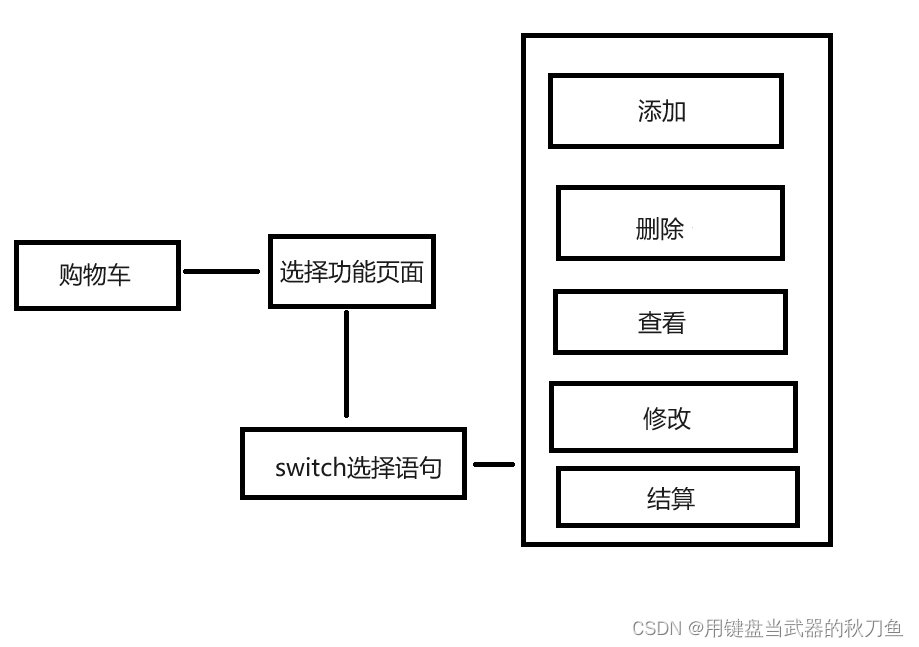
public class GoodsShop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("欢迎来到购物车管理系统");
obj [] arr = new obj[50];//obj[50]为购物车的数量上限
obj obj = new obj();//调用obj
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//输入
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入1进入增加页面");
System.out.println("输入2进入查看页面");
System.out.println("输入3进入修改页面");
System.out.println("输入4进入删除页面");
System.out.println("输入5进入结算页面");
double shuzi = scanner.nextDouble();
switch ((int) shuzi) {
case 1 : obj.add();break;//调用增
case 2 : obj.cha();break;//调用查
case 3 : obj.del();break;//调用删
case 4 : obj.gai();break;//调用改
case 5 : obj.sum();break;//调用结算
default:
System.out.println("请重新输入");
}
}
}
}
class obj {
String name;//商品名
int numb;//商品数量
int id;//商品编码
double money;//商品价格
public static void add(){
System.out.println("欢迎来到增加页面");
}
public static void cha(){
System.out.println("欢迎来到查看商品页面");
}
public static void del(){
System.out.println("欢迎来到删除页面");
}
public static void gai(){
System.out.println("欢迎来到修改页面");
}
public static void sum(){
System.out.println("欢迎来到结算页面");
}
}
上面部分的图片与代码配合来看更容易理解
正式进入个个部分的具体内容编程
第一部分:添加商品页面
这一模块的作用,使用者通过键盘输入内容,将内容以一个数组存放
我们就要传入两个值,一个是键盘输入,一个是数组
public static void add(obj[]arr,Scanner scanner){//传值
System.out.println("欢迎来到增加页面");
System.out.println("输入商品名");
String name1 = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输入商品ID");
int id1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入商品数量");
int shuliang1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入商品价格");
double money1 = scanner.nextDouble();
}提示与输入值顺带的也写好
将输入的值,封装成goods对象
//封装成一个对象
obj goods = new obj();
goods.id = id1;
goods.money = money1;
goods.name = name1;
goods.numb = shuliang1;然后封装的对象用循环挨个装进数组中
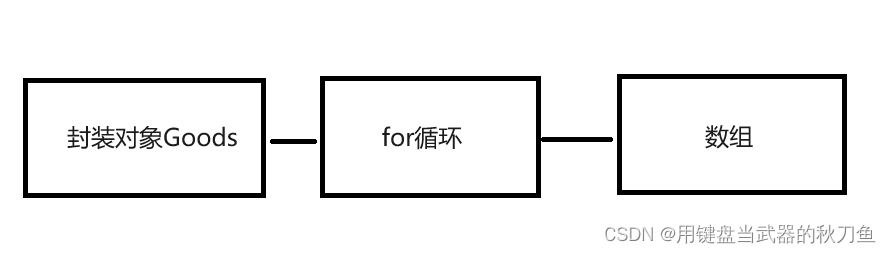
//挨个装进去
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
arr[i] = goods;
}
System.out.println("成功将"+ goods.name + "装入购物车");第二个模块,查看商品
商品是用一个数组装着的,那么怎么查看数组就是怎么查看商品
所以,需要给cha()方法传入一个数组
public static void cha(obj [] arr){//传入方法
System.out.println("欢迎来到查看商品页面");
System.out.println("===========================");
System.out.println("ID" + "\t" + "\t" +"商品名" + "\t" + "商品数量" + "\t" + "商品价格");
}然后输出数组
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
obj good = arr[i];
if (arr[i] != null)
{
System.out.println(good.id + "\t" + good.name + "\t" + "\t" +good.numb +"\t"+"\t" + good.money);
}
else
break;
}
}为什么要用选择语句?看看不用的情况
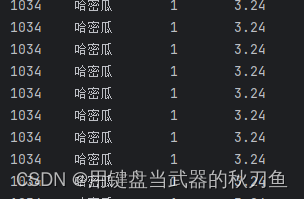
没错,他直接把整个购物车充满了,我们定义了数组的数量为50,又因为传址,直接将全部值变成了一样
这个选择语句的作用是,当arr[i] 无值的时候跳出程序,这样就不会有多余的数组了
当你用了if判断的时候,又出现bug了,还是一直输出怎么办!
回过头来看看
//挨个装进去
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == null) {
arr[i] = goods;
break;
}
}应该要在挨个添加进数组的时候进行一个选择,这样就可以防止传址
大致的介绍一下
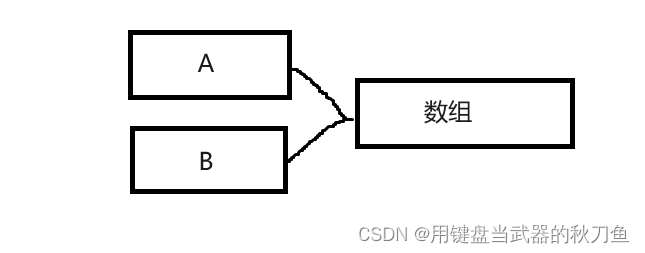
他们用的是同一个东西,A改B改,B改A改
第三个模块——删除商品
前面介绍了null这个值,就是当数组是空的时候会显示bull
现在数组不是空的,就让它变成空的
先完成一个简单,传入一个数组
public static void del(obj [] arr){
System.out.println("欢迎来到删除页面");
}用循环将每个数组输出,如果有值就将值变成null,没值就跳出
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++)
{
obj goods = arr[i];
if (arr[i] != null)
{
arr[i] = null;
}
else
break;
}
第四个模块——修改商品数量
商品是数组,修改要输入,所以需要传入一个数组,一个输入
public static void gai(obj [] arr , Scanner scanner){
System.out.println("欢迎来到修改页面");
}第二步,要进行一个选择,判断它到底是不是购物车里面的值
为了区分修改和重复使用改功能,我们另外声明一个方法
传入两个值,一个商品,一个商品值,根据id会简单点,因为id在现实中是很难进行改变的
public static obj getID(obj [] arr,int id)
{
}还是通过循环,将对象的值传给数组,进行选择,如果等于返回对象
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
obj goods = arr[i];
if (goods.id == id)
return goods;
else
return null;
}
return null;//遍历50次还是空正式的开始写修改
先来点简单的——来个提示和输入
System.out.println("欢迎来到修改页面");
System.out.println("输入修改商品的ID");
int nub = scanner.nextInt();用封装对象调用刚刚的方法
obj goods = getID(arr,nub);根据那个方法,如果我们输入的值,符合购物车里的id,就会将与这个id相同的数组返回
进入选择语句,如果等于就修改,不等于就输入提示
数字的交换,如何将A,b的值交换,就能完成修改
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入修改商品的ID");
int nub = scanner.nextInt();
obj goods = getID(arr, nub);
if (nub != goods.id) {
System.out.println("没有该商品");
} else {
System.out.println("修改" + goods.name + "的数量");
int nub1 = scanner.nextInt();
goods.numb = nub1;
System.out.println("修改成功");
cha(arr);
break;
}
}因为不可能只用一次,可能会进行多次修改,所以使用一个循环
为了更好的看出来,我们调用一次cha()方法
哎!到这里为什么会变成删除,那是因为我在开始的代码中把3和4的提示打错字了!!!
第五个模块——结算金额
给个思路,自己写
因为是结算购物车的金额,所以需要传入一个数组
传入完数组后,通过循环,将封装对象挨个传入数组
进行IF选择语句,当数组的值不为空,就调用个数,金额进行一个乘法运算
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
全代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GoodsShop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("欢迎来到购物车管理系统");
obj [] arr = new obj[50];//obj[50]为购物车的数量上限
obj obj = new obj();//调用obj
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//输入
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入1进入增加页面");
System.out.println("输入2进入查看页面");
System.out.println("输入3进入删除页面");
System.out.println("输入4进入修改页面");
System.out.println("输入5进入结算页面");
double shuzi = scanner.nextDouble();
switch ((int) shuzi) {
case 1 : obj.add(arr,scanner);break;//调用增
case 2 : obj.cha(arr);break;//调用查
case 3 : obj.del(arr);break;//调用删
case 4 : obj.gai(arr,scanner);break;//调用改
case 5 : obj.sum(arr);break;//调用结算
default:
System.out.println("请重新输入");
}
}
}
}
class obj {
String name;//商品名
int numb;//商品数量
int id;//商品编码
double money;//商品价格
public static void add(obj[]arr,Scanner scanner){//传值
System.out.println("欢迎来到增加页面");
System.out.println("输入商品名");
String name1 = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输入商品ID");
int id1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入商品数量");
int shuliang1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入商品价格");
double money1 = scanner.nextDouble();
//封装成一个对象
obj goods = new obj();
goods.id = id1;
goods.money = money1;
goods.name = name1;
goods.numb = shuliang1;
//挨个装进去
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == null) {
arr[i] = goods;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("成功将"+ goods.name + "装入购物车");
}
public static void cha(obj [] arr){
System.out.println("欢迎来到查看商品页面");
System.out.println("===========================");
System.out.println("ID" + "\t" + "\t" +"商品名" + "\t" + "商品数量" + "\t" + "商品价格");
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
obj good = arr[i];
if (arr[i] != null)
{
System.out.println(good.id + "\t" + good.name + "\t" + "\t" +good.numb +"\t"+"\t" + good.money);
}
else
break;
}
}
public static void del(obj [] arr){
System.out.println("欢迎来到删除页面");
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++)
{
obj goods = arr[i];
if (arr[i] != null)
{
arr[i] = null;
}
else
break;
}
}
public static void gai(obj [] arr , Scanner scanner){
System.out.println("欢迎来到修改页面");
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入修改商品的ID");
int nub = scanner.nextInt();
obj goods = getID(arr, nub);
if (nub != goods.id) {
System.out.println("没有该商品");
} else {
System.out.println("修改" + goods.name + "的数量");
int nub1 = scanner.nextInt();
goods.numb = nub1;
System.out.println("修改成功");
break;
}
}
}
public static obj getID(obj [] arr,int id)
{
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
obj goods = arr[i];
if (goods.id == id)
return goods;
else
return null;
}
return null;//遍历50次还是空
}
public static void sum(obj[]arr){
System.out.println("欢迎来到结算页面");
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++)
{
obj goods = arr[i];
if (arr[i] != null)
{
System.out.println(goods.numb * goods.money + "元");
}
else
break;
}
}
}
其中用的最多的语句是迭代语句和选择语句
其次就是封装的使用
本质上就是通过不同的语句对封装对象的操作

![[NOIP2011 提高组] 铺地毯](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/017d747244d9ae1ebdeb6aa14824a7d4.png)