比较不同计数器的运算方式,其中有一个数是延迟打一拍的效果,目的是使得两个计数器的结果相同。
- 1,第一种
- 2,第二种
- 3,第三种
第三种方案,完成实现。
1,第一种
(1)RTL
module c(
input clk,
input rst_n,
// input a,
// input b,
output cnt1,
output cnt2
);
reg [4:0] cnt1, cnt2;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt1 <= 0;
cnt2 <= 0;
end
else if(cnt1 <= 16) begin
cnt1 <= cnt1 + 1;
cnt2 <= cnt1;
end
else begin
cnt1 <= 0;
cnt2 <= 0;
end
end
endmodule
(2)TB
module tb_c;
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
wire [4:0] cnt1;
wire [4:0] cnt2;
always #10 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
clk = 1; rst_n =1;
#20; rst_n = 0;
#40; rst_n = 1;
end
c uu(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.cnt1(cnt1),
.cnt2(cnt2)
);
endmodule
(3)仿真
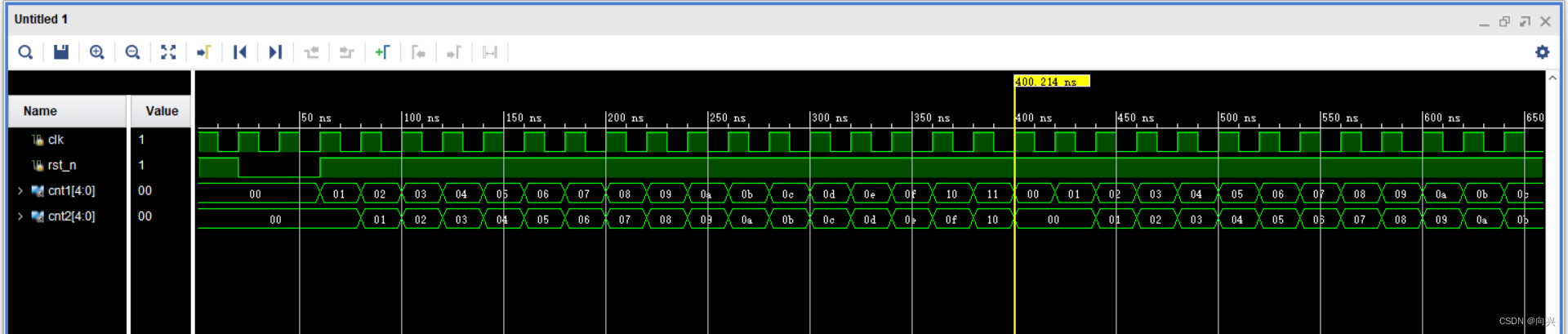
2,第二种
(1)RTL
module c(
input clk,
input rst_n,
// input a,
// input b,
output cnt1,
output cnt2
);
reg [4:0] cnt1, cnt2;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt1 <= 0;
cnt2 <= 0;
end
else if(cnt2 <= 16) begin
cnt1 <= cnt1 + 1;
cnt2 <= cnt1;
end
else begin
cnt1 <= 0;
cnt2 <= 0;
end
end
endmodule
(2)TB
module tb_c;
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
wire [4:0] cnt1;
wire [4:0] cnt2;
