链表的介绍:
1) 链表是以节点的方式来储存的,是链式存储结构
2)每个节点包含data域和next域,next域指向下一个节点
3)链表内存储的元素不一定连续
4)链表分带头节点的链表和不带头节点的链表

注:此处head为头节点并不存储数据,仅仅用来标识链表的头
单链表应用实例:
增:
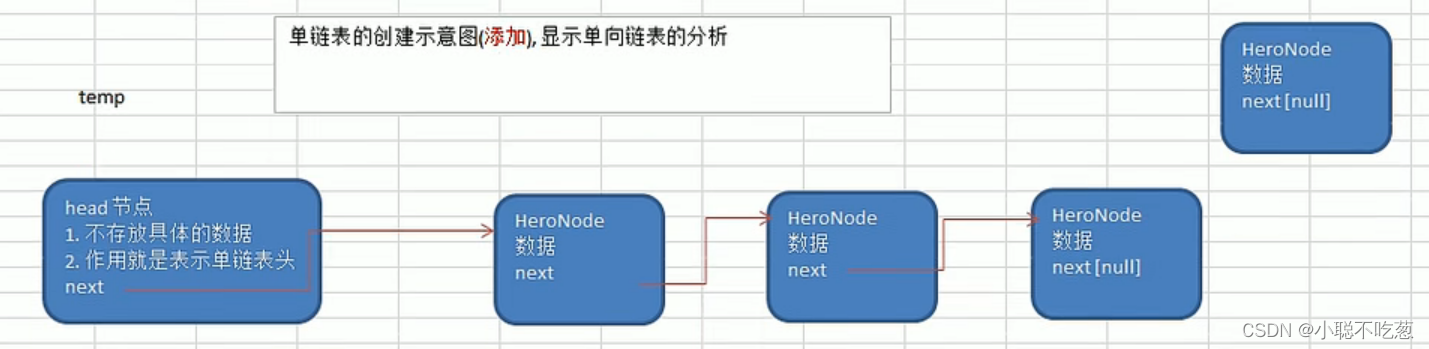
思路分析1:
(1)先创建一个head节点
(2)后面没添加一个节点,就直接加入链表的最后
遍历:
(1)通过一个辅助变量遍历,帮助遍历整个链表
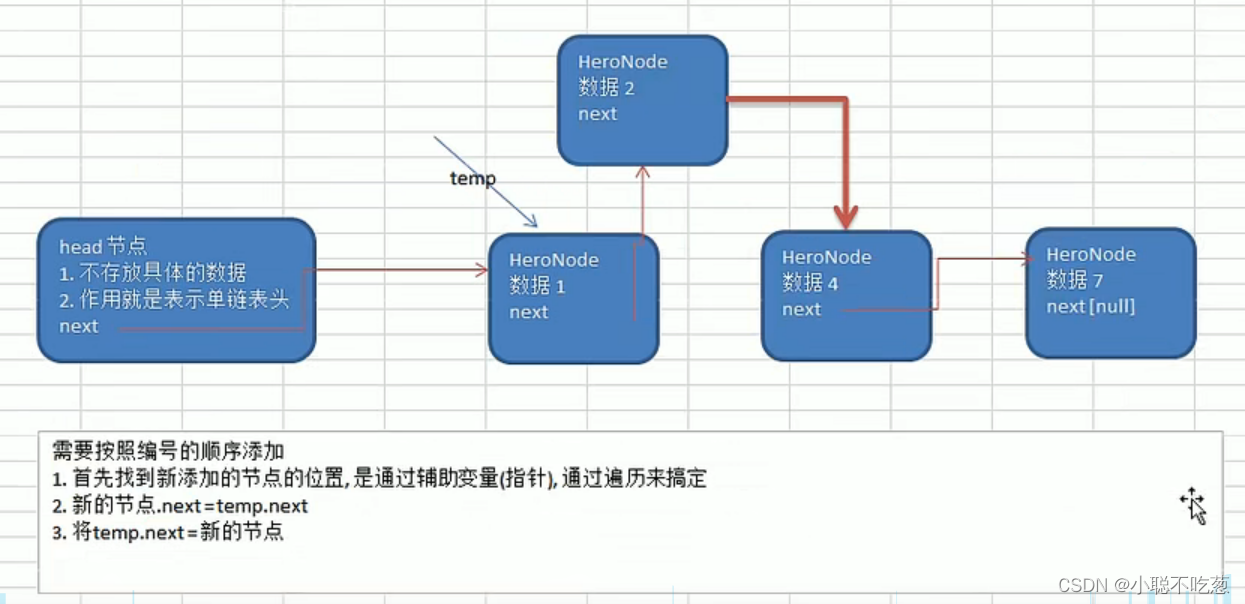
思路分析2:

改:
思路:
(1)先找到该节点,通过遍历
(2)temp.name== newHeroNode.name
temp.nickname == newHeroNode.name


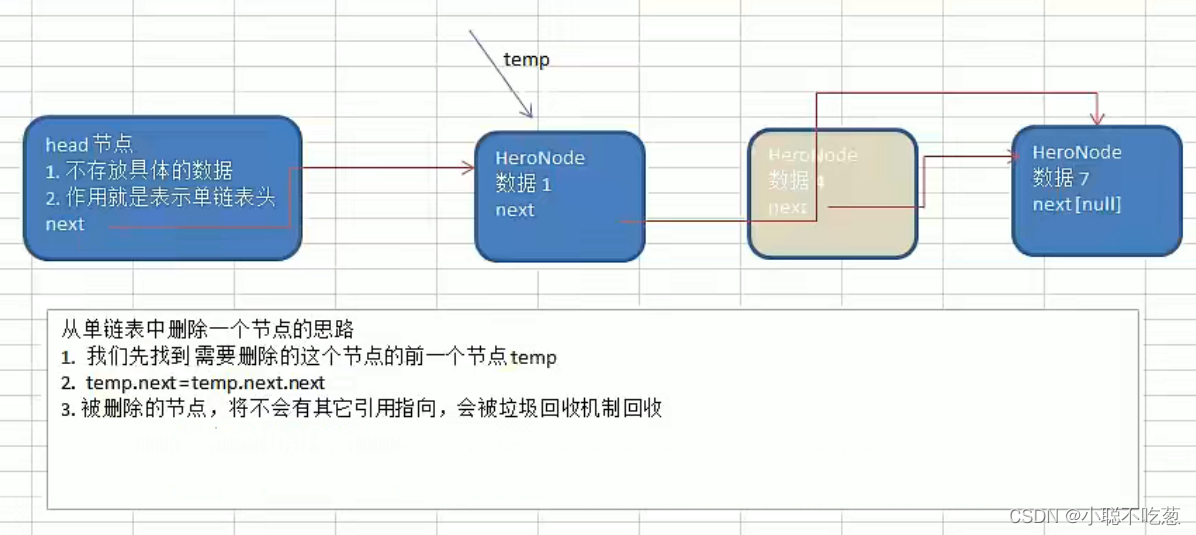
删:
思路分析:
即需要将指针指向新的节点即可

完整代码:
/**
* 应用实例:
* 使用带head头的单项链表实现-水浒英雄排行榜管理:
* 1、完成对英雄任务的增删改查
* 2、第一种方法在添加英雄时,直接添加到链表的尾部
* 3、第二种方法在添加英雄时,根据排名将英雄插入到指定位置
*/
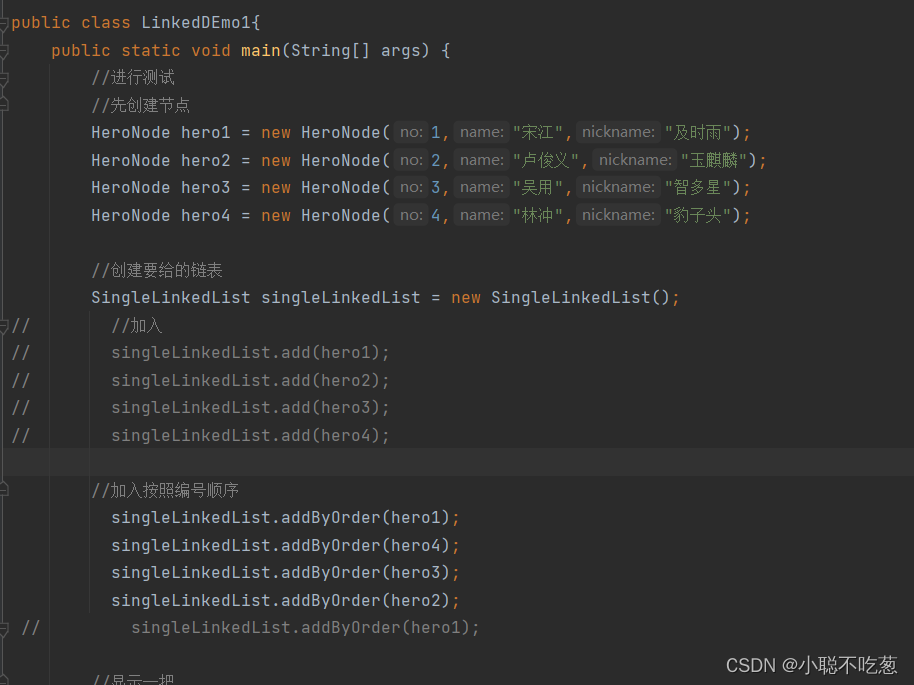
public class LinkedDEmo1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//进行测试
//先创建节点
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2,"卢俊义","玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3,"吴用","智多星");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4,"林冲","豹子头");
//创建要给的链表
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
// //加入
