参考资料
- Spring系列第25篇:@Value【用法、数据来源、动态刷新】
- 【基础系列】SpringBoot配置信息之配置刷新
- 【基础系列】SpringBoot之自定义配置源的使用姿势
- 【基础系列】SpringBoot应用篇@Value注解支持配置自动刷新能力扩展
- Spring Boot 中动态更新 @Value 配置
一. 应用场景
⏹在SpringBoot工程中,我们一般会将一些配置信息放到application.properties配置文件中,
然后创建一个配置类通过@value注解读取配置文件中的配置信息后,进行各种业务处理。
⏹但是有的情况下我们需要对配置信息进行更改,但是更改之后就需要重启一次项目,
影响客户使用。
⏹我们可以将配置信息存放到数据库中,但是每使用一次配置信息就要去数据库查询显然也不合适。
🤔@Value注解所对应的数据源来自项目的Environment中,我们可以将数据库或其他文件中的数据,加载到项目的Environment中,然后@Value注解就可以动态获取到配置信息了。
二. 前期准备
⏹模拟获取数据库(其他存储介质: 配置文件,redis等)中的配置数据
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
public class DbUtil {
// 从数据库获取邮件的用户名信息
public static Map<String, Object> getMailInfoFromDb() {
// 模拟从数据库或者其他存储介质中获取到的用户名信息
String username = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 6);
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
// 此处的"mail.username" 对应 @Value("${mail.username}")
result.put("mail.username", username);
return result;
}
}
⏹配置类
- @RefreshScope是我们自定义的注解,用来动态的从项目的
Environment中更新@Value所对应的值。 application.properties中的配置信息最终会被读取到项目的Environment中,但是还有其他方式向Environment中手动放入值,${mail.username}的值来源于我们自己手动放入Environment中的值。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* 邮件配置信息
*/
@Configuration
@RefreshScope
@Data
public class MailConfig {
@Value("${mail.username}")
private String username;
}
⏹前台页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>@value注解动态刷新</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn1">点击发送请求,动态刷新@value注解</button>
</body>
<script th:src="@{/js/public/jquery-3.6.0.min.js}"></script>
<script th:inline="javascript">
$("#btn1").click(function() {
$.ajax({
url: "/test03/updateValue",
type: 'POST',
data: JSON.stringify(null),
contentType: 'application/json;charset=utf-8',
success: function (data, status, xhr) {
console.log(data);
}
});
});
</script>
</html>
三. 实现Scope接口,创建自定义作用域类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.Scope;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class BeanRefreshScope implements Scope {
public static final String SCOPE_REFRESH = "refresh";
private static final BeanRefreshScope INSTANCE = new BeanRefreshScope();
// 用此map来缓存bean
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 禁止实例化
private BeanRefreshScope() {
}
public static BeanRefreshScope getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
// 清理当前实例缓存的map
public static void clean() {
INSTANCE.beanMap.clear();
}
@Override
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
Object bean = beanMap.get(name);
if (bean == null) {
bean = objectFactory.getObject();
beanMap.put(name, bean);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object remove(String name) {
return beanMap.remove(name);
}
@Override
public void registerDestructionCallback(String name, Runnable callback) {
}
@Override
public Object resolveContextualObject(String key) {
return null;
}
@Override
public String getConversationId() {
return null;
}
}
四. 创建自定义作用域注解
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 使用自定义作用域
@Scope(BeanRefreshScope.SCOPE_REFRESH)
@Documented
public @interface RefreshScope {
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode() default ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS;
}