always #10 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
clk = 1; rst_n =1;
#20; rst_n = 0;
#40; rst_n = 1;
end
c uu(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.cnt1(cnt1),
.cnt2(cnt2)
);
endmodule
(3)仿真
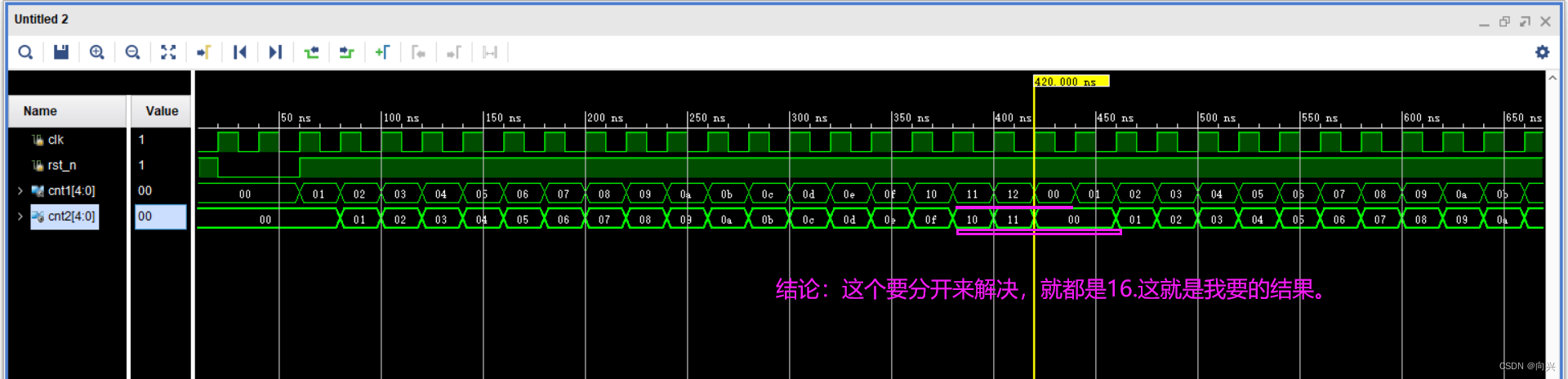
3,第三种
(1)RTL
module c(
input clk,
input rst_n,
// input a,
// input b,
output cnt1,
output cnt2
);
reg [4:0] cnt1, cnt2;
// 1
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt1 <= 0;
end
else if(cnt1 < 16) begin
cnt1 <= cnt1 + 1; // 1
end
else begin
cnt1 <= 0;
end
end
// 2
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
cnt2 <= 0;
end
else if(cnt2 < 16) begin
cnt2 <= cnt1; // 0
end
else begin
cnt2 <= 0;
end
end
endmodule
(2)TB
module tb_c;
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
wire [4:0] cnt1;
wire [4:0] cnt2;
always #10 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
clk = 1; rst_n =1;
#20; rst_n = 0;
#40; rst_n = 1;
end
c uu(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.cnt1(cnt1),
.cnt2(cnt2)
);
endmodule
(3)仿真
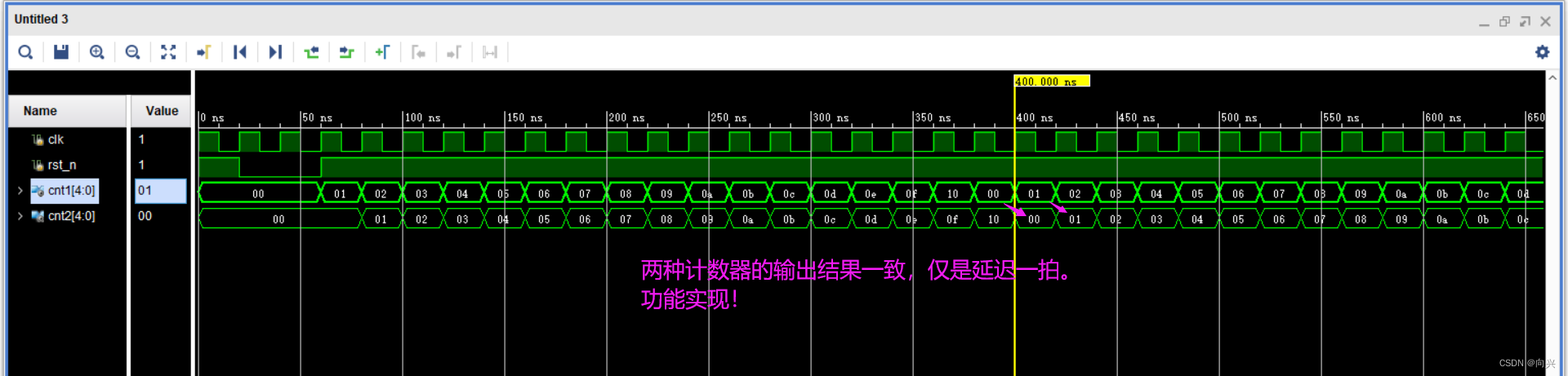







![[git] rebase 合并多个commit](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/198305990cf2445883dd6d7897494d88.png)