// singleLinkedList.add(hero1);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero2);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero3);
// singleLinkedList.add(hero4);
//加入按照编号顺序
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero1);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero4);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero3);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero2);
// singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero1);
//显示一把
singleLinkedList.list();
//test the code to modify the node
HeroNode newHeroNode = new HeroNode(2,"小路","玉麒麟??");
singleLinkedList.update(newHeroNode);
System.out.println("\n the situation after changing");
singleLinkedList.list();
// test to delete a node
singleLinkedList.del(1);
singleLinkedList.del(2);
singleLinkedList.del(3);
singleLinkedList.del(1);
singleLinkedList.del(4);
System.out.println("the situation after delete");
singleLinkedList.list();
}
}
//定义一个SingleLinkedlist管理英雄
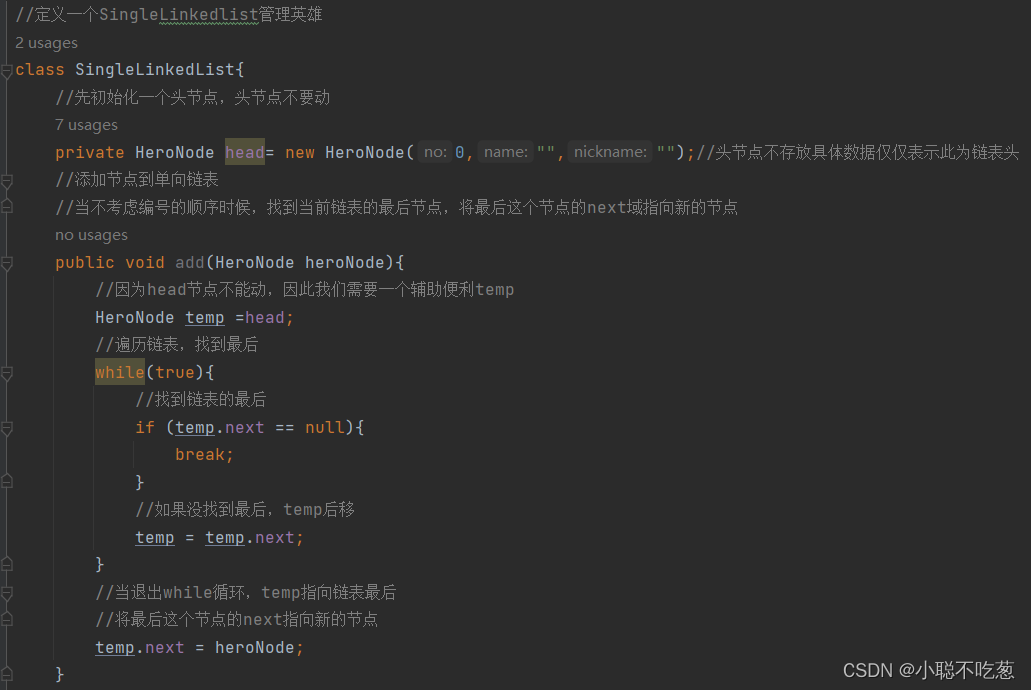
class SingleLinkedList{
//先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动
