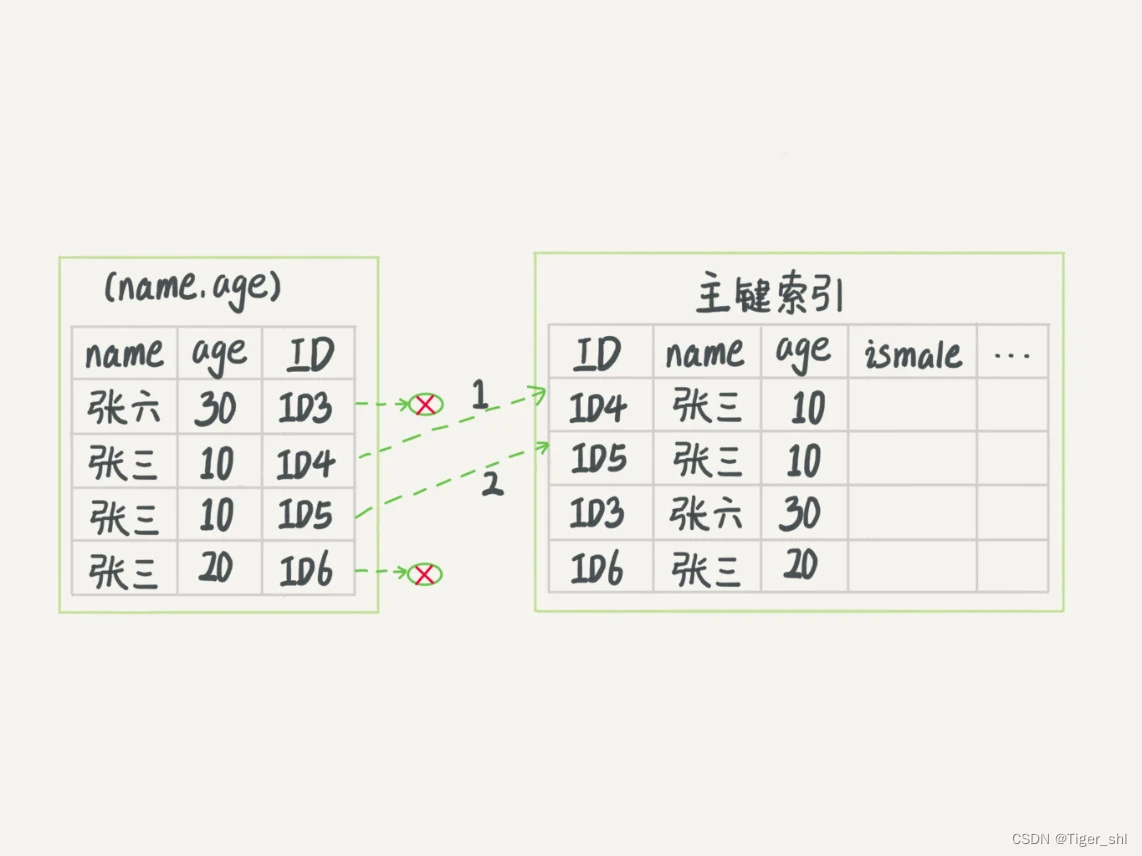
前言
上一章我们分析了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的源码逻辑,其中核心逻辑do while中调用parser.parse(candidates)方法,解析candidates中的候选配置类。然后本章我们主要分析ConfigurationClassParser的parse方法到底做了什么。
parse
configCandidates在项目启动的时候只有我们的AopConfig类,也就是说这个parse方法其实就是解析启动类。
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
当前我的启动类是AopConfig,属于AnnotatedBeanDefinition,会进入到第一个if逻辑里。parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());第一个参数传入的元数据,第二个参数传入的是beanName。
private static final Predicate<String> DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER = className ->
(className.startsWith("java.lang.annotation.") || className.startsWith("org.springframework.stereotype."));
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
processConfigurationClass方法传递了一个ConfigurationClass和一个Predicate,Predicate就是为了判断ClassName的,ConfigurationClass包含了元数据、beanName等信息。
processConfigurationClass
进入方法的第一个if用于判断是否包含@Condition注解,反正含义就是看这个候选配置类需不需要跳过,里面的其他逻辑就不关注了。下面其实就是核心逻辑了,我们继续拆解分析。
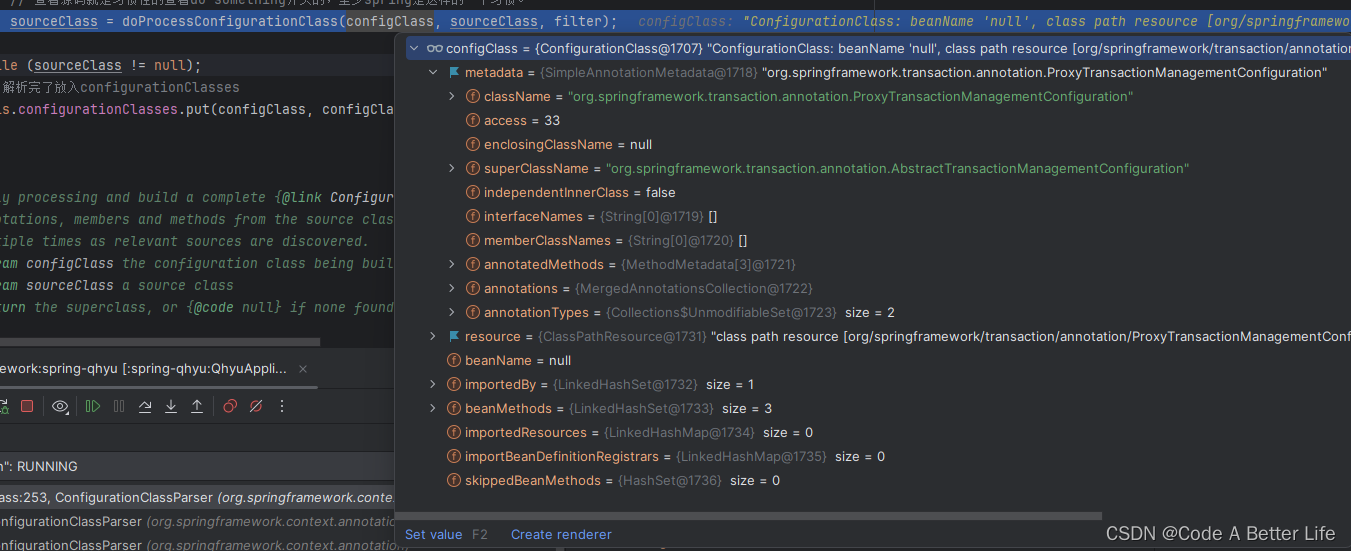
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
// 查看这个配置类是不是存在了,如果存在就走下面的if逻辑
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
}
else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
// 此处使用了个do while
do {
// 查看源码就是习惯性的查看do something开头的,至少spring是这样的一个习惯。
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
// 解析完了放入configurationClasses
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
existingClass是看配置类是不是已经解析过了,为什么启动的时候要判断是否存在,原因就是因为底下有个do while循环。这个方法后续会调用很多次。如果不存在会走底下的do while逻辑,就是本章的核心内容。这里会很绕,我尽量讲清楚。
