文章目录
- AQS后序课程笔记
- AQS源码
- ReentryLock锁的原理分析
- 公平锁以及非公平锁源码详解
- Aquire方法调用原码流程分析
- 第一步、tryAquire
- 第二步、addwrite
- 第三步:aquireQueued
- AQS释放锁的过程
- 第一步、释放锁
- 第二步进入aquireQueue
- AQS异常情况下走Cancel流程分析
- 第一种队尾的情况:
- 第二种出队的情况:
- 总结:
- ReentryLock加锁流程
- 1:尝试获取锁
- 2.尝试获取锁失败进入addWriter
- 3:经过在抢枪tryAquire自旋后了在进入队列阻塞的
- 读写锁
- ReentryReadWriteLock实例
- 锁降级以及锁饥饿
- 为什么要有锁降级,思想是什么?
- 写锁降级成读锁
- 读锁不能升级成写锁
- 读写锁互斥
- 为什么有stampLock
- Optimistic Reading(乐观读模式)及传统读写模式案例代码
- 缺点:
AQS后序课程笔记
- 源码
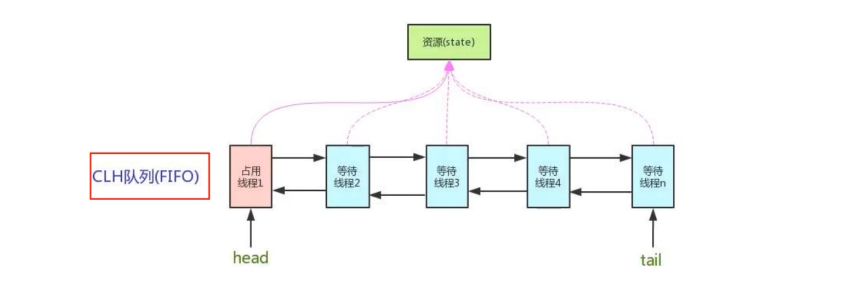
AQS使用一个volatile的int类型的成员变量来表示同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列完成资源获取排队工作,将每条要去抢占资源的线程封装成一个NODE节点来实现锁的分配,通过CAS完成对State值的修改
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wCBf97SK-1671620584184)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219194050095.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/645f05d69a6347ddbb6728d965754189.png)
- AQS同步队列的基本结构
- AQS的本质是一个双向队列加一个状态为state

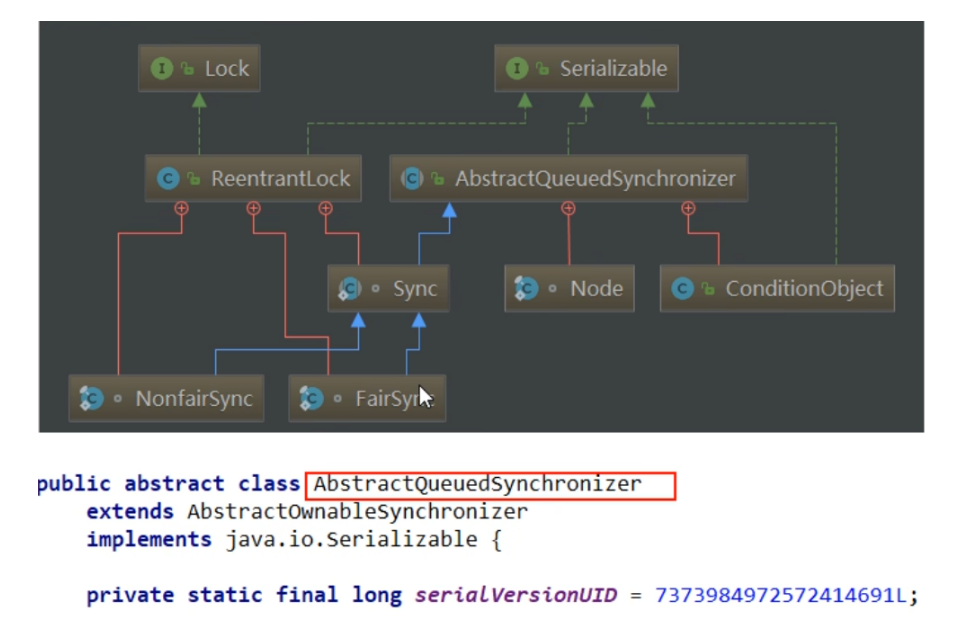
AQS源码
- 源码解读
是一个双向队列,然后包含头和尾同时,Node进行线程资源的封装,更据CAS的state来进行锁的竞争,阻塞就加入到队列尾部
