文章目录
- 1.数组篇
- 1.1 704-二分查找
- 1.2 27-移除数组
- 1.3 977-有序数组的平方
- 1.4* 209--长度最小的子数组(滑动窗口)
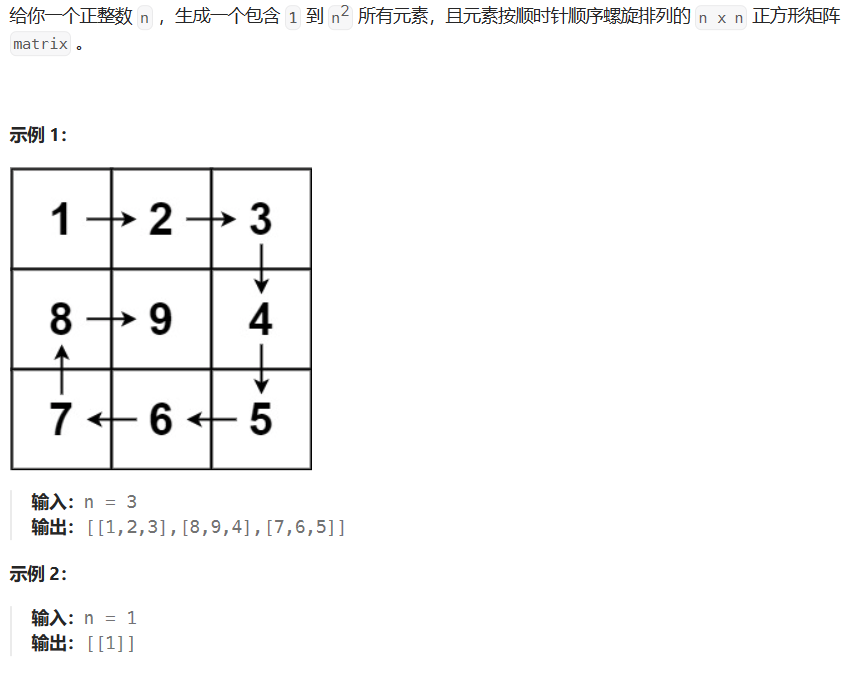
- 1.5* 59-螺旋矩阵II
- 2. 链表篇
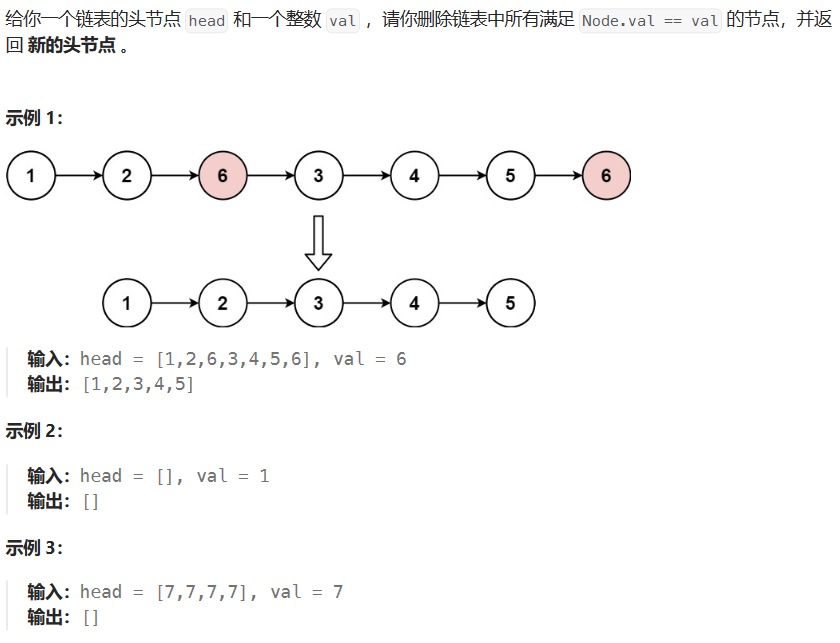
- 2.1 203-移除链表元素
- 2.2 707-设计链表
- 2.3 206-反转链表
- 2.4* 24-两两交换链表中的节点(跳针)
- 2.5* 19-删除链表的倒数第N个节点(快慢指针)
- 2.6* 链表相交
- 2.7 142-环形链表II
- 3. 哈希篇
- 3.1 242-有效的字母异位词
- 3.2* 1002-查找共用字符
- 3.3 349-两个数组的交集
- 3.4 202-快乐数
- 3.5 1-两数之和
- 3.6* 454-四数相加II
- 3.7 383-赎金信
- 4. 双指针篇
- 4.1 15-三数之和(双指针)
- 4.2 18-四数之和
- 5. 字符串篇
- 5.1 344-反转字符串
- 5.2 541-反转字符串II
- 5.3* 151-反转字符串中的单词
- 5.4 182-动态口令
- 5.5* 459-重复的子字符串
- 5.6* 28-找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(KMP)
- 6. 栈和队列篇
- 6.1 232-用栈实现队列
- 6.2 225-用队列实现栈
- 6.3 20-有效的括号
- 6.4 1047-删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
- 6.5 150-逆波兰表达式求值
- 6.6* 239-滑动窗口最大值(双端队列)
- 6.7* 347-前K个高频元素(优先级队列)
1.数组篇
1.1 704-二分查找
704

