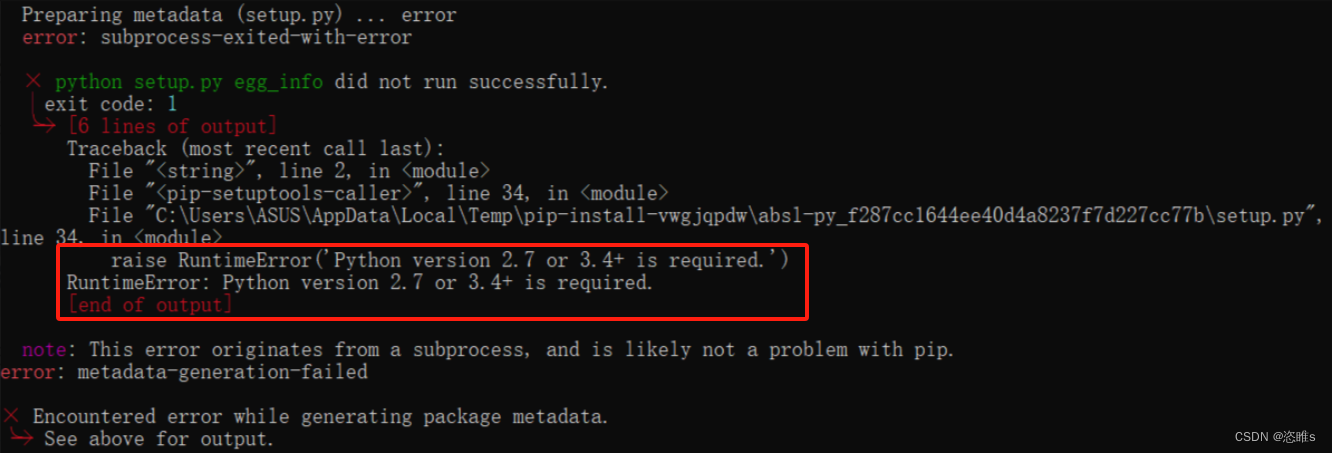
在实际应用中,经常需要在同一个节点内接受数据,在回调函数中将数据进行处理,再将新数据重新发布在另一个新话题上。
实现步骤:
1. 定义一个数据处理类SubscribeAndPublish,设置2个pub成员对象和1个sub成员对象为public。
2. 在主函数中发布原始消息;
3. 将callback定义为成员函数,并使用新的pub将消息发布出去。
测试程序代码如下:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include"std_msgs/String.h"
class SubscribeAndPublish
{
public:
SubscribeAndPublish()
{
//Topic you want to publish
pub_ = n_.advertise<std_msgs::String>("/published_topic", 1);
pub_callback = n_.advertise<std_msgs::String>("/callback_topic", 1);
//Topic you want to subscribe
sub_ = n_.subscribe("/published_topic", 1, &SubscribeAndPublish::callback, this); //注意这里,和平时使用回调函数不一样了。
}
void callback(const std_msgs::String& input)
{
std_msgs::String output;
output.data = input.data;
output.data.append(" treated!");
//.... do something with the input and generate the output...
ROS_INFO("callbacked and published on /callback_topic");
pub_callback.publish(output);
// ROS_INFO("callback published");
}
public:
ros::NodeHandle n_;
ros::Publisher pub_;
ros::Publisher pub_callback;
ros::Subscriber sub_;
};//End of class SubscribeAndPublish
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//Initiate ROS
ros::init(argc, argv, "subscribe_and_publish");
//Create an object of class SubscribeAndPublish that will take care of everything
SubscribeAndPublish SAPObject;
std_msgs::String msg;
msg.data = "from main";
ros::Rate loop_rate(1);
while (ros::ok())
{
SAPObject.pub_.publish(msg);
ROS_INFO("main published on /published_topic");
ros::spinOnce();//处理订阅话题的所有回调函数callback(),
loop_rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
} 打印来原始话题的消息和新话题的消息:
rostopic echo /published_topicrostopic echo /callback_topic得到原始数据和处理过后的数据的结果。