前言:
本篇参考 github 上 [CAPEv2](CAPEv2/Emotet.py at f2ab891a278b2875c79b4f2916d086f870b54ed5 · kevoreilly/CAPEv2 (github.com)) 沙箱的提取代码,在前面奇安信攻防社区-APT 恶意 DLL 分析及 C2 配置提取(子 DLL 篇) 分析的基础上尝试编写自动化配置提取,如有错误还请指正。
编写环境:
语言:python
外部库:
yara——匹配规则,锁定 C2 配置及密钥配置位置,pip install yara-python
Cryptodome——提取整合加密密钥并导出 pip install pycryptodomex
pefile——应用 PE 结构模板,定位文件头和节表区的字段和数据
标准库:struct、socket、itertools
编译器:
vscode
样本IOC:
| HASH | 值 |
|---|---|
| MD5 | 4e22717b48f2f75fcfd47531c780b218 |
| SHA1 | 60b637e95b1f2d14faaa71085b7e26321bfeeb6d |
| SHA256 | 7f94107c9becbcc6ca42070fca7e1e63f29cdd85cbbd8953bbca32a1b4f91219 |
ECC 密钥提取:
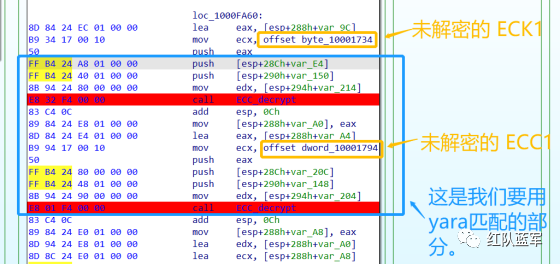
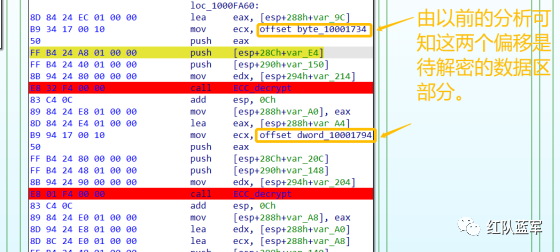
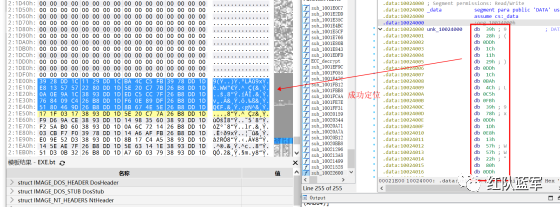
首先在 IDA 或 XDBG 中定位到解密的代码的特征数据区,由于之前分析得很详细了,所以我们直接放上截图:(蓝框就是我们认定的特征区)
编写密钥区的 Yara 规则:
Yara 规则怎么写呢,把地址部分的都模糊查询,指令码部分的字节都一一对应:
比如说上面蓝框的第一行 FF B4 24 A8 01 00 00 push [esp+28Ch+var_E4] ,由于 IDA 中在识别函数的过程中插入了 var_E4 变量,所以我们对确切的地址部分有点模糊,我们看 xdbg 中的同样位置。
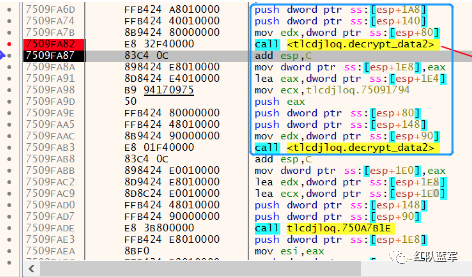
可以发现真实的指令应该是 pust dword ptr ss:[esp+1A8],根据 x86 指令码和机器码的转换大概可以确定 FF B4 对应着 push,24 对应着后面的 esp 的基地偏移量寻址,所以第一行我们提取出的 Yara 规则是 FF B4 [3] 00 00。
最后两个全 0 字节是因为这里是基于 ss 16 位段选择为基址的,而程序是 32 位,所以开头的 2 个字节 16 位就一定会空下来。
其它行同理,所以最后蓝框中的 Yara 规则就是 *{FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8}*。
写成 Yara 规则代码就是:
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet ECC Extra"
strings:
$ref_ecc = {FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3]00 00 FF B4 [3]00 00 8B 94 [3]00 00 E8}
condition:
$ref_ecc
}
"""
利用 Yara 库 API 定位特征区首地址:
首先参考官方文档了解 Yara API 和 类对象:在 Python 中使用 YARA — yara 4.2.0 文档(https://yara.readthedocs.io/en/v4.2.3/yarapython.html)
我们要用到的 API 如下:



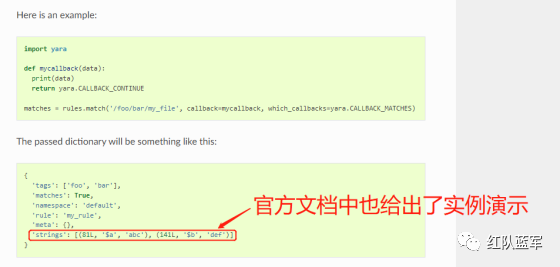
懂了之后就尝试编写代码获取特征区首地址了:
我们这里用的 yara 是基于静态扫描,也就是说它不会展开内存来匹配,所以匹配都是基于文件字节码的,返回值也是特征区在文件中的匹配,特别要注意的是它返回的偏移是 10 进制的,所以我们要自己转为十六进制。
import yara
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet ECC Extra"
strings:
$ref_ecc = {FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3]00 00 FF B4 [3]00 00 8B 94 [3]00 00 E8}
condition:
$ref_ecc
}
"""
def yara_scan(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
print(yara_scan(file_data)) #返回的结果为 {'$ref_ecc': '0xee6d'}