====

属性说明:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3Jq1Mcmm-1671620584189)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219200709419.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dfa2472c86944a239cd12f9a4308416f.png)
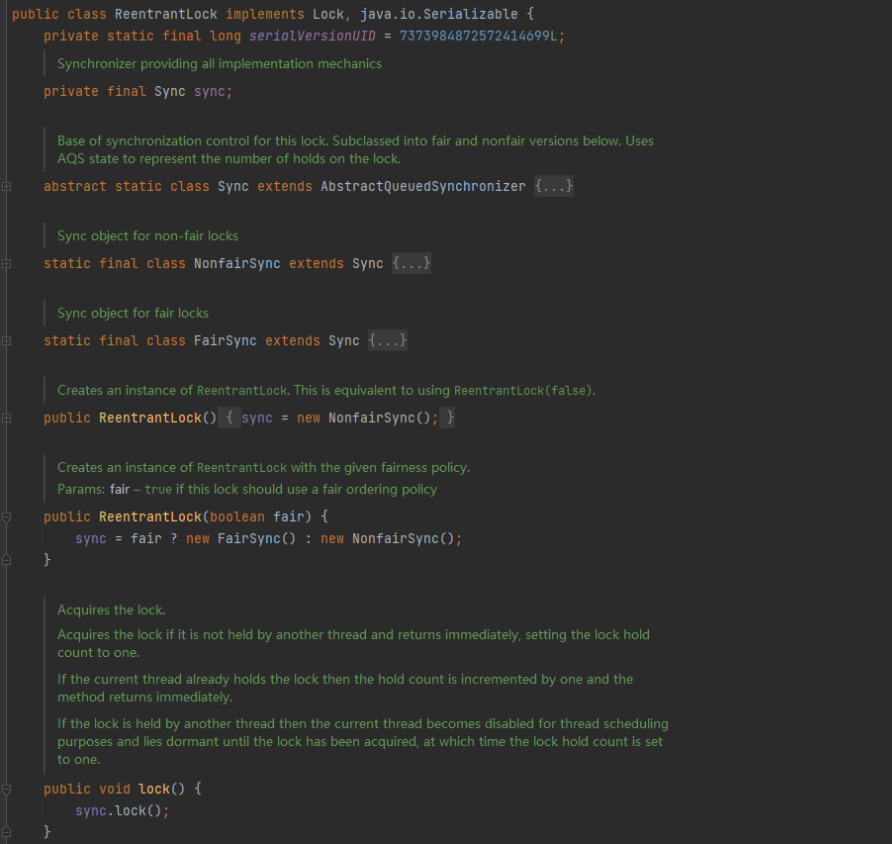
- ReentryLock
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-SZMh3xN6-1671620584189)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219202656495.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ac7f25a5be4f48a196703a86dffed68a.png)
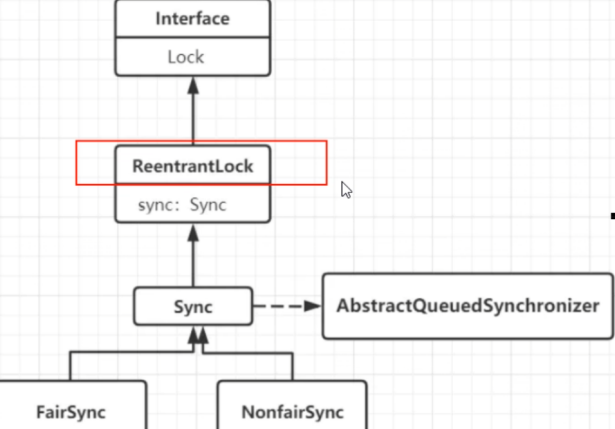
ReentryLock锁的原理分析
- lock 的底子是操作Sync
//我们默认是false,代表创建的是非公平锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
* given fairness policy.
*
* @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
公平锁以及非公平锁源码详解
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ueB7vVxn-1671620584190)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219204728742.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b3ca61eb0b0548f2aa517c1a03aa638b.png)
