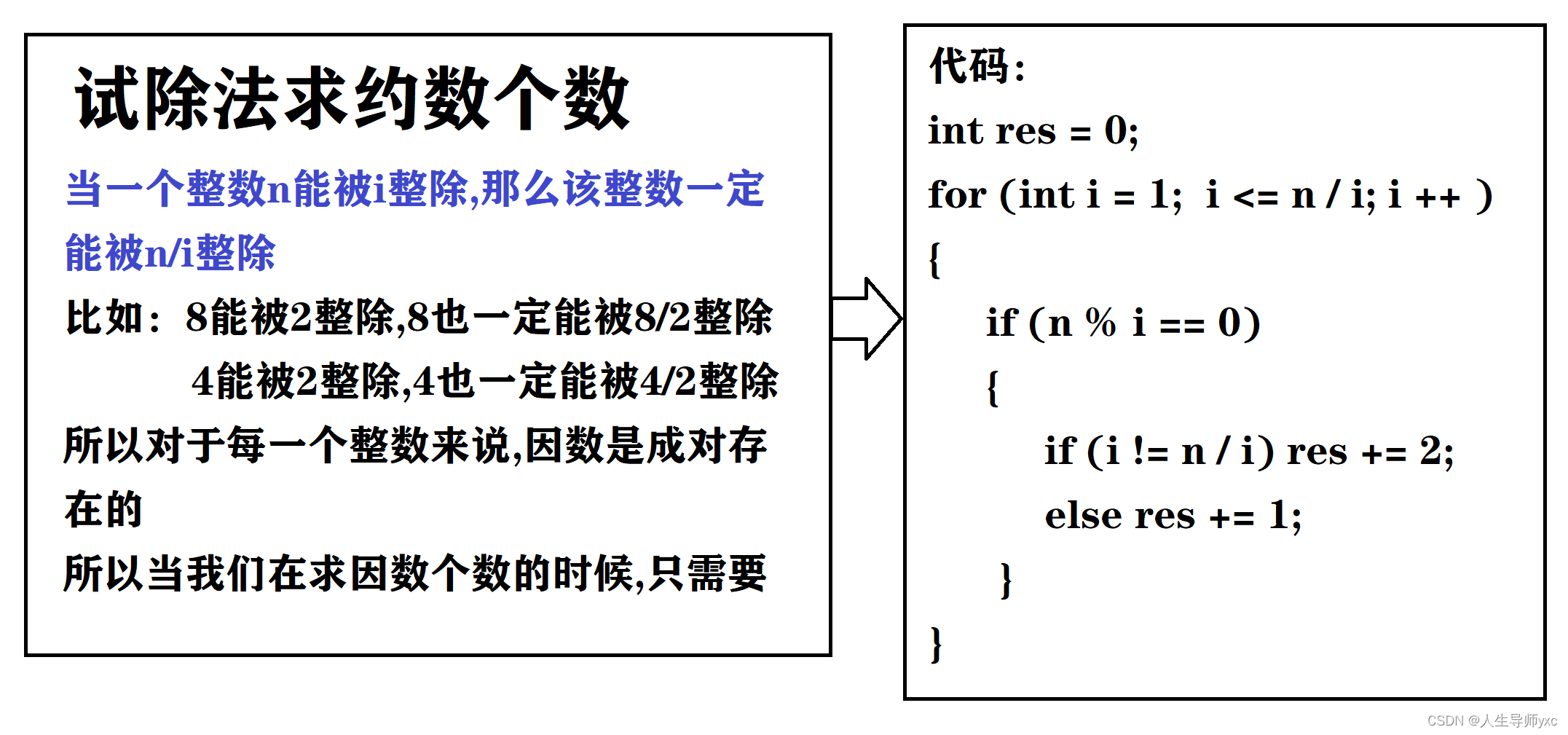
模板:
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n / i; i ++ )
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
if (i == n / i) res += 2;
else res += 1;
}
}—————————————这就是纯暴力解法,时间复杂度高——————————————
通过算数基本定理来求约数个数
思路:

模板:
unordered_map<int, int> prime;//prime[质因子] = 次方
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//分解质因数
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
prime[i] ++;
}
}
}
if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
long long res = 1;
for (auto it = prime.begin(); it != prime.end(); it ++)
{
res = res * (prime->second + 1);
}870. 约数个数
输入样例:
3
2
6
8代码展示:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
unordered_map<int, int> prime;