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);还是可以单独拿出来描述一下:
方法的参数包括一个可为null的className和一个Predicate<String>类型的filter,还可能抛出IOException异常。
方法的执行逻辑如下:
1、首先,检查className是否为null或者经过filter筛选后返回true。如果是这种情况,直接返回预先设定的objectSourceClass对象。
2、如果className以"java"开头,表示该类是核心Java类型,将不使用ASM(Java字节码操作库)进行处理。此时,尝试加载该类,并使用ClassUtils.forName方法获取类的Class对象。如果加载失败,将抛出ClassNotFoundException异常并包装为NestedIOException。
3、如果以上条件都不满足,说明className表示的类不是核心Java类型,那么使用metadataReaderFactory(可能是一个元数据读取工厂)获取className对应的元数据读取器(MetadataReader),并将其传递给SourceClass的构造函数,创建一个新的SourceClass对象。
doProcessConfigurationClass
首先我的AopConfig有两个注解,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy和@ComponentScan(value = {“com.qhyu.cloud.**”}),当然我们的springboot项目一般都是约定大于配置的方式,不写这个ComponentScan注解。
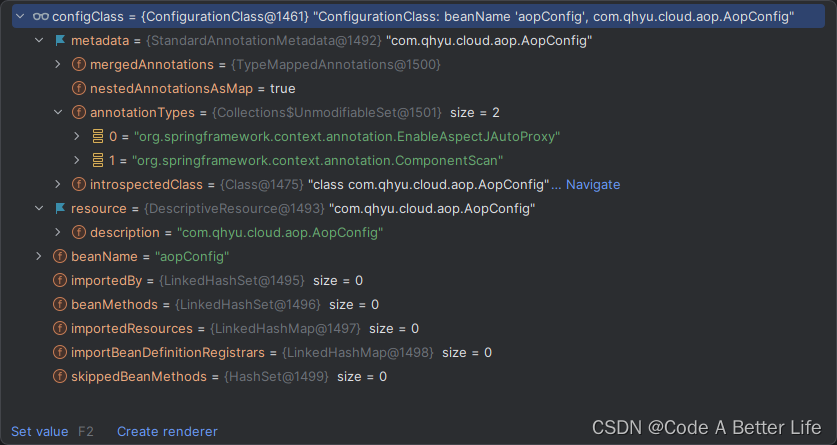
下面是整个方法的源码和我的个人注释信息,我们这边还是先将源码整体放出来,然后再拆解分析。
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// 如果这个候选配置类中有Component注解,走下面的逻辑
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 我们的AopConfig候选配置类就会走到下面这个逻辑
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
// componentScans不为空,第一个条件满足
// sourceClass.getMetadata()不为null;通过Conditional注解来控制bean是否需要注册,控制被@Configuration标注的配置类是否需要被解析 第二个条件false,取反。
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析
// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
片段一
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
当前AopConfig启动类是没有Component注解的,不会进入这个逻辑。代码中的英文注释说的是首先递归处理任何成员(嵌套)类,也就是说如果@Component注解注释的类中没有内部类(嵌套类)也不会做任何处理。
片段二
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
