SpringBoot+Vue前后端文件传输问题总结
- 一、文件上传功能
- 前端:文件上传
- 1.File
- 2.FormData(常用)
- 3.Blob
- 4.ArrayBuffer
- 5.Base64
- 后端:文件接收
- 1.MultipartFile
- 二、文件下载功能
- 后端:文件传输
- 前端:文件接收
- 1.设置响应类型为'blob'
- 2.文件解析及下载
- 三、开发中遇到的问题
- 前端代码:
- 后端代码:
解决前后端文件传输的问题有以下几种解决方案:
1.文件上传时,前端以二进制流文件发送到后端,后端通过多种方式(MultipartFile/byte[]/File)进行接受,处理后进行存储;文件下载时,后端通常返回前端二进制流(byte[])的形式,并将文件附带信息(fileName、contentType)放在response header中一并传输到前端供其解析与下载。
2.微服务项目中,通常搭建网盘模块提供文件上传下载功能,供文件传输业务使用。
一、文件上传功能
前端:文件上传
前端文件上传主要有以下五种方式
- File
- FormData
- Blob
- ArrayBuffer
- Base64
1.File
文件上传 enctype 要用 multipart/form-data,而不是 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
<form action="http://localhost:8080/files" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="POST">
<input name="file" type="file" id="file">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
2.FormData(常用)
采用这种方式进行文件上传,主要是掌握文件上传的请求头和请求内容。
<template>
<div>
<el-form ref="form" :model="form" >
<el-form-item v-show="!form.isURL" label="文件" prop="file">
<el-upload
ref="upload"
:limit="1"
accept="*"
action="#"
class="el-input"
drag>
<i class="el-icon-upload"></i>
<div class="el-upload__text">拖拽文件或者单击以选择要上传的文件</div>
</el-upload>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="说明" prop="description">
<el-input v-model="form.description" autosize type="textarea"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="uploadFile()">上 传</el-button>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
import {downLoadFile} from "@/utils/downloadFile";
export default {
data() {
return {
form: {
description: '',
file: {},
}
}
},
methods: {
uploadFile() {
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', this.form.file.raw);
formData.append('description', this.form.description);
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/files', formData,{ headers: { 'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data' }}).then(res => {
console.log(res.data);
})
}
}
}
</script>
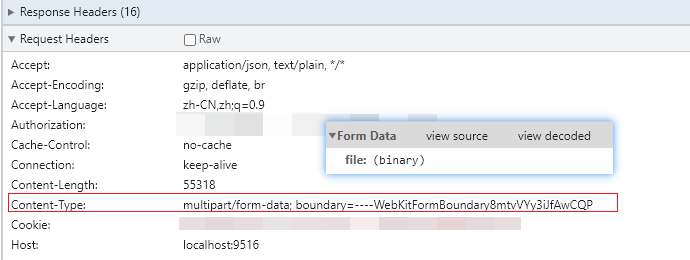
3.Blob
Blob 对象表示一个不可变、原始数据的类文件对象。Blob 表示的不一定是JavaScript原生格式的数据。File 接口基于Blob,继承了 blob 的功能并将其扩展使其支持用户系统上的文件。
1.直接使用 blob 上传
const json = { hello: "world" };
const blob = new Blob([JSON.stringify(json, null, 2)], { type: 'application/json' });
const form = new FormData();
form.append('file', blob, 'test.json');
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/files', form);
2.使用 File 对象,再进行一次包装
const json = { hello: "world" };
const blob = new Blob([JSON.stringify(json, null, 2)], { type: 'application/json' });
const file = new File([blob], 'test.json');
form.append('file', file);
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/files', form)
4.ArrayBuffer
ArrayBuffer 对象用来表示通用的、固定长度的原始二进制数据缓冲区、是最贴近文件流的方式。在浏览器中,ArrayBuffer每个字节以十进制的方式存在。
const bufferArrary = [137,80,78,71,13,10,26,10,0,0,0,13,73,72,68,82,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,3,0,0,0,37,219,86,202,0,0,0,6,80,76,84,69,0,0,255,128,128,128,76,108,191,213,0,0,0,9,112,72,89,115,0,0,14,196,0,0,14,196,1,149,43,14,27,0,0,0,10,73,68,65,84,8,153,99,96,0,0,0,2,0,1,244,113,100,166,0,0,0,0,73,69,78,68,174,66,96,130];
const array = Uint8Array.from(bufferArrary);
const blob = new Blob([array], {type: 'image/png'});
const form = new FormData();
form.append('file', blob, 'test.png');
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/files', form)
这里需要注意的是 new Blob([typedArray.buffer], {type: 'xxx'}),第一个参数是由一个数组包裹。里面是 typedArray 类型的 buffer。
5.Base64
const base64 = 'iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAEAAAABAQMAAAAl21bKAAAABlBMVEUAAP+AgIBMbL/VAAAACXBIWXMAAA7EAAAOxAGVKw4bAAAACklEQVQImWNgAAAAAgAB9HFkpgAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==';