- 公平锁
/**
* Sync object for fair locks
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
- 非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
//非公平锁的尝试获取锁源码
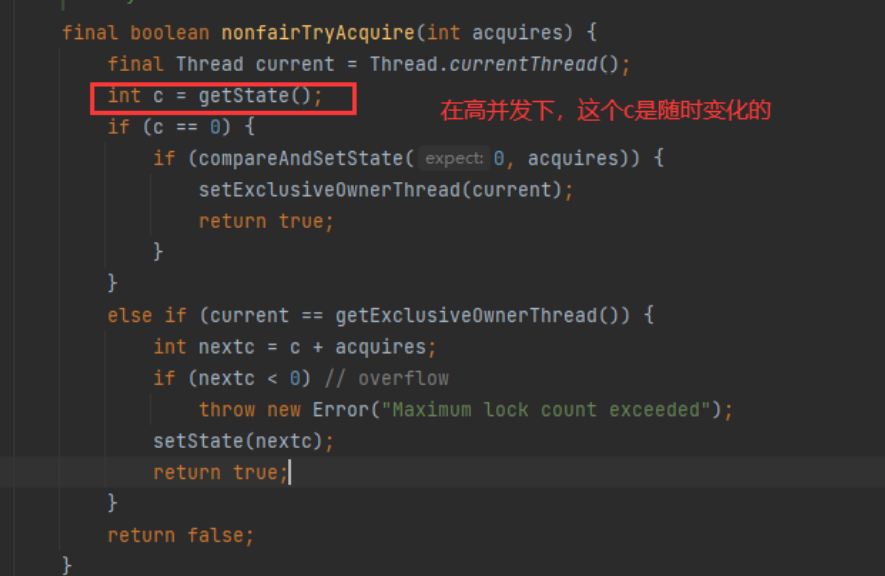
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3POx8quR-1671620584190)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219204845791.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fbad6277bd9c488ea4a7fdde92661979.png)
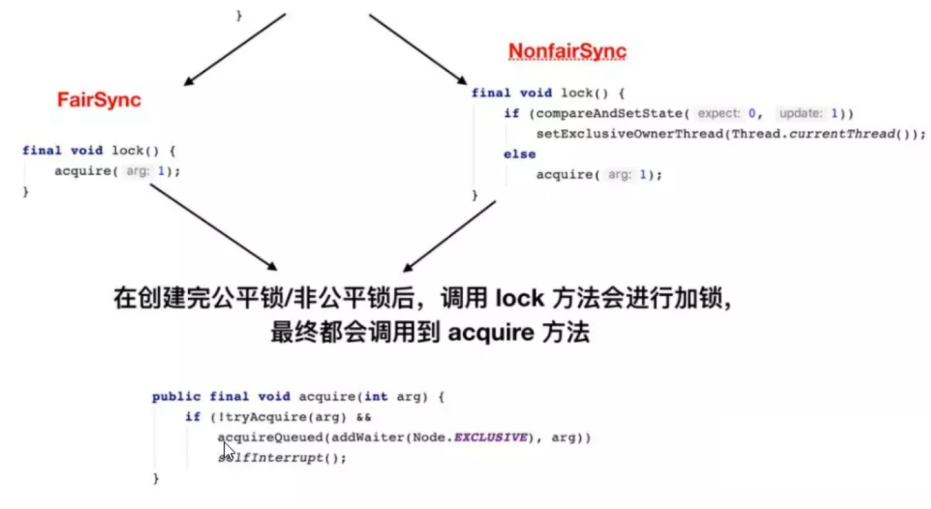
Aquire方法调用原码流程分析
- 调用Lock方法时,无论公平还是非公平都会最终调用到acquire字段;
第一步、tryAquire
执行流程1.,非公平锁由于此时state已经是1了,然后走else分支,调用aquire方法,进来后走进If分支条件的tryAquire(),匹配后锁竞争失败,因此前置的!fasle为true->走auireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE))
/**
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used
* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
//非公平锁的尝试获取锁源码
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
- tryAquire代码
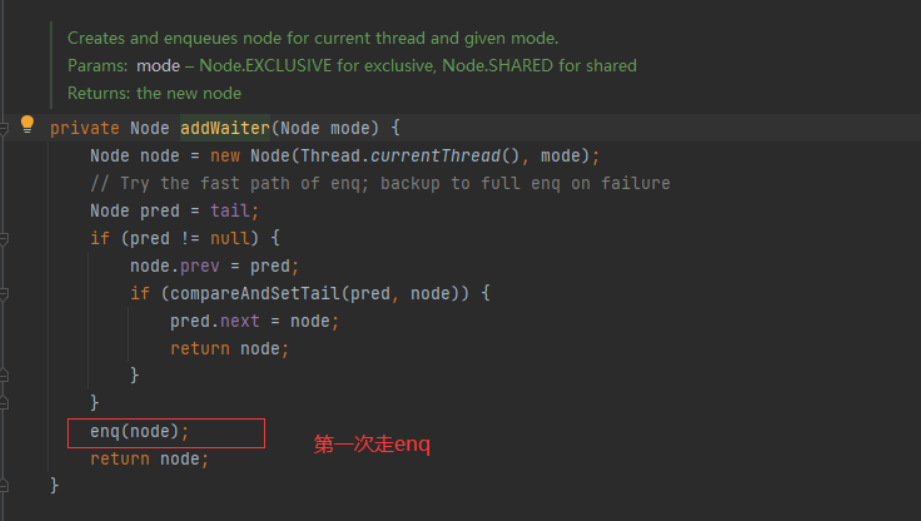
第二步、addwrite
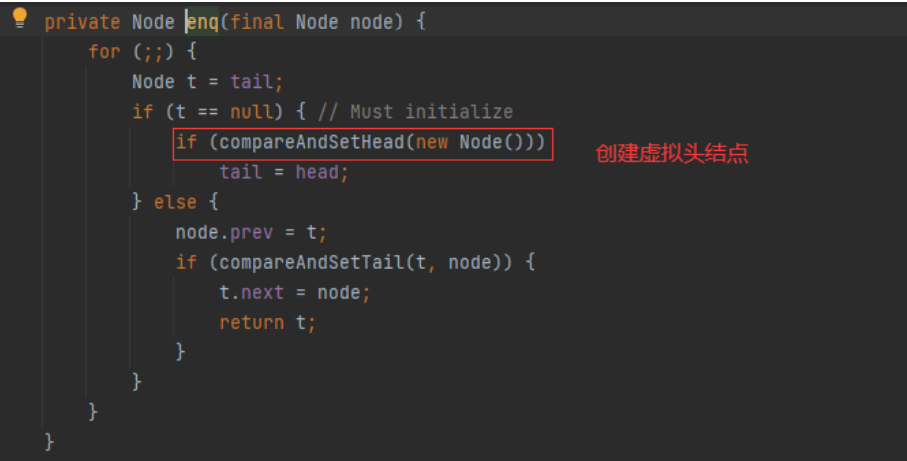