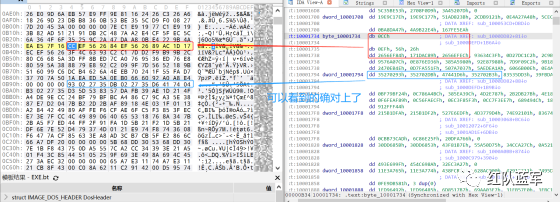
验证一下:
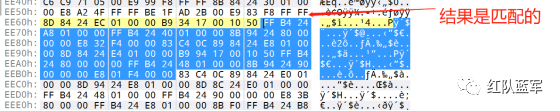
从特征区首中定位要解密的数据区:
两个数据分别在 0xee6d 起始的特征区中 -5 和 +44 处,我们可以设两个变量为 delta1 = -5 , delta2 = 44; 后面写代码时会用到。
因为在编译时变量引用都被替换编译成 VA 了,所以我们需要把 VA 转 RVA,再获取 FOA(文件偏移),这需要另一个外部库 pefile — pefile documentation(https://pefile.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/pefile.html)

编写脚本如下:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet ECC Extra"
strings:
$ref_ecc = {FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3]00 00 FF B4 [3]00 00 8B 94 [3]00 00 E8}
condition:
$ref_ecc
}
"""
def yara_scan(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
def positioning_data(filebuf):
conf_dict = {}
pe = None
pe = pefile.PE(data=filebuf, fast_load=False)
image_base = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase #获取载入基址,用于从 VA 转 RVA
yara_matches = yara_scan(filebuf)
if yara_matches.get("$ref_ecc"):
ref_ecc_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_ecc"],16)
delta1 = -5
delta2 = 44
ref_eck_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta1 : ref_ecc_offset + delta1 + 4])[0] - image_base #struct.unpack(format, buffer),根据格式字符串 format 从缓冲区 buffer 解包,返回元祖,所以这里用[0]来提取。I 是 unsigned int 类型
ref_ecs_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta2 : ref_ecc_offset + delta2 + 4])[0] - image_base
eck_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_eck_rva) #获取此 RVA 对应的文件偏移量。
ecs_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_ecs_rva)
return "eck_offset:",hex(eck_offset),"ecs_offset",hex(ecs_offset)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
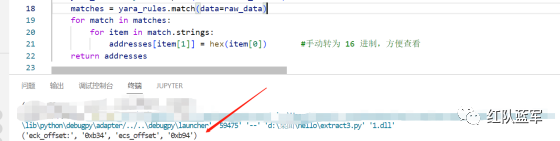
print(positioning_data(file_data)) #返回的结果为('eck_offset:', '0xb34', 'ecs_offset', '0xb94')
编写 ECC 解密代码:(成功提取)
以前的分析中说过了公钥在加密中的数据格式,第一个 Dword 是解密的 key,第二个 Dword 是公钥的长度,剩下的是加密的数据。
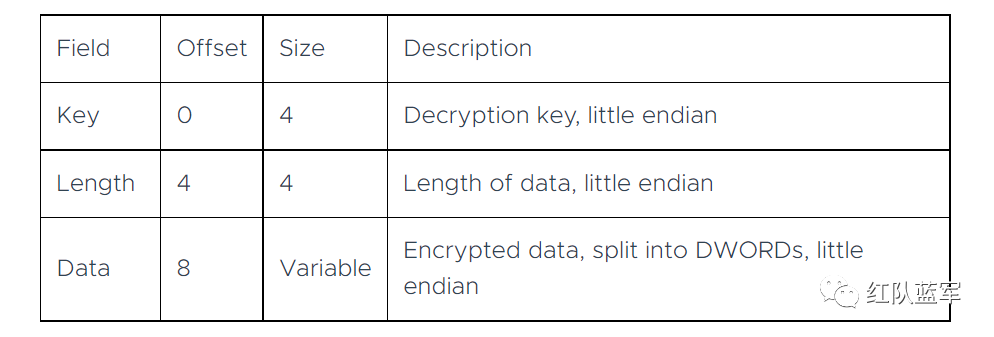
我们可以用一个 xor 函数来实现异或解密并依旧用 struct.unpack 来把 4 字节格式化输出,因为一个 key 要重复对后面的数据解密使用,所以我们这里用 python 标准库 itertools 的 API itertools --- 为高效循环而创建迭代器的函数 — Python 3.10.6 文档(https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/socket.html?highlight=socket#module-socket)
xor 函数如下:
from itertools import cycle
def xor_data(data, key):