while (n --)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
prime[i] ++;
}
}
if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
}
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : prime) res = res * (p.second + 1) % mod;
printf("%lld\n",res);
}————————————————————next—————————————————————
通过算术基本定理求约数之和
思路:

模板:
unordered_map<int, int> prime;//prime[质因子] = 次方
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//分解质因数
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
prime[i] ++;
}
}
}
if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
long long res = 1;
for (auto it = prime.begin(); it != prime.end(); it ++)
{
int a = it->first, b = it->second;
long long t = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < b; i ++) t = t * a + 1;
res = res * t;
}871. 约数之和
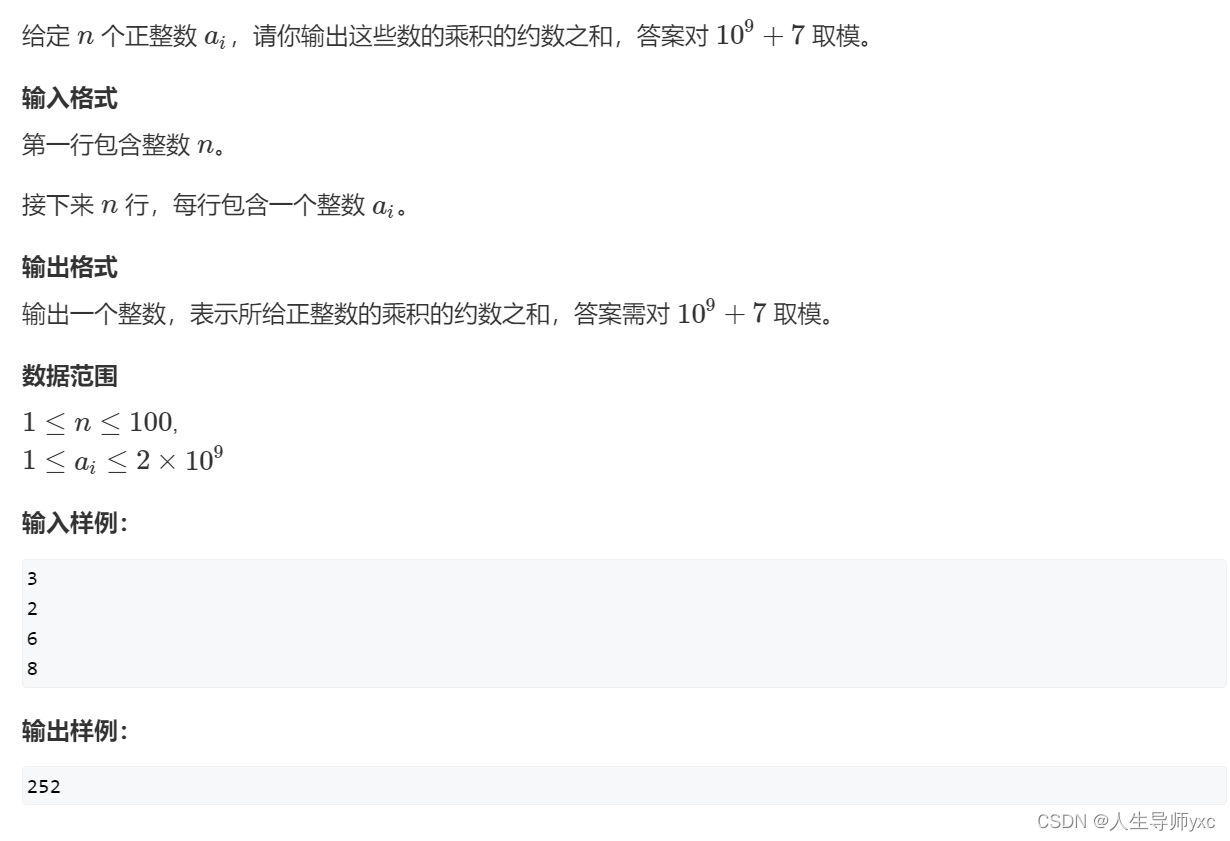
输入样例:
3
2
6
8代码展示:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
unordered_map<int, int> prime;
while (n --)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
while (x % i == 0)
{
prime[i] ++;
x /= i;
}
}
if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
}
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : prime)
{
int a = p.first, b = p.second;
LL t = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < b; i ++ ) t = (t * a + 1) % mod;
res = res * t % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
}———————————————————next—————————————————————
求最大公约数
思路:

模板:
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