直接看注释,处理任何被@PropertySource注解修饰的class
片段三
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 我们的AopConfig候选配置类就会走到下面这个逻辑
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
// componentScans不为空,第一个条件满足
// sourceClass.getMetadata()不为null;通过Conditional注解来控制bean是否需要注册,控制被@Configuration标注的配置类是否需要被解析 第二个条件false,取反。
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析
// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
处理任何被@ComponentScan注解修时的类,当然这里还包括@ComponentScans注解,componentScans属性会获取到注解的信息,如下图所示:
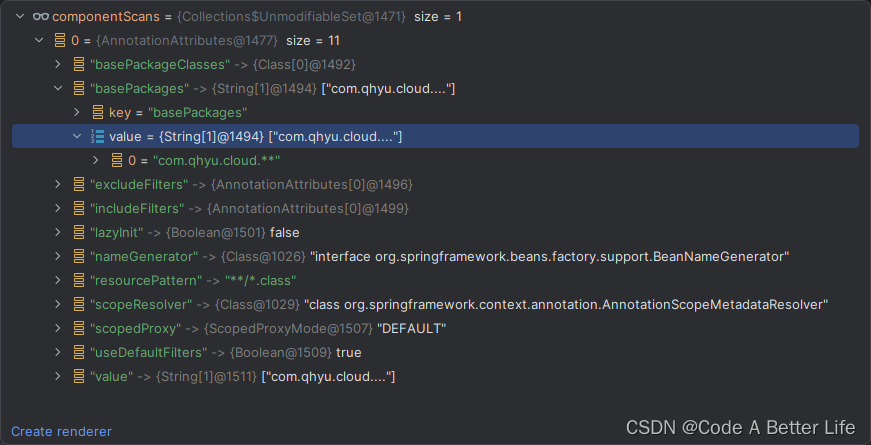
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN))
首先componentScans属性肯定不为空,所以第一个条件是ture,然后看是否应该跳过,当前AopConfig不存在Condition注解,返回false,此处取反,所以if条件返回true,进入if逻辑。
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析
// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
这个循环,获取的AnnotaionAttributes就是我们的@ComponentScan(value = {“com.qhyu.cloud.**”})注解的信息。然后会调用使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析,主要就是扫描我们定义的路径下的所有需要被Spring管理的bean,组装程BeanDefinitionHolder返回到scannedBeanDefinitions集合,同时这些bean的定义信息会被注入到bean工厂中,本章在此处不会深入的去分析里面的源码,将在下一章节进行分析。
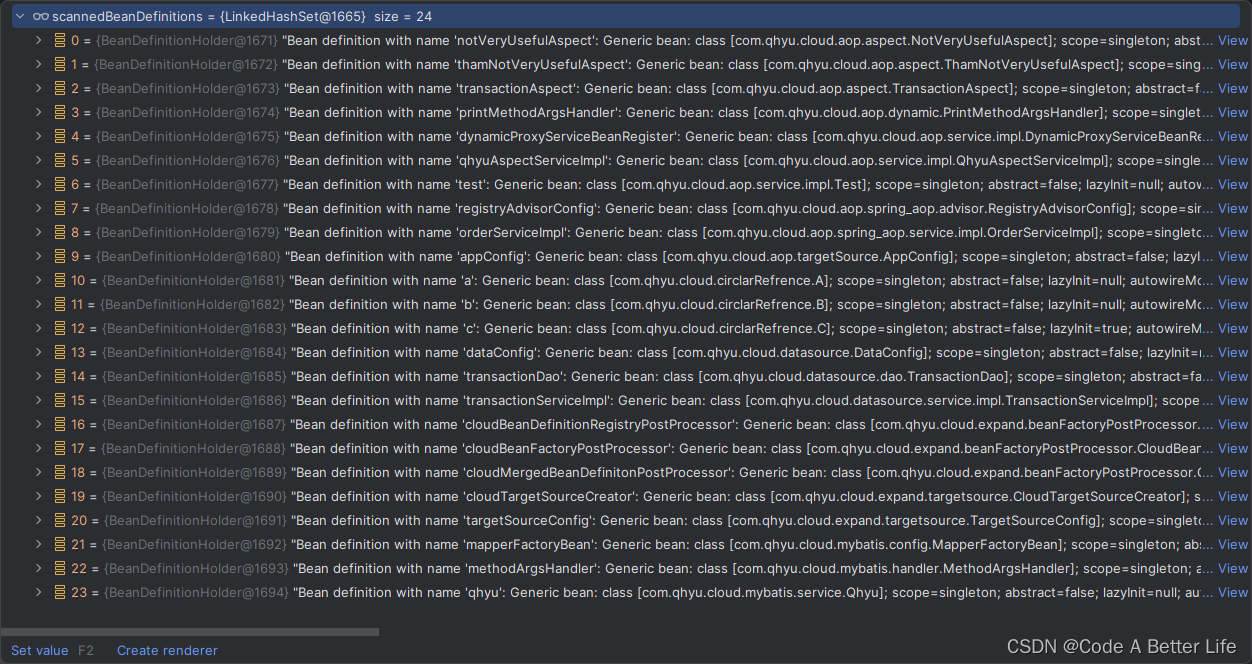
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
这段源码在之前已经分析过了,第二章节,如果发现我们scannedBeanDefinitions中还存在配置类,就继续解析,也就是把这些beanDefinition都注册到bean工厂中。
如果不是配置类或者处理完了配置类之后会继续往下走他的逻辑。
片段四
处理被@Import注解修时的类
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
比如我们的AopConfig不是有个@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解嘛,这个注解里面会有个@Import,所以AopConfig解析之后会执行configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());代码,在ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions方法中this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);这行代码会读取出来进行注册。