return bytes(c ^ k for c, k in zip(data, cycle(key)))
#将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。cycle不断返回一样的副本。
#所以返回类似于[(data1,key),(data2,key)……],然后用列表推导式从中获取元祖的两个元素
但是输出的是 ECC 密钥并不是可读的,因为它们只是一串字节码,我们需要把它格式化为 ECC 密钥该有的形式,可以从 pycryptodome 官方文档中找到可用的 API ECC — PyCryptodome 3.15.0 文档(https://pycryptodome.readthedocs.io/en/latest/src/public_key/ecc.html#ecc-table)


所以最终的 ECC 密钥提取脚本如下:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
from Cryptodome.PublicKey import ECC
from itertools import cycle
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet ECC Extra"
strings:
$ref_ecc = {FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3]00 00 FF B4 [3]00 00 8B 94 [3]00 00 E8}
condition:
$ref_ecc
}
"""
def yara_scan(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
def xor_data(data, key):
return bytes(c ^ k for c, k in zip(data, cycle(key)))
#将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。cycle不断返回一样的副本。
#所以返回类似于[(data1,key),(data2,key)……],然后用列表推导式从中获取元祖的两个元素
def extract_ecc(filebuf):
conf_dict = {}
pe = None
pe = pefile.PE(data=filebuf, fast_load=False)
image_base = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase #获取载入基址,用于从 VA 转 RVA
yara_matches = yara_scan(filebuf)
if yara_matches.get("$ref_ecc"):
ref_ecc_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_ecc"],16)
delta1 = -5
delta2 = 44
ref_eck_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta1 : ref_ecc_offset + delta1 + 4])[0] - image_base #struct.unpack(format, buffer),根据格式字符串 format 从缓冲区 buffer 解包,返回元祖,所以这里用[0]来提取。
ref_ecs_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta2 : ref_ecc_offset + delta2 + 4])[0] - image_base #struct.unpack(format, buffer),根据格式字符串 format 从缓冲区 buffer 解包,返回元祖,所以这里用[0]来提取。
eck_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_eck_rva)
ecs_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_ecs_rva)
key = filebuf[eck_offset : eck_offset + 4]
size = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[eck_offset + 4 : eck_offset + 8])[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
eck_offset += 8
eck_key = xor_data(filebuf[eck_offset : eck_offset + size], key)
key_len = struct.unpack("<I", eck_key[4:8])[0] #ECC密钥还有长度的?
