一、接收 Form 表单数据
1,基本的接收方法
(1)下面样例 Controller 接收 form-data 格式的 POST 数据:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello1")
public String postHello1(@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestParam("age") Integer age) {
return "name:" + name + "\nage:" + age;
}
}
(2)下面是一个简单的测试样例:

2,参数没有传递的情况
(1)如果没有传递参数 Controller 将会报错,这个同样有如下两种解决办法:
- 使用 required = false 标注参数是非必须的。
- 使用 defaultValue 给参数指定个默认值。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello2")
public String postHello2(@RequestParam(name = "name", defaultValue = "xxx") String name,
@RequestParam(name = "age", required = false) Integer age) {
return "name:" + name + "\nage:" + age;
}
}
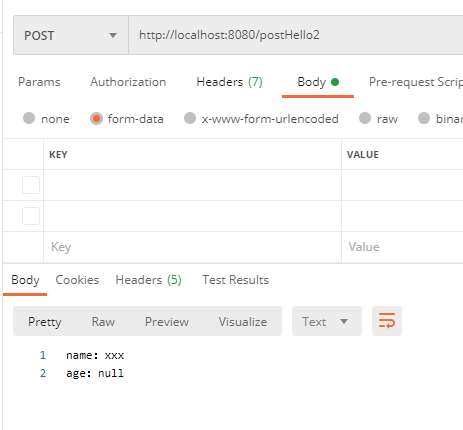
3,使用 map 来接收参数
(1)Controller 还可以直接使用 map 来接收所有的请求参数:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello3")
public String postHello3(@RequestParam Map<String,Object> params) {
return "name:" + params.get("name") + "\nage:" + params.get("age");
}
}
(2)下面是一个简单的测试样例:

4,接收一个数组
(1)表单中有多个同名参数,Controller 这边可以定义一个数据进行接收:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello4")
public String postHello4(@RequestParam("name") String[] names) {
String result = "";
for(String name:names){
result += name + "\n";
}
return result;
}
}
(2)下面是一个简单的测试样例:
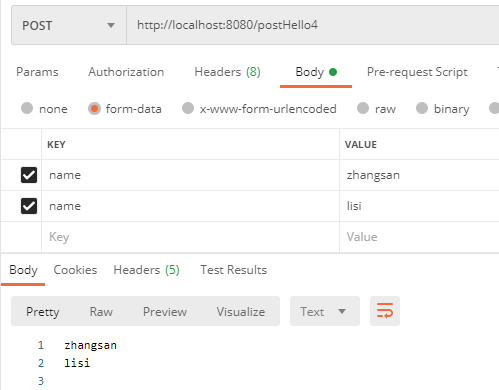
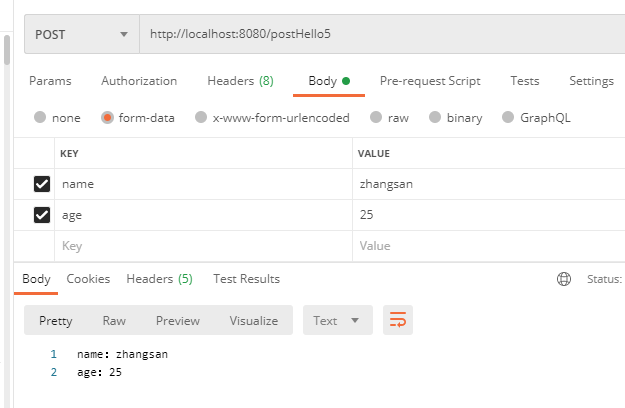
5,使用对象来接收参数
1)如果一个 post 请求的参数太多,我们构造一个对象来简化参数的接收方式:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello5")
public String postHello5(User user) {
return "name:" + user.getName() + "\nage:" + user.getAge();
}
}
(2)User 类的定义如下,到时可以直接将多个参数通过 getter、setter 方法注入到对象中去:
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
(3)下面是一个简单的测试样例:
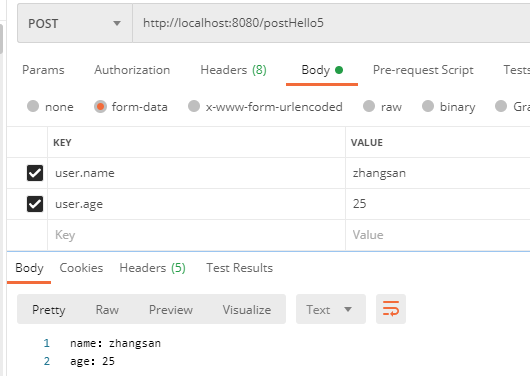
(4)如果传递的参数有前缀,且前缀与接收实体类的名称相同,那么参数也是可以正常传递的:
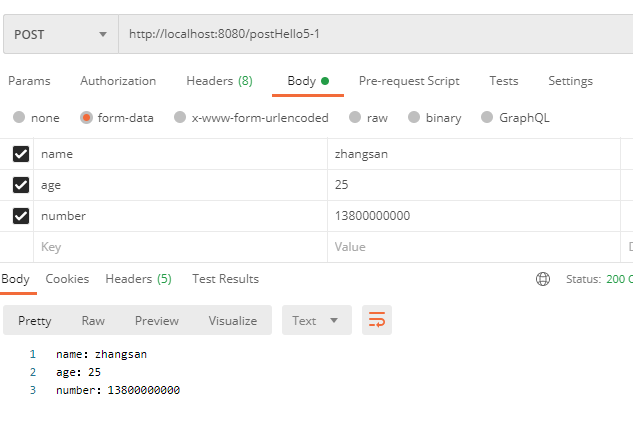
(5)如果一个 post 请求的参数分属不同的对象,也可以使用多个对象来接收参数:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello5-1")
public String hello(User user, Phone phone) {
return "name:" + user.getName() + "\nage:" + user.getAge()
+ "\nnumber:" + phone.getNumber();
}
}
6,使用对象接收时指定参数前缀
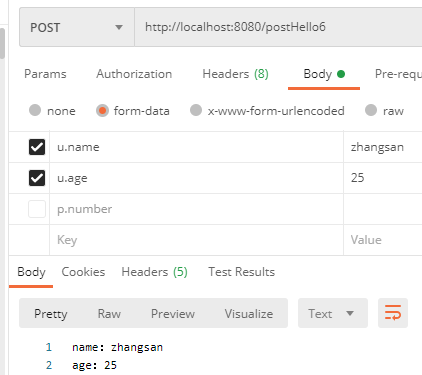
(1)如果传递的参数有前缀,且前缀与接收实体类的名称不同相,那么参数无法正常传递:

(2)我们可以结合 @InitBinder 解决这个问题,通过参数预处理来指定使用的前缀为 u.
除了在 Controller 里单独定义预处理方法外,我们还可以通过 @ControllerAdvice 结合 @InitBinder 来定义全局的参数预处理方法,方便各个 Controller 使用。具体做法参考我之前的文章:
- SpringBoot - @ControllerAdvice的使用详解3(请求参数预处理 @InitBinder)
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/postHello6")
public String postHello6(@ModelAttribute("u") User user) {
return "name:" + user.getName() + "\nage:" + user.getAge();
}
@InitBinder("u")
private void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("u.");
}
}
(3)重启程序再次发送请求,可以看到参数已经成功接收了:
二、接收字符串文本数据
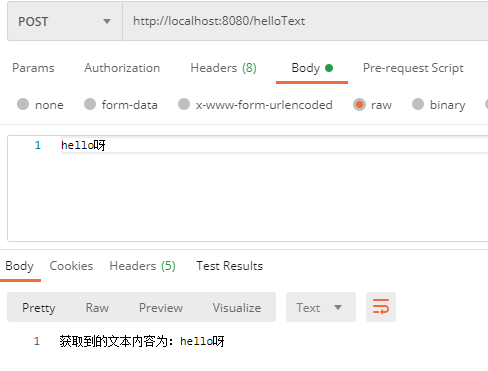
(1)如果传递过来的是 Text 文本,我们可以通过 HttpServletRequest 获取输入流从而读取文本内容。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.ServletInputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/helloText")
public String hello(HttpServletRequest request) {
ServletInputStream is = null;
try {
is = request.getInputStream();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
sb.append(new String(buf, 0, len));
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
return "获取到的文本内容为:" + sb.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
三、接收 JSON 数据
1,使用 Map 来接收数据
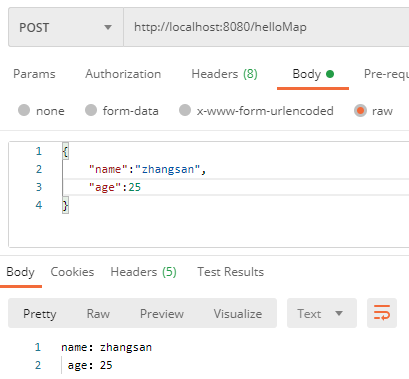
(1)如果把 json 作为参数传递,我们可以使用 @requestbody 接收参数,将数据转换 Map:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/helloMap")
public String helloMap(@RequestBody Map params) {
return "name:" + params.get("name") + "\n age:" + params.get("age");
}
}
(2)下面是一个简单的测试样例:
2,使用 Bean 对象来接收数据
(1)如果把 json 作为参数传递,我们可以使用 @requestbody 接收参数,将数据直接转换成对象:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/helloBean")
public String hello(@RequestBody User user){
return user.getName() + " " + user.getAge();
}
}
(2)下面是一个简单的测试样例:
(4)如果传递的 JOSN 数据是一个数组也是可以的,Controller 做如下修改:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/helloList")
public String helloList(@RequestBody List<User> users){
String result = "";
for(User user:users){
result += user.getName() + " " + user.getAge() + "\n";
}
return result;
}
}