private HeroNode head= new HeroNode(0,"","");//头节点不存放具体数据仅仅表示此为链表头
//添加节点到单向链表
//当不考虑编号的顺序时候,找到当前链表的最后节点,将最后这个节点的next域指向新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
//因为head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助便利temp
HeroNode temp =head;
//遍历链表,找到最后
while(true){
//找到链表的最后
if (temp.next == null){
break;
}
//如果没找到最后,temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
//当退出while循环,temp指向链表最后
//将最后这个节点的next指向新的节点
temp.next = heroNode;
}
//第二种方式在添加英雄时候,根据排名将英雄插入到指定的位置
//(如果有这个排名,则添加失败,并给出提示)
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode){
//头指针不能动,通过辅助指针来遍历
//因为单链表,因为我们找的temp是位于添加位置的前一个节点,否则插入不了
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false; //标识添加的编号是否存在,默认为false
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {//说明temp已经在链表最后
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {
//位置找到了,就在temp的后面
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
//说明希望添加的heronode的编号已经存在
flag = true; //说明编号存在
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//后移,遍历当前链表
}
//判断flag 的值
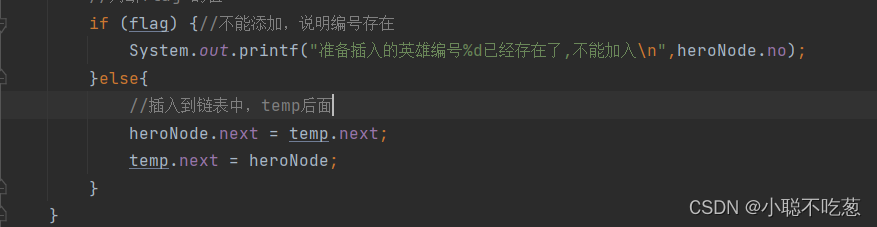
if (flag) {//不能添加,说明编号存在
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄编号%d已经存在了,不能加入\n",heroNode.no);
}else{
//插入到链表中,temp后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
//修改节点的信息,根据编号来修改,即no编号不能改
//1、根据newHeroNode的no来修改即可
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode){
//判断是否为空
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("link is empty");
return;
}
//find the node need to modify, according to the number
//Define an auxiliary variable
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while(true){
if (temp.next==null){
break;// reach the end of the link
}
if(temp.no == newHeroNode.no){
//find it
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
//according to the flag to determine whether to find nodes that need to be modified
if(flag == true){
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
}else{
//did not find it
System.out.printf("Node with number %d not found",newHeroNode.no);
}
}
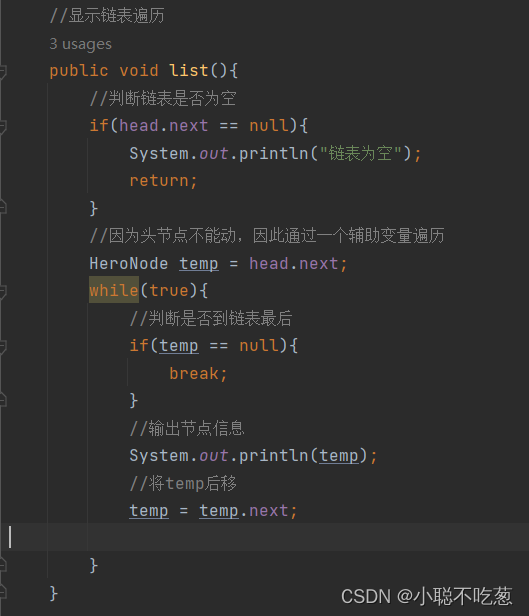
//显示链表遍历
public void list(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//因为头节点不能动,因此通过一个辅助变量遍历
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while(true){
//判断是否到链表最后
if(temp == null){
break;
}
//输出节点信息
System.out.println(temp);
//将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
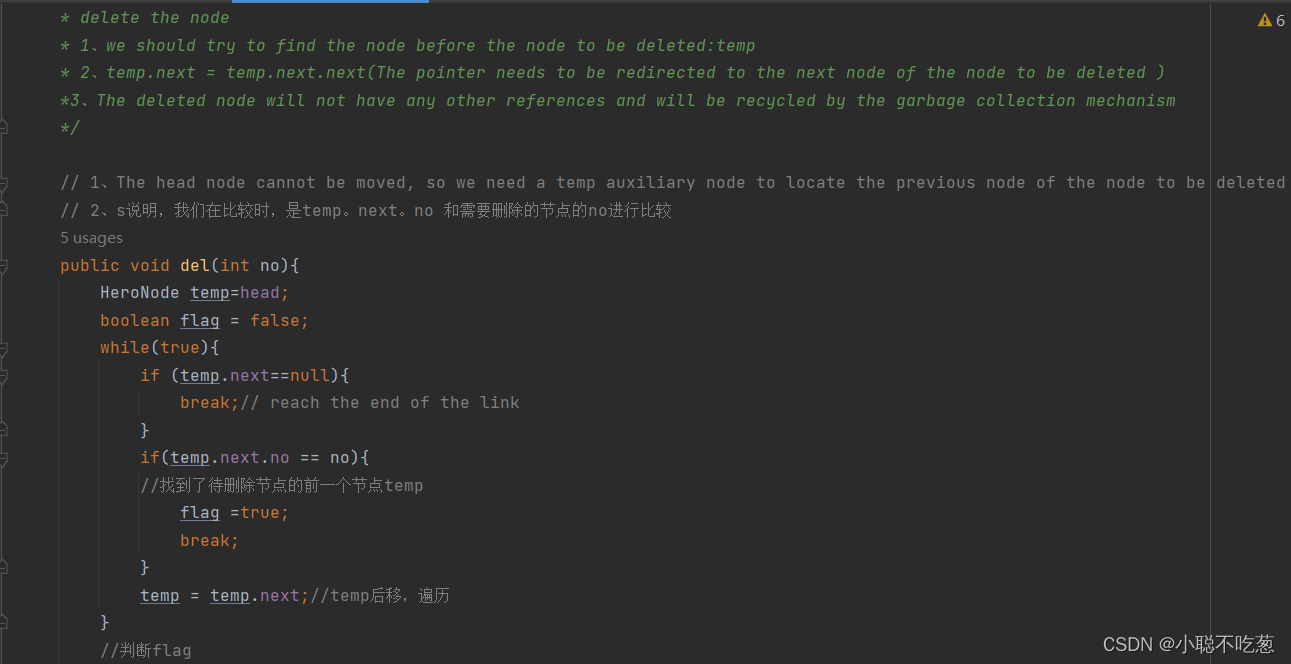
/**
* delete the node
* 1、we should try to find the node before the node to be deleted:temp
* 2、temp.next = temp.next.next(The pointer needs to be redirected to the next node of the node to be deleted )
*3、The deleted node will not have any other references and will be recycled by the garbage collection mechanism
*/
// 1、The head node cannot be moved, so we need a temp auxiliary node to locate the previous node of the node to be deleted
// 2、s说明,我们在比较时,是temp。next。no 和需要删除的节点的no进行比较
public void del(int no){
HeroNode temp=head;
boolean flag = false;
while(true){
if (temp.next==null){
break;// reach the end of the link
}
if(temp.next.no == no){
//找到了待删除节点的前一个节点temp
flag =true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//temp后移,遍历
}
//判断flag
if(flag){
//可以删除
temp.next =temp.next.next;
}else{
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n" ,no);
}
}
}
//定义一个HeroNode,每个HeroNode对象就是一个节点
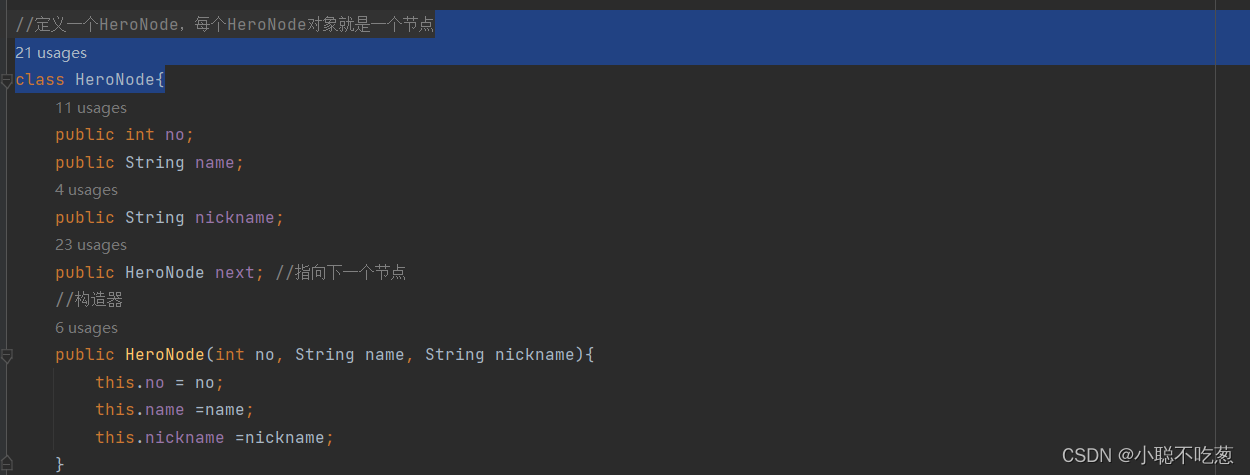
class HeroNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next; //指向下一个节点
//构造器
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname){
this.no = no;
this.name =name;
this.nickname =nickname;
}
//为了显示方法,我们重写toString(toString方法是Java中的一个方法,它用于将一个对象转换成字符串表示形式。这个方法通常被用于调试或者打印对象的时候,
// 它可以返回对象的内容或者状态信息。默认情况下,toString方法返回的是对象的类名和内存地址,但是我们可以根据需要重写这个方法来返回自定义的字符串。)
/**
* toString重写和不重写的区别
* 1、当不重写toString方法时,当直接输入一个对象时,是调用Object.toString方法,默认的返回结果是:全类名+@+哈希值的十六进制
* 2、当重写toString方法时,打印对象或者拼接对象时,都会调用该对象声名好的toString形式,返回返回结果和声明结果保持一致
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
"}";
}
}

![[论文笔记]UNILM](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/2d1261c204cbcbe50002d7933098b7ce.png)





![[H5动画制作系列 ]帧代码运行顺序测试](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cf87bef194dc46fdb11aaea8954dd7ed.png)