一、概述
目前操作 Excel 比较流行的就是 Apache POI 和阿里巴巴的 easyExcel。
1.1 POI 简介
Apache POI 是用 Java 编写的免费开源的跨平台的 Java API,Apache POI 提供 API 给 Java 程序对 Microsoft Office 格式文档读和写的常用功能。POI 为 “Poor Obfuscation Implementation” 的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。其常用的结构如下:
HSSF -- 提供读写 03 版本的 Excel 常用功能。
XSSF -- 提供读写 07 版本的 Excel 常用功能。
HWPF -- 提供读写 Word 格式的常用功能
HSLF -- 提供读写 ppt 格式的常用功能。
HDGF -- 提供读写 visio 格式的常用功能
1.2 easyExcel 简介
easyExcel 是阿里巴巴开源的一个 excel 处理框架,以使用简单、节省内存著称。easyExcel 能大大减少占用内存的主要原因是在解析 Excel 时没有将文件数据一次性全部加载到内存中,而是从磁盘上一行行读取数据,逐个解析。
easyExcel 官网地址:https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
1.3 xls 和 xlsx 区别
常用的 excel 文档有两种结尾形式,分别为 xls 和 xlsx,其中以 xls 结尾的文档属于 03 版本的,它里面最多可以存储 65536 行数据。而以 xlsx 结尾的文档属于 07 版本的,它理论上可以存储无限行数据,这就是两者之前的区别。
二、POI 常用操作
2.1 添加 maven 依赖
<dependencies>
<!--xls(03 版本)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--xlsx(07 版本)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日期格式化工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.2 写入 Excel 操作
2.2.1 一般文件写入
2.2.1.1 03 版本
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testWrite03() throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("我是 sheet1 页");
// 3、创建一行
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
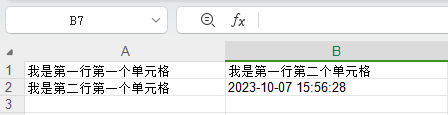
// 4、创建一个单元格
Cell cell11 = row1.createCell(0);
cell11.setCellValue("我是第一行第一个单元格");
Cell cell12 = row1.createCell(1);
cell12.setCellValue("我是第一行第二个单元格");
// 第二行
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.createCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue("我是第二行第一个单元格");
Cell cell22 = row2.createCell(1);
String time = new DateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
cell22.setCellValue(time);
// 03 版本的使用 xls 结尾
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH+"统计表03类型.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("Excel03 写入完成了");
}
}
2.2.2.2 07 版本
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testWrite07() throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("我是 sheet1 页");
// 3、创建一行
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
// 4、创建一个单元格
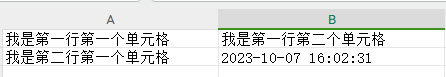
Cell cell11 = row1.createCell(0);
cell11.setCellValue("我是第一行第一个单元格");
Cell cell12 = row1.createCell(1);
cell12.setCellValue("我是第一行第二个单元格");
// 第二行
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.createCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue("我是第二行第一个单元格");
Cell cell22 = row2.createCell(1);
String time = new DateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
cell22.setCellValue(time);
// 07 版本的使用 xlsx 结尾
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH+"统计表07类型.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("Excel07 写入完成了");
}
}
2.2.2 大文件写入
2.2.2.1 03 版本
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testWrite03BigData() throws Exception {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 1、创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 3、写入数据
for(int rowNum =0;rowNum<65537;rowNum++){