五. 刷新配置类的工具类
@Value注解所对应的值来源于项目的Environment中,也就是来源于ConfigurableEnvironment中。- 每当需要更新配置的时候,调用我们自定义的
refreshMailPropertySource方法,从各种存储介质中获取最新的配置信息存储到项目的Environment中。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
// import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class RefreshConfigUtil {
// 获取环境配置对象
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
private final static String MAIL_CONFIG_NAMW = "mail_config";
// @Autowired
// private GenericApplicationContext context;
/**
* 模拟改变数据库中的配置信息
*/
public void updateDbConfigInfo() {
// 更新context中的mailPropertySource配置信息
this.refreshMailPropertySource();
// 清空BeanRefreshScope中所有bean的缓存
BeanRefreshScope.getInstance();
BeanRefreshScope.clean();
}
public void refreshMailPropertySource() {
/**
* @Value中的数据源来源于Spring的「org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource」中
* 此处为获取项目中的全部@Value相关的数据
*/
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
propertySources.forEach(System.out::println);
// 模拟从数据库中获取配置信息
Map<String, Object> mailInfoFromDb = DbUtil.getMailInfoFromDb();
// 将数据库查询到的配置信息放到MapPropertySource中(MapPropertySource类是spring提供的一个类,是PropertySource的子类)
MapPropertySource mailPropertySource = new MapPropertySource(MAIL_CONFIG_NAMW, mailInfoFromDb);
// 将配置信息放入 环境配置对象中
propertySources.addLast(mailPropertySource);
}
}
六. 配置类加载
- 实现了
CommandLineRunner接口,在项目启动的时候调用一次run方法。 - 将自定义作用域 和 存储介质中的数据添加到项目中。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ConfigLoad implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Autowired
private RefreshConfigUtil refreshConfigUtil;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 将我们自定义的作用域添加到Bean工厂中
beanFactory.registerScope(BeanRefreshScope.SCOPE_REFRESH, BeanRefreshScope.getInstance());
// 将从存储介质中获取到的数据添加到项目的Environment中。
refreshConfigUtil.refreshMailPropertySource();
}
}
七. 测试
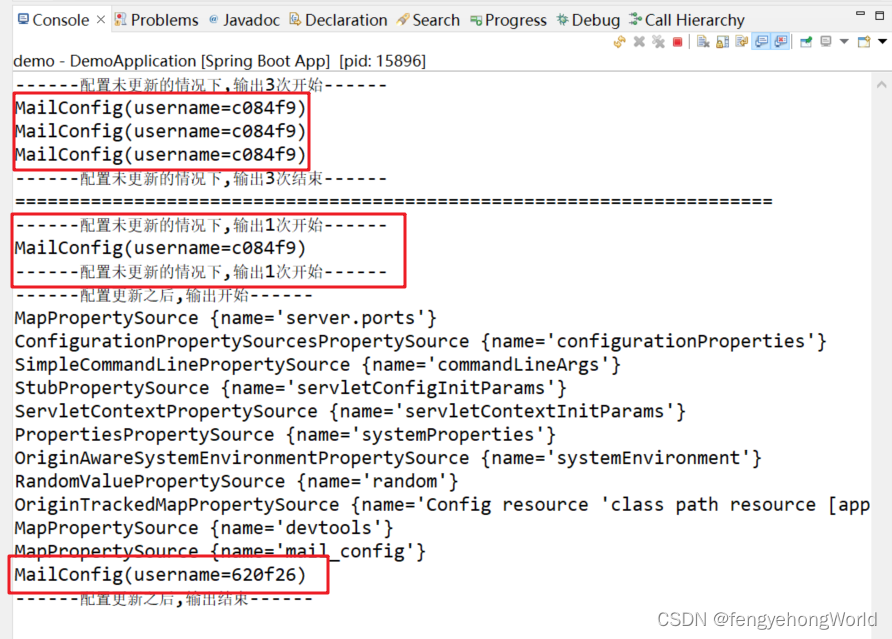
- 进入测试页面的时候,获取3次配置类
- 在测试页面点击更新按钮的时候,更新配置类之后,打印配置类,观察配置信息的变化。
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test03")
public class Test03Controller {
@Autowired
private GenericApplicationContext context;
@Autowired
private RefreshConfigUtil refreshConfigUtil;
@Autowired
private MailConfig mailConfig;
@GetMapping("/init")
public ModelAndView init() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("------配置未更新的情况下,输出3次开始------");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(mailConfig);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);
}
System.out.println("------配置未更新的情况下,输出3次结束------");
System.out.println("======================================================================");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("test03");
return modelAndView;
}
@PostMapping("/updateValue")
@ResponseBody
public void updateValue(@RequestBody Test03Form form) throws Exception {
System.out.println("------配置未更新的情况下,输出1次开始------");
MailConfig mailInfo = context.getBean(MailConfig.class);
System.out.println(mailInfo);
System.out.println("------配置未更新的情况下,输出1次开始------");
System.out.println("------配置更新之后,输出开始------");
refreshConfigUtil.updateDbConfigInfo();
System.out.println(mailInfo);
System.out.println("------配置更新之后,输出结束------");
}
}

注意事项:
本文只是进行了相关实践,相关原理请参照参考资料。
特别是参考资料1的文章。