文章目录
- 一、扣减库存不加锁
- 二、加一把jvm锁试试看
- 三、引入分布式锁
- 四、try finally
- 五、设置key的过期时间
- 六、原子设置锁和过期时间
- 七、给线程设置唯一id
- 八、锁续命redisson
- 九、redisson加锁释放锁的逻辑
- 十、redisson源码分析
一、扣减库存不加锁
先看一段扣减库存的代码
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
return "end";
}
这段代码明显有很严重的并发问题,多线程并发执行的时候,假如三个线程同时执行,如果原先300的库存,理论三个线程执行完剩余库存是297,但是因为代码没有任何锁的控制,会导致同时读取300的库存,同时扣减1,又同时设置299到redis中去,会导致超卖问题
二、加一把jvm锁试试看
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
synchronized(this){
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}
return "end";
}
但是这还会有问题,如果是单机那确实没问题,但是在分布式环境下,还是会存在并发安全问题
三、引入分布式锁
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
Boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "zhuge");//利用redis加分布式锁
if (!result) {
return "error_code";
}
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockKey);//释放锁
return "end";
}
但这只能算一个入门级别的分布式锁,假如业务代码出问题了,那么最后释放锁的代码就不会去执行,就会导致死锁
四、try finally
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
Boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "zhuge");//利用redis加分布式锁
if (!result) {
return "error_code";
}
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally{
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockKey);//释放锁
}
return "end";
}
这样就保证了,即使业务代码出问题了也能去释放锁。
但是还是有问题,假如机器宕机了也会出现死锁
五、设置key的过期时间
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
Boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "zhuge");//利用redis加分布式锁
stringRedisTemplate.expire(lockKey, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//加上过期时间
if (!result) {
return "error_code";
}
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally{
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockKey);//释放锁
}
return "end";
}
但是还是有问题,因为上锁和设置过期时间是两步操作,存在原子性问题(如果加了锁,还没来得及执行设置过期时间的代码 ,就宕机了依然存在问题)
六、原子设置锁和过期时间
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
Boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //jedis.setnx(k,v)
if (!result) {
return "error_code";
}
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally{
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockKey);//释放锁
}
return "end";
}
但是这样写还是会有问题,假如业务代码+接口响应时间的执行时间超过了10s,那么key就自动过期了,会导致其他线程抢占到锁,但是之前的线程执行结束的时候,会去释放锁,但是释放的不是自己的锁,而是后来的线程的锁
七、给线程设置唯一id
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
String clientId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, clientId, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //jedis.setnx(k,v)
if (!result) {
return "error_code";
}
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally{
if (clientId.equals(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(lockKey))) {//判断当前的clientid和枷锁的id是否相同
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
}
}
return "end";
}
但是,还是有问题;就是锁释放的时候,依然存在原子性问题
我们发现上述的大部分问题都是锁过期导致,那么我们引入锁续命的概念
八、锁续命redisson
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.6.5</version>
</dependency>
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
String lockKey = "lock:product_101";
//获取锁对象
RLock redissonLock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
//加分布式锁
redissonLock.lock(); // .setIfAbsent(lockKey, clientId, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock")); // jedis.get("stock")
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + ""); // jedis.set(key,value)
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally{
//解锁
redissonLock.unlock();
}
return "end";
}
九、redisson加锁释放锁的逻辑
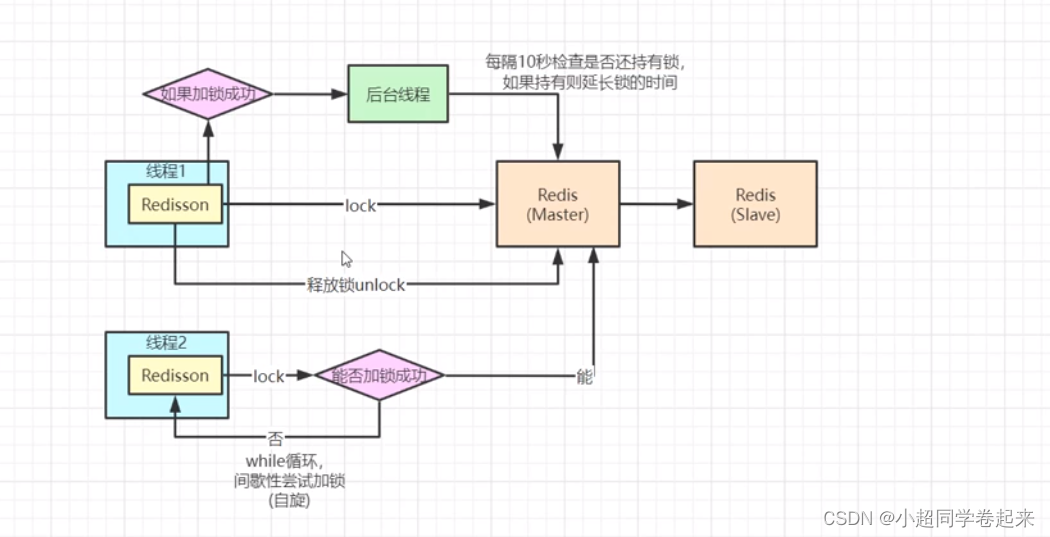
十、redisson源码分析
我们进入 redissonLock.lock();方法内部
public void lock() {
try {
this.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
this.lockInterruptibly(-1L, (TimeUnit)null);
}
再进入 lockInterruptibly方法
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);//这是核心逻辑
if (ttl != null) {
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while(true) {
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
if (ttl >= 0L) {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
this.unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
}
}
再进入 tryAcquire方法
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return get(tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() { //tryLockInnerAsync方式执行结束,会回调addListener方法
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