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for(int cellNum=0;cellNum<10;cellNum++){
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH+"统计表03大数据类型.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double)(end-begin)/1000);
}
}缺点:最多只能处理 65536 行,否则会抛出异常。
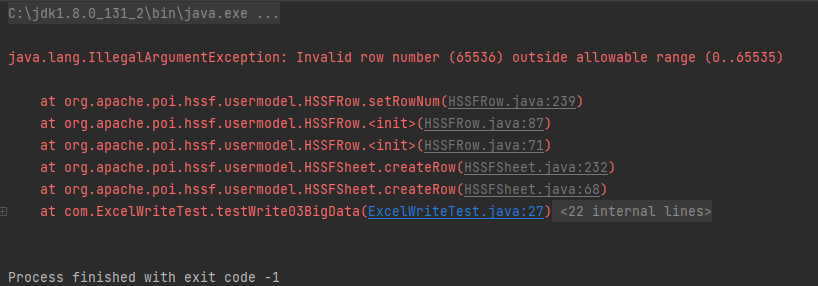
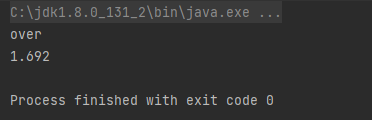
优点:写入过程中写入缓存,不操作磁盘,最后一次性写入磁盘,速度快。将 65537 改成65536 再次执行程序,结果如下,可以看到 1.692s 就完成了写入操作,速度还是很快的。
2.2.2.2 07 版本
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testWrite07BigData() throws Exception {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 1、创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 3、写入数据
for(int rowNum =0;rowNum<100000;rowNum++){
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for(int cellNum=0;cellNum<10;cellNum++){
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH+"统计表07大数据类型.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double)(end-begin)/1000);
}
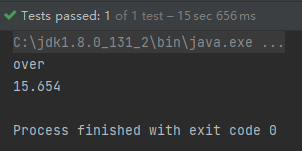
}缺点:写数据时速度非常慢,非常耗内存,也会发生内存溢出,如100万条。
优点:可以写较大的数据量,如20万条。
2.2.2.3 07 版本优化
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.streaming.SXSSFWorkbook;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testWrite07BigDataS() throws Exception {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 1、创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
// 2、创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 3、写入数据
for(int rowNum =0;rowNum<100000;rowNum++){
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for(int cellNum=0;cellNum<10;cellNum++){
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH+"统计表07大数据类型优化.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
// 清除产生的临时文件
((SXSSFWorkbook)workbook).dispose();
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double)(end-begin)/1000);
}
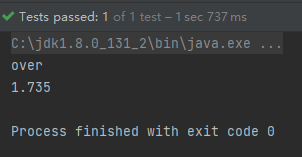
}优点:可以写非常大的数据量,如 100万 条甚至更多条,数据速度快,占用更少的内存。
需要注意的是:代码在过程中会产生临时文件,需要清理临时文件。默认有 100 条记录被保存在内存中,如果超过这数量,则最前面的数据被写入临时文件。如果想自定义内存中数据的数量,可以使用 new SXSSFWorkbook(数量) 。
SXSSFWorkbook 来至官方的解释:实现 “BigGridDemo” 策略的流式 XSSFWorkbook 版本。这允许写入非常大的文件而不会耗尽内存,因为任何时候只有可配置的行部分被保存在内存中。请注意,仍然可能会消耗大量内存,这些内存基于您正在使用的功能,例如合并区域,注释……仍然只存储在内存中,因此如果广泛使用,可能需要大量内存。
2.3 读取 Excel 操作
2.3.1 03 版本
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class ExcelRead {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testRead03() throws Exception {
// 1、获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH+"统计表03类型.xls");
// 2、创建文件簿,使用 excel 能操作的这边都可以操作
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 3、得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 4、得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
// 5、得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 读取值的时候需要注意类型,String 和数字调用的方法是不同的。
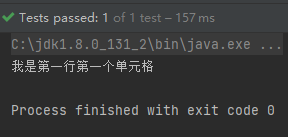
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
2.3.2 07 版本
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class ExcelRead {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testRead07() throws Exception {