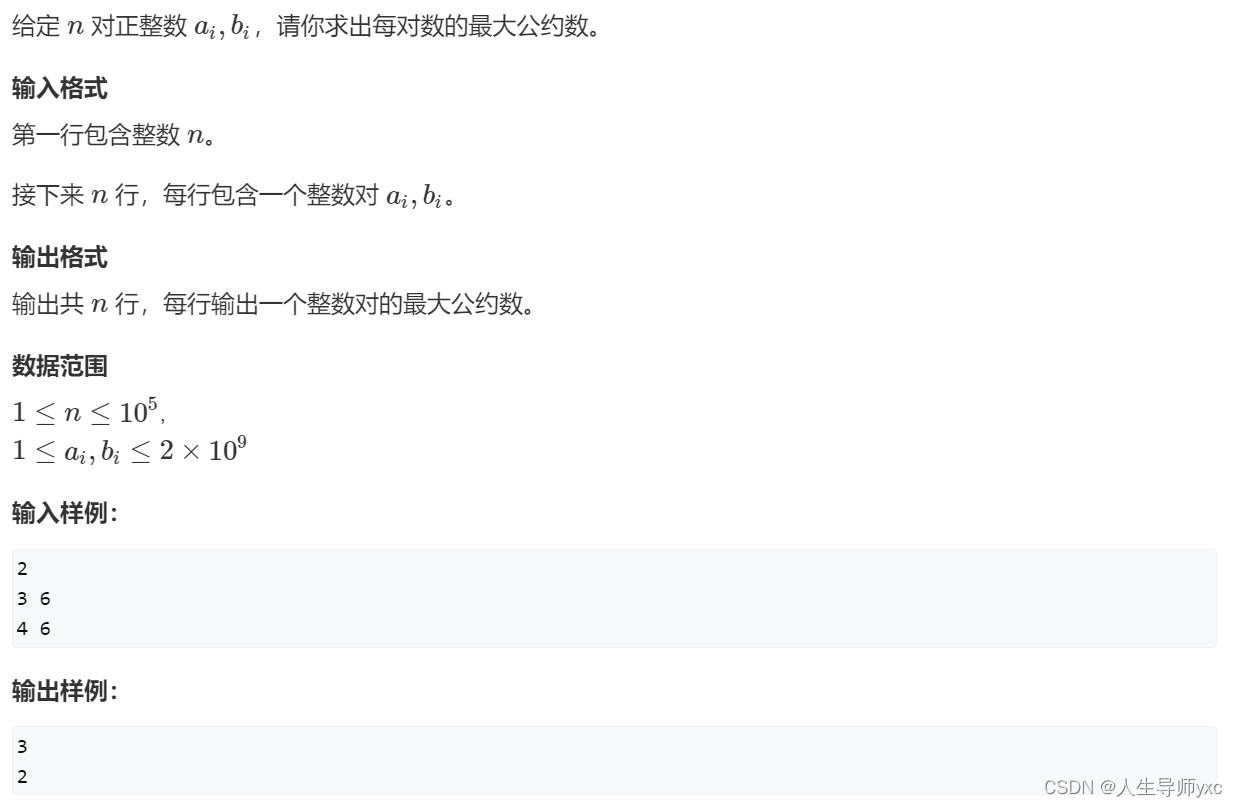
}输入样例:
2
3 6
4 6AcWing 872. 最大公约数
代码展示:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int ans = gcd(a, b);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
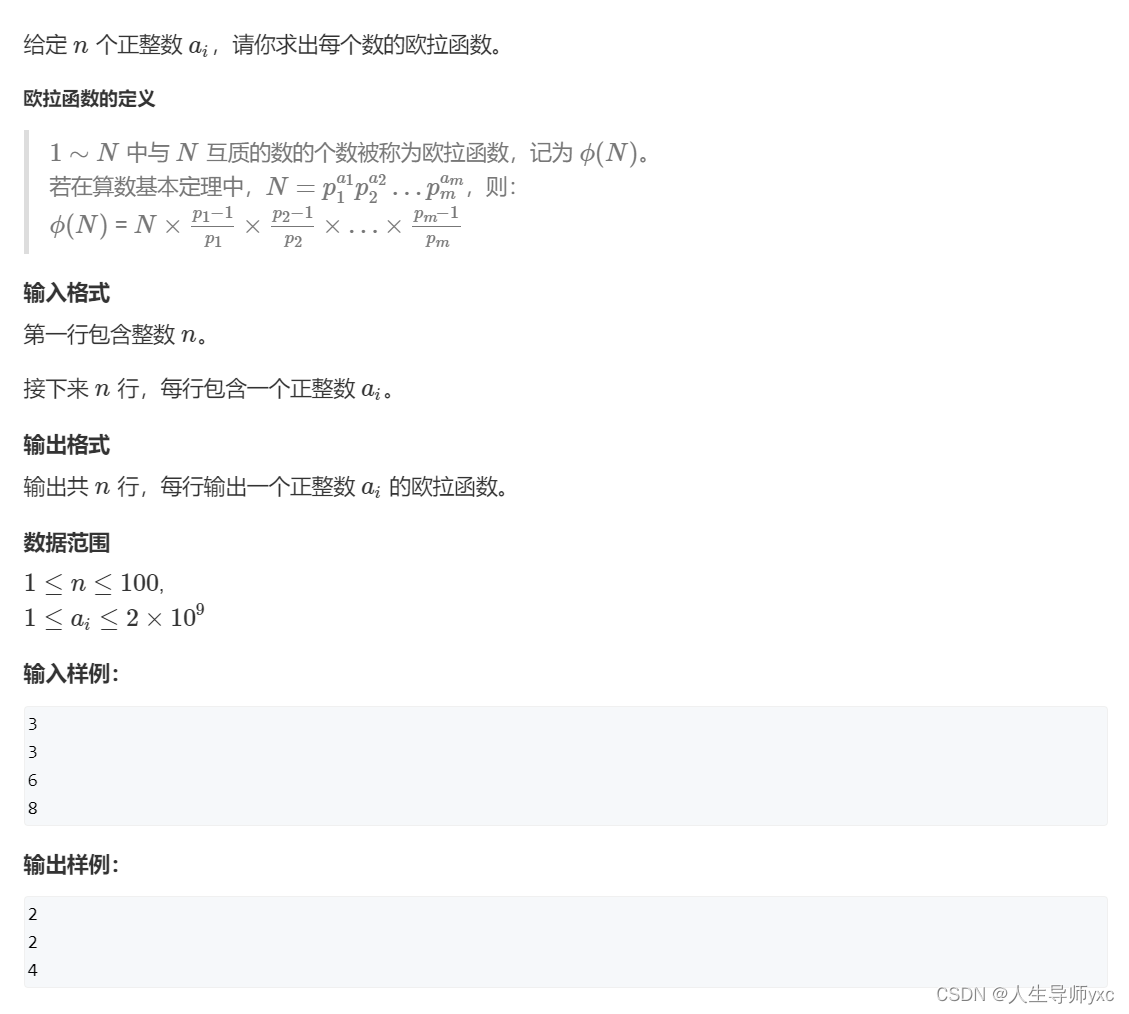
}欧拉函数
基本思路:
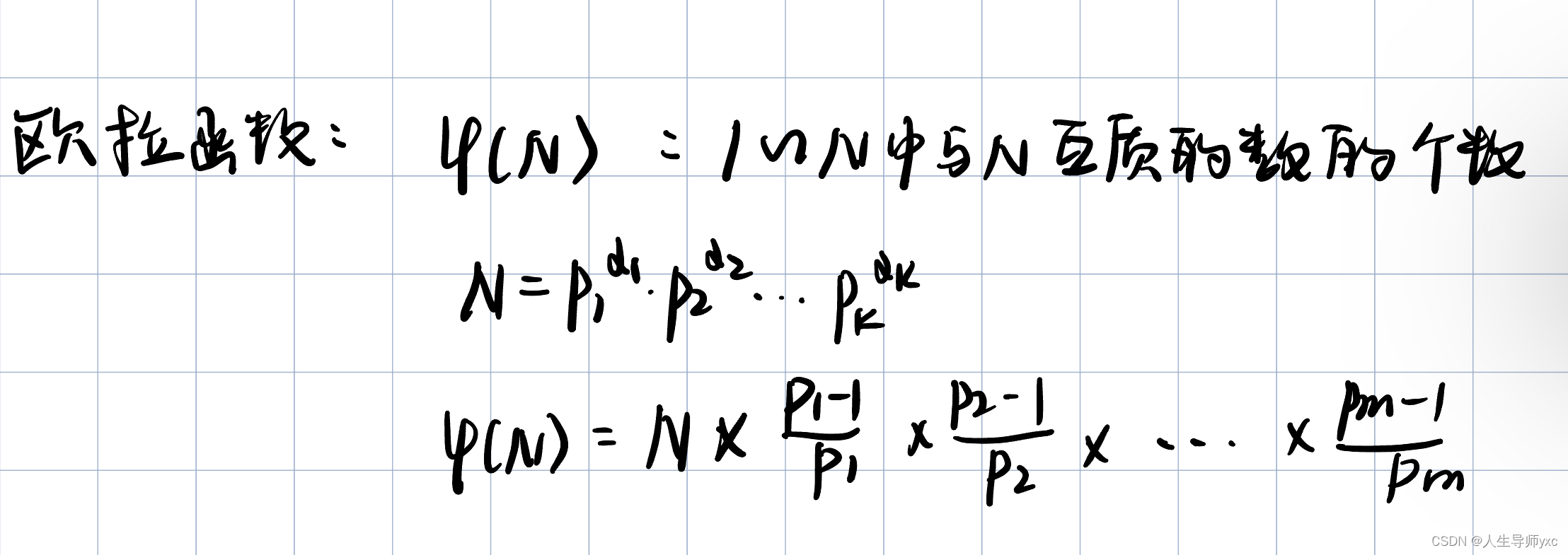
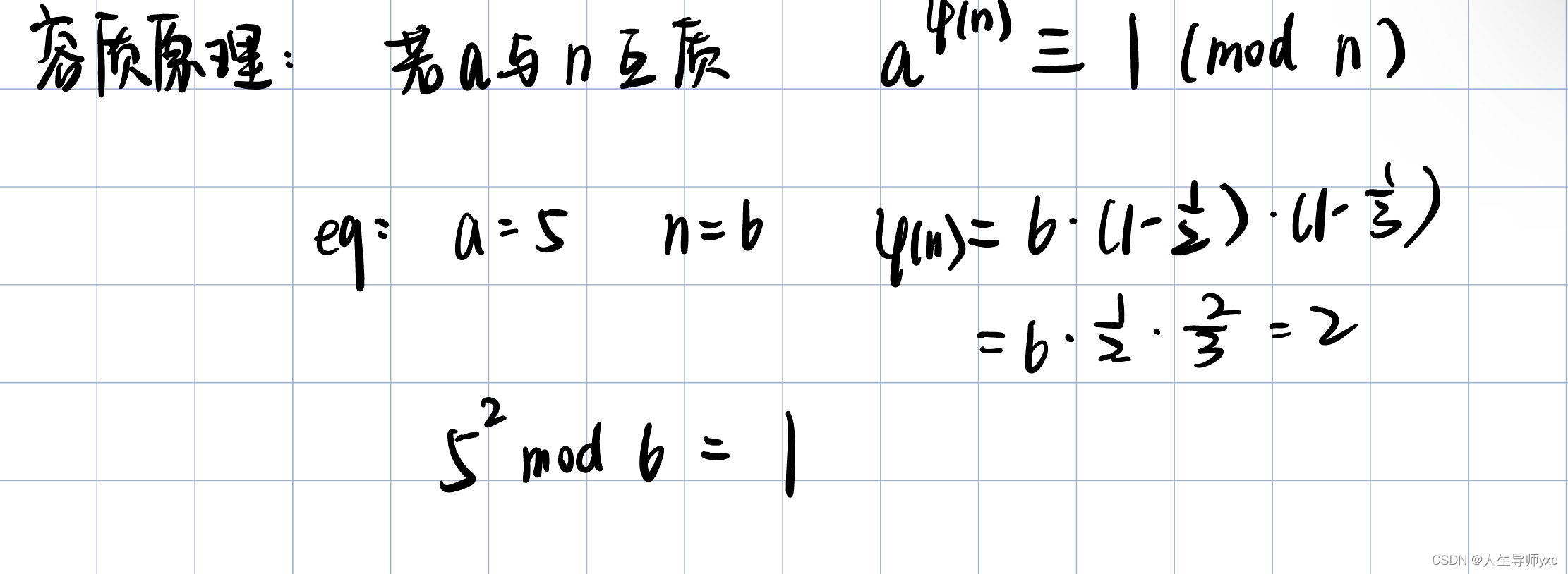

模板(暴力):
long long res = x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
res = res * (i - 1) / i;
}
}
if (x > 1) res = res * (x - 1) / x;Acwing873. 欧拉函数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
long long res = x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
res = res * (i - 1) / i;
}
}
if (x > 1) res = res * (x - 1) / x;
cout << res << endl;
}
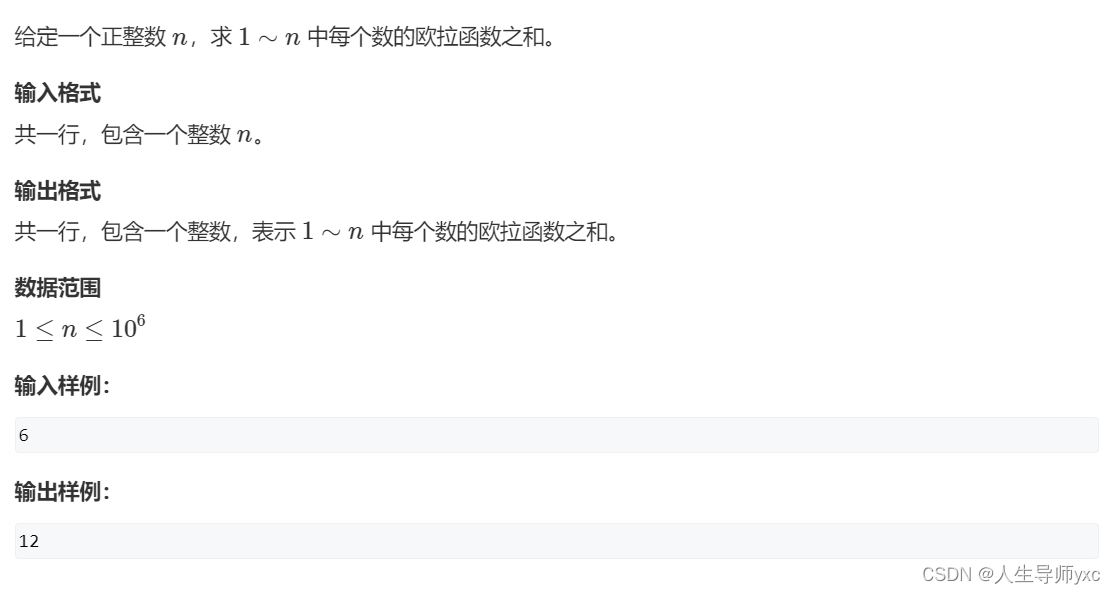
}模板(线性筛法):
