GLSL中的函数和C函数很相似,它有一个函数名、一个返回值类型,如果函数不是在main函数之前声明的,我们还必须在代码文件顶部声明一个原型。我们对每个光照类型都创建一个不同的函数:定向光、点光源和聚光。
当我们在场景中使用多个光源时,通常使用以下方法:我们需要有一个单独的颜色向量代表片段的输出颜色。对于每一个光源,它对片段的贡献颜色将会加到片段的输出颜色向量上。所以场景中的每个光源都会计算它们各自对片段的影响,并结合为一个最终的输出颜色。大体的结构会像是这样:
out vec4 FragColor;
void main()
{
// 定义一个输出颜色值
vec3 output;
// 将定向光的贡献加到输出中
output += someFunctionToCalculateDirectionalLight();
// 对所有的点光源也做相同的事情
for(int i = 0; i < nr_of_point_lights; i++)
output += someFunctionToCalculatePointLight();
// 也加上其它的光源(比如聚光)
output += someFunctionToCalculateSpotLight();
FragColor = vec4(output, 1.0);
}实际的代码对每一种实现都可能不同,但大体的结构都是差不多的。我们定义了几个函数,用来计算每个光源的影响,并将最终的结果颜色加到输出颜色向量上。例如,如果两个光源都很靠近一个片段,那么它们所结合的贡献将会形成一个比单个光源照亮时更加明亮的片段。
定向光
我们需要在片段着色器中定义一个函数来计算定向光对相应片段的贡献:它接受一些参数并计算一个定向光照颜色。
首先,我们需要定义一个定向光源最少所需要的变量。我们可以将这些变量储存在一个叫做DirLight的结构体中,并将它定义为一个uniform。需要的变量在上一节中都介绍过:
struct DirLight {
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
uniform DirLight dirLight;接下来我们可以将dirLight传入一个有着以下原型的函数。
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir);
和C/C++一样,如果我们想调用一个函数(这里是在main函数中调用),这个函数需要在调用者的行数之前被定义过。在这个例子中我们更喜欢在main函数以下定义函数,所以上面要求就不满足了。所以,我们需要在main函数之上定义函数的原型,这和C语言中是一样的。
你可以看到,这个函数需要一个DirLight结构体和其它两个向量来进行计算。如果你认真完成了上一节的话,这个函数的内容应该理解起来很容易:
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction);
// 漫反射着色
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// 镜面光着色
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// 合并结果
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
点光源
和定向光一样,我们也希望定义一个用于计算点光源对相应片段贡献,以及衰减,的函数。同样,我们定义一个包含了点光源所需所有变量的结构体:
struct PointLight {
vec3 position;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
#define NR_POINT_LIGHTS 4
uniform PointLight pointLights[NR_POINT_LIGHTS];
你可以看到,我们在GLSL中使用了预处理指令来定义了我们场景中点光源的数量。接着我们使用了这个NR_POINT_LIGHTS常量来创建了一个PointLight结构体的数组。GLSL中的数组和C数组一样,可以使用一对方括号来创建。现在我们有四个待填充数据的PointLight结构体。
点光源函数的原型如下:
vec3 CalcPointLight(PointLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir);
这个函数从参数中获取所需的所有数据,并返回一个代表该点光源对片段的颜色贡献的vec3。我们再一次聪明地从之前的教程中复制粘贴代码,完成了下面这样的函数:
vec3 CalcPointLight(PointLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
// 漫反射着色
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// 镜面光着色
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// 衰减
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance +
light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// 合并结果
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
将这些功能抽象到这样一个函数中的优点是,我们能够不用重复的代码而很容易地计算多个点光源的光照了。在main函数中,我们只需要创建一个循环,遍历整个点光源数组,对每个点光源调用CalcPointLight就可以了。
合并结果
现在我们已经定义了一个计算定向光的函数和一个计算点光源的函数了,我们可以将它们合并放到main函数中。
void main()
{
// 属性
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
// 第一阶段:定向光照
vec3 result = CalcDirLight(dirLight, norm, viewDir);
// 第二阶段:点光源
for(int i = 0; i < NR_POINT_LIGHTS; i++)
result += CalcPointLight(pointLights[i], norm, FragPos, viewDir);
// 第三阶段:聚光
//result += CalcSpotLight(spotLight, norm, FragPos, viewDir);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
每个光源类型都将它们的贡献加到了最终的输出颜色上,直到所有的光源都处理完了。最终的颜色包含了场景中所有光源的颜色影响所合并的结果。如果你想的话,你也可以实现一个聚光,并将它的效果加到输出颜色中。我们会将CalcSpotLight函数留给读者作为练习。
设置定向光结构体的uniform应该非常熟悉了,但是你可能会在想我们该如何设置点光源的uniform值,因为点光源的uniform现在是一个PointLight的数组了。这并不是我们以前讨论过的话题。
很幸运的是,这并不是很复杂,设置一个结构体数组的uniform和设置一个结构体的uniform是很相似的,但是这一次在访问uniform位置的时候,我们需要定义对应的数组下标值:
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[0].constant", 1.0f);
在这里我们索引了pointLights数组中的第一个PointLight,并获取了constant变量的位置。但这也意味着不幸的是我们必须对这四个点光源手动设置uniform值,这让点光源本身就产生了28个uniform调用,非常冗长。你也可以尝试将这些抽象出去一点,定义一个点光源类,让它来为你设置uniform值,但最后你仍然要用这种方式设置所有光源的uniform值。
别忘了,我们还需要为每个点光源定义一个位置向量,所以我们让它们在场景中分散一点。我们会定义另一个glm::vec3数组来包含点光源的位置:
glm::vec3 pointLightPositions[] = {
glm::vec3( 0.7f, 0.2f, 2.0f),
glm::vec3( 2.3f, -3.3f, -4.0f),
glm::vec3(-4.0f, 2.0f, -12.0f),
glm::vec3( 0.0f, 0.0f, -3.0f)
};
接下来我们从pointLights数组中索引对应的PointLight,将它的position值设置为刚刚定义的位置值数组中的其中一个。同时我们还要保证现在绘制的是四个灯立方体而不是仅仅一个。只要对每个灯物体创建一个不同的模型矩阵就可以了,和我们之前对箱子的处理类似。
如果你还使用了手电筒的话,所有光源组合的效果将看起来和下图差不多:
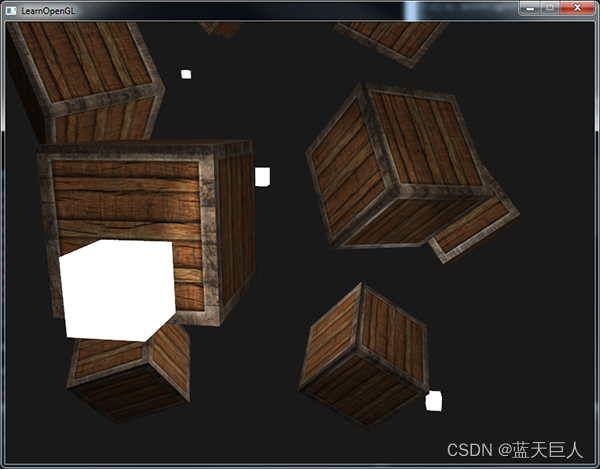
你可以看到,很显然天空中有一个全局照明(像一个太阳),我们有四个光源分散在场景中,以及玩家视角的手电筒。看起来是不是非常不错?
6.multiple_lights.vs
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoords;
out vec3 FragPos;
out vec3 Normal;
out vec2 TexCoords;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal;
TexCoords = aTexCoords;
gl_Position = projection * view * vec4(FragPos, 1.0);
}6.multiple_lights.fs
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Material {
sampler2D diffuse;
sampler2D specular;
float shininess;
};
struct DirLight {
vec3 direction;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
struct PointLight {
vec3 position;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
struct SpotLight {
vec3 position;
vec3 direction;
float cutOff;
float outerCutOff;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
#define NR_POINT_LIGHTS 4
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform DirLight dirLight;
uniform PointLight pointLights[NR_POINT_LIGHTS];
uniform SpotLight spotLight;
uniform Material material;
// function prototypes
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir);
vec3 CalcPointLight(PointLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir);
vec3 CalcSpotLight(SpotLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir);
void main()
{
// properties
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
// == =====================================================
// Our lighting is set up in 3 phases: directional, point lights and an optional flashlight
// For each phase, a calculate function is defined that calculates the corresponding color
// per lamp. In the main() function we take all the calculated colors and sum them up for
// this fragment's final color.
// == =====================================================
// phase 1: directional lighting
vec3 result = CalcDirLight(dirLight, norm, viewDir);
// phase 2: point lights
for(int i = 0; i < NR_POINT_LIGHTS; i++)
result += CalcPointLight(pointLights[i], norm, FragPos, viewDir);
// phase 3: spot light
result += CalcSpotLight(spotLight, norm, FragPos, viewDir);
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}
// calculates the color when using a directional light.
vec3 CalcDirLight(DirLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-light.direction);
// diffuse shading
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// specular shading
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// combine results
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
// calculates the color when using a point light.
vec3 CalcPointLight(PointLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
// diffuse shading
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// specular shading
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// combine results
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}
// calculates the color when using a spot light.
vec3 CalcSpotLight(SpotLight light, vec3 normal, vec3 fragPos, vec3 viewDir)
{
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - fragPos);
// diffuse shading
float diff = max(dot(normal, lightDir), 0.0);
// specular shading
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), material.shininess);
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - fragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// spotlight intensity
float theta = dot(lightDir, normalize(-light.direction));
float epsilon = light.cutOff - light.outerCutOff;
float intensity = clamp((theta - light.outerCutOff) / epsilon, 0.0, 1.0);
// combine results
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 diffuse = light.diffuse * diff * vec3(texture(material.diffuse, TexCoords));
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * vec3(texture(material.specular, TexCoords));
ambient *= attenuation * intensity;
diffuse *= attenuation * intensity;
specular *= attenuation * intensity;
return (ambient + diffuse + specular);
}6.light_cube.vs
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
}6.light_cube.fs
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(1.0); // set all 4 vector values to 1.0
}#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <stb_image.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include <learnopengl/shader_m.h>
#include <learnopengl/camera.h>
#include <iostream>
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
unsigned int loadTexture(const char *path);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
// lighting
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// tell GLFW to capture our mouse
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// build and compile our shader zprogram
// ------------------------------------
Shader lightingShader("6.multiple_lights.vs", "6.multiple_lights.fs");
Shader lightCubeShader("6.light_cube.vs", "6.light_cube.fs");
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
float vertices[] = {
// positions // normals // texture coords
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// positions all containers
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3( 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3( 2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3( 2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3( 1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3( 1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3( 1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)
};
// positions of the point lights
glm::vec3 pointLightPositions[] = {
glm::vec3( 0.7f, 0.2f, 2.0f),
glm::vec3( 2.3f, -3.3f, -4.0f),
glm::vec3(-4.0f, 2.0f, -12.0f),
glm::vec3( 0.0f, 0.0f, -3.0f)
};
// first, configure the cube's VAO (and VBO)
unsigned int VBO, cubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)(6 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// second, configure the light's VAO (VBO stays the same; the vertices are the same for the light object which is also a 3D cube)
unsigned int lightCubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &lightCubeVAO);
glBindVertexArray(lightCubeVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// note that we update the lamp's position attribute's stride to reflect the updated buffer data
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// load textures (we now use a utility function to keep the code more organized)
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned int diffuseMap = loadTexture(FileSystem::getPath("resources/textures/container2.png").c_str());
unsigned int specularMap = loadTexture(FileSystem::getPath("resources/textures/container2_specular.png").c_str());
// shader configuration
// --------------------
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setInt("material.diffuse", 0);
lightingShader.setInt("material.specular", 1);
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// per-frame time logic
// --------------------
float currentFrame = static_cast<float>(glfwGetTime());
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// be sure to activate shader when setting uniforms/drawing objects
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("viewPos", camera.Position);
lightingShader.setFloat("material.shininess", 32.0f);
// directional light
lightingShader.setVec3("dirLight.direction", -0.2f, -1.0f, -0.3f);
lightingShader.setVec3("dirLight.ambient", 0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
lightingShader.setVec3("dirLight.diffuse", 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f);
lightingShader.setVec3("dirLight.specular", 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
// point light 1
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[0].position", pointLightPositions[0]);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[0].ambient", 0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[0].diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[0].specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[0].constant", 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[0].linear", 0.09f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[0].quadratic", 0.032f);
// point light 2
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[1].position", pointLightPositions[1]);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[1].ambient", 0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[1].diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[1].specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[1].constant", 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[1].linear", 0.09f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[1].quadratic", 0.032f);
// point light 3
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[2].position", pointLightPositions[2]);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[2].ambient", 0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[2].diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[2].specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[2].constant", 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[2].linear", 0.09f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[2].quadratic", 0.032f);
// point light 4
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[3].position", pointLightPositions[3]);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[3].ambient", 0.05f, 0.05f, 0.05f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[3].diffuse", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
lightingShader.setVec3("pointLights[3].specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[3].constant", 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[3].linear", 0.09f);
lightingShader.setFloat("pointLights[3].quadratic", 0.032f);
// spotLight
lightingShader.setVec3("spotLight.position", camera.Position);
lightingShader.setVec3("spotLight.direction", camera.Front);
lightingShader.setVec3("spotLight.ambient", 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
lightingShader.setVec3("spotLight.diffuse", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setVec3("spotLight.specular", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("spotLight.constant", 1.0f);
lightingShader.setFloat("spotLight.linear", 0.09f);
lightingShader.setFloat("spotLight.quadratic", 0.032f);
lightingShader.setFloat("spotLight.cutOff", glm::cos(glm::radians(12.5f)));
lightingShader.setFloat("spotLight.outerCutOff", glm::cos(glm::radians(15.0f)));
// view/projection transformations
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
lightingShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightingShader.setMat4("view", view);
// world transformation
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
lightingShader.setMat4("model", model);
// bind diffuse map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, diffuseMap);
// bind specular map
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, specularMap);
// render containers
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
// calculate the model matrix for each object and pass it to shader before drawing
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
lightingShader.setMat4("model", model);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
// also draw the lamp object(s)
lightCubeShader.use();
lightCubeShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightCubeShader.setMat4("view", view);
// we now draw as many light bulbs as we have point lights.
glBindVertexArray(lightCubeVAO);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, pointLightPositions[i]);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f)); // Make it a smaller cube
lightCubeShader.setMat4("model", model);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &lightCubeVAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
// -------------------------------------------------------
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
}
// utility function for loading a 2D texture from file
// ---------------------------------------------------
unsigned int loadTexture(char const * path)
{
unsigned int textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
int width, height, nrComponents;
unsigned char *data = stbi_load(path, &width, &height, &nrComponents, 0);
if (data)
{
GLenum format;
if (nrComponents == 1)
format = GL_RED;
else if (nrComponents == 3)
format = GL_RGB;
else if (nrComponents == 4)
format = GL_RGBA;
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl;
stbi_image_free(data);
}
return textureID;
}