class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
int begin =0;
int end = nums.size()-1;
int mid;
while(begin <= end) // -1,0,3,5,9,12
{
mid = begin+(end - begin)/2;
if(nums[mid] < target)
begin = mid+1;
else if(nums[mid] > target)
end = mid-1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
};
1.2 27-移除数组
27

class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int fast = 0,slow = 0;
while(fast != nums.size())
{
if(nums[fast] == val)
{
fast++;
}
else
{
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
fast++;
slow++;
}
}
return slow;
}
};
1.3 977-有序数组的平方
977

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortedSquares(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size()-1;
int flag = right;
vector<int> v(right+1);
while(left <= right)
{
int leftq = nums[left]*nums[left] ;
int rightq = nums[right]*nums[right];
if(rightq >= leftq)
{
v[flag--] = rightq;
right--;
}
else
{
v[flag--] = leftq;
left++;
}
}
return v;
}
};
1.4* 209–长度最小的子数组(滑动窗口)
209

class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0,right = 0,sum = 0,min = INT_MAX;
while(right < nums.size())
{
sum+=nums[right]; //统计左右指针之间的数据和
while(sum >= target) //当期间数据大于等于target时进入,左指针向右移动
{
int newmin = right - left + 1;
min = newmin < min ? newmin : min; //期间数据个数
sum -= nums[left];
left++;
}
right++;
}
return min==INT_MAX ? 0 : min;
}
};
时间复杂度为 O(N)
1.5* 59-螺旋矩阵II
59
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> vv(n,vector<int>(n,0));
int num = 0; //计数
int k = 0; //活跃数字(填数坐标)
int i = 0; //k依附坐标
int j = n - 1; //k依附坐标
while(i <= j) //当为奇数时会k == i == j,循环进入却没有填入操作
{
k = i;
while(k < j)
vv[i][k++] = ++num;
k = i;
while(k < j)
vv[k++][j] = ++num;
k = j;
while(k > i)
vv[j][k--] = ++num;
k = j;
while(k > i)
vv[k--][i] = ++num;
++i;
--j;
}
if(n%2)
vv[(n-1)/2][(n-1)/2] = ++num;
return vv;
}
};
2. 链表篇
2.1 203-移除链表元素
203
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(ListNode* prev,ListNode* cur,int val)
{
if(cur == nullptr)
return;
Recursion(cur,cur->next,val);
if(cur->val == val)
{
ListNode* tmp = cur;
prev->next = cur->next;
cur = cur->next;
delete tmp;
}
}
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
while(head != nullptr && head->val == val)
head = head->next;
if(head != nullptr && head->next != nullptr)
Recursion(head,head->next,val);
return head;
}
};
2.2 707-设计链表
707

