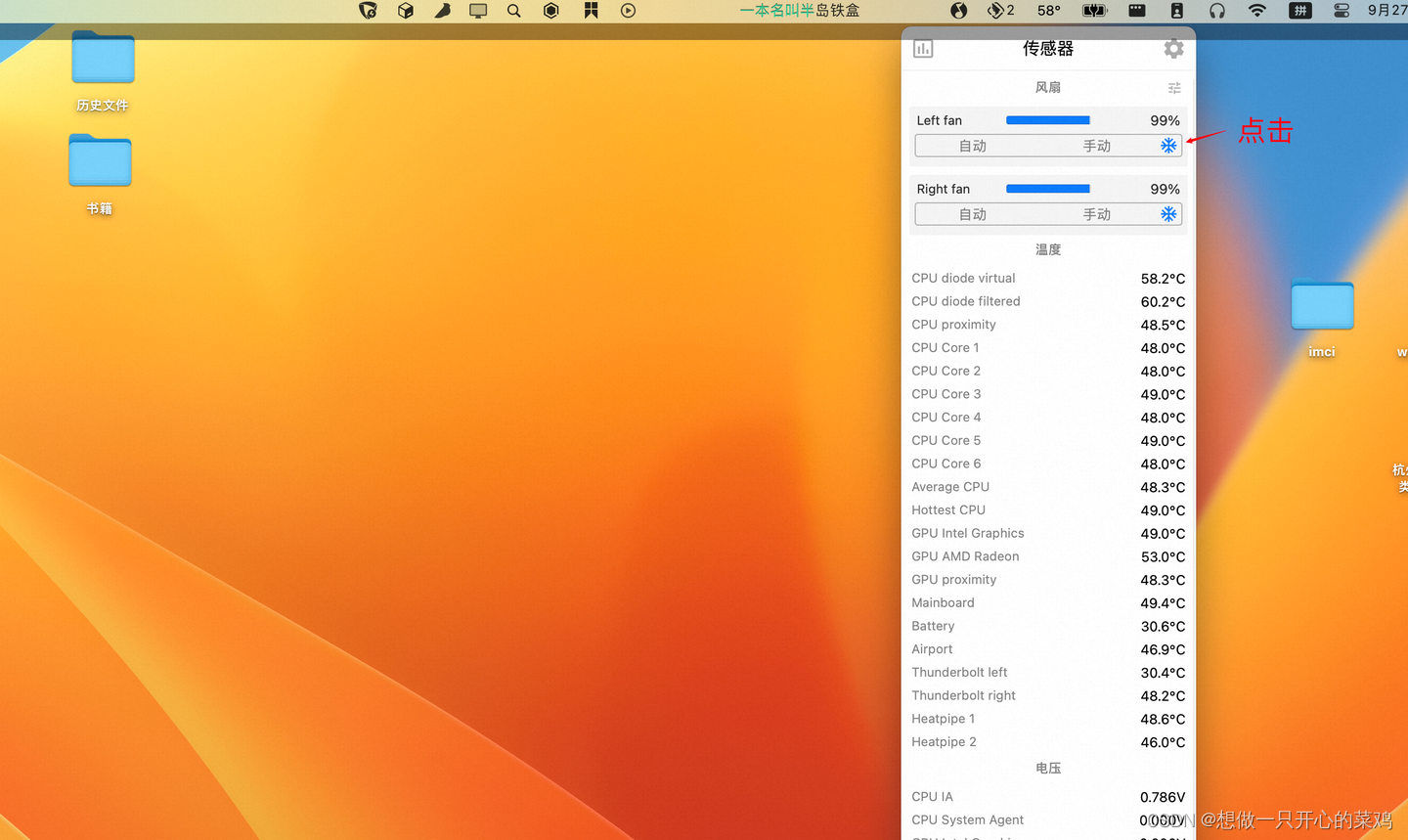
148.排序链表
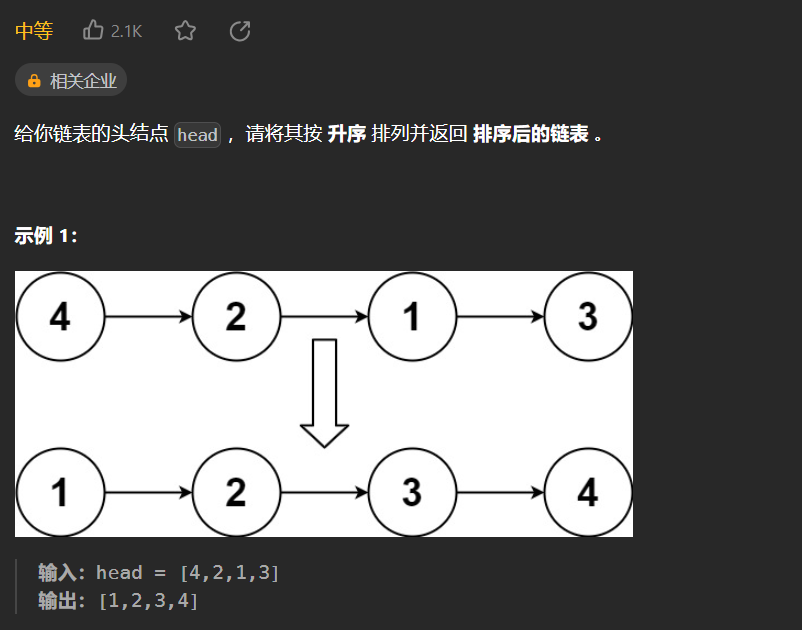
对链表进行排序最适合的算法就是归并排序:
对链表自顶向下归并排序的过程:
- 找到链表的中点,以中点为分界,将链表拆分成两个子链表,寻找链表的中点可以使用快慢指针的做法,快指针每次移动 2步,慢指针每次移动 1步,当快指针到达链表末尾时,慢指针指向的链表节点即为链表的中点
- 对两个子链表分别排序
- 将两个排序后的子链表合并,得到完整的排序后的链表
上述过程可以通过递归实现。递归的终止条件是链表的节点个数小于或等于 1,即当链表为空或者链表只包含 1个节点时,不需要对链表进行拆分和排序。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return sortList(head,null);
}
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head,ListNode tail){
if(head == null){
return head;
}
if(head.next == tail){
head.next = null;
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head,fast = head;
while(fast != tail){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if(fast!=tail){
fast = fast.next;
}
}
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode list1 = sortList(head,mid);
ListNode list2= sortList(mid,tail);
ListNode sorted = merge(list1,list2);
return sorted;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ //合并两个有序链表
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummy,temp1 = head1,temp2 = head2;
while(temp1 !=null &&temp2 !=null){
if(temp1.val <= temp2.val){
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
}else{
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(temp1!=null){
temp.next = temp1;
}else if(temp2!=null){
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}