conf_dict.setdefault(
"ECC ECK1",
ECC.construct(
curve="p256",
point_x=int.from_bytes(eck_key[8 : 8 + key_len], "big"),
point_y=int.from_bytes(eck_key[8 + key_len :], "big"),
).export_key(format="PEM"),
)
key = filebuf[ecs_offset : ecs_offset + 4]
size = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ecs_offset + 4 : ecs_offset + 8])[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
ecs_offset += 8
ecs_key = xor_data(filebuf[ecs_offset : ecs_offset + size], key)
key_len = struct.unpack("<I", ecs_key[4:8])[0]
conf_dict.setdefault(
"ECC ECS1",
ECC.construct(
curve="p256",
point_x=int.from_bytes(ecs_key[8 : 8 + key_len], "big"),
point_y=int.from_bytes(ecs_key[8 + key_len :], "big"),
).export_key(format="PEM"),
)
return conf_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
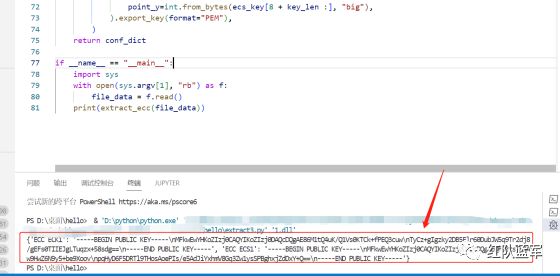
print(extract_ecc(file_data)) #最终输出{'ECC ECK1': '-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAE86M1tQ4uK/Q1Vs0KTCk+fPEQ3cuw\nTyCz+gIgzky2DB5Elr60DubJW5q9Tr2dj8/gEFs0TIIEJgLTuqzx+58sdg==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----', 'ECC ECS1': '-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEQF90tsTY3Aw9HwZ6N9y5+be9Xoov\npqHyD6F5DRTl9THosAoePIs/e5AdJiYxhmV8Gq3Zw1ysSPBghxjZdDxY+Q==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----'}
C2 配置提取:
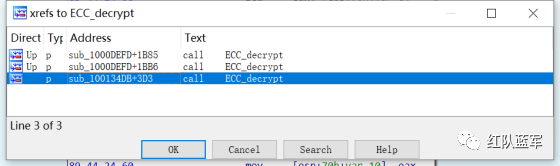
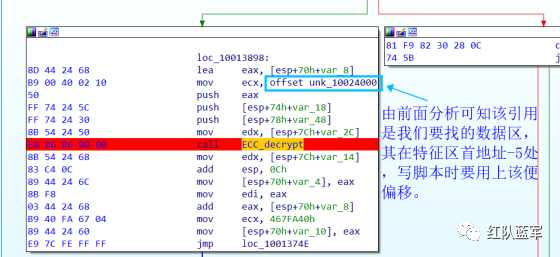
还是一样先定位到特征数据区,由于用的同一个解密函数,所以我们可以直接用 IDA 的热键 X 来交叉引用来寻找第三个,也就是 C2 配置区。
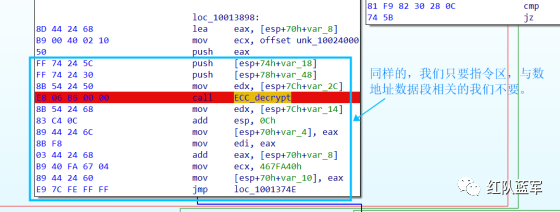
同理编写 C2 区的 Yara 规则:
同理,参考前面的密钥区的 Yara 规则,地址部分的都模糊查询,指令码部分的字节都一一对应。所以蓝框区的 Yara 规则就是 {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
合成 Yara 规则代码就是:
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet C2 Extra"
strings:
$snippet = {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
condition:
$snippet
}
"""
同理定位特征区首地址:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet C2 Extra"
strings:
$ref_c2 = {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
condition:
$ref_c2
}
"""
def yara_scan2(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
print(yara_scan2(file_data)) #返回的结果为{'$ref_c2': '0x12ca2'}
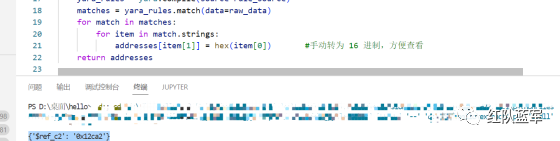

同理定位要解密的数据区:
编写脚本如下:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet C2 Extra"
strings:
$ref_c2 = {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
condition:
$ref_c2
}
"""
def yara_scan2(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
def positioning_c2_data(filebuf):
conf_dict = {}
pe = None
pe = pefile.PE(data=filebuf, fast_load=False)
image_base = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase #获取载入基址,用于从 VA 转 RVA
yara_matches = yara_scan2(filebuf)
if yara_matches.get("$ref_c2"):
delta = -5
c2list_va_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_c2"],16)
c2_list_va = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[c2list_va_offset + delta : c2list_va_offset + delta + 4])[0]
c2_list_rva = c2_list_va - image_base
c2_list_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(c2_list_rva)
return "c2_list_offset:",hex(c2_list_offset)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
print(positioning_c2_data(file_data)) #返回的结果为('c2_list_offset:', '0x21e00')