class MyLinkedList {
public:
struct ListNode
{
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int val)
:val(val)
,next(nullptr)
{}
};
MyLinkedList()
{
head = new ListNode(0);
size = 0;
}
int get(int index) {
if(size <= index) //判断是否可以进行循环
return -1;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
return cur->val;
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(size < index) //判断是否可以进行循环
return;
ListNode* newnode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode* cur = head;
while(index--)
cur = cur->next; //cur 在index前
newnode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
size++;
}
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(size <= index)
return;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
ListNode* del = cur->next;
ListNode* delnext = del->next;
cur->next = delnext;
delete del;
size--;
}
private:
ListNode* head; //头节点
int size;
};
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList* obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj->get(index);
* obj->addAtHead(val);
* obj->addAtTail(val);
* obj->addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj->deleteAtIndex(index);
*/
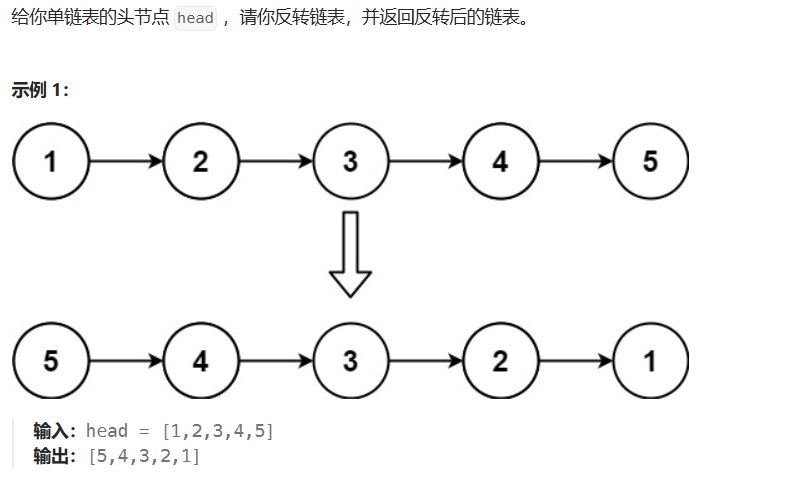
2.3 206-反转链表
206

