目录
- 一、是什么?
- 二、demo演示
- 三、应用之同步等待多线程准备完毕
- 四、 应用之同步等待多个远程调用结束
- 五、CountDownLatch 原理
一、是什么?
CountdownLatch 用来进行线程同步协作,等待所有线程完成倒计时。
其中构造参数用来初始化等待计数值,await() 用来等待计数归零,countDown() 用来让计数减一
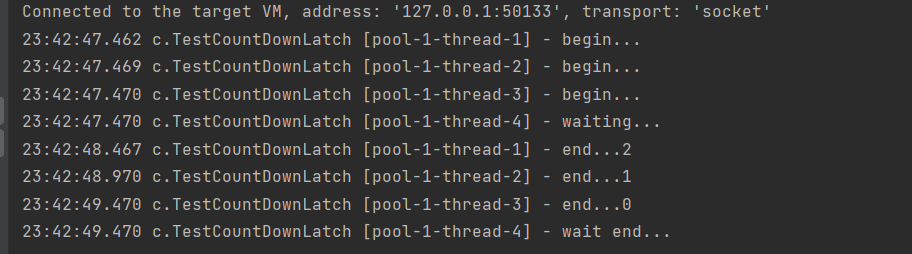
二、demo演示
public class TestCountDownLatch {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
test5();
}
private static void test5() {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1.5);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(2);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(()->{
try {
log.debug("waiting...");
latch.await();
log.debug("wait end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
三、应用之同步等待多线程准备完毕
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10, (r) -> {
return new Thread(r, "t" + num.getAndIncrement());
});
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
String[] all = new String[10];
Random r = new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int x = j;
service.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
all[x] = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "(" + (i + "%") + ")";
System.out.print("\r" + Arrays.toString(all));
}
latch.countDown();
});
}
latch.await();
System.out.println("\n游戏开始...");
service.shutdown();
}
四、 应用之同步等待多个远程调用结束
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
log.debug("begin");
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(4);
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/order/{1}", Map.class, 1);
log.debug("{}",response);
latch.countDown();
});
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response1 = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 1);
log.debug("{}",response1);
latch.countDown();
});
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response2 = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 2);
log.debug("{}",response2);
latch.countDown();
});
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response3 = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/logistics/{1}", Map.class, 1);
log.debug("{}",response3);
latch.countDown();
});
latch.await();
log.debug("执行完毕");
service.shutdown();
}
五、CountDownLatch 原理
AQS