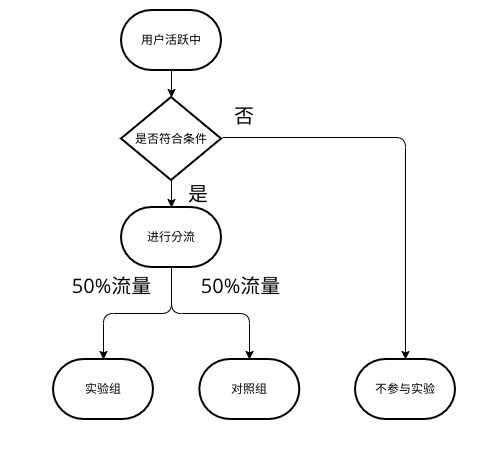
一、前言
除了众所周知的 JEP 之外,Java 21 还有更多内容。首先请确认 java 版本:
$ java -version
openjdk version "21" 2023-09-19
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 21+35-2513)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 21+35-2513, mixed mode, sharing)我们一起来看看 String 和它的朋友们 Collections、Date、Time、HttpClient、并发、Math 和 BigInteger 的新增一些 API。
二、String(Java21新增)
String 新增了 indexOf() 方法,允许在起始索引和结束索引之间查找单个字符或子字符串。
public int indexOf(int ch, int beginIndex, int endIndex);
public int indexOf(String str, int beginIndex, int endIndex);示例:
String text = "牛牛帮";
int index = text.indexOf("0", 5, 15);三、Character(Java21新增)
Character 类新增了几个方法来支持 Emoji 表情符号,新增了五个方法:isEmoji()、isEmojiComponent()、isEmojiModifier()、isEmojiModifierBase() 和 isEmojiPresentation()。
public static boolean isEmoji(int codePoint);
public static boolean isEmojiPresentation(int codePoint);
public static boolean isEmojiModifier(int codePoint);
public static boolean isEmojiModifierBase(int codePoint);
public static boolean isEmojiComponent(int codePoint);
public static boolean isExtendedPictographic(int codePoint);所有这些方法都接受一个 int 类型的码点作为参数,判断传入的码点是否具有对应的表情符号。
四、StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder(Java21新增)
StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 新增了 repeat() 方法重复单个字符或字符串多次。
StringBuilder:
@Override
public StringBuilder repeat(int codePoint, int count);
@Override
public StringBuilder repeat(CharSequence cs, int count);StringBuffer:
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer repeat(int codePoint, int count);
@Override
public synchronized StringBuffer repeat(CharSequence cs, int count);五、Charset(Java18)
Charset 新增了一个带 fallback 的 forName()方法。
public static Charset forName(String charsetName, Charset fallback);六、正则分组优化(Java20)
提取地址中的省市区县,代码如下:
笔者有幸用过正则分组,需求是提取地址中的省市区县,代码如下:
private static final Pattern PATTERN = Pattern.compile("(?<province>[^省]+自治区|.*?省|.*?行政区|.*?市)(?<city>[^市]+自治州|.*?地区|.*?行政单位|.+盟|市辖区|.*?市|.*?县)(?<county>[^县]+县|.+区|.+市|.+旗|.+海域|.+岛)?(?<town>[^区]+区|.+镇)?(?<village>.*)");
public static Map<String, String> getAddressResolution(String address) {
Matcher matcher = PATTERN.matcher(address);
String province, city, county, town, village;
Map<String, String> row = new HashMap<>();
while (matcher.find()) {
province = matcher.group("province");
row.put("province", province == null ? "" : province.trim());
city = matcher.group("city");
row.put("city", city == null ? "" : city.trim());
county = matcher.group("county");
row.put("county", county == null ? "" : county.trim());
town = matcher.group("town");
row.put("town", town == null ? "" : town.trim());
village = matcher.group("village");
row.put("village", village == null ? "" : village.trim());
}
return row;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String address = "湖南省长沙市岳麓区永青路668号";
System.out.println(getAddressResolution(address));
// {province=湖南省, city=长沙市, county=岳麓区, town=, village=永青路668号}
}Matcher、MatchResult、Pattern 现在新增了 namedGroups() 相关方法, getAddressResolution() 方法简化成这样了:
public static Map<String, String> getAddressResolution(String address) {
Matcher matcher = PATTERN.matcher(address);
Map<String, String> row = new HashMap<>();
if (matcher.matches()) {
Map<String, Integer> groupMap = matcher.namedGroups();
groupMap.forEach((key, group) -> row.put(key, matcher.group(group)));
}
return row;
}七、集合
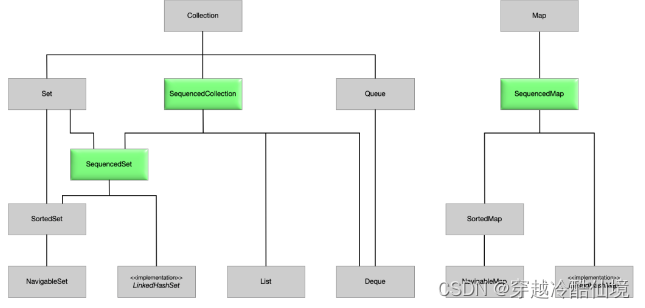
Collections 框架中添加了 SequencedCollection、SequencedSet 和 SequencedMap 三个接口(Java21 新增)。
interface SequencedCollection<E> extends Collection<E> {
// new method
SequencedCollection<E> reversed();
// methods promoted from Deque
void addFirst(E);
void addLast(E);
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
}
interface SequencedSet<E> extends Set<E>, SequencedCollection<E> {