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
int phi[N];
void oula(int x)
{
phi[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= x; i ++)
{
if (!st[i])
{
primes[cnt ++] = i;
phi[i] = i - 1;
}
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= x / i; j ++)
{
st[i * primes[j]] = true;
phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i] * (primes[j] - 1) / primes[j];
if (i % primes[j] == 0)
{
phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i];
break;
}
}
}
}运用线性筛算欧拉函数思路:

Acwing874. 筛法求欧拉函数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
int phi[N];
void oula(int x)
{
phi[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= x; i ++)
{
if (!st[i])
{
primes[cnt ++] = i;
phi[i] = i - 1;
}
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= x / i; j ++)
{
st[i * primes[j]] = true;
phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i] * (primes[j] - 1) / primes[j];
if (i % primes[j] == 0)
{
phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
oula(n);
long long res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) res += phi[i];
cout << res << endl;
}
快速幂
基本思路:
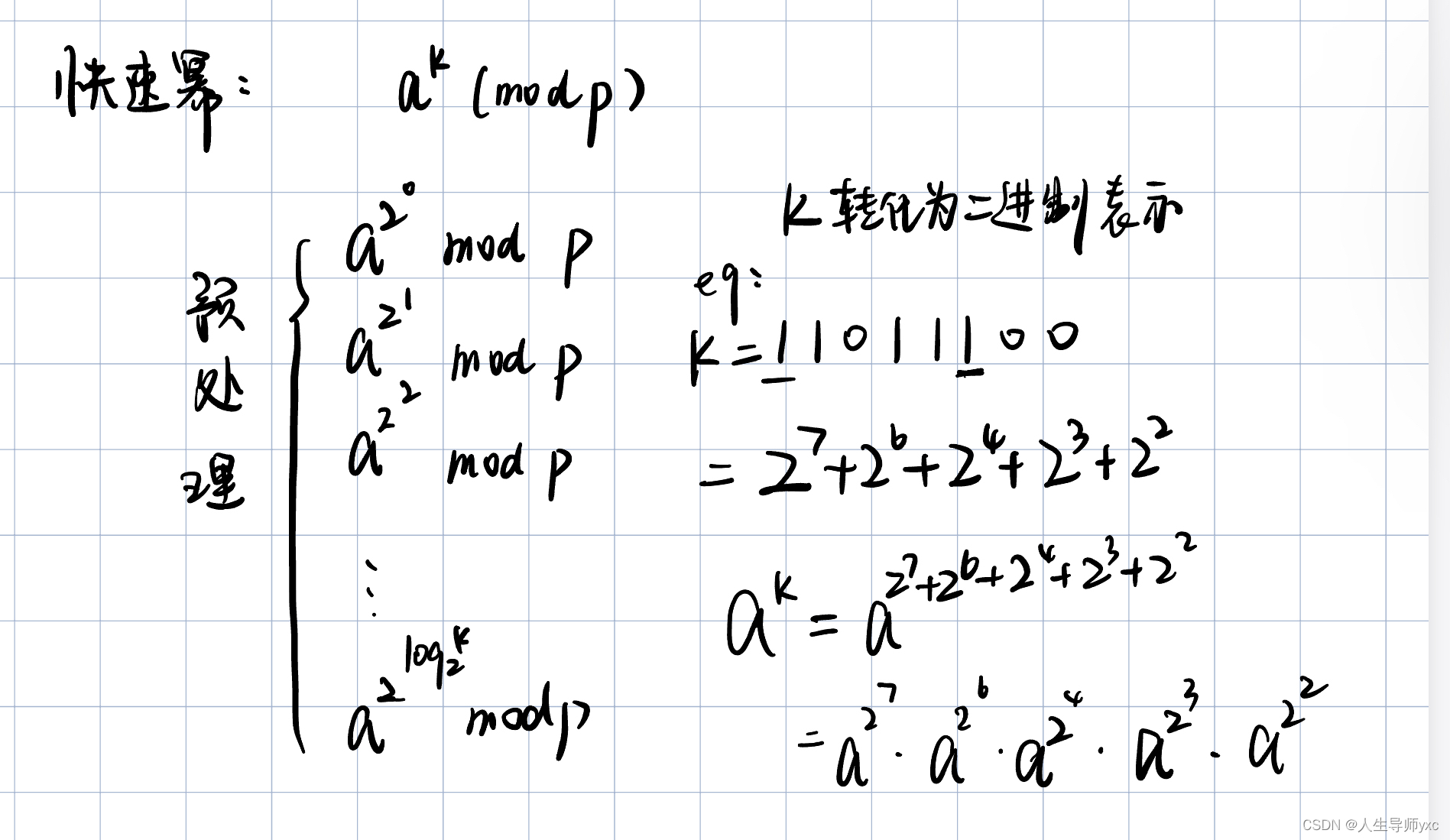
模板:
typedef long long LL;
LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
{
LL res = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
k >>= 1;
a = (LL)a * a % p;
}
return res;
}AcWing 875. 快速幂

#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
{
LL res = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
k >>= 1;