// 1、获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH+"统计表07类型.xlsx");
// 2、创建文件簿,使用 excel 能操作的这边都可以操作
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 3、得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 4、得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
// 5、得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(1);
// 读取值的时候需要注意类型,String 和数字调用的方法是不同的。
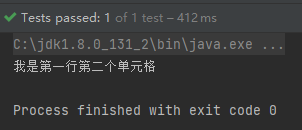
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
2.3.3 读取不同类型
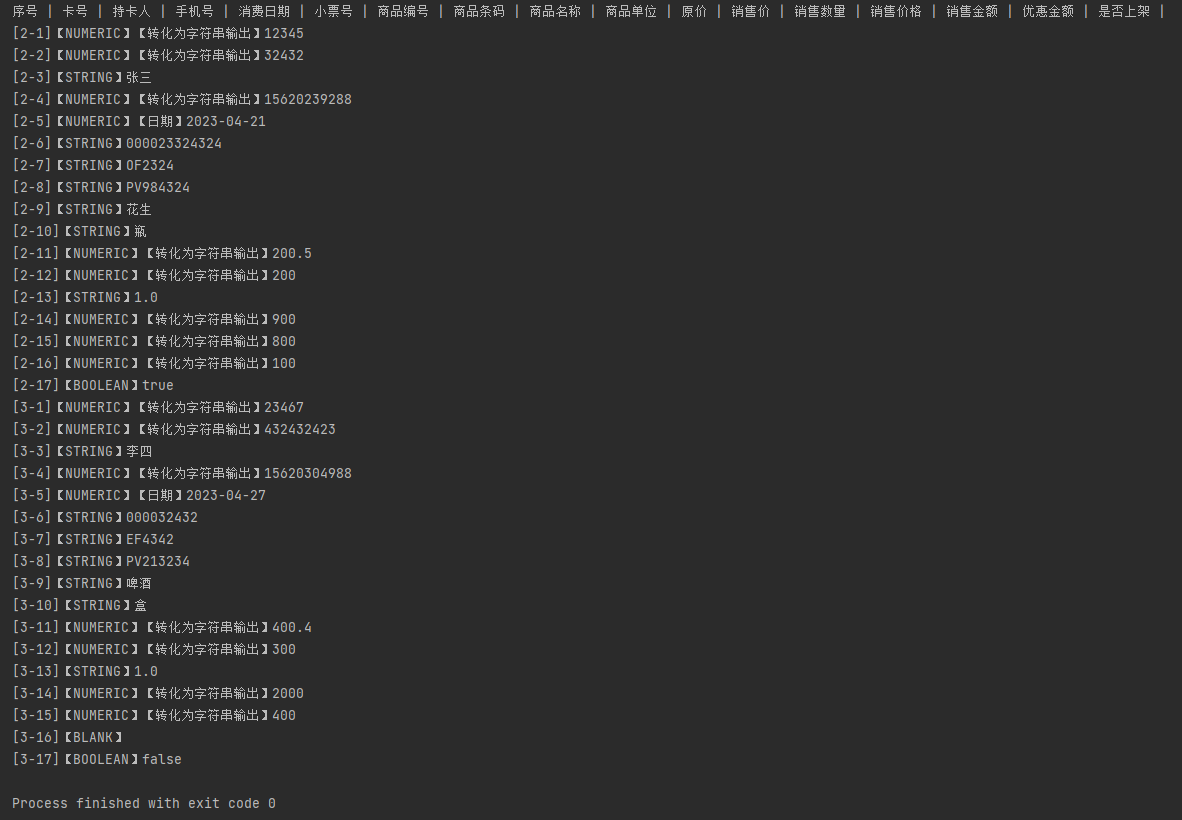
表格的内容如下所示:

代码如下所示:
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFDateUtil;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Date;
public class ExcelRead {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testCellType() throws Exception{
// 1、获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH+"03商品信息.xls");
// 2、创建文件簿,使用 excel 能操作的这边都可以操作
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 3、得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 4、获取标题内容
Row rowTitle = sheet.getRow(0);
if(rowTitle != null){
// 获取列的数量
int cellCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for(int cellNum=0;cellNum<cellCount;cellNum++){
Cell cell = rowTitle.getCell(cellNum);
if(cell != null){
// 获取列的类型
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
// 获取具体的列名
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(cellValue+" | ");
}
}
}
System.out.println();
// 5、获取表中的内容
// 获取有多少行的记录
int rowCount = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
for(int rowNum=1;rowNum<rowCount;rowNum++){
// 获取第一行数据
Row rowData = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if(rowData !=null){
// 读取行中的列
int cellCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for(int cellNum=0;cellNum<cellCount;cellNum++){
System.out.print("["+(rowNum+1)+"-"+(cellNum+1)+"]");
Cell cell = rowData.getCell(cellNum);
// 匹配类的数据类型
if(cell != null){
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue="";
switch(cellType){
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("【STRING】");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: //布尔
System.out.print("【BOOLEAN】");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK: //空
System.out.print("【BLANK】");
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: //数字(分为日期和普通数字)
System.out.print("【NUMERIC】");
if(HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)){ // 日期
System.out.print("【日期】");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
}else{
// 非日期格式,转换成字符串格式
System.out.print("【转化为字符串输出】");
cell.setCellType(HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR: //字符串
System.out.print("【数据类型错误】");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
2.3.4 读取公式
操作的表格内容如下所示:
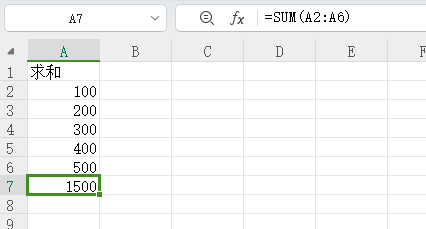
代码如下所示:
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class ExcelRead {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\";
@Test
public void testFormula() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "03求和.xls");
// 1.创建一个工作簿。使得excel能操作的,这边他也能操作。