SequencedSet<E> reversed(); // covariant override
}
interface SequencedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> {
// new methods
SequencedMap<K,V> reversed();
SequencedSet<K> sequencedKeySet();
SequencedCollection<V> sequencedValues();
SequencedSet<Entry<K,V>> sequencedEntrySet();
V putFirst(K, V);
V putLast(K, V);
// methods promoted from NavigableMap
Entry<K, V> firstEntry();
Entry<K, V> lastEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry();
}添加这 3 个新接口后,Java 集合类图发生了变化,图示:
除了这些,现在还可以使用多个工厂方法创建具有给定初始容量的不同类型的 Map(Java19新增)。
HashMap.newHashMap(100);
HashSet.newHashSet(100);
LinkedHashMap.newLinkedHashMap(100);
LinkedHashSet.newLinkedHashSet(100);
WeakHashMap.newWeakHashMap(100); Map 创建看起来很简单,但实际上却有一些技巧。例如,HashMap 内部是基于数组构建的,当该数组装满时,它会被复制到一个更大的数组中。所以阿里《JAVA开发手册》也建议设置 HashMap 的初始容量。问题在于,实际上并不仅仅是复制,第一个数组的所有键值对都需要重新计算哈希值,以便放置在新数组的正确位置上。由于哈希值的计算取决于数组的大小,每个数组的存储位置很可能不同。因此,我们不能简单地将第一个数组的内容复制到第二个数组中。为了避免冲突,当数组达到 75% 的容量时,就被认为已经满了。因此,要创建一个可以存储 100 个键值对的 Map,实际上需要一个大小为 134 的数组。考虑到数组的大小必须是 2 的次方,因此实际上会创建一个大小为 256 的数组。这种计算很容易出错,所以现在有了一个工厂方法。现在我们只需要调用 newHashMap(size),传递所需的容量就好了。
八、日期和时间 API(Java19新增)
Date and Time API 的一个很好的增加功能是 DateTimeFormatter 的本地化支持ofLocalizedPattern() 工厂方法,传递一个字符串格式,它会生成一个本地化的模式。
DateTimeFormatterBuilder 也已更新,添加了一个 appendLocalized() 方法,用于添加一个本地化模式(类型为字符串)。
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedPattern("yM");
System.out.println(now.format(formatter)); // 2023年9月九、IO流
PrintStream 在 Java18 中新增了 charset()方法用于获取使用的字符集。
public Charset charset();HttpClient、ExecutorService 和 ForkJoinPool 类在 17 和 21 之间实现了 AutoCloseable。现在可以使用 try-with-resources语句来创建实例。
十、Math 和 BigInteger
Math 类和 BigInteger 类也得到了一些关注。首先,Math类添加了一系列方法。
// 执行两个数字的向上取整除法运算,并返回大于或等于除法结果的最小整数。
public static int ceilDiv(int x, int y);
public static long ceilDiv(long x, int y);
public static long ceilDiv(long x, long y);
// 执行两个数字的向上取整除法运算,但是在被除数不能被除数整除时,
// 会抛出ArithmeticException异常。
public static int ceilDivExact(int x, int y);
public static long ceilDivExact(long x, long y);
// 这个方法返回的是两个数字进行向上取整除法运算后的余数。
public static int ceilMod(int x, int y);
public static int ceilMod(long x, int y);
public static long ceilMod(long x, long y);
// 这个方法用于对两个数字进行整除运算,并确保结果是一个整数。
// 如果除数无法整除被除数,将会抛出ArithmeticException异常。
public static int divideExact(int x, int y);
public static long divideExact(long x, long y);
// 执行两个数字的向下取整除法运算,但是在被除数不能被除数整除时,
// 会抛出ArithmeticException异常。
public static int floorDivExact(int x, int y);
public static long floorDivExact(long x, long y);添加了 clamp() 方法可以处理 int、long、float 和 double 原始类型,将提供的值限制在给定的最小值和最大值之间。
public static int clamp(long value, int min, int max);
public static long clamp(long value, long min, long max);
public static double clamp(double value, double min, double max);
public static float clamp(float value, float min, float max); 还有一个方法:unsignedMultiplyHigh(),用于将两个长整型数作为无符号数相乘,并将64位高位作为长整型返回。
public static long unsignedMultiplyHigh(long x, long y);BigInteger 类增加了一个功能:在并行中执行乘法运算,使用了 Fork/Join 框架。
public BigInteger parallelMultiply(BigInteger val);十一、Thread
关于 VirtualThread 的内容这里不做过多介绍,想必各位会在各种途径看到各式各样的文章。在这里,我只想介绍两个方面。
首先,Thread 现在添加了 join()方法和 sleep()方法,两者都接受 Duration 作为参数,Duration 语义化更加易用。另外就是 isVirtual()方法,用于判断线程是否为虚拟线程。
public static void sleep(Duration duration) throws InterruptedException;
public final boolean join(Duration duration) throws InterruptedException;
public final boolean isVirtual();另外需要重点介绍的一个是在 Future 接口中添加的新方法。实际上有三个方法:
resultNow()和exceptionNow() 这两个方法不会抛出已检查异常,因此代码中不再需要 try catch,使用起来更加方便。但请注意,如果调用这些方法并且使用的 Future 对象尚未完成,那么将会得到一个 IllegalStateException异常。需要在确保 Future 对象产生了结果或异常时调用这些方法。
第三个方法是 state(),可以调用它来检查 Future 对象的当前状态。返回值是一个新的枚举:Future.State。
enum State {
/**
* 表示任务尚未完成
*/
RUNNING,
/**
* 表示任务成功完成
*/
SUCCESS,
/**
* 表示任务完成但出现异常
*/
FAILED,
/**
* 表示任务被取消。
*/
CANCELLED
}因此,通过这个API,现在可以更精确地监控任务的进展情况。