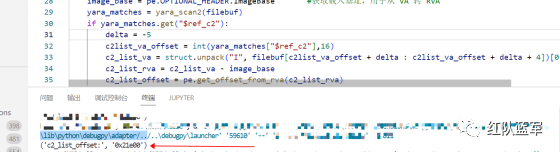
同理编写 C2 解密代码:(成功提取)
以前的分析中说过了公钥在加密中的数据格式,第一个 Dword 是解密的 key,第二个 Dword 是公钥的长度,剩下的是加密的数据,其中 C2 数据格式如下,以 8 个字节为一个单位。

和前面一样,我们使用 xor 函数解密,不同的是这里提取的是 IP ,所以我们需要引用 IP 相关的标准库 socket。对于 IP 数据我们先用 struct.unpack 把 4 字节区域格式化整合出来,再用 socket 库的 inet_ntoa API 把其转换成点分十进制形式。对于端口数据我们直接用 struct.unpack 把 2 字节区域整合出来即可。socket --- 底层网络接口 — Python 3.10.6 文档(https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/socket.html?highlight=socket#module-socket )

所以最终的 C2 密钥提取脚本如下:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
from itertools import cycle
import socket
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet C2 Extra"
strings:
$ref_c2 = {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
condition:
$ref_c2
}
"""
def yara_scan2(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
def xor_data(data, key):
return bytes(c ^ k for c, k in zip(data, cycle(key)))
def extra_c2_data(filebuf):
conf_dict = {}
pe = None
pe = pefile.PE(data=filebuf, fast_load=False)
image_base = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase #获取载入基址,用于从 VA 转 RVA
yara_matches = yara_scan2(filebuf)
if yara_matches.get("$ref_c2"):
delta = -5
c2list_va_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_c2"],16)
c2_list_va = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[c2list_va_offset + delta : c2list_va_offset + delta + 4])[0]
c2_list_rva = c2_list_va - image_base
c2_list_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(c2_list_rva)
key = filebuf[c2_list_offset : c2_list_offset + 4]
presize = filebuf[c2_list_offset + 4 : c2_list_offset + 8]
size = struct.unpack("I", presize)[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
c2_list_offset += 8
c2_list = xor_data(filebuf[c2_list_offset:], key)
offset = 0
while offset < size:
ip = struct.unpack(">I", c2_list[offset : offset + 4])[0]
c2_address = socket.inet_ntoa(struct.pack("!L", ip)) #将 32 位压缩 IPv4 地址(一个 类字节对象,长 4 个字节)转换为标准的点分十进制字符串形式(如 '123.45.67.89' )
port = str(struct.unpack(">H", c2_list[offset + 4 : offset + 6])[0])
if not c2_address or not port:
break
conf_dict.setdefault("address", []).append(f"{c2_address}:{port}")
c2found = True
offset += 8
return conf_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
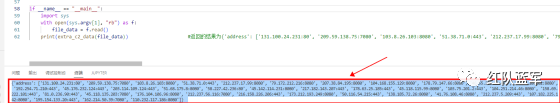
print(extra_c2_data(file_data)) #返回的结果为{'address': ['131.100.24.231:80', '209.59.138.75:7080', '103.8.26.103:8080', '51.38.71.0:443', '212.237.17.99:8080', '79.172.212.216:8080', '207.38.84.195:8080', '104.168.155.129:8080', '178.79.147.66:8080', '46.55.222.11:443', '103.8.26.102:8080', '192.254.71.210:443', '45.176.232.124:443', '203.114.109.124:443', '51.68.175.8:8080', '58.227.42.236:80', '45.142.114.231:8080', '217.182.143.207:443', '178.63.25.185:443', '45.118.115.99:8080', '103.75.201.2:443', '104.251.214.46:8080', '158.69.222.101:443', '81.0.236.90:443', '45.118.135.203:7080', '176.104.106.96:8080', '212.237.56.116:7080', '216.158.226.206:443', '173.212.193.249:8080', '50.116.54.215:443', '138.185.72.26:8080', '41.76.108.46:8080', '212.237.5.209:443', '107.182.225.142:8080', '195.154.133.20:443', '162.214.50.39:7080', '110.232.117.186:8080']}
整合代码如下:
import yara
import pefile
import struct
from Cryptodome.PublicKey import ECC
from itertools import cycle
import socket
rule_source = """
rule Emotet
{
meta:
description = "Emotet ECC Extra"
strings:
$ref_c2 = {FF 74 [2] FF 74 [2] 8B 54 [2] E8 [4] 8B 54 [2] 83 C4 0C 89 44 [2] 8B F8 03 44 [2] B9 [4] 89 44 [2] E9}
$ref_ecc = {FF B4 [3] 00 00 FF B4 [3] 00 00 8B 94 [3] 00 00 E8 [4] 83 C4 0C 89 84 [3] 00 00 8D 84 [3] 00 00 B9 [4] 50 FF B4 [3]00 00 FF B4 [3]00 00 8B 94 [3]00 00 E8}
condition:
$ref_c2 or $ref_ecc
}
"""
def yara_scan(raw_data):
addresses = {}
yara_rules = yara.compile(source=rule_source)
matches = yara_rules.match(data=raw_data)
for match in matches:
for item in match.strings:
addresses[item[1]] = hex(item[0]) #手动转为 16 进制,方便查看
return addresses
def xor_data(data, key):
return bytes(c ^ k for c, k in zip(data, cycle(key)))
#将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。cycle不断返回一样的副本。
#所以返回类似于[(data1,key),(data2,key)……],然后用列表推导式从中获取元祖的两个元素
def emotet_extract(filebuf):
conf_dict = {}
pe = None
pe = pefile.PE(data=filebuf, fast_load=False)
image_base = pe.OPTIONAL_HEADER.ImageBase #获取载入基址,用于从 VA 转 RVA
yara_matches = yara_scan(filebuf)
if yara_matches.get("$ref_c2"):
delta = -5
c2list_va_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_c2"],16)
c2_list_va = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[c2list_va_offset + delta : c2list_va_offset + delta + 4])[0]
c2_list_rva = c2_list_va - image_base
c2_list_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(c2_list_rva)
key = filebuf[c2_list_offset : c2_list_offset + 4]
presize = filebuf[c2_list_offset + 4 : c2_list_offset + 8]
size = struct.unpack("I", presize)[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
c2_list_offset += 8
c2_list = xor_data(filebuf[c2_list_offset:], key)
offset = 0
while offset < size:
ip = struct.unpack(">I", c2_list[offset : offset + 4])[0]
c2_address = socket.inet_ntoa(struct.pack("!L", ip)) #将 32 位压缩 IPv4 地址(一个 类字节对象,长 4 个字节)转换为标准的点分十进制字符串形式(如 '123.45.67.89' )
port = str(struct.unpack(">H", c2_list[offset + 4 : offset + 6])[0])
if not c2_address or not port:
break
conf_dict.setdefault("address", []).append(f"{c2_address}:{port}")
c2found = True
offset += 8
if yara_matches.get("$ref_ecc"):
ref_ecc_offset = int(yara_matches["$ref_ecc"],16)
delta1 = -5
delta2 = 44
ref_eck_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta1 : ref_ecc_offset + delta1 + 4])[0] - image_base #struct.unpack(format, buffer),根据格式字符串 format 从缓冲区 buffer 解包,返回元祖,所以这里用[0]来提取。
ref_ecs_rva = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ref_ecc_offset + delta2 : ref_ecc_offset + delta2 + 4])[0] - image_base #struct.unpack(format, buffer),根据格式字符串 format 从缓冲区 buffer 解包,返回元祖,所以这里用[0]来提取。
eck_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_eck_rva)
ecs_offset = pe.get_offset_from_rva(ref_ecs_rva)
key = filebuf[eck_offset : eck_offset + 4]
size = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[eck_offset + 4 : eck_offset + 8])[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
eck_offset += 8
eck_key = xor_data(filebuf[eck_offset : eck_offset + size], key)
key_len = struct.unpack("<I", eck_key[4:8])[0] #ECC密钥还有长度的?