片段五
处理任何@ImportResource annotations
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
片段六
处理各个@Bean的方法
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
片段七
处理接口上的默认方法
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
片段八
处理superclass,超类,如果有的话。可以发现这里面有个return,其他的片段都是返回的void,此处如果返回的话,外部的do while就会继续执行。
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
整理流程梳理
方法的执行逻辑如下:
-
首先,检查配置类 configClass 是否被 @Component 注解标记。如果是,则递归处理任何成员类(嵌套类)。
-
处理任何 @PropertySource 注解。遍历配置类中的 @PropertySource 注解,如果当前环境实现了 ConfigurableEnvironment 接口,则进行属性源的处理。否则,记录日志,表明忽略该注解。
-
处理任何 @ComponentScan 注解。获取配置类中的 @ComponentScan 注解,如果存在且满足相关条件(componentScans 不为空,且配置类满足条件判断),则使用 componentScanParser 来解析注解,执行组件扫描操作,并注册相应的 BeanDefinition 信息。如果扫描到的定义中包含其他配置类,则递归解析这些配置类。
-
处理任何 @Import 注解。根据配置类中的 @Import 注解,获取需要导入的类,并进行处理。这些导入的类可以是其他配置类,也可以是其他普通的类。处理过程中,可能会继续递归解析导入的类。
-
处理任何 @ImportResource 注解。根据配置类中的 @ImportResource 注解,获取资源的位置和读取器类型,并进行处理。通常,这些资源是 XML 配置文件。解析过程中,可能会使用 BeanDefinitionReader 来读取并注册相关的 BeanDefinition。
-
处理配置类中的每个 @Bean 方法。获取配置类中所有的 @Bean 方法的元数据,并将其添加到 configClass 对象中。
-
处理接口的默认方法。如果配置类实现了接口,并且接口中定义了默认方法,则对这些默认方法进行处理。
-
处理父类(如果存在)。如果配置类有父类,并且父类不是 Java 核心类,也不在已知的父类列表中,则将父类添加到已知的父类列表中,并返回父类的注解元数据,以便进行递归处理。
-
如果没有父类,则处理完成,返回 null。
总结
本章主要分析了ConfigurationClassParser的parse方法的源码,其中设计到的ComponentScanAnnotationParser的parse方法我们没有深入分析,这里面涉及到的是将我们启动类目录或者@ComponentScan注解的basePackages目录下的我们需要交给容器管理的bean的定义信息注册将在下一章进行分析。