a = (LL)a * a % p;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a, k, p;
cin >> a >> k >> p;
cout << qmi(a, k, p) << endl;
}
}快速幂求逆元思路:

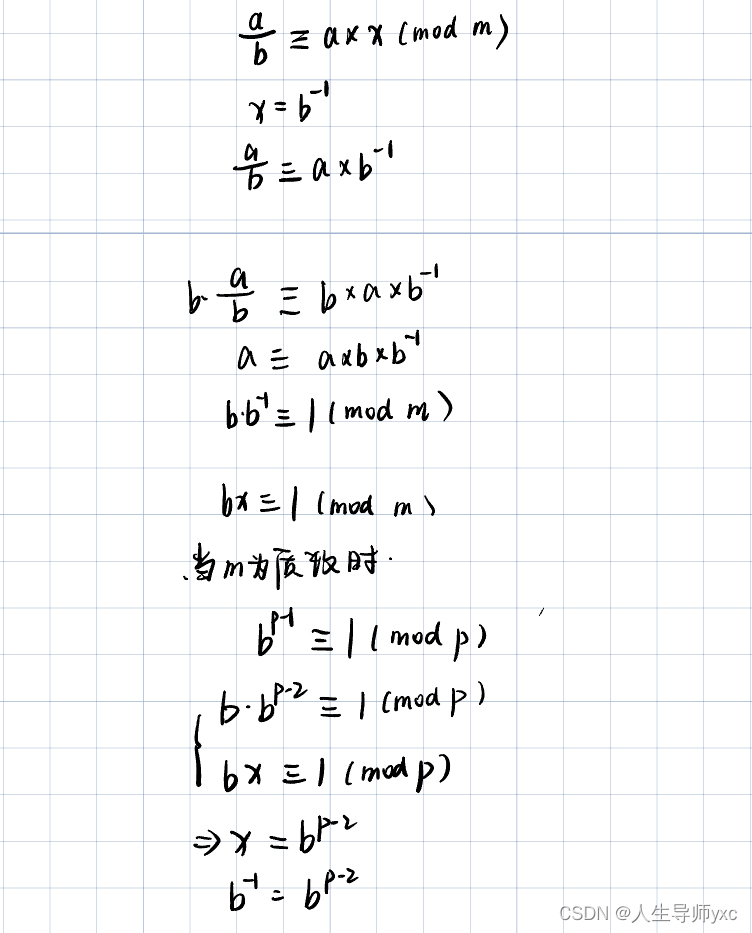 AcWing 876. 快速幂求逆元
AcWing 876. 快速幂求逆元

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
{
LL res = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
k >>= 1;
a = (LL) a * a % p;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a, p;
cin >> a >> p;
if (a % p) cout << qmi(a, p - 2, p) << endl;
else puts("impossible");
}
}
扩展欧几里得
基本思路:

模板:
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
{
if (b == 0)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y = y - a / b * x;
return d;
}Acwing877. 扩展欧几里得算法

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
{
if (b == 0)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y = y - a / b * x;
return d;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a, b, x, y;
cin >> a >> b;
exgcd(a, b, x, y);
cout << x << ' ' << y << endl;
}
}裴蜀定理:
对任何整数a、b和它们的最大公约数d,关于未知数x和y的线性不定方程(称为裴蜀等式):若a,b是整数,且gcd(a,b)=d,那么对于任意的整数x,y,ax+by都一定是d的倍数,特别地,一定存在整数x,y,使ax+by=d成立。
 Acwing878. 线性同余方程
Acwing878. 线性同余方程

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
{
if (b == 0)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y = y - a / b * x;
return d;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --)
{
int a, b, m, x, y;
cin >> a >> b >> m;
int d = exgcd(a, m, x, y);
if (b % d) puts("impossible");
else cout << (LL)x * (b / d) % m << endl;
}
}