一 std::list 介绍
list 是 c++ 中的序列式容器,其实现是双向链表,每个元素都有两个指针,分别指向前一个节点与后一个节点
链表与数组都是计算机常用的内存数据结构,与数组连续内存空间不一样的地方在于,链表的空间是不连续的,链表是将一块块不连续的内存串联起来使用。
正是由于链表的内存不连续这一特点,所以不能像数组一样,可以根据位置随机的访问每个元素,而链表我们压根不知道每个元素的实际位置到底在哪块内存区域。
查找某个元素需要遍历整个链表,直到找到目标元素位置,时间复杂度是 O(n);
在链表中插入一个元素与删除一个元素的时间复杂度是 O(1);
二 c++ 中 stl 链表结构
1. list 结构
list 结构 (借用侯捷老师的一张图片来):
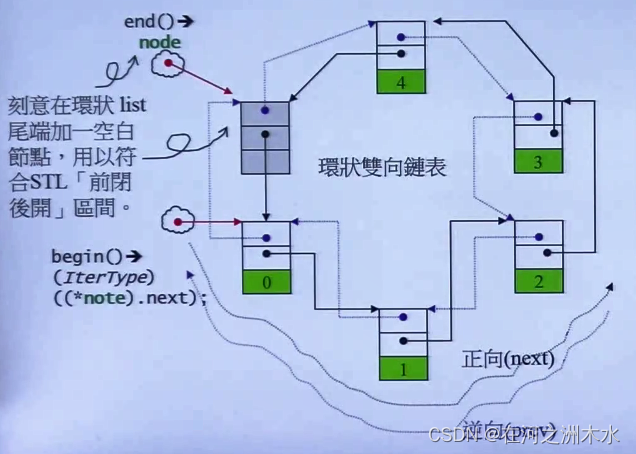
由上面的结构上可以看出,list 是一个循环链表,链表的尾端是一个空节点,不存储任何数据。
三 c++ 中 stl 链表使用
1 构造函数
| 构造函数 | 说明 |
| list() | 空构造函数 |
| list( size_type count, const T& value) | 初始化一个元素数量为 count 个的 value 元素 |
| list( std::initializer_list<T> init) | 利用列表初始化 list |
| list( InputIt first, InputIt last) | 利用迭代器的起始于终止位置初始化 list |
2 容器修改
| 函数 | 说明 |
| clear() | 清空所有元素 |
| insert | 在指定位置插入元素 |
| emplace | 在指定位置插入元素, 可以通过直接传入元素类的构造参数实现原地构造 |
| erase | 移除指定元素 |
| push_back | append 元素到链表的尾部 |
| pop_back | 将链表尾部元素弹出 |
| push_front | append 元素到链表的头部 |
| pop_front | 将链表头部元素弹出 |
| emplace_back | append 元素到链表的尾部, 可以通过直接传入元素类的构造参数实现原地构造 |
| emplace_front | append 元素到链表的头部, 可以通过直接传入元素类的构造参数实现原地构造 |
3 容器访问
| 函数 | 说明 |
| begin | 返回头部元素的迭代器 |
| end | 返回尾部元素的迭代器 |
| rbegin | 返回尾部元素的迭代器 |
| rend | 返回头部元素的迭代器 |
| front | 返回头部元素的引用 |
| back | 返回尾部元素的引用 |
4 容器容量
| 函数 | 说明 |
| empty | 判断 list是否为空 |
| size | 返回 list 存储元素的个数 |
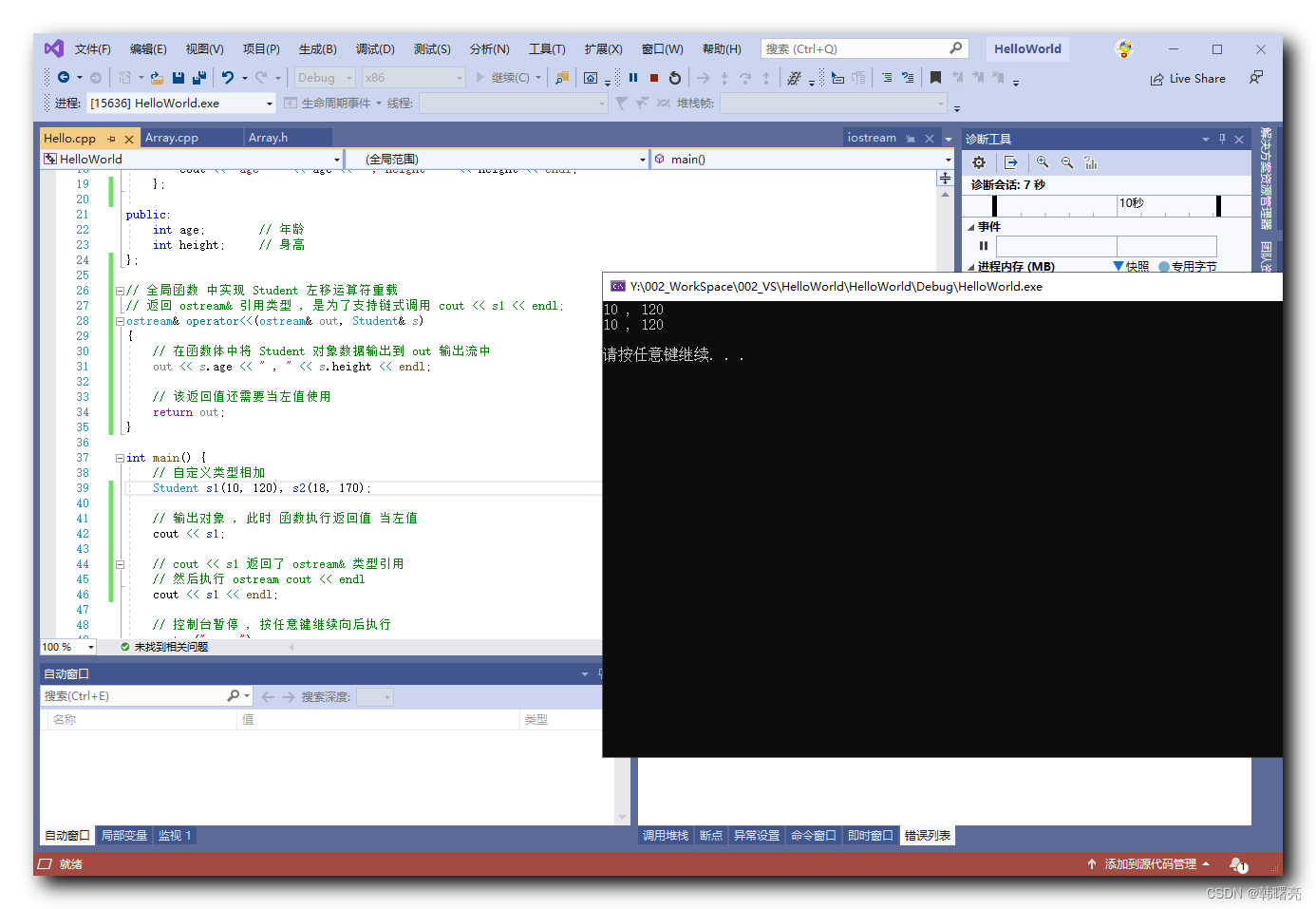
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
int main()
{
// 1. 构造函数
std::list<int> list;
auto iter = list.begin();
std::cout << *iter << "--- " << std::endl;;
// 2. 容器修改
list.push_back(1);
list.push_back(2);
list.push_back(3);
list.push_back(4);
list.push_back(5);
list.push_front(11);
list.push_front(22);
list.pop_back();
list.pop_front();
list.insert(list.begin(), 666);
// 3. 容器访问
for(auto iter = list.begin(); iter != list.end();iter++)
{
std::cout << *iter << " "; // 666 11 1 2 3 4
}
std::cout << "" << std::endl;
for(auto iter = list.rbegin(); iter != list.rend();iter++)
{
std::cout << *iter << " "; // 4 3 2 1 11 666
}
std::cout << "" << std::endl;
std::cout << "first: " << list.front() << ", finish: " << list.back() << std::endl; // first: 666, finish: 4
// 4. 容器容量
std::cout << "empyt: " << list.empty() << std::endl; // 0
std::cout << "size: "<< list.size() << std::endl; // 6
list.clear();
std::cout << "empyt: " << list.empty() << std::endl; // 1
std::cout << "size: "<< list.size() << std::endl; // 0
return 0;
}四 简单实现
// my_list.h
#include<memory>
#include<iostream>
template<typename T>
struct _List_Node
{
typedef _List_Node node;
_List_Node()
{
prev = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