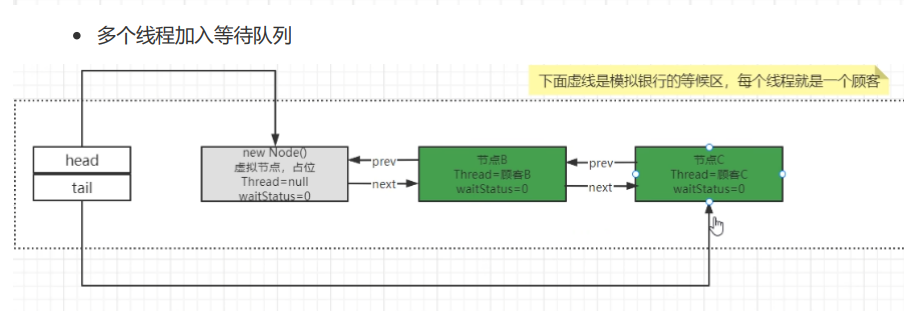
执行流程2 addWriter;调用Node节点的方法,是一个双向链表;初始化的时候创建了一个虚拟头节点,首尾相连
- 创建虚拟哨兵节点
具体如下:

private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node; //上面第二张图
return t;
}
}
}
}
/**
* CAS tail field. Used only by enq.-》变成尾指针
*/
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
第三步:aquireQueued
执行流程三:调用aquireQueued,进行线程入队之后坐稳->根据源码后面的可知每次都是后入队列的将前面的唤醒,前面的waitState = -1
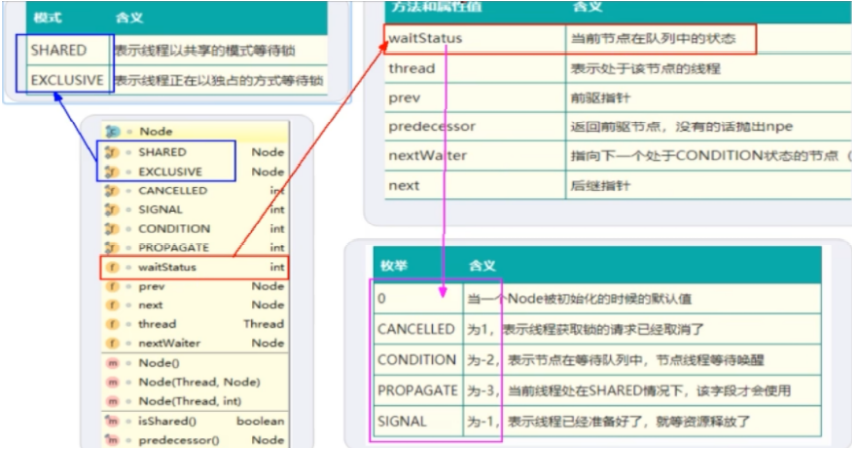
1.Node代表当前线程对象,arg代表此时Thread的state值
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yWOXPTIt-1671620584196)(C:\Users\裴承林\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20221219220435973.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6b9a6a2d230140e1b61db4fc033ca5a3.png)
2.当线程A一直持有锁的时候,会先走shouldParkAfterFaildAcquire
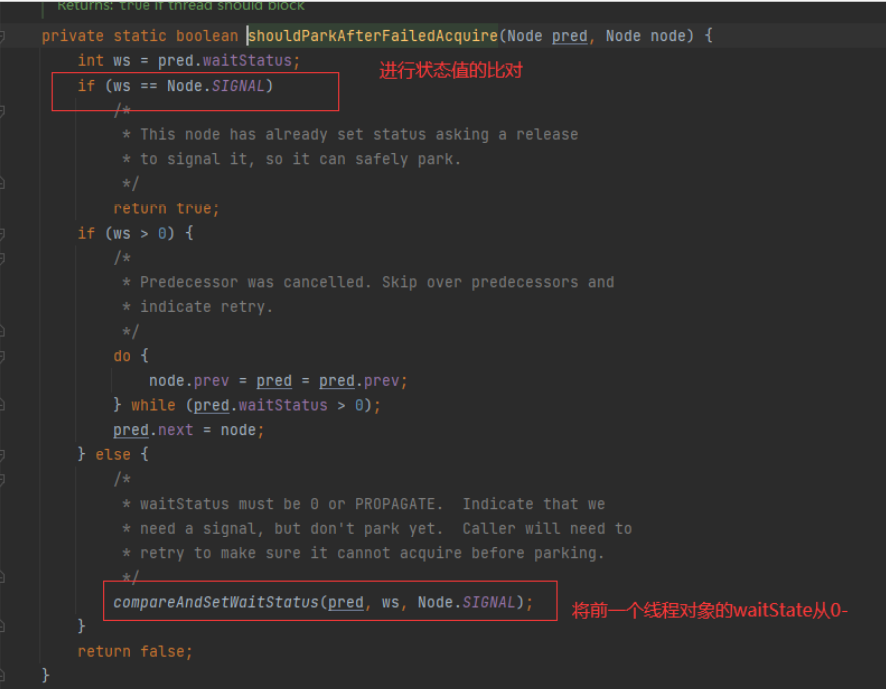
3.由于第一次初始化时waitstate是0,因此第一次是false,进行for循环,再来一次,此时ws=pred.waitStatus==1;返回true;接着调用LockSupport,park阻塞
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
//1.创建双向队列
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
//2.
