二叉树是这么一种树状结构:每个节点最多有两个孩子,左孩子和右孩子
重要的二叉树结构
完全二叉树(complete binary tree)是一种二叉树结构,除最后一层以外,每一层都必须填满,填充时要遵从先左后右
平衡二叉树(balance binary tree)是一种二叉树结构,其中每个节点的左右子树高度相差不超过 1
存储
存储方式分为两种
定义树节点与左、右孩子引用(TreeNode)
使用数组,前面讲堆时用过,若以 0 作为树的根,索引可以通过如下方式计算
父 = floor((子 - 1) / 2)
左孩子 = 父 * 2 + 1
右孩子 = 父 * 2 + 2
遍历
遍历也分为两种
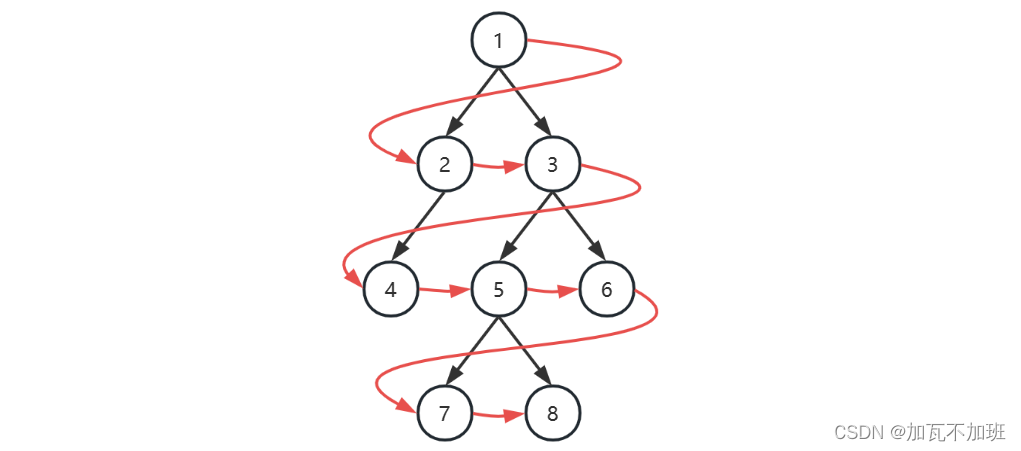
广度优先遍历(Breadth-first order):尽可能先访问距离根最近的节点,也称为层序遍历(双端队列--二叉树 Z 字层序遍历_加瓦不加班的博客-CSDN博客)
深度优先遍历(Depth-first order):对于二叉树,可以进一步分成三种(要深入到叶子节点)对应的有动态界面
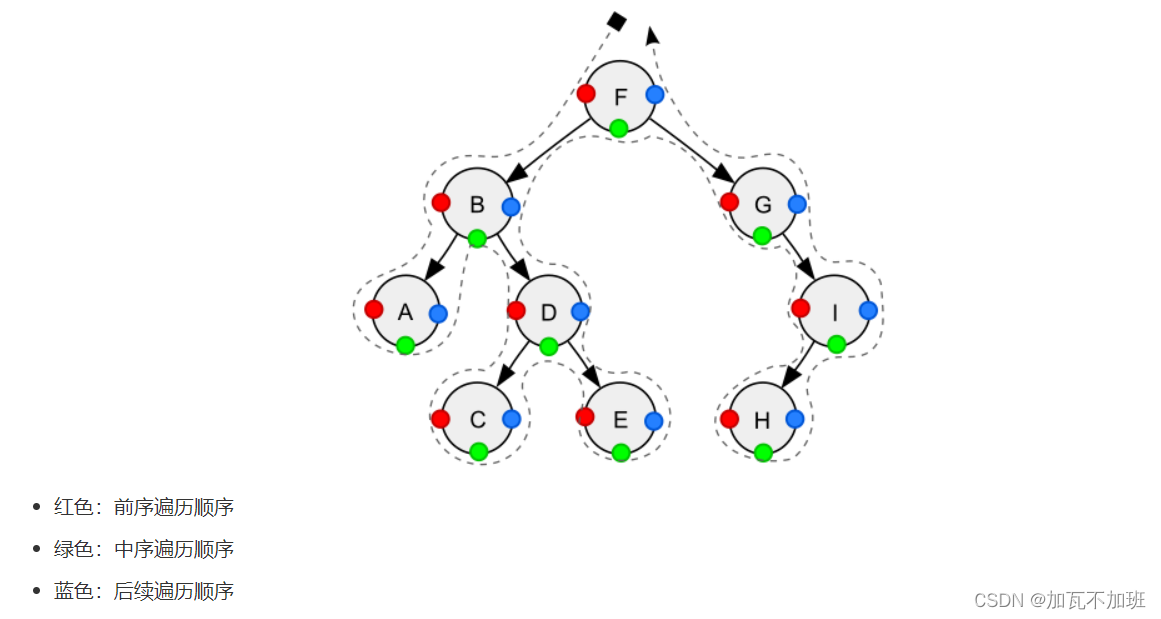
pre-order 前序遍历,对于每一棵子树,先访问该节点,然后是左子树,最后是右子树
in-order 中序遍历,对于每一棵子树,先访问左子树,然后是该节点,最后是右子树
post-order 后序遍历,对于每一棵子树,先访问左子树,然后是右子树,最后是该节点
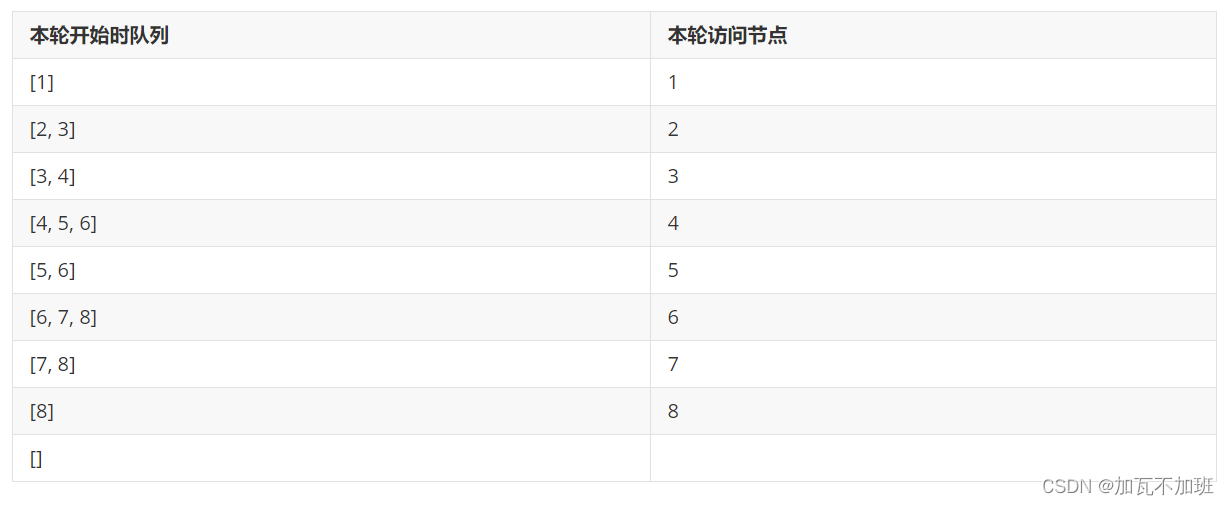
广度优先
-
初始化,将根节点加入队列
-
循环处理队列中每个节点,直至队列为空
-
每次循环内处理节点后,将它的孩子节点(即下一层的节点)加入队列
注意
以上用队列来层序遍历是针对 TreeNode 这种方式表示的二叉树
对于数组表现的二叉树,则直接遍历数组即可,自然为层序遍历的顺序
深度优先
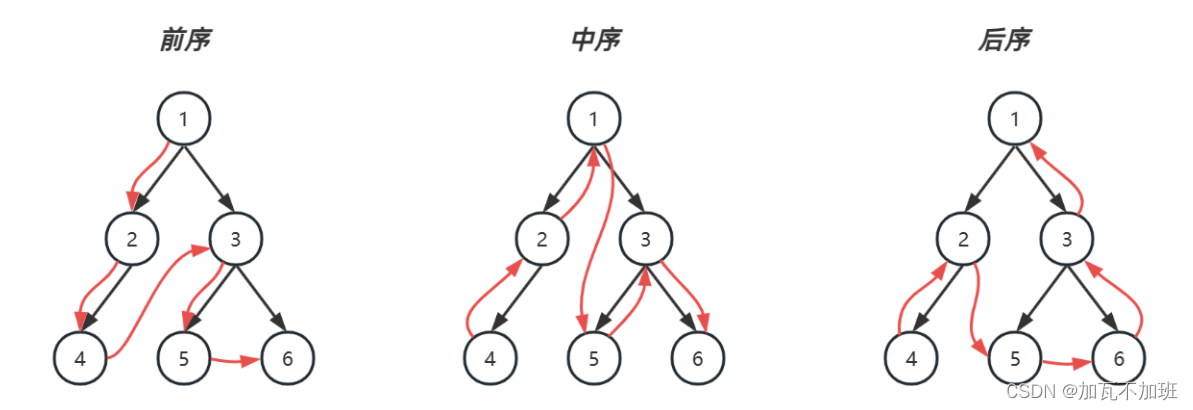
递归实现
/**
* <h3>前序遍历:对于每一棵子树,先访问该节点,然后是左子树,最后是右子树</h3>
* @param node 节点
*/
static void preOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//先访问该节点
System.out.print(node.val + "\t"); // 值
//然后是左子树
preOrder(node.left); // 左
//最后是右子树
preOrder(node.right); // 右
}
/**
* <h3>中序遍历:对于每一棵子树,先访问左子树,然后是该节点,最后是右子树</h3>
* @param node 节点
*/
static void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//先访问左子树
inOrder(node.left); // 左
//然后是该节点
System.out.print(node.val + "\t"); // 值
//最后是右子树
inOrder(node.right); // 右
}
/**
* <h3>后序遍历:对于每一棵子树,先访问左子树,然后是右子树,最后是该节点</h3>
* @param node 节点
*/
static void postOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//先访问左子树
postOrder(node.left); // 左
//然后是右子树
postOrder(node.right); // 右
//最后是该节点
System.out.print(node.val + "\t"); // 值
}测试用例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 5 6
*/
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(4), 2, null),
1,
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(5), 3, new TreeNode(6))
);
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
}非递归实现
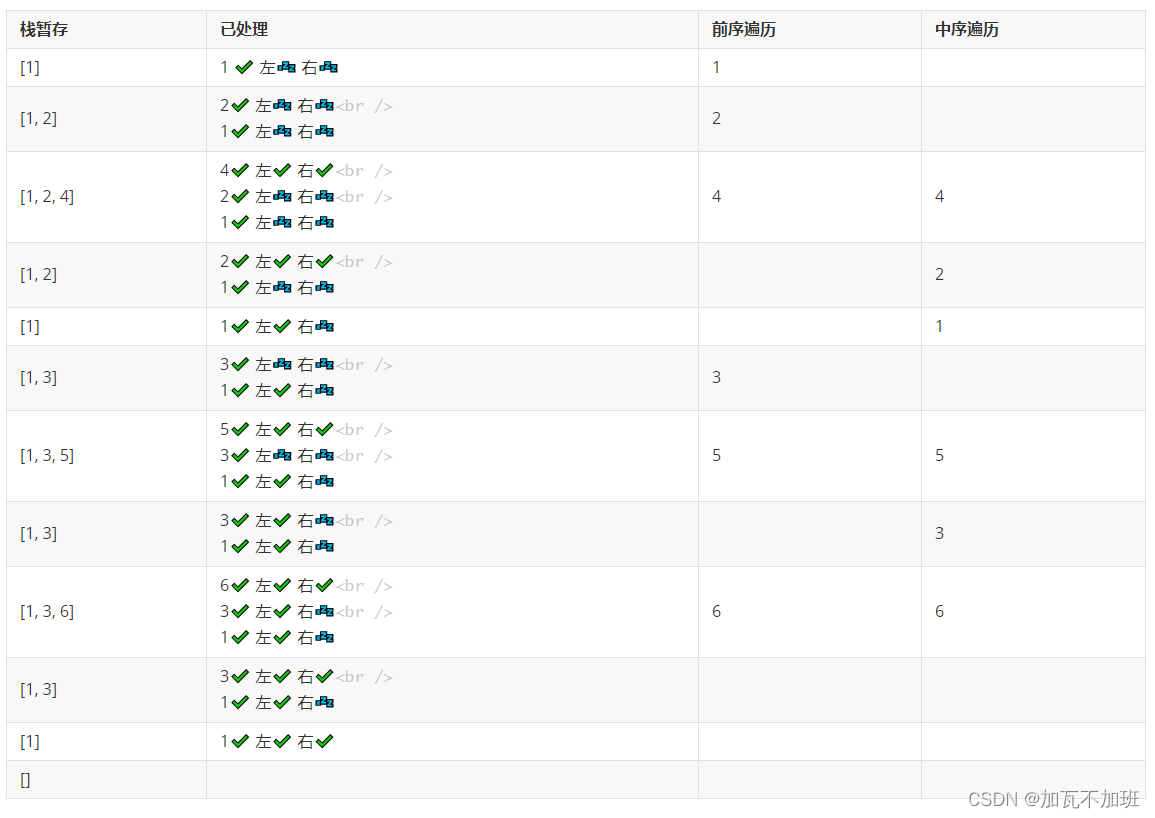
前序遍历
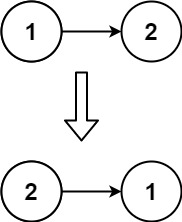
例如:去的路:1——》2——》4 回的路:4——》2——》1
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(4), 2, null),
1,
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(5), 3, new TreeNode(6))
);
LinkedListStack<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
//curr != null是为了限制去的路 !stack.isEmpty()是为了判断回的路
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);//记住回来的路,将之前路过的节点放入栈
System.out.println(curr);
curr = curr.left;
} else {
//往回走
TreeNode pop = stack.pop();
//回的时候看看当前节点右边有没有节点,有则记录右边节点
curr = pop.right;
}
}中序遍历
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(4), 2, null),
1,
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(5), 3, new TreeNode(6))
);
LinkedListStack<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
} else {
TreeNode pop = stack.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
curr = pop.right;
}
}后序遍历
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(4), 2, null),
1,
new TreeNode(new TreeNode(5), 3, new TreeNode(6))
);
LinkedListStack<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
TreeNode pop = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || curr != null) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
} else {
//首先拿到栈顶元素
TreeNode peek = stack.peek();
//确保左右子树都处理完成,再弹栈
if (peek.right == null || peek.right == pop) {
pop = stack.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
} else {
curr = peek.right;
}
}
}对于后序遍历,向回走时,需要处理完右子树才能 pop 出栈。如何知道右子树处理完成呢?
如果栈顶元素的 right == null 表示没啥可处理的,可以出栈
如果栈顶元素的 right != null,
那么使用 lastPop 记录最近出栈的节点,即表示从这个节点向回走
如果栈顶元素的 right==lastPop 此时应当出栈
对于前、中两种遍历,实际以上代码从右子树向回走时,并未走完全程(stack 提前出栈了)后序遍历以上代码是走完全程了
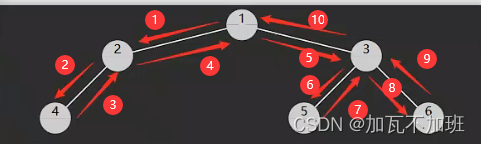
通用写法
下面是一种统一的写法,依据后序遍历修改,对于前、中、后序遍历都通用
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root; // 代表当前节点
TreeNode pop = null; // 最近一次弹栈的元素
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (curr != null) {
colorPrintln("前: " + curr.val, 31);
stack.push(curr); // 压入栈,为了记住回来的路
curr = curr.left;
} else {
TreeNode peek = stack.peek();
// 右子树可以不处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
if (peek.right == null) {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树处理完成, 对中序来说, 无需打印
else if (peek.right == pop) {
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树待处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
else {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
curr = peek.right;
}
}
}
public static void colorPrintln(String origin, int color) {
System.out.printf("\033[%dm%s\033[0m%n", color, origin);
}一张图演示三种遍历