const byteCharacters = atob(base64);
const byteNumbers = new Array(byteCharacters.length);
for (let i = 0; i < byteCharacters.length; i++) {
byteNumbers[i] = byteCharacters.charCodeAt(i);
}
const array = Uint8Array.from(byteNumbers);
const blob = new Blob([array], {type: 'image/png'});
const form = new FormData();
form.append('file', blob, 'test.png');
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/files', form);
后端:文件接收
1.MultipartFile
MultipartFile是SpringMVC提供简化上传操作的工具类。在不使用框架之前,都是使用原生的HttpServletRequest来接收上传的数据,文件是以二进制流传递到后端的,然后需要我们自己转换为File类,MultipartFile主要是用表单的形式进行文件上传,在接收到文件时,可以获取文件的相关属性,比如文件名、文件大小、文件类型等等。
- 需要注意,
@RequestParam MultipartFile file,因此前端传来的需要有形参file,即上文formData.append('file', this.form.file.raw);
@PostMapping("/upLoadFile")
public void upLoadFile(@RequestBody MultipartFile file) {
// 获取文件的完整名称,文件名+后缀名
System.out.println(file.getOriginalFilename());
// 文件传参的参数名称
System.out.println(file.getName());
// 文件大小,单位:字节
System.out.println(file.getSize());
// 获取文件类型,并非文件后缀名
System.out.println(file.getContentType());
try {
// MultipartFile 转 File
File resultFile = FileUtil.multipartFile2File(file);
System.out.println(resultFile.getName());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.info("文件转换异常");
}
}
FileUtil工具类
public class FileUtil {
/**
* file转byte
*/
public static byte[] file2byte(File file){
byte[] buffer = null;
try{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int n;
while ((n = fis.read(b)) != -1)
{
bos.write(b, 0, n);
}
fis.close();
bos.close();
buffer = bos.toByteArray();
}catch (FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return buffer;
}
/**
* byte 转file
*/
public static File byte2file(byte[] buf, String filePath, String fileName){
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
File file = null;
try{
File dir = new File(filePath);
if (!dir.exists() && dir.isDirectory()){
dir.mkdirs();
}
file = new File(filePath + File.separator + fileName);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
bos.write(buf);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
if (bos != null){
try{
bos.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fos != null){
try{
fos.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return file;
}
/**
* multipartFile转File
**/
public static File multipartFile2file(MultipartFile multipartFile){
File file = null;
if (multipartFile != null){
try {
file=File.createTempFile("tmp", null);
multipartFile.transferTo(file);
System.gc();
file.deleteOnExit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
log.warn("multipartFile转File发生异常:"+e);
}
}
return file;
}
}
二、文件下载功能
后端:文件传输
@GetMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<Resource> download( @RequestParam("fileId") String fileId) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(fileId)) {
File file = new File("test.jpg");
String fileName = file.getName();
String contentType = file.getContentType();
FileSystemResource fileSource = new FileSystemResource(file)
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "attachment;filename=" + fileName)
.header("filename", fileName)
// 配置使前端可以获取的header中的
.header(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_EXPOSE_HEADERS, "filename")
.contentLength(resource.contentLength())
.contentType(parseMediaType(contentType))
.body(fileSource);
}
return (ResponseEntity<Resource>) ResponseEntity.badRequest();
}

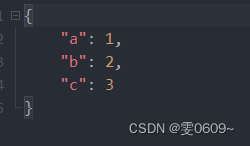
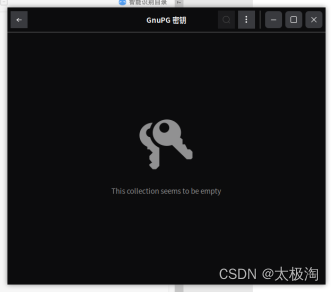
如果后端返回的是如下图一样的,那么就是传输的文件流
前端:文件接收
1.设置响应类型为’blob’
Blob:按文本或二进制的格式进行读取,在axios请求中设置response: 'blob'。
假设这是一个返回文件流的请求:
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/download', {
response: 'blob'
})
如果是post请求还需要在请求头里携带Content-Type: ‘multipart/form-data’
axios.post('http://localhost:8080/download', {
response: 'blob',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data'
}
})
2.文件解析及下载
axios.get(`http://localhost:8080/download?fileId=${fileId}`, { responseType: 'blob', observe: 'response' })
.then(response => {
const headers = response.headers;
console.log(response.headers)
const filename = headers['x-filename'];
const contentType = headers['content-type'];
const linkElement = document.createElement('a');
try {
const blob = new Blob([response.data], { type: contentType });
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
linkElement.setAttribute('href', url);
linkElement.setAttribute('download', filename);
const clickEvent = new MouseEvent('click',{
view: window,
bubbles: true,
cancelable: false
});
linkElement.dispatchEvent(clickEvent);
return null;
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('下载文件时出错:', error);
});
三、开发中遇到的问题
1.后端无法使用统一的结果返回类(统一结果返回类会被序列化为JSON),故需要使用可以携带二进制流文件(byte[])的返回类,即ResponseEntity<Resource>,通常需要将文件配置(文件名、文件类型)保存在http response headers头中,将二进制流文件放在ResponseEntity的body中。
2.前端发送请求时,要注意http请求的config配置(headers与responseType与observe),另外可以将文件解析下载的操作封装成一个js工具。
3.前后端交互时,axios请求放在response header里的文件名时,会出问题,跨前后端分离发送http请求时,默认reponse header中只能取到以下5个默认值,要想取得其他的字段需要在后端设置Access-Control-Expose-Headers 配置前端想要获取的header。
- Content-Language
- Content-Type
- Expires
- Last-Modified
- Pragma
前端代码:
downloadPackage(row) {
this.$api.downloadOtaPackage(row.id.id)
.then(res => {
downLoadFile(res)
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('下载文件时出错:', error);
});
},
downLoadFile.js
export function downLoadFile (res) {
// 获取响应头中的filename contentType
const headers = res.headers;
const filename = headers['x-filename'];
const contentType = headers['content-type'];
// 创建一个a链接标签
const linkElement = document.createElement('a');
try {
// 将返回的文件流转换成一个blob文件对象
const blob = new Blob([res.data], { type: contentType });
// 生成一个文件对象的url地址
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
// 将文件对象的url地址赋值给a标签的href属性
linkElement.setAttribute('href', url);
// 为a标签添加download属性并指定文件的名称
linkElement.setAttribute('download', filename);
// 调用a标签的点击函数
const clickEvent = new MouseEvent('click',
{
view: window,
bubbles: true,
cancelable: false
}
);
linkElement.dispatchEvent(clickEvent);
// 释放URL对象
URL.revokeObjectURL(url);
// 将页面的a标签删除
document.body.removeChild(linkElement);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
}
}
后端代码:
@GetMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<Resource> downloadOtaPackage(
@ApiParam(value = "OTA包Id", required = true) @RequestParam("otaPackageId") String otaPackageId
) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(otaPackageId)) {
ResponseEntity<Resource> responseEntity = iOtaClient.downloadOtaPackage(otaPackageId);
ByteArrayResource resource = (ByteArrayResource) responseEntity.getBody();
String fileName = responseEntity.getHeaders().get("x-filename").get(0);
String contentType = responseEntity.getHeaders().getContentType().toString();
// return FileResult.success(resource, fileName, contentType);
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, "attachment;filename=" + fileName)
.header("x-filename", fileName)
.header(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_EXPOSE_HEADERS, "x-filename")
.contentLength(resource.contentLength())
.contentType(parseMediaType(contentType))
.body(resource);
}
return (ResponseEntity<Resource>) ResponseEntity.badRequest();
}
参考文章:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/120834588
- https://www.cnblogs.com/liuxianbin/p/13035809.html