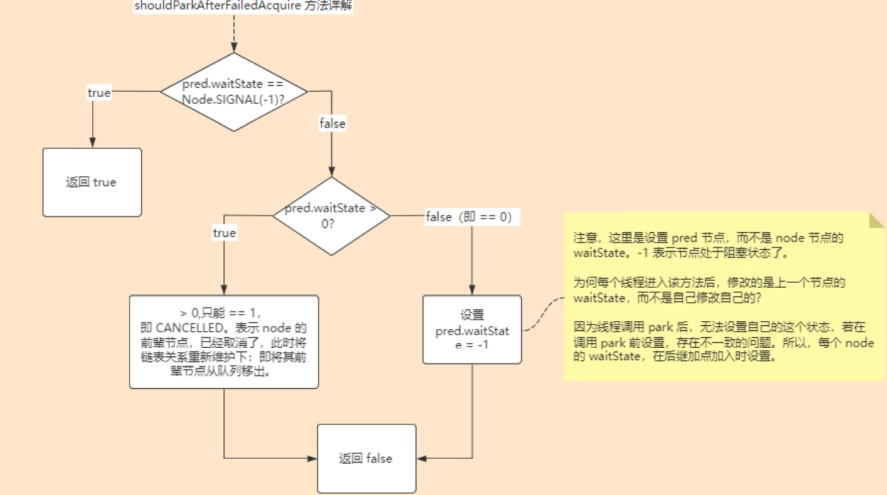
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
//3.
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
AQS释放锁的过程
第一步、释放锁
B获得到线程:首先是A释放之后,state变成0,代表空闲了,紧接着我们将B节点要进行唤醒,将waitState=-1变成0(B这里是需要竞争锁的,以防现在过来一个X线程来竞争);获取到之后B节点置为null同时将之前的虚拟节点删除掉,如下图
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QLxmdwmi-1671620584198)(E:/img/image-20221220115803308.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bbf6b3ec59ee4c54bba66da019f66897.png)
//0.释放锁,releases=1
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
//将正在要退出的线程进行锁的释放
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
//1.先进来判断,第一次虚拟节点的waitstate=-1
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//2.unparkSuccessor
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); //将虚拟节点置为0
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); //调用这个进行释放锁
}
/**
* CAS waitStatus field of a node.
*/
private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node,
int expect,
int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset,
expect, update);
}
第二步进入aquireQueue
此时经过释放锁后,tryAquire(arg)此时为true;//tryquire是在判断是否需要竞争的;然后接着走最开始那个图的流程,
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;// 返回是否被是否被打断
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
AQS异常情况下走Cancel流程分析
当队列中有一个突然不想排了,怎么办?比如说5号节点走了是一种情况,4号节点走了是一个情况、或者34节点走了又是一个情况
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Izy4nidB-1671620584199)(E:/img/image-20221220133117758.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/86df3ff607654c73bef3aa112038adea.png)
/**
* Cancels an ongoing attempt to acquire.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
第一种队尾的情况:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UM7vnwow-1671620584199)(E:/img/image-20221220133803241.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5c1c69cb53634612b21318623b507ea8.png)
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
//1.要走了对位这个线程肯定置为null
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
Node pred = node.prev; //2.记录前置节点
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
Node predNext = pred.next;
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; //3.waitstate值改成了1
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) { //4.将我们的尾部前面的节点置为tail
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null); //5.将尾部值改为Null
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
第二种出队的情况:
当我们的4号要出队列的时候
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
Node pred = node.prev; //1.pred代表3号节点线程
while (pred.waitStatus > 0) //2.是代表有多个出队列的情况,要一直找到没有取消的为止
