参考文献
基于峰谷分时电价引导下的电动汽车充电负荷优化_欧名勇2020
主要内容
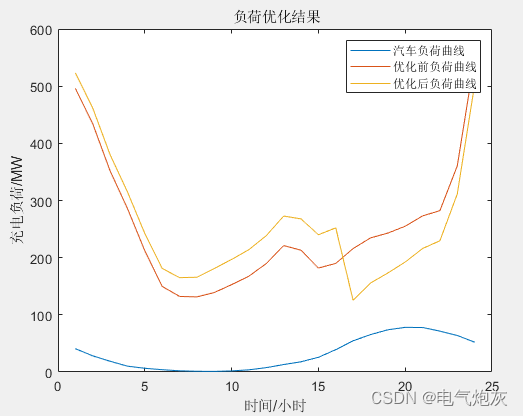
利用蒙特卡洛方法对2种不同充电方式进行模拟并对其进行分析;分析用户响应度对电动汽车有序充电的影响,建立峰谷分时电价对电动汽车负荷影响的模型,在模拟出电动汽车无序充电负荷的基础上,用实际案例对模型进行验证,利用多目标优化遗传算法进行求解,验证峰谷分时电价对电网负荷优化的有效性。
部分程序
for run = 1:no_runs
%% 原始种群
xl_temp=repmat(xl, pop_size,1);
xu_temp=repmat(xu, pop_size,1);
x = xl_temp+((xu_temp-xl_temp).*rand(pop_size,V));
%% Evaluate objective function
for i =1:pop_size
[ff(i,:),err(i,:)] =feval(fname, x(i,:)); % 目标函数评估
end
error_norm=normalisation(err); % 约束违规的归一化
population_init=[x ff error_norm];
[population,front]=NDS_CD_cons(population_init); % 对初始种群的非统治性排序
%% 一代开始
for gen_count=1:gen_max
gen_count
% selection (Parent Pt of 'N' pop size)
parent_selected=tour_selection(population); % 10 Tournament selection
%% Reproduction (Offspring Qt of 'N' pop size)
child_offspring = genetic_operator(parent_selected(:,1:V)); % SBX交叉和突变
for ii = 1:pop_size
[fff(ii,:) err(ii,:)]=feval(fname, child_offspring(ii,:)); % 后代目标函数评估
end
error_norm=normalisation(err);
child_offspring=[child_offspring fff error_norm];
%% INtermediate population (Rt= Pt U Qt of 2N size)
population_inter=[population(:,1:V+M+1) ; child_offspring(:,1:V+M+1)];
[population_inter_sorted, front]=NDS_CD_cons(population_inter); % 对子代的排序
%% Replacement - N
new_pop=replacement(population_inter_sorted, front);
population=new_pop;
end
new_pop=sortrows(new_pop,V+1);
paretoset(run).trial=new_pop(:,1:V+M+1);
Q = [Q; paretoset(run).trial]; % 结合每次运行中获得的帕累托解决方案
end
%% Result and Pareto plot
figure(2)
if run==1
plot(new_pop(:,V+1),new_pop(:,V+2),'*')
else
[pareto_filter front]=NDS_CD_cons(Q) ; % 在组合的Pareto解决方案集上应用非控制性排序
rank1_index=find(pareto_filter(:,V+M+2)==1); % 筛选等级1帕累托的最佳解决方案
pareto_rank1=pareto_filter(rank1_index,1:V+M);
plot(pareto_rank1(:,V+1),pareto_rank1(:,V+2),'*') % 最终帕累托图
end
运行结果