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 2.得到表。
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(6);
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 拿到计算公司
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new HSSFFormulaEvaluator((HSSFWorkbook) workbook);
// 输出单元格内容
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
switch (cellType){
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
String cellFormula = cell.getCellFormula();
System.out.println(cellFormula);
// 计算
CellValue evaluate = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
String cellValue = evaluate.formatAsString();
System.out.println(cellValue);
break;
}
}
}
三、EasyExcel 常用操作
3.1 添加 maven 依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 主要是这个依赖,剩下的依赖都是测试用到的 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>lambada</groupId>
<artifactId>lambada</artifactId>
<version>1.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!--test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>3.2 写操作
先模拟一个实体类,如下所示:
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelIgnore;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.Date;
@Getter
@Setter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class DemoData {
@ExcelProperty("字符串标题")
private String string;
@ExcelProperty("日期标题")
private Date date;
@ExcelProperty("数字标题")
private Double doubleData;
/**
* 忽略这个字段
*/
@ExcelIgnore
private String ignore;
}然后写入文档即可,如下所示:
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.util.ListUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class TestWrite {
@Test
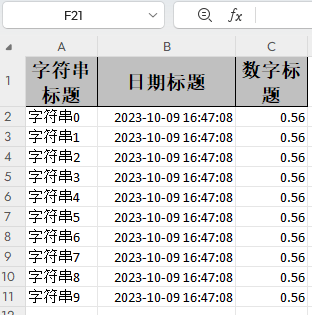
public void simpleWrite() {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\easyexcel统计表03类型.xlsx";
EasyExcel.write(PATH, DemoData.class)
.sheet("模板")
.doWrite(() -> {
// 分页查询数据
return data();
});
}
private List<DemoData> data() {
List<DemoData> list = ListUtils.newArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
DemoData data = new DemoData();
data.setString("字符串" + i);
data.setDate(new Date());
data.setDoubleData(0.56);
list.add(data);
}
return list;
}
}
3.3 读操作
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.Date;
@Getter
@Setter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class DemoData {
private String string;
private Date date;
private Double doubleData;
}import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.PageReadListener;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.junit.Test;
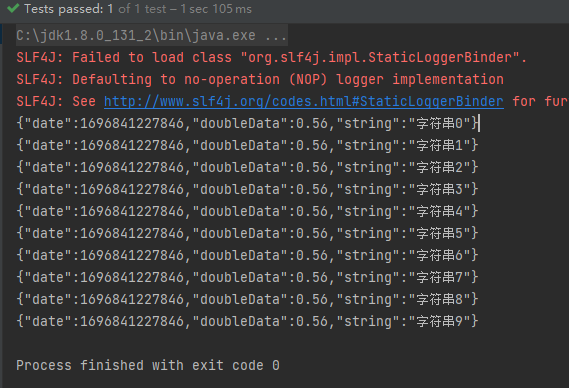
public class TestRead {
@Test
public void simpleRead() {
String PATH ="F:\\idea_home\\poi-excel\\easyexcel统计表03类型.xlsx";
// 这里 需要指定读用哪个class去读,然后读取第一个sheet 文件流会自动关闭
// 这里每次会读取3000条数据 然后返回过来 直接调用使用数据就行
EasyExcel.read(PATH, DemoData.class, new PageReadListener<DemoData>(dataList -> {
for (DemoData demoData : dataList) {
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(demoData));
}
})).sheet().doRead();
}
}
3.4 更多操作
详细的文档地址:https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel