1.汉诺塔问题
在经典汉诺塔问题中,有 3 根柱子及 N 个不同大小的穿孔圆盘,盘子可以滑入任意一根柱子。一开始,所有盘子自上而下按升序依次套在第一根柱子上(即每一个盘子只能放在更大的盘子上面)。移动圆盘时受到以下限制:
(1) 每次只能移动一个盘子;
(2) 盘子只能从柱子顶端滑出移到下一根柱子;
(3) 盘子只能叠在比它大的盘子上。
//确定子问题处理方式是相同的
//确定递归函数的函数头传参
//确定函数体也就子问题的处理方式
//判断函数出口
class Solution {
public:
void hanota(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C) {
int n=A.size();
dfs(A,B,C,n);
}
void dfs(vector<int>& A,vector<int>&B ,vector<int>& C,int n){
if(n==1){
C.push_back(A.back());//这里一定是要A.back(),可以画一下递归展开图
A.pop_back();
return;
}//函数出口
dfs(A,C,B,n-1);//不关心如何递归下去的,认为该函数一定能够帮我做到把a上的n-1数据借助c挪动b上
C.push_back(A.back());//这里一定是要A.back(),可以画一下递归展开图
A.pop_back();
dfs(B,A,C,n-1);//同样认为该函数一定能把b上残留的n-1个数据借助a放到c上面
}
};2.合并升序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* newHead=merge(list1,list2);
return newHead;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2){
if(l1==nullptr) return l2;
if(l2==nullptr) return l1;
if(l1->val<l2->val){
l1->next=merge(l1->next,l2);
return l1;//返回拼好的头节点
}
else{
l2->next=merge(l2->next,l1);
return l2;
}
}
};3. 反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr)return head;
ListNode* newhead=reverseList(head->next);//认为一定可以返回一个已经逆序的子链表
head->next->next=head;//让已经逆序的子序列的头节点指向子序列的上一个头节点
head->next=nullptr;
return newhead;//这里newhead一直是没有移动过的,一直都是新的链表的头结点。
}
};4. 两两交换链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr)
{
return head;
}
ListNode* new_head=head->next;
ListNode* tmp=head->next->next;//小心中途修改的问题
head->next->next=head;
head->next=swapPairs(tmp);
return new_head;
}
};5. Pow(x,n)
-100.0 < x < 100.0-2^31 <= n <= 2^31-1-10^4 <= x^n <= 10^4
本题需要注意负数的情况和超int取值范围的情况
这样会语法报错。。。
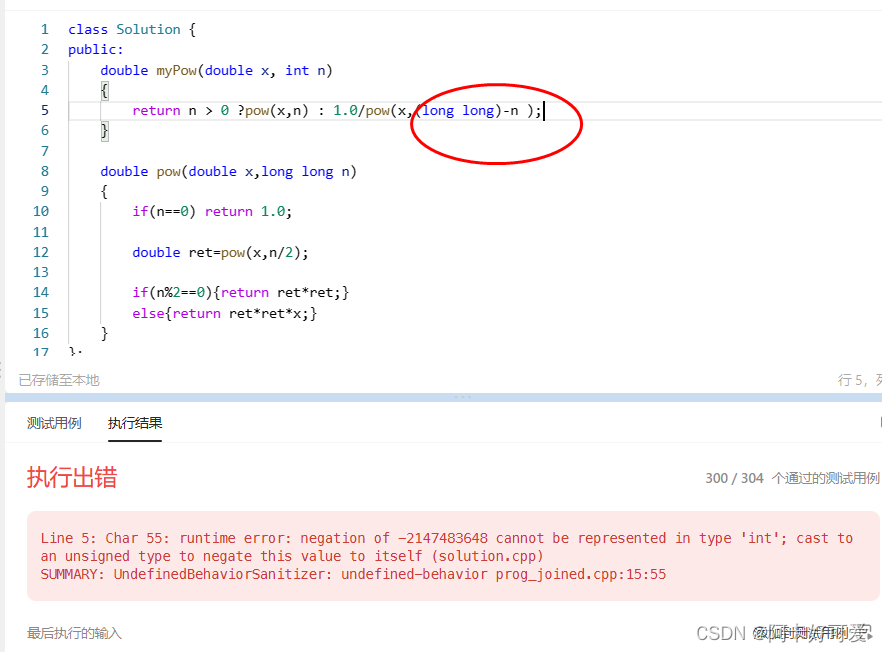
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n)
{
return n > 0 ?pow(x,n) : 1.0/pow(x,-(long long)n );
}
double pow(double x,long long n)
{
if(n==0) return 1.0;
double ret=pow(x,n/2);
if(n%2==0){return ret*ret;}
else{return ret*ret*x;}
}
};6. 布尔逻辑二叉树
class Solution {
public:
bool evaluateTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root->left==nullptr)
{
if(root->val==1)return true;
else return false;
}
bool left=evaluateTree(root->left);
bool right=evaluateTree(root->right);
if(root->val==2)
{
return left || right;
}
else
{
return left && right;
}
}
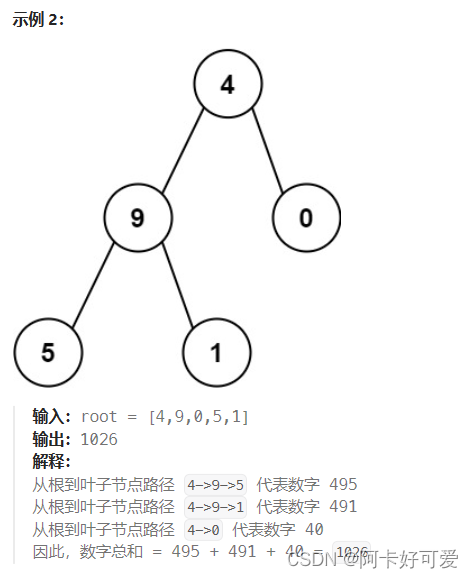
};7.根到叶子之和
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
//函数头设计,我们认为传入一个节点,那么就会算出此节点到所有节点的数字之和
//函数体:从上一层获得此前的所有数字组合再拼上此层,所以需要多设计一个参数来记录
//函数出口:当没有孩子的时候
class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root,0);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root,int presum)
{
// if(root==nullptr)
// {
// return presum;题目给的一定是有一个节点
// }
presum=presum*10+root->val;
std::cout<<presum<<std::endl;
int ret=0;//因为函数的功能是用来计算之和并返回,所以不能直接presum传入,此处presum只是用于记录已经遍历了的数字。
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr){
return presum;
}
if(root->left) ret+=dfs(root->left,presum);
if(root->right) ret+= dfs(root->right,presum);
return ret;
}
};8.二叉树剪枝
给定一个二叉树 根节点 root ,树的每个节点的值要么是 0,要么是 1。请剪除该二叉树中所有节点的值为 0 的子树。
节点 node 的子树为 node 本身,以及所有 node 的后代。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
//函数体设计
//返回一个已经剪枝的根节点
//函数出口:当自己是空的时候返回空,处理动作一致
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* pruneTree(TreeNode* root) {
// if(root==nullptr)
// {
// return nullptr;
// }
if(root->left) root->left=pruneTree(root->left);
if(root->right) root->right=pruneTree(root->right);
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr&&root->val==0)
//走到头才算是树枝当树枝被剪完了自己也就是树枝的。
{
//delete root;
root=nullptr;
// return nullptr;
}
return root;
}
};9.验证二叉搜索树(注意剪枝)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
long long prev_val=LONG_MIN;
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
{
return true;
}
bool left=isValidBST(root->left);
if(left==false) return false;//剪枝
bool cur=false;
if(root->val>prev_val)
{
prev_val=root->val;
cur=true;
}
if(right==false) return false;//剪枝
bool right=isValidBST(root->right);
//cout<< root->val;
return left&&right&&cur;
}
};10. 二叉搜索树第k小的元素(二叉搜索树中序遍历是一个有序序列)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int count;
int ret;
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
count=k;
return dfs(root);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==nullptr){
return ret;
}
ret=dfs(root->left);
if(count==0)
{
return ret;
}
ret=root->val;
count--;
ret=dfs(root->right);
return ret;
}
};11. 二叉树的所有路径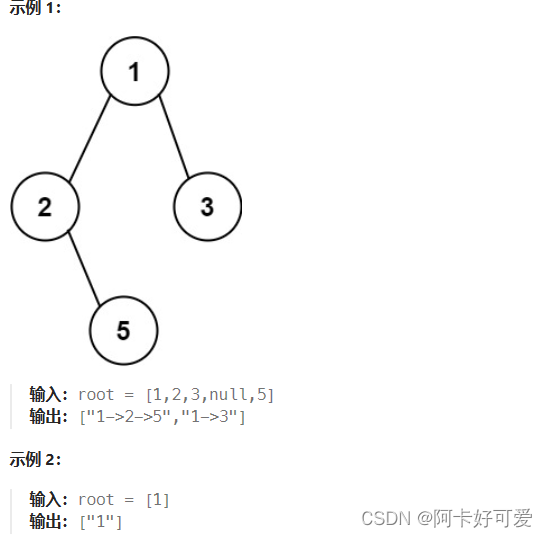
12. 全排列
1.此处path设置为全局变量更好,虽然回溯时需要修改,但是节省一些空间并且效率更高。:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<bool> check;//用于记录哪些数字使用过了而达到剪枝的效果,回溯的时候需要把使用过的数字还回去
vector<int> path;//这里的path最好使用全局变量
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
check.resize(nums.size());
dfs(nums,path);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums,vector<int> path)
{
if(nums.size()==path.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(check[i]==true)
{
continue;
}
check[i]=true;
vector<int> tmp=path;
tmp.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,tmp);
check[i]=false;
}
}
};2. 修改后:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<bool> check;//用于记录哪些数字使用过了而达到剪枝的效果,回溯的时候需要把使用过的数字还回去
vector<int> path;//这里的path最好使用全局变量
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
check.resize(nums.size());
dfs(nums,path);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums,vector<int>& path)
{
if(nums.size()==path.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(check[i]==true)
{
continue;
}
check[i]=true;
// vector<int> tmp=path;
// tmp.push_back(nums[i]);
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,path);
check[i]=false;//向下递归完后恢复现场
path.pop_back();
}
}
};13. 二叉树的所有路径
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
13. 二叉树的所有路径
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> ret;
string path;
int i=0;
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==nullptr) return ret;//假设会传入空,最好不要写在dfs函数里面
dfs(root,path);
return ret;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root,string path)
{
path+=to_string(root->val);
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr)
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
path+="->";
if(root->left) dfs(root->left,path);
if(root->right) dfs(root->right,path);//剪枝,并且达到了不会传入空的效果
}
};14. 子集
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
//vector<bool> check;
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums)
{
dfs(nums,0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums ,int pos)
{
ret.push_back(path);
for(int i=pos;i<nums.size();i++)
{
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,i+1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};15. 异或和按位或分清楚
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

class Solution {
public:
int ret;//返回值总和
int tmp=0;//记录当前层异或的值
int subsetXORSum(vector<int>& nums) {
dfs(nums,0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums,int pos)
{
ret+=tmp;
for(int i=pos;i<nums.size();i++)
{
tmp^=nums[i];
dfs(nums,i+1);
tmp^=nums[i];
}
}
};16. 全排列 ||
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<bool> check;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
check.resize(nums.size(),false);
//没有上句会报错Line 84: Char 2: runtime error: store to null pointer of type 'std::_Bit_type' (aka 'unsigned long') (stl_bvector.h)
dfs(nums);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums)
{
if(path.size()==nums.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(check[i]==true ||( i!=0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && check[i-1] == false ))
//check[i-1]==false;说明nums[i]和nums[i-1]同层进行判断比较。
{
continue;
}
check[i]=true;
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums);
check[i]=false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
};17. 电话号码
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

class Solution {
public:
vector<string> ret;
string path;
vector<string> hash={" ", " ", "abc", "def", "ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits)
{
if(digits.size()==0){
return ret;
}
dfs(digits,0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(string& digits,int pos)
{
if(path.size()==digits.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(auto a: hash[digits[pos]-'0'] )
{
path.push_back(a);
dfs(digits,pos+1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};18. 括号生成
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

class Solution {
public:
int max;
int left,right;
vector<string> ret;
string path;
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n)
{
max=n;
dfs();
return ret;
}
void dfs()
{
if(right == max)
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
if(left < max)
{
path.push_back('(');
++left;
dfs();
--left;
path.pop_back();
}
if(right < left)
{
path.push_back(')');
right++;
dfs();
right--;
path.pop_back();
}
}
};19. 组合
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台

class Solution {
public:
int max;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
max=k;
dfs(1,n);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int pos,int& n)
{
if(path.size() == max )
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i=pos;i<n+1;++i)
{
path.push_back(i);
dfs(i+1,n);//是要传入i+1而不是pos+1
path.pop_back();
}
}
};20.目标和
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
注意单单int的反复加加减减还是非常耗时的,这里不是拷贝一个vector之类的对象,所以反而恢复现场的操作会更慢从而超时。

class Solution {
public:
// int ret=0;
// int path;
// int now_target;
// int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target)
// {
// now_target=target;
// dfs(0,1,nums);
// return ret;
// }
// void dfs(int pos,int level,vector<int>& nums)
// {
// if(nums.size()+1 == level)
// {
// if(path==now_target)
// {
// ret++;
// }
// return;
// }
// {
// path+=nums[pos];
// dfs(pos+1,level+1,nums);
// path-=nums[pos];
// }
// {
// path-=nums[pos];
// dfs(pos+1,level+1,nums);
// path+=nums[pos];
// }
// }
int ret=0;
//int path;
int now_target;
int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
int path=0;
now_target=target;
dfs(0,1,nums,path);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int pos,int level,vector<int>& nums,int path)
{
if(nums.size()+1 == level)
{
if(path==now_target)
{
ret++;
}
return;
}
{
//path+=nums[pos];
dfs(pos+1,level+1,nums,path+nums[pos]);
//path-=nums[pos];
}
{
dfs(pos+1,level+1,nums,path-nums[pos]);
}
}
};