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
//3.5号节点线程
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; //4.此时4号节点的waitState变成了1
//5.因为我们不是tail;因此走else分支
else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
//6. next是5号节点
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); //7.将3号的指向5号
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
总结:
ReentryLock加锁流程
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-U64uGXq9-1671620584200)(E:/img/image-20221220141216070.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7036572d92374b6582aabd2684d9a221.png)
- 流程图
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-cjGxcVTa-1671620584200)(E:/img/image-20221220141408923.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3a0f6f837d3942628185264a8403e4dc.png)
-
lock分为公平锁和非公平锁,lock()都是调用aquire方法,如果尝试获取锁tryAquire获取到了,就直接返回了,大多数情况会失败,然后就要入队列aquireQueued
public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
1:尝试获取锁
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5B9Ey3Eq-1671620584201)(E:/img/image-20221220141644996.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/16c31dde782f4d919ed055c843cc7a27.png)
- hasQueuedPredecessors(公平锁)

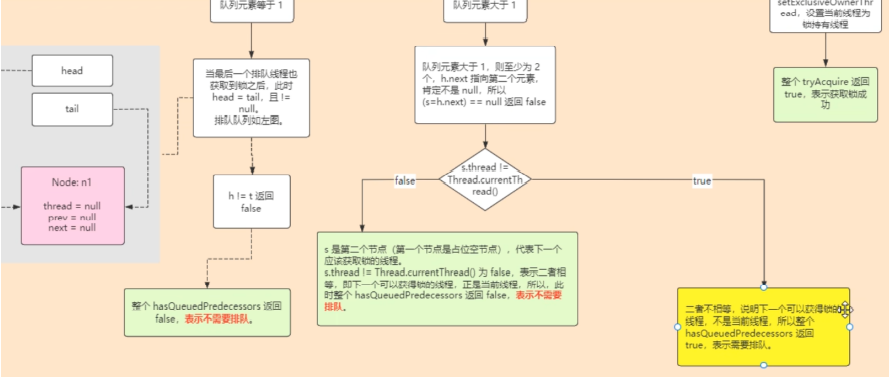
2.尝试获取锁失败进入addWriter
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-46egXNkz-1671620584203)(E:/img/image-20221220142938326.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a64c07e08adc4d3e8fb62ef0c17d1c82.png)
初始化
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4jk3gP3g-1671620584203)(E:/img/image-20221220143037909.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8cb904cb235c42428d94489ccb87d7f0.png)
加入队列后了
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RJOTy03t-1671620584204)(E:/img/image-20221220143156181.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fd3f0374d75b4a10a0da0eff72ac048e.png)
3:经过在抢枪tryAquire自旋后了在进入队列阻塞的
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DsKsXXWU-1671620584204)(E:/img/image-20221220155035794.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/967b2653f37e427e9bd2f85b88a20316.png)
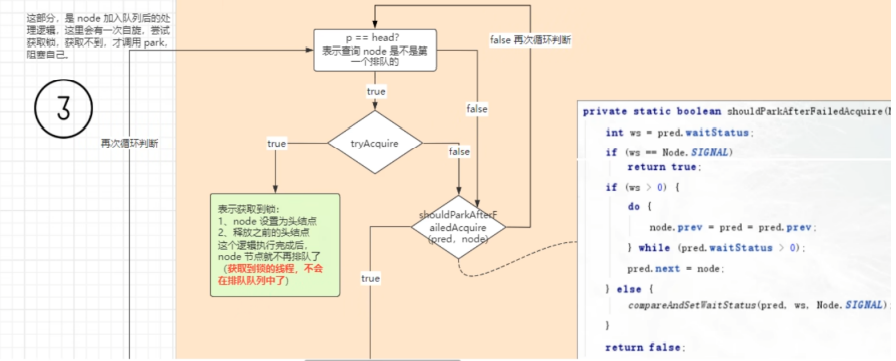
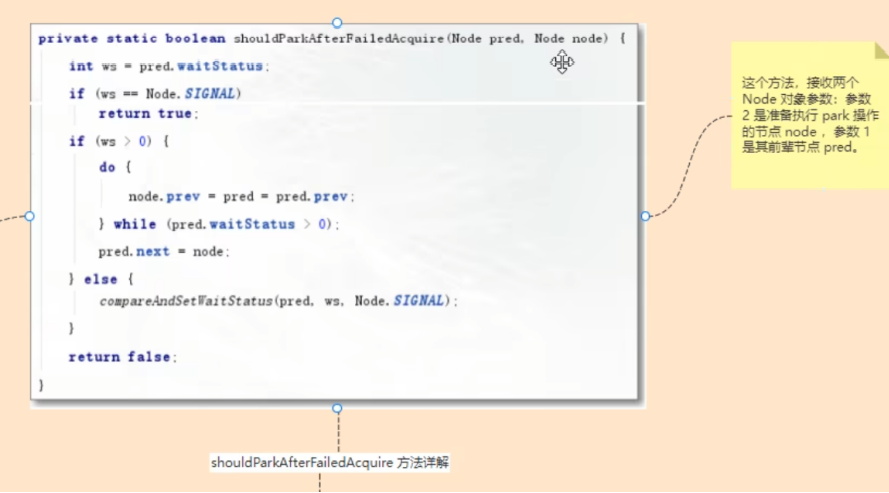
- 当线程进入队列时,当自选竞争失败后走到shouldParkFaildAcquire,需要将waitState得值进行修改;最开始初始化加进来的时候state都是0;后面加进队列后waitState=-1了;
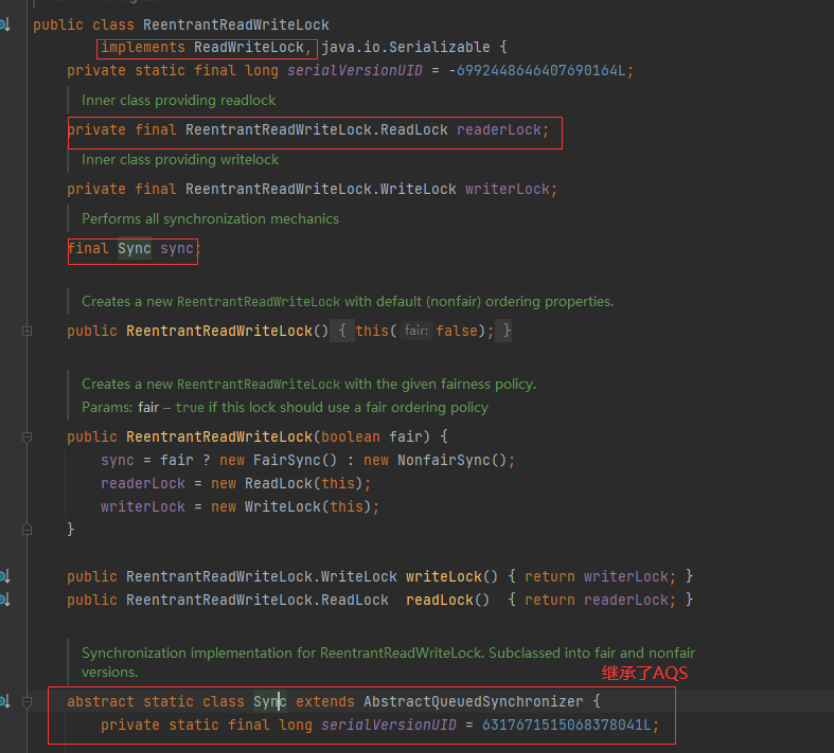
读写锁
什么是读写锁?
一个资源能够被多个读线程访问,或者一个写线程访问、但是不能存在读写线程
public interface ReadWriteLock {
/**
* Returns the lock used for reading.
*
* @return the lock used for reading
*/
Lock readLock();
/**
* Returns the lock used for writing.