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(ListNode*&head,ListNode* prev,ListNode* cur)
{
if(!cur->next)
{
head = cur;
head->next = prev;
return;
}
Recursion(head,cur,cur->next);
cur->next = prev;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next)
return head;
Recursion(head,nullptr,head);
return head;
}
};
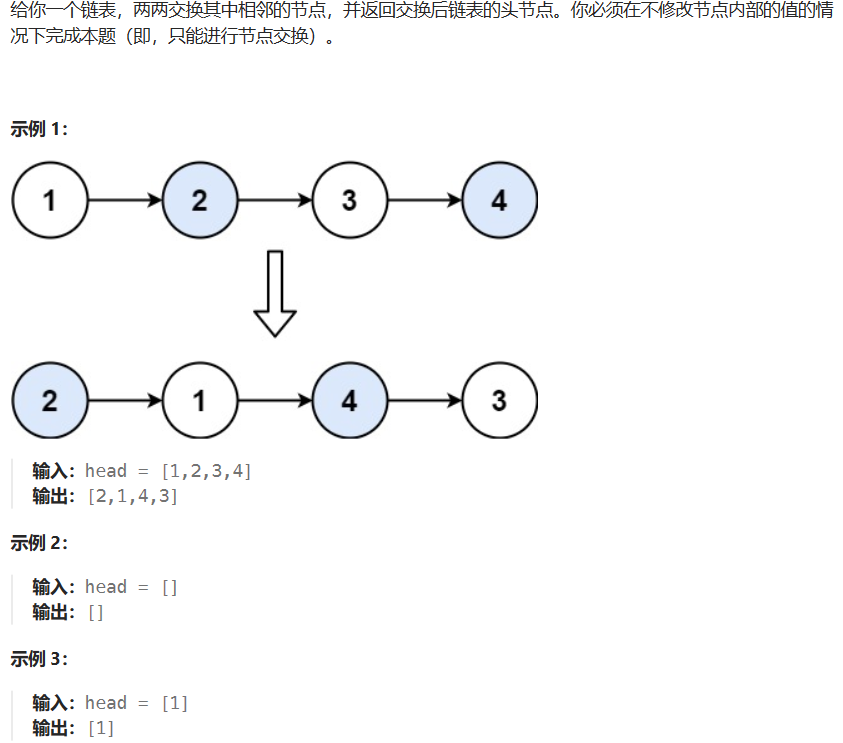
2.4* 24-两两交换链表中的节点(跳针)
24
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void Recursion(ListNode*& head,ListNode* prev,ListNode* cur,ListNode* next)
{
if(cur == nullptr || cur->next == nullptr) //当到头时,也就是cur在倒数第二个
return;
Recursion(head,cur->next,cur->next->next,next); //next一直停留,为第一组第二个
next = cur->next; //next置为未交换前的后一组的第二个,隔指
if(prev == nullptr) //执行初始最后一次递归
head = next;
else
prev->next = next;
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = cur;
return;
}
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) //如果只有<两个直接return
return head;
Recursion(head,nullptr,head,head->next); //prev当作空
return head;
}
};
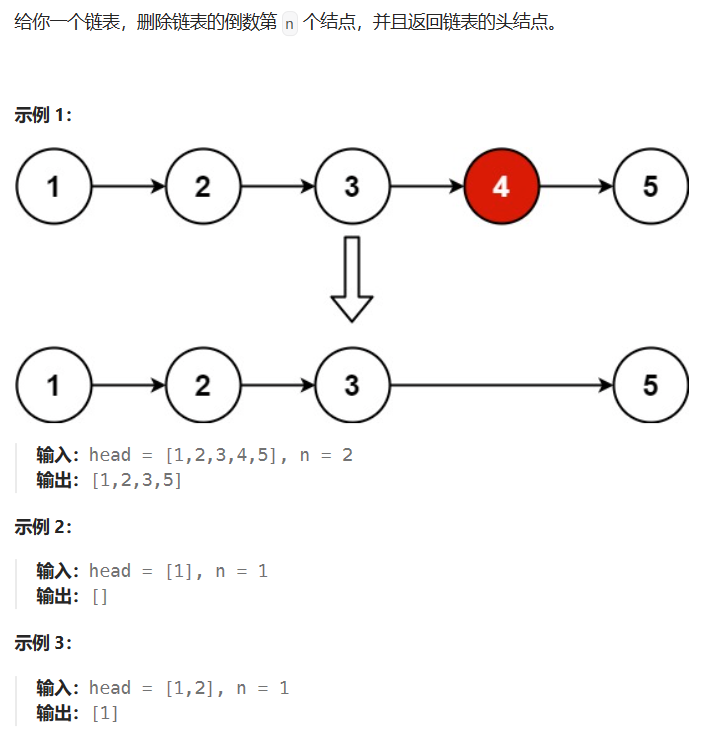
2.5* 19-删除链表的倒数第N个节点(快慢指针)
19

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//void Reucursion(ListNode* prev,ListNode* cur)
//{
//
//} 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(n--)
fast = fast->next; //fast先走,然后再走
if(!fast) //fast如果走到头了,倒过来就说明等同于头删
{
head = head->next;
delete slow;
return head;
}
while(fast->next) //fast第二次行动,直到走到尾
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//此时slow位置就是要删除节点的上一位
//开始删除
ListNode* tmp = slow->next;
slow->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
return head;
}
};
2.6* 链表相交
链表相交


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(!headA || !headB)
return nullptr;
ListNode* pa = headA,* pb = headB;
while(pa!=pb)
{
pa = pa==nullptr? headB : pa->next;
pb = pb==nullptr? headA : pb->next;
}
return pa;
}
};
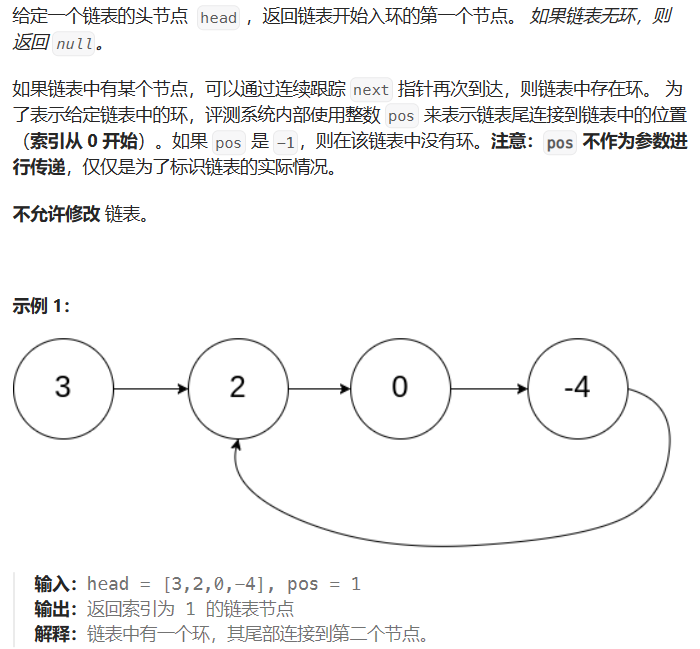
2.7 142-环形链表II
142
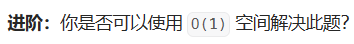
方法一:哈希表
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> circle;
while(head)
{
if(circle.count(head))
return head;
circle.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。我们恰好需要访问链表中的每一个节点。
空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 为链表中节点的数目。我们需要将链表中的每个节点都保存在哈希表当中。
方法二:快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
if(!fast->next)
return nullptr;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
ListNode* cmcross = head;
while(cmcross != slow)
{
slow = slow->next;
cmcross = cmcross->next;
}
return cmcross;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
fast走两步,slow走一步,相遇后:头节点和slow一起向前走,相遇即为循环节点
3. 哈希篇
3.1 242-有效的字母异位词
242

class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
int record[26] = {0};
for(auto& e : s)
record[e-'a']++;
for(auto& e : t)
record[e-'a']--;
for(auto& e : record)
{
if(e > 0 || e < 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为 s的长度。
空间复杂度:O(S),其中 S 为字符集大小,此处 S=26
3.2* 1002-查找共用字符
1002

class Solution {
public:
vector<string> commonChars(vector<string>& words) {
int record[26] = {0};
int size = words.size(); // 判断几个字符串
vector<string> vs;
for (auto e : words[0])
record[e - 'a']++;
for (int i = 1; i < size; ++i) // 修改为从1遍历到size-1
{
// 用临时数组存储当前单词中字符的出现次数
int temp[26] = {0};
for (auto e : words[i])
temp[e - 'a']++;
// 更新record数组,保留每个字符在所有单词中的最小出现次数
for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j)
record[j] = min(record[j], temp[j]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
{
while (record[i] > 0)
{
// 将字符插入到vs中,出现次数由record[i]控制
vs.push_back(string(1, 'a' + i));
record[i]--;
}
}
return vs;
}
};
3.3 349-两个数组的交集
349

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_set<int> start(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());
unordered_set<int> result; //去重
for(int num : nums2)
{
if(start.find(num) != start.end())
result.insert(num);
}
return vector<int>(result.begin(),result.end());
}
};
当数组数据确认量少时
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_set<int> result_set; // 存放结果,之所以用set是为了给结果集去重
int hash[1005] = {0}; // 默认数值为0
for (int num : nums1) // nums1中出现的字母在hash数组中做记录
hash[num] = 1;
for (int num : nums2) // nums2中出现话,result记录
if (hash[num] == 1)
result_set.insert(num);
return vector<int>(result_set.begin(), result_set.end());
}
};
3.4 202-快乐数
202

class Solution {
public:
int get(int num)
{
int sum = 0;
while (num)
{
sum += (num % 10) * (num % 10);
num /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_set<int> us;
int tmp = n; // 使用tmp保存当前的数值
while (tmp != 1 && us.find(tmp) == us.end()) // 当tmp变为1或出现循环时停止
{
us.insert(tmp);
tmp = get(tmp);
}
return tmp == 1; // 如果tmp最终等于1,说明是快乐数,返回true,否则返回false
}
};
3.5 1-两数之和
1


class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int,int> um; //key为值,value为坐标
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
{
auto it = um.find(target - nums[i]);
if(it != um.end())
return {i,it->second};
um.insert(make_pair(nums[i],i));
}
return {};
}
};
T:O(N) S:O(N)
3.6* 454-四数相加II
454

class Solution {
public:
int fourSumCount(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, vector<int>& nums3, vector<int>& nums4) {
unordered_map<int,int> um; //key为值,value为出现次数
for(int num1 : nums1)
for(int num2 : nums2)
um[num1+num2]++;
int count = 0;
for(int num3 : nums3)
for(int num4 : nums4)
if(um.find(0-(num3+num4)) != um.end())
count+=um[(0-(num3+num4))];
return count;
}
};
3.7 383-赎金信
383

class Solution {
public:
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine) {
int hash[26] = {0};
for(char e : magazine)
hash[e - 'a']++;
for(char e : ransomNote)
if(--hash[e-'a'] < 0)
return false;
return true;
}
};
4. 双指针篇
4.1 15-三数之和(双指针)
15

哈希其实过于复杂,实现起来不如双指针
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int size = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> vv;
for(int i = 0; i < size - 2; ++i) //i为固定的数据
{
//为避免重复答案,对固定数据进行判断
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1])
continue;
int left = i+1; //中间数据
int right = size-1; //末尾数据
while(left < right)
{
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum > 0)
right--;
else if(sum < 0)
left++;
else
{
vv.push_back({nums[i] , nums[left] , nums[right]});
//为了避免重复答案,要对下一组数据进行判断
while(left<right && nums[left] == nums[left+1])
left++;
while(left<right && nums[right] == nums[right-1])
right--;
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return vv;
}
};
4.2 18-四数之和
18

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int size = nums.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size;++i) //固定第一个
{
if(i>0&&nums[i-1] == nums[i])
continue;
for(int j = i+1;j<size;++j) //固定第二个
{
if(j>i+1&&nums[j-1] == nums[j]) //j>i+1,防止 2 2 2 2 情况
continue;
int left = j+1;
int right = size-1;
while(left<right)
{
long long sum =(long long)nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[left]+nums[right];
if(sum < target)
left++;
else if(sum > target)
right--;
else
{
ans.push_back({nums[i],nums[j],nums[left],nums[right]});
while(left<right && nums[left] == nums[left+1])
left++;
while(left<right && nums[right] == nums[right-1])
right--;
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
5. 字符串篇
5.1 344-反转字符串
344

reverse函数也可以
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
int size = s.size();
for(int left = 0,right = size-1 ; left < right ; ++left,--right)
swap(s[left],s[right]);
}
};
5.2 541-反转字符串II
541

class Solution {
public:
string reverseStr(string s, int k) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i += (2 * k))
{
if (i + k <= s.size())
reverse(s.begin() + i, s.begin() + i + k );
else
reverse(s.begin() + i, s.end());
}
return s;
}
};
5.3* 151-反转字符串中的单词
151


class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
while(s[0] == ' ')
s.erase(s.begin()); //去除开头多余空格
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());//blue is sky the
while(s[0] == ' ')
s.erase(s.begin()); //去除开头多余空格
int count = 0, size = 0, flag = 0;
for(int i =0 ; i < s.size();++i)
{
count++; //表示当前为第几个字符
size++; //表示这个单词有几个字符
if(s[i] == ' ')
{
reverse(s.begin()+flag, s.begin()+flag+size-1);
flag = count; //记录下一个单词的起始位置
size = 0;
while(s[i+1] == ' ') //删除中间多余空格
s.erase(s.begin()+i+1);
}
}
reverse(s.begin()+flag,s.end());
return s;
}
};
5.4 182-动态口令
182

class Solution {
public: //1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -> 4 5 6 7 1 2 3
//7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -> 7 6 5 4 1 2 3 -> 4 5 6 7 1 2 3
string dynamicPassword(string password, int target) {
int size = password.size();
int newstart = size - target;
reverse(password.begin(),password.end());
reverse(password.begin(),password.begin()+newstart);
reverse(password.begin()+newstart,password.end());
return password;
}
};
5.5* 459-重复的子字符串
459

class Solution {
public:
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s)
{
string tmp(s.begin(),s.end());
tmp+=s;
tmp.erase(tmp.begin());
tmp.erase(tmp.end()-1);
//删去头尾
if(tmp.find(s) == string::npos)
return false;
//在tmp内寻找s,找到了就说明是重复组成的
//abab ->(a)b abab a(b)
//abcdabcd -> (a)bcd abcdabcd abc(d)
return true;
}
};
5.6* 28-找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(KMP)
28

class Solution {
public:
//aabaabaafa aabaaf
//前缀表的作用就是再两个字符串匹配失败时,能回到最近的匹配位置,记录能回到位置下标
void getNext(int* next, const string& s)
{
//-1 0 -1 0 1 -1
//a a b a a f
int j = -1;
next[0] = j;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++)
{
//能进入就说明前面已经有重复的了
//进不去说明和前面一样继续重复
while (j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1]) // 前后缀不相同了
j = next[j]; // 向前回退
if (s[i] == s[j + 1]) // 找到相同的前后缀
j++;
next[i] = j; // 将j(前缀的长度)赋给next[i]
}
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle)
{
int size_ndl = needle.size();
int size_hstk = haystack.size();
int next[size_ndl];
getNext(next, needle);
int j = -1; // // 因为next数组里记录的起始位置为-1
for (int i = 0; i < size_hstk; i++)
{
// 注意i就从0开始
//当数据和前缀表有重合时且当下不对应
//while放在if(匹配)前面,防止j一直++匹配成功后又进入循环判断下一个不匹配而重置j
while(j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j + 1])
j = next[j]; // j 寻找之前匹配的位置 //重新加载前缀表
if (haystack[i] == needle[j + 1]) // 匹配,j和i同时向后移动
j++; // i的增加在for循环里
if (j == (size_ndl - 1) ) // //当数据和前缀表完全重合
return (i - size_ndl + 1);
}
return -1;
}
};
6. 栈和队列篇
6.1 232-用栈实现队列
232

class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(s2.empty()) //s2就相当于队列,s1存储数据,反转数据存入s2;
{
while(!s1.empty())
{
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
}
int ans = s2.top();
s2.pop();
return ans;
}
int peek() {
int tmp = this->pop();
s2.push(tmp);
return tmp;
}
bool empty() {
if(s1.empty() && s2.empty())
return true;
return false;
}
private:
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
};
6.2 225-用队列实现栈
225

class MyStack {
public:
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
if(!q1.empty())
q1.push(x);
else
q2.push(x);
}
int pop() { //将其中一个队列中size-1个元素全部移入另一个队列,留下的元素pop
int ans;
if(!q1.empty()) //q1不为空,将元素移动到q2
{
while(q1.size() != 1)
{
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
ans = q1.front();
q1.pop();
}
else
{
while(q2.size() != 1)
{
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
ans = q2.front();
q2.pop();
}
return ans;
}
int top() {
int tmp = this->pop();
this->push(tmp);
return tmp;
}
bool empty() {
if(q1.empty() && q2.empty())
return true;
return false;
}
private:
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
};
6.3 20-有效的括号
20

class Solution {
public://{([])}
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> st;
for(char e : s)
{
if(e=='[' || e=='(' || e=='{') //左符号进入栈中
st.push(e);
else
{
if(st.empty())
return false;
else if(e == ')' && st.top()=='('
|| e == '}' && st.top() == '{'
|| e == ']' && st.top() == '[')
st.pop(); //找到对应的符号后删除左符号
else
return false; //如果不符合这个规则,那么就不构成
}
}
return st.empty(); //如果最后为空,则说明全部对应上了,否则即false
}
};
6.4 1047-删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1047

class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string s) {
stack<int> st;
for(char e : s)
{
if(st.empty() || e!=st.top())
st.push(e);
else
st.pop();
}
//将栈中的正确答案转移至string类
string ans;
while(!st.empty())
{
ans+=st.top();
st.pop();
}
//由于从栈中获取数据,因此答案要反转回来
reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end());
return ans;
}
};
6.5 150-逆波兰表达式求值
150

class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> st;
for(string& e : tokens)
{
if(e=="+" || e=="*" || e=="/" || e=="-")//如果为符号,则取栈顶两个数字进行运算
{
int second = st.top();
st.pop();
int first = st.top();
st.pop();
//取栈顶两个数据
if(e=="+")
st.push(first+second);
else if(e=="-")
st.push(first-second);
else if(e=="*")
st.push(first*second);
else if(e=="/")
st.push(first/second);
}
else //如果为数字则入栈
st.push(stoi(e));
}
return st.top();
}
};
6.6* 239-滑动窗口最大值(双端队列)
239

class Solution {
public:
void push(int num)
{
while(!dq.empty() && dq.back() < num) //dq中第一个元素始终保证为最大值
dq.pop_back();
dq.push_back(num);
}
void pop(int num)
{
if(!dq.empty() && dq.front() == num)
dq.pop_front();
}
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> ans;
//创建第一组滑动窗口
for(int i = 0; i<k; ++i)
push(nums[i]);
ans.push_back(dq.front()); //放入第一组滑动窗口的最大值
//开始处理后面的窗口
int tmp = k;
while(tmp < nums.size())
{
pop(nums[tmp-k]); //尝试删除dq中最大数字(滑动窗口滑过了这个数字,需要更新,因此删除)
push(nums[tmp++]); //尝试更新
ans.push_back(dq.front());
}
return ans;
}
private:
deque<int> dq; //双端队列
};
6.7* 347-前K个高频元素(优先级队列)
347

class Solution {
public:
struct SecondCmp
{
bool operator()(const pair<int,int>& x,const pair<int,int>& y)
{
return x.second<y.second;
}
};
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> ans;
unordered_map<int,int> um; //key:元素 value:出现次数
for(auto& e : nums)
um[e]++;
//使优先级队列升序排列,c++20适用
//priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,decltype([]
//(const pair<int,int>& x,const pair<int,int>& y){
// return x.second<y.second;
//})> pq;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,SecondCmp> pq;
for(auto& e : um)
pq.push(make_pair(e.first,e.second));
while(k--)
{
ans.push_back(pq.top().first);
pq.pop();
}
return ans;
}
};
![[Realtek sdk-3.4.14b]RTL8197FH-VG 2.4G to WAN吞吐量低于60%的问题分析及解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cc1d006ddffc491691addd066a3e6ea0.png)