conf_dict.setdefault(
"ECC ECK1",
ECC.construct(
curve="p256",
point_x=int.from_bytes(eck_key[8 : 8 + key_len], "big"),
point_y=int.from_bytes(eck_key[8 + key_len :], "big"),
).export_key(format="PEM"),
)
key = filebuf[ecs_offset : ecs_offset + 4]
size = struct.unpack("I", filebuf[ecs_offset + 4 : ecs_offset + 8])[0] ^ struct.unpack("I", key)[0]
ecs_offset += 8
ecs_key = xor_data(filebuf[ecs_offset : ecs_offset + size], key)
key_len = struct.unpack("<I", ecs_key[4:8])[0]
conf_dict.setdefault(
"ECC ECS1",
ECC.construct(
curve="p256",
point_x=int.from_bytes(ecs_key[8 : 8 + key_len], "big"),
point_y=int.from_bytes(ecs_key[8 + key_len :], "big"),
).export_key(format="PEM"),
)
return conf_dict
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
with open(sys.argv[1], "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
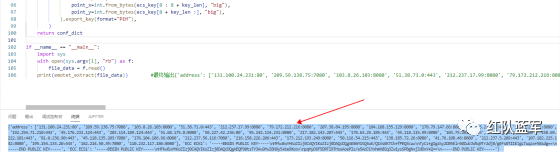
print(emotet_extract(file_data)) #最终输出{'address': ['131.100.24.231:80', '209.59.138.75:7080', '103.8.26.103:8080', '51.38.71.0:443', '212.237.17.99:8080', '79.172.212.216:8080', '207.38.84.195:8080', '104.168.155.129:8080', '178.79.147.66:8080', '46.55.222.11:443', '103.8.26.102:8080', '192.254.71.210:443', '45.176.232.124:443', '203.114.109.124:443', '51.68.175.8:8080', '58.227.42.236:80', '45.142.114.231:8080', '217.182.143.207:443', '178.63.25.185:443', '45.118.115.99:8080', '103.75.201.2:443', '104.251.214.46:8080', '158.69.222.101:443', '81.0.236.90:443', '45.118.135.203:7080', '176.104.106.96:8080', '212.237.56.116:7080', '216.158.226.206:443', '173.212.193.249:8080', '50.116.54.215:443', '138.185.72.26:8080', '41.76.108.46:8080', '212.237.5.209:443', '107.182.225.142:8080', '195.154.133.20:443', '162.214.50.39:7080', '110.232.117.186:8080'], 'ECC ECK1': '-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAE86M1tQ4uK/Q1Vs0KTCk+fPEQ3cuw\nTyCz+gIgzky2DB5Elr60DubJW5q9Tr2dj8/gEFs0TIIEJgLTuqzx+58sdg==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----', 'ECC ECS1': '-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEQF90tsTY3Aw9HwZ6N9y5+be9Xoov\npqHyD6F5DRTl9THosAoePIs/e5AdJiYxhmV8Gq3Zw1ysSPBghxjZdDxY+Q==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----'}
总结:
编写这种脚本时,你得知道你要什么功能,然后依照功能去找函数,找外部库。比如说我可能不知道有 pefile 这个外部库,但是我知道我需要 PE 的结构字段 Imagebase,RVA 转 FOA 这些功能,照着这些功能去搜索总能找到的。然后就是学习看官方文档,很多库在网络上的使用教程其实很少,但是官方文档描述得也不赖,而且看了这几个官方文档后发现格式排版,API 介绍,结构体对象等都有相通的地方,所以得多尝试从官方文档中找答案。
参考:
https://github.com/kevoreilly/CAPEv2/blob/f2ab891a278b2875c79b4f2916d086f870b54ed5/modules/processing/parsers/CAPE/Emotet.py
https://forum.butian.net/share/1804
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/socket.html?highlight=socket#module-socket
https://pefile.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/pefile.html
https://yara.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/itertools.html?highlight=itertools#itertools.cycle


![命令执行绕过 [GXYCTF2019]Ping Ping Ping1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c4a9c1cb751347df8c54f0de26ebaeaf.png)




![Flask框架配置celery-[1]:flask工厂模式集成使用celery,可在异步任务中使用flask应用上下文,即拿即用,无需更多配置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/92a5319c10354348b1c7ba2819c89045.png)