*
* @return the lock used for writing
*/
Lock writeLock();
}
ReentryReadWriteLock实例
/**
* @Author: sakura
* @Date: 2022/12/20 17:01
* @Description: 读写锁demo
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ReentryReadWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyResource resource = new MyResource();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
resource.write(finalI +"",finalI+"");
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
resource.read(finalI +"");
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
//新写锁
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
resource.write(finalI+"",finalI+"");
},"新写锁线程->"+String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
class MyResource{//资源类、模拟一个简单的缓存
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//===ReentryReadWriteLock 读写互斥
ReadWriteLock rwlock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public void write(String key,String value){
rwlock.writeLock().lock();
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"正在写入");
map.put(key,value);
try{
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(500);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"写入完成");
}finally {
rwlock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
public void read(String key){
rwlock.readLock().lock();
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"正在读入");
String result = map.get(key);
try{
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(2000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"读入完成"+result);
}finally {
rwlock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
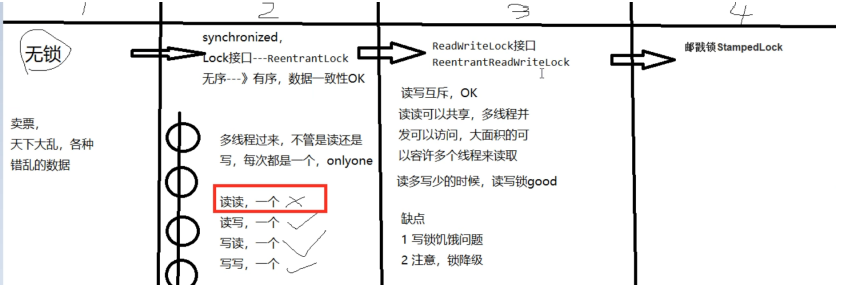
- 读写锁的意义(ReentrantReadWriteLock)
- 主要解决的是读写场景下,读读共存的情况比较多,但是缺点是由于写的比较少,易出现写锁饥饿问题也就是写锁等待的时间太长了

锁降级以及锁饥饿
- 锁降级
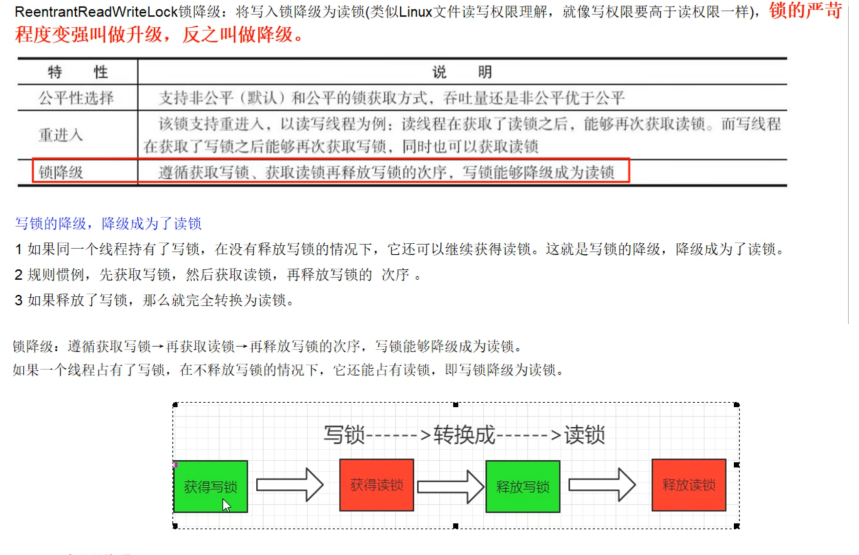

为什么要有锁降级,思想是什么?
- 源代码图
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5Prkvi6q-1671620584210)(E:/img/image-20221220195720263.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/063a565651c5495d9ec5c4079912ddcc.png)

为什么需要锁降级呢?