_List_Node(T& da):data(da)
{
prev = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
_List_Node(T&& da):data(da)
{
prev = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
~_List_Node()
{
prev = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
node* prev;
node* next;
T data;
};
template<typename T>
struct _List_Iterator
{
typedef T valueType;
typedef T& refrence;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef _List_Node<T> node;
_List_Iterator(node* val):data(val)
{
}
_List_Iterator& operator++()
{
this->data = this->data->next;
return *this;
}
_List_Iterator operator++(int)
{
_List_Iterator tmp = *this;
++(*this);
return tmp;
}
_List_Iterator& operator--()
{
this->data = this->data->prev;
return *this;
}
_List_Iterator operator--(int)
{
_List_Iterator tmp = *this;
--(*this);
return tmp;
}
T& operator*()
{
return this->data->data;
}
bool operator != (_List_Iterator& other)
{
return this->data != other->data;
}
bool operator == (_List_Iterator& other)
{
return this->data == other.data;
}
bool operator != (_List_Iterator&& other)
{
return this->data != other.data;
}
bool operator == (_List_Iterator&& other)
{
return this->data == other.data;
}
node* data;
};
template<typename T>
class my_list
{
typedef _List_Node<T> node;
typedef _List_Iterator<T> iterator;
public:
my_list():count(0)
{
next_curr = new node;
pre_curr = next_curr;
finish = new node;
next_curr->next = finish;
finish->next = next_curr;
pre_curr->prev = finish;
finish->prev = pre_curr;
}
~my_list()
{
node* tmp = pre_curr;
while (tmp != nullptr) {
node* tt = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = tt;
}
}
void push_back(T& val)
{
std::cout << "count: " << count << std::endl;
if(count == 0)
next_curr->data = val;
else {
node* tmp = new node(val);
tmp->next = next_curr->next;
tmp->next->prev = tmp;
next_curr->next = tmp;
tmp->prev = next_curr;
next_curr = next_curr->next;
}
count++;
}
void push_back(T&& val)
{
push_back(val);
}
void push_front(T& val)
{
if(count == 0)
pre_curr->data = val;
else {
node* tmp = new node(val);
tmp->prev = pre_curr->prev;
pre_curr->prev->next = tmp;
tmp->next = pre_curr;
pre_curr->prev = tmp;
pre_curr = pre_curr->prev;
}
count++;
}
void push_front(T&& val)
{
push_front(val);
}
void pop_back()
{
if(count == 0)
{
return;
} else
{
node* tmp = next_curr;
next_curr->prev->next = next_curr->next;
next_curr->next->prev = next_curr->prev;
next_curr = next_curr->prev;
delete tmp;
count--;
}
}
void pop_front()
{
if(count == 0)
{
return;
} else
{
node* tmp = pre_curr;
finish->next = pre_curr->next;
pre_curr->next->prev = finish;
pre_curr = pre_curr->next;
delete tmp;
count--;
}
}
int size()
{
return count;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(pre_curr);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(finish);
}
iterator rbegin()
{
return iterator(finish->prev);
}
iterator rend()
{
return iterator(pre_curr->prev);
}
void insert(iterator pos, T& val)
{
node* tmp = new node(val);
pos.data->prev->next = tmp;
tmp->prev = pos.data->prev;
tmp->next = pos.data;
pos.data->prev = tmp;
if(pos.data == pre_curr)
{
pre_curr = pre_curr->prev;
}
else if(pos.data == next_curr){
next_curr = next_curr->next;
}
count++;
}
void insert(iterator pos, T&& val)
{
insert(pos, val);
}
template<typename ... Args>
void emplace(iterator pos, Args... args)
{
node* tmp = new node(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
pos.data->prev->next = tmp;
tmp->prev = pos.data->prev->next;
tmp->next = pos.data;
pos.data->prev = tmp;
count++;
}
void erase(iterator pos)
{
node* tmp = pos.data;
tmp->prev = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
count--;
}
void clear()
{
while (pre_curr->next != finish) {
pop_back();
}
count = 0;
}
T& front()
{
return pre_curr->data;
}
T& back()
{
return next_curr->data;
}
bool empty()
{
return count == 0;
}
public:
node* next_curr = nullptr;
node* pre_curr = nullptr;
node* finish = nullptr;
int count;
};
// main.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<my_list.h>
int main()
{
// 1. 构造函数
my_list<int> list;
// 2. 容器修改
list.push_back(1);
list.push_back(2);
list.push_back(3);
list.push_back(4);
list.push_back(5);
list.push_front(11);
list.push_front(22);
// 22 11 1 2 3 4 5
list.pop_back();
list.pop_front();
list.insert(list.begin(), 666);
// 3. 容器访问
for(auto iter = list.begin(); iter != list.end();iter++)
{
std::cout << *iter << " "; // 666 11 1 2 3 4
}
std::cout << "" << std::endl;
for(auto iter = list.rbegin(); iter != list.rend();iter--)
{
std::cout << *iter << " "; // 4 3 2 1 11 666
}
std::cout << "" << std::endl;
std::cout << "first: " << list.front() << ", finish: " << list.back() << std::endl; // first: 666, finish: 4
// 3. 容器容量
std::cout << "empty: " << list.empty() << std::endl; // 0
std::cout << "size: "<< list.size() << std::endl; // 6
list.clear();
std::cout << "empyt: " << list.empty() << std::endl; // 1
std::cout << "size: "<< list.size() << std::endl; // 0
return 0;
}


![socket.error: [Errno 10049]错误](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/eba3ada035f14233b92c5b963b452be3.png)