return;
}
Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
leaseTime 上面传进来是-1,会进入 tryLockInnerAsync
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + //判断是否有key,keys[1]等同于getName()
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + //第一遍肯定是空的,所以设置hash结构,key就是getName(),也就是我们定义的“lock:product_101”,filed是getLockName(threadId)相当于clientId,value为1表示可重入
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +//设置key的超时时间internalLockLeaseTime,默认30s
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
final UUID id;
String getLockName(long threadId) {
return id + ":" + threadId;
}
我们会发现 原来底层就是一段lua脚本,这段lua脚本执行的主体逻辑就是加锁,加锁成功返回nil(null)
我们继续看看门狗的逻辑
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {//加锁失败就返回
return;
}
Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();//一般加锁成功,这里返回的就是null
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);//超时时间的刷新,也就是锁续命逻辑
}
}
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(final long threadId) {
if (expirationRenewalMap.containsKey(getEntryName())) {
return;
}
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {//这个run方法会在延时之后执行,延时多久呢,internalLockLeaseTime / 3,30/3 =10s
RFuture<Boolean> future = commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +//判断主线程是否结束了
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +//没结束,就续命internalLockLeaseTime
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {//续命逻辑执行完会回调此方法
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
expirationRenewalMap.remove(getEntryName());
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", future.cause());
return;
}
if (future.getNow()) {//如果续命成功会返回1,进入if
// reschedule itself
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);//再次调用此方法,又会等待10s再次去执行续命逻辑
}
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (expirationRenewalMap.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), task) != null) {
task.cancel();
}
}
以上就是redisson的看门狗续命逻辑
我们继续再看看,其他线程加锁失败的底层逻辑,还是加锁的那段lua脚本
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + //判断是否有key,keys[1]等同于getName()
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + //第一遍肯定是空的,所以设置hash结构,key就是getName(),也就是我们定义的“lock:product_101”,filed是getLockName(threadId)相当于clientId,value为1表示可重入
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +//设置key的超时时间internalLockLeaseTime,默认30s
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",//加锁失败会走这段逻辑,返回这把锁剩余的超时时间
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
我们返回到 lockInterruptibly方法
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);//加锁成功,返回的null
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
//下面是失败的逻辑,ttl=那把锁剩余的超时时间
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);//又尝试加锁,相当于刷新了ttl超时时间
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message
if (ttl >= 0) {//如果超时时间大于0,调用getLatch方法,返回一个信号量,然后tryacquire,获取一个许可,阻塞ttl的时间,等ttl时间一到,重新进入while循环
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
}
信号量的阻塞等待不会占用cpu,所以解释了上图中的 间歇性等待机制
public Semaphore getLatch() {
return latch;
}
有阻塞,必有唤醒机制,不可能让这些线程干巴巴全部阻塞在这,等超时时间
没有抢到锁的线程会去监听一个队列,等待释放锁发布订阅,我们去看解锁逻辑
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + //判断锁是否还存在
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +//不存在就发布消息,
"return 1; " +
"end;" +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " + //判断这把锁是不是当前线程加的
"return nil;" +//不是,就返回nul
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " + //是,就把key对应的value -1 = 0
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +//直接解锁
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +//发布消息
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
上面是发布消息,那么阻塞的线程在哪去订阅消息的呢?
阻塞的线程在订阅的时候,会去监听这个onMessage消息
@Override
protected void onMessage(RedissonLockEntry value, Long message) {
if (message.equals(unlockMessage)) {//这是解锁lua脚本里的0
value.getLatch().release();//唤醒机制
while (true) {
Runnable runnableToExecute = null;
synchronized (value) {
Runnable runnable = value.getListeners().poll();
if (runnable != null) {
if (value.getLatch().tryAcquire()) {
runnableToExecute = runnable;
} else {
value.addListener(runnable);
}
}
}
if (runnableToExecute != null) {
runnableToExecute.run();
} else {
return;
}
}
}
}
至此,redisson源码主体的加锁,解锁,等待锁,唤醒源码分析完毕!