- 要是为了保证数据的可见性,如果当前线程不获取读锁而是直接释放写锁, 假设此刻另一个线程(记作线程T)获取了写锁并修改了数据,那么当前线程无法感知线程T的数据更新。如果当前线程获取读锁,即遵循锁降级的步骤,则线程T将会被阻塞,直到当前线程使用数据并释放读锁之后,线程T才能获取写锁进行数据更新
————————————————
- 为了提高程序执行性能,可能存在一个事务线程不希望自己的操作被别的线程中断,而这个事务操作可能分成多部分操作更新不同的数据(或表)甚至非常耗时。如果长时间用写锁独占,显然对于某些高响应的应用是不允许的,所以在完成部分写操作后,退而使用读锁降级,来允许响应其他进程的读操作。只有当全部事务完成后才真正释放锁。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43519310/article/details/100107346
写锁降级成读锁
public class ReadWriteLockReduce {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock();
//锁降级
//1.获取写锁
writeLock.lock();
System.out.println("write");
//2.获取读锁
readLock.lock();
System.out.println("read");
//3.释放写锁
writeLock.unlock();
//4.释放读锁
readLock.unlock();
}
}
读锁不能升级成写锁
public class ReadWriteLockReduce {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock();
//锁降级
//2.获取读锁
readLock.lock();
System.out.println("read");
//1.获取写锁
writeLock.lock();
System.out.println("write");
//3.释放写锁
writeLock.unlock();
//4.释放读锁
readLock.unlock();
}
}
读写锁互斥

ReentryReadWriteLock**读过程中不允许写、**只有等待线程释放读锁、才能获取写锁、写是需要等待的,因此容易出现锁饥饿、因此也是悲观锁
为什么有stampLock
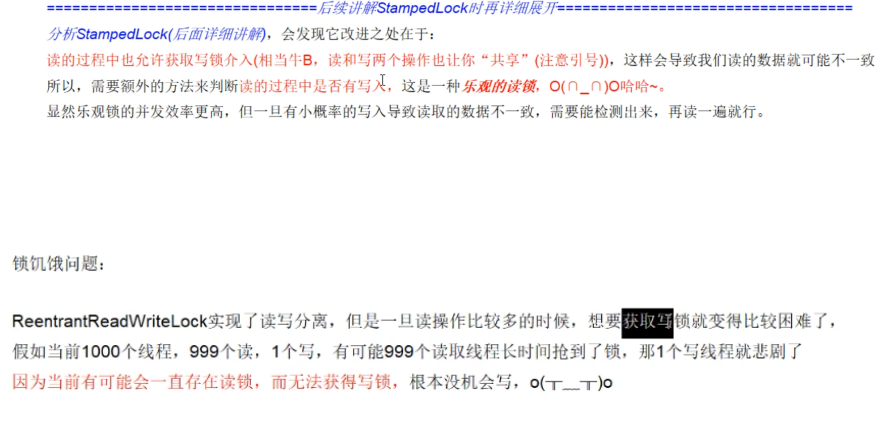
原因:
在第三阶段的时候、我们有了读写锁或锁降级时,一旦读操作比较多的时候,想要获取写锁困难,因为读未完成的时候写状态是不能的,容易造成写锁饥饿。因此stampLock解决的是读状态可以进行写操作进行共享;因此是一种乐观锁认为不会有数据修改,同时如果修改了,导致读取的数据不一致,升级为读写锁,在读一遍。
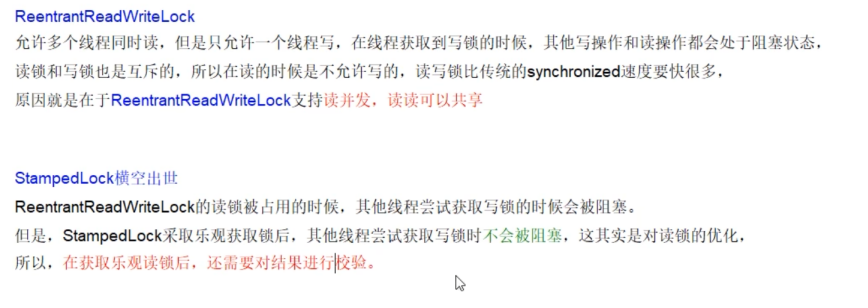
对于短的只读代码;使用乐观模式通常可以减少争用并提高吞吐量

Optimistic Reading(乐观读模式)及传统读写模式案例代码
/**
* @Author: sakura
* @Date: 2022/12/21 16:31
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class StampLock {
static int number = 37;
static StampedLock stampLock = new StampedLock();
/**
* 线程的写入
*/
public void write(){
long l = stampLock.writeLock();
try{
number = number+1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写线程正在写入");
}finally {
stampLock.unlockWrite(l);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"写现场已经结束修改了");
}
}
/**
* 线程的读入;悲观锁状态
* @param
*/
public void read(){
long stamp = stampLock.readLock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"come in readLock....4 seconds continue"+number);
//休息四秒钟、进行模拟
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"正在读取中.....");
}
try{
int result = number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"获取到成员变量"+result);
System.out.println("写线程没有执行成功,读写锁进行互斥");
}finally {
stampLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
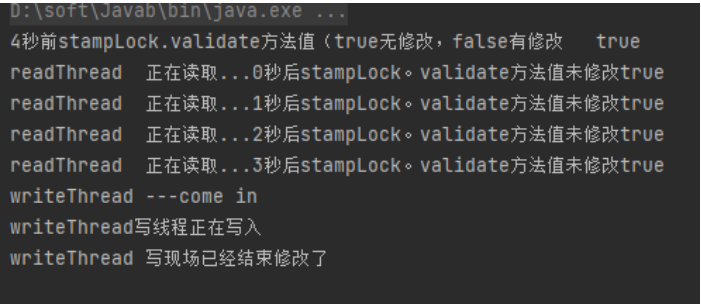
public void tryOptimisticRead(){
long stamp = stampLock.tryOptimisticRead();
int result = number;
System.out.println("4秒前stampLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改"+"\t"+stampLock.validate(stamp));
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"正在读取..."+i+"秒"
+"后stampLock。validate方法值未修改"+stampLock.validate(stamp));
}
if(!stampLock.validate(stamp)){
System.out.println("有人修改");
stamp = stampLock.readLock();
try{
System.out.println("从乐观读升级为悲观读");
result = number;
System.out.println("重新被关获取读"+result);
}finally {
stampLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StampLock resoure = new StampLock();
new Thread(()->
resoure.read(),"readThread").start();
//暂停几秒钟
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"writeThread come in...");
resoure.write();
},"writeThread").start();
}
}
new Thread(()->{
resoure.tryOptimisticRead();
},"readThread").start();
//暂停两秒钟
// try {
// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//暂停6秒
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"---come in");
resoure.write();
},"writeThread").start();
缺点: