目录
一、ncurse
1.1 为什么需要用ncurse:
1.2 ncurse的输入输出:
1.2.1 如何使用ncurse:
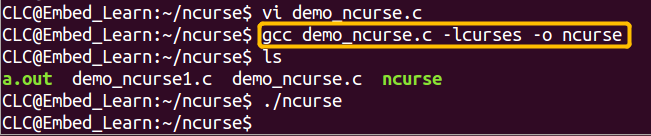
1.2.2 编译ncurse的程序:
1.2.3 测试输入一个按键ncurse的响应速度:
1.3 ncurse上下左右键获取:
1.3.1 如何查看宏定义的.h文件:
1.3.2 ncurse上下左右键获取:
二、地图规划
2.1 地图规划算法显示第一行:
2.2 实现贪吃蛇完整地图:
2.3 优化贪吃蛇地图:
三、显示贪吃蛇身子
3.1 显示贪吃蛇身子的一个节点:
3.2 显示贪吃蛇完整身子:
3.3 显示贪吃蛇完整身子改进:
四、贪吃蛇移动
4.1 按下▶贪吃蛇向右移动:
4.2 贪吃蛇撞墙重新开始:
4.3 贪吃蛇脱缰自由向右行走
五、Linux线程引入
5.1 贪吃蛇方向移动和刷新界面一起实现面临的问题:
5.2 线程的基本用法:
5.3 线程demo案例:
5.4 使用线程解决贪吃蛇方向移动和刷新界面一起实现面临的问题:
六、贪吃蛇跑起来
6.1 实现贪吃蛇四方向的风骚走位:
6.2 用绝对值方式来解决不合理的走位:
6.3 贪吃蛇吃饭了(食物的位置是随机的):
七、项目代码
-
项目运行环境:Linux,基于Ncurse图形库的C语言小游戏
-
项目的目的和意义:起到承上启下的作用,对于前面学的C语言的基础和数据结构链表做一个比较好的巩固,对于后面的Linux系统编程的开发做铺垫
-
项目基础要求:C语言基础、Linux基本操作
/*项目步骤*/ (1)选择ncurses库的原因 在进行贪吃蛇游戏时,贪吃蛇的行进方向需要你按下上下左右键进行操控,如果使用C语言自带的函数,例如:scanf或者getchar之类的,需要你按下回车键,程序才能进行响应,而这显然是十分不方便的,但是ncurses库就很好的解决了这个问题。ncurses库自带的函数getch就能实现迅速便捷的贪吃蛇方向响应。 (2)ncurses库的基本入门 对于该项目而言,ncurses库我们不需要进行过于深入的学习,只需要知道一些基本的函数使用即可。下列程序中的函数,就是一个基于ncurses库的基本代码框架。 #include <curses.h> int main() { initscr();//ncurse界面的初始化函数 printw("this is a curses window\n");//在ncurse模式下的printf getch();//等待用户的输入,如果没有这句话,程序就退出了,看不到运行的结果,也就是无法看到上面那句话 endwin();//程序退出,恢复shell终端的显示,如果没有这句话,shell终端字乱码,坏掉 return 0; } (3)贪吃蛇地图的整体规划 整个贪吃蛇地图的大小将它设置成一个20*20的近似正方形,使用"|"来表示左右边框,使用"--"来表示上下边框。 (4)实现贪吃蛇第一个节点的显示 (5)显示贪吃蛇的完整身子 注意,在这里,我们设置两个全局变量,struct Snake *head和struct Snake *tail,一个指向贪吃蛇的头,一个指向贪吃蛇的尾。在将第一个节点打印完后,将尾指向头,即:head = tail。每一次节点的添加,我们调用一个单独的函数去执行,并其使用尾插法实现。 (6)实现贪吃蛇的右移 贪吃蛇的移动,整体来说就是链表节点的删除与添加。我们首先实现贪吃蛇的右移,每当按键按下时,贪吃蛇右移一格,即左侧的头结点删除head = head->next,右侧再次添加一个新的节点。新节点的坐标应该是行不变,列加一。注意:不要忘记清楚垃圾节点。 (7)实现贪吃蛇的撞墙死亡 将贪吃蛇的尾节点坐标进行判断,判断其是否达到边界坐标。满足条件时,将贪吃蛇重新初始化。注意:不要忘记清楚垃圾节点。 (8)实现贪吃蛇的自由行走 在这里,我们发现了一个问题,地图需要实时刷新进行贪吃蛇位置的变更,这是一个while(1)的死循环,而获取键值也是一个实时读取的操作,因此也是一个while(1)死循环,代码执行逻辑上出现了问题,所以我们引入了线程的概念。 (9)了解什么是线程 (10)用线程解决上述问题,实现贪吃蛇的分骚走位 开辟两个线程,一个用来执行地图刷新操作,一个用来获取键值。 pthread_create(&t1,NULL,refreshScreen,NULL); pthread_create(&t2,NULL,changeDir,NULL); (11)解决贪吃蛇的不合理走位 在这里,我们使用绝对值法来解决问题,abs函数的作用便是取绝对值,我们将上下左右键,两两对应,宏定义为1,-1,2,-2之类的数就能成功解决问题。 (12)实现贪吃蛇食物的打印 (13)实现食物的随机出现 取随机数,C语言有一个自带的函数可以解决这个问题,rand()函数可以实现随机取数,我们只要再对它进行取余操作,便可以防止食物出现在地图以外的位置。 (14)实现贪吃蛇咬到自己结束游戏,重新开始的操作 当贪吃蛇的尾节点与自身除尾巴节点以外的其他节点进行比较后,若行列数相同,则初始化整个贪吃蛇,注意:不要忘记垃圾节点的清除(我们可以在每次贪吃蛇初始化之前进行这个操作)。一、ncurse
1.1 为什么需要用ncurse:
-
因为的按键响应牛逼哄哄
-
1.2 ncurse的输入输出:
-
ncurse用的最多的地方是在Linux内核编译之前的内核配置
-
1.2.1 如何使用ncurse:

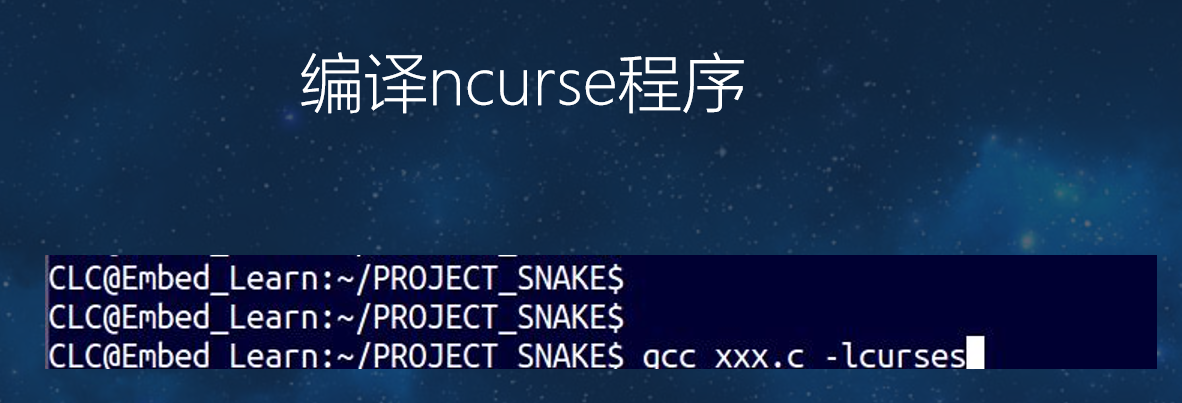
1.2.2 编译ncurse的程序:
1.2.3 测试输入一个按键ncurse的响应速度:
1 #include <curses.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 char c;
6
7 initscr();
8 c = getch();
9 printw("you Input :%c\n",c);
10 getch();
11 endwin();
12 return 0;
13 } -
使用ncurse的好处是:按下一个按键不需要按下回车,直接就可以输出c的值,和我们C语言的其他输入函数好用
1.3 ncurse上下左右键获取:
1.3.1 如何查看宏定义的.h文件:
vi /usr/include/curses.h //查看宏定义.h文件的指令
:q //退出查看

1.3.2 ncurse上下左右键获取:

1 #include <curses.h>
2
3 int main()
4 {
5 int key;
6
7 initscr();
8 keypad(stdscr,1); //这个函数允许使用功能键,例如:F1、F2、方向键等功能键。几乎所有的交互式程序都需要使用功能 键,因为绝大多数用户界面主要用方向键进行操作。使用keypad(stdscr,TURE)就为“标准屏幕”(stdscr)激活了功能键。
9
10 while(1){
11 key = getch();
12 switch(key){
13 case KEY_DOWN:
14 printw("DOWN\n");
15 break;
16 case KEY_UP:
17 printw("up\n");
18 break;
19 case KEY_LEFT:
20 printw("LEFT\n");
21 break;
22 case KEY_RIGHT:
23 printw("RIGHT\n");
24 break;
25 }
26
27
28 }
29 endwin();
30 return 0;
31 }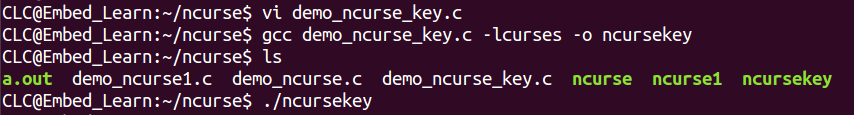

-
我们按下上下左右▲▼◀▶之后,可以获取到上下左右的打印信息
二、地图规划
2.1 地图规划算法显示第一行:
#include <curses.h>
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse(); //初始化Ncurse
gamPic(); //地图规划显示第一行
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}![]()
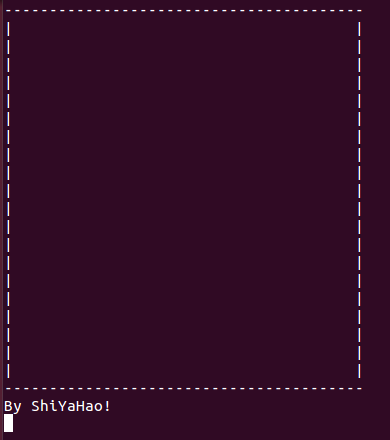
2.2 实现贪吃蛇完整地图:
#include <curses.h>
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse(); //初始化Ncurse
gamPic(); //实现贪吃蛇地图
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
2.3 优化贪吃蛇地图:
#include <curses.h>
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){ //第0行打“--”
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) { //第0行-19行的第0列和第20列打“|”
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){ //第19行打“--”
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n"); //作者
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse();
gamPic();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
//实现的贪吃蛇地图和上面一样,只不过是优化了一下代码三、显示贪吃蛇身子
3.1 显示贪吃蛇身子的一个节点:
#include <curses.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake node1 = {2,2,NULL};
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(node1.hang == hang && node1.lie == lie){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse();
gamPic();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
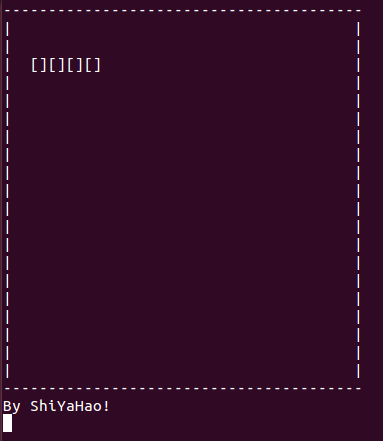
3.2 显示贪吃蛇完整身子:
#include <curses.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake node1 = {2,2,NULL};
struct Snake node2 = {2,3,NULL};
struct Snake node3 = {2,4,NULL};
struct Snake node4 = {2,5,NULL};
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = &node1;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse();
node1.next = &node2;
node2.next = &node3;
node3.next = &node4;
gamPic();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
3.3 显示贪吃蛇完整身子改进:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL; //指向链表头
struct Snake *tail = NULL; //指向链表尾
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic() //地图规划
{
int hang;
int lie;
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake)); //创建新节点
if(new == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
new->hang = tail->hang; //新节点的行等于链表尾的行
new->lie = tail->lie+1; //新节点的行等于链表尾的列+1
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new; //从链表尾部插入新节点
tail = new; //新节点当作尾部
}
void initSnake()
{
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake)); //创建链表头
if(head == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
head->hang = 2;
head->lie = 2;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head; //第一个节点链表头和链表尾是一样的
addNode(); //调用一次代表增加一个节点
addNode();
addNode();
}
int main()
{
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
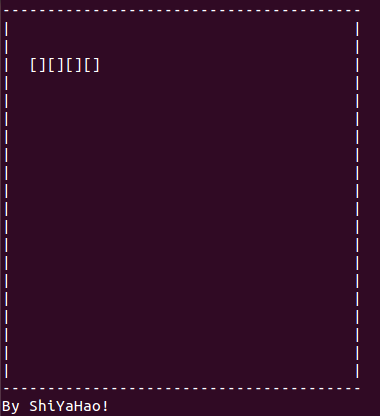
}
四、贪吃蛇移动
4.1 按下▶贪吃蛇向右移动:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(head == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
head->hang = 2;
head->lie = 2;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode(); //增加一个节点
deletNode(); //删除头节点
}
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
while(1){
con = getch(); //con获取键值
if(con == KEY_RIGHT){ //如果是右键
moveSnake(); //向右移动
gamPic(); //必须刷新一下界面,否则看不到🐍移动
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}4.2 贪吃蛇撞墙重新开始:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(new == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
while(head != NULL){ 判断蛇是否为空,清理内存
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(head == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
//判断蛇的尾巴碰到上下左右的四个边框后就重新开始
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
while(1){
con = getch();
if(con == KEY_RIGHT){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}4.3 贪吃蛇脱缰自由向右行走
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(new == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(head == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
while(1){ //之前受方向键控制,现在自由行走
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh(); //刷新界面
usleep(100000); //延时100ms
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}五、Linux线程引入
5.1 贪吃蛇方向移动和刷新界面一起实现面临的问题:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!\n");
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(new == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
if(head == NULL){
printw("malloc error\n");
}
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
int main()
{
int key;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}-
在上面的程序中main函数中有两个while(1)循环,这样就会出现问题,程序运行的现象是:获取按键值的这个while循环根本不会执行,那该如何解决?于是引入“Linux线程”!
-
在贪吃蛇运动过程中,我们需要改变蛇的移动方向,这是就需要不停扫描键盘输入的值来判断方向,同时还需要不停的刷新界面,为了多个while循环并存这里需要引入linux线程。
5.2 线程的基本用法:
#include <pthread.h> // 头文件
pthread_t:当前Linux中可理解为:typedef unsigned long int pthread_t;
如:pthread_t t1; //多线程定义
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,refreshInterface,NULL);
参数1:传出参数,保存系统为我们分配好的线程ID
参数2:通常传NULL,表示使用线程默认属性。若想使用具体属性也可以修改该参数。
参数3:函数指针,指向线程主函数(线程体),该函数运行结束,则线程结束。
参数4:线程主函数执行期间所使用的参数,如要传多个参数, 可以用结构封装。
使用多线程的函数必须返回指针型,如void *refreshInterface()
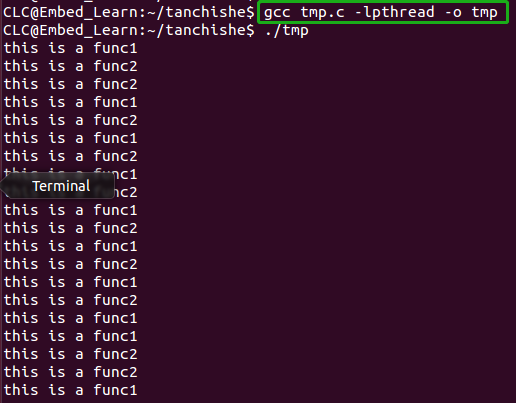
注:gcc xxx.c -lcurses -lpthead //编译需要连接pthead库5.3 线程demo案例:
/*
在这个程序当中只有func1一个函数会被执行,func2函数根本不会执行
想要解决这个问题就需要引入Linux的线程
*/
#include <stdio.h>
void pfunc1()
{
while(1){
printf("this is a pfunc1\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
void pfunc2()
{
while(1){
printf("this is a pfunc2\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pfunc1();
pfunc2();
return 0;
}/*
引入Linux线程修改代码,func1和func2两个函数都可以执行
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h> //线程头文件
void* func1()
{
while(1){
printf("this is a func1\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
void* func2()
{
while(1){
printf("this is a func2\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t th1; //定义一个th1线程
pthread_t th2; //定义一个th2线程
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, func1, NULL);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, func2, NULL);
while(1);
return 0;
}
5.4 使用线程解决贪吃蛇方向移动和刷新界面一起实现面临的问题:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
int key;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
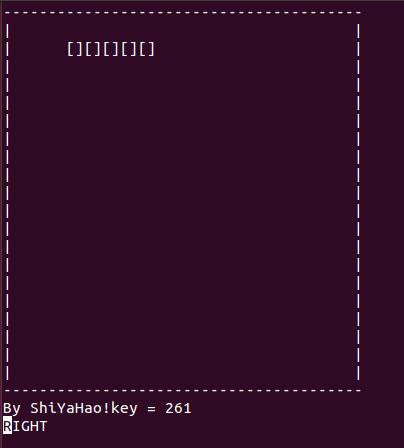
printw("By ShiYaHao!key = %d\n",key);
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
void* refreshJieMian()
{
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
initNcurse();
initSnake();
//注意:线程创建要放在初始化后面,不然就会导致程序段错误(答疑老师解决)
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, refreshJieMian, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, changeDir, NULL);
gamPic();
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
-
蛇在向右移动的同时也可以按方向键,这就是引入线程之后的牛逼之处!
六、贪吃蛇跑起来
6.1 实现贪吃蛇四方向的风骚走位:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN 2
#define LEFT 3
#define RIGHT 4
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
int key;
int dir;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");:
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!key = %d\n",key);
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
switch(dir){
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
dir = RIGHT;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
void* refreshJieMian()
{
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
dir = DOWN;
break;
case KEY_UP:
dir = UP;
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
dir = LEFT;
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
dir = RIGHT;
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, refreshJieMian, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, changeDir, NULL);
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
6.2 用绝对值方式来解决不合理的走位:
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
int key;
int dir;
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
noecho();
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao!key = %d\n",key);
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
switch(dir){
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
dir = RIGHT;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deletNode();
if(tail->hang == 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
void refreshJieMian()
{
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
void turn(int direction) 通过绝对值判断相反方向不触发
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction)){
dir = direction;
}
}
void changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
turn(DOWN);
break;
case KEY_UP:
turn(UP);
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
turn(LEFT);
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
turn(RIGHT);
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, refreshJieMian, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, changeDir, NULL);
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
6.3 贪吃蛇吃饭了(食物的位置是随机的):
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
struct Snake
{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
int key;
int dir;
struct Snake food;
void initFood()
{
int x = rand()%20;
int y = rand()%20;
food.hang = x;
food.lie = y;
}
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1);
noecho();
}
int hasSnakeNode(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
int hasFood(int i, int j)
{
if(food.hang == i && food.lie == j){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void gamPic()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);
for(hang=0; hang<20; hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19) {
for(lie=0; lie<=20; lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(hasSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else if(hasFood(hang,lie)){
printw("##");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0; lie<20; lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
printw("By ShiYaHao! food.hang = %d,food.lie = %d\n",food.hang,food.lie);
}
}
}
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new =(struct Snake *) malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
new->next = NULL;
switch(dir){
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p;
dir = RIGHT;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
initFood();
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
if(hasFood(tail->hang,tail->lie)){
initFood();
}else{
deletNode();
}
if(tail->hang < 0 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
void* refreshJieMian()
{
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamPic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
void turn(int direction)
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction)){
dir = direction;
}
}
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
turn(DOWN);
break;
case KEY_UP:
turn(UP);
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
turn(LEFT);
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
turn(RIGHT);
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamPic();
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, refreshJieMian, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, changeDir, NULL);
while(1);
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}七、项目代码
#include <curses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
struct Snake{
int hang;
int lie;
struct Snake *next;
};
struct Snake *head = NULL;
struct Snake *tail = NULL;
struct Snake food;
int key;
int dir;
void addNode(); /*从尾部插入新节点*/
//void initNcurses(); /*ncurses库的初始化函数*/
//void gameMap(); /*贪吃蛇地图的初始化*/
//int printSnakeNode(int i,int j); /*在地图上打印贪吃蛇的节点*/
//void initSnake(); /*初始化贪吃蛇*/
//void deletNode(); /*删除头结点*/
//void moveSnake(); /*实现贪吃蛇的移动*/
//void *refreshScreen(); /*线程实现图像刷新*/
//void *changeDir(); /*线程实现贪吃蛇方向的改变*/
//void turn(int direction); /*防止出现不合理走位*/
//void creatFood(); /*随机出现食物*/
//int hasFood(int i,int j); /*打印食物*/
//int ifSnakeDie(); /*判断贪吃蛇是否死亡*/
/*随机出现食物*/
void creatFood()
{
int x = rand()%20;
int y = rand()%19+1;
food.hang = x;
food.lie = y;
}
int hasFood(int i,int j)
{
if(food.hang == i && food.lie == j){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/*ncurses库的初始化函数*/
void initNcurses()
{
initscr();//ncurse界面的初始化函数
keypad(stdscr,1);//使用keypad函数,才可以使用键盘功能键
noecho();//防止打印无关键值
}
/*贪吃蛇地图的初始化*/
void gameMap()
{
int hang;
int lie;
move(0,0);//把光标的位置移到头,实现地图刷新时的覆盖
for(hang=0;hang<20;hang++){
if(hang == 0){
for(lie=0;lie<20;lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang>=0 && hang<=19){
for(lie=0;lie<=20;lie++){
if(lie == 0 || lie == 20){
printw("|");
}else if(printSnakeNode(hang,lie)){
printw("[]");
}else if(hasFood(hang,lie)){
printw("##");
}else{
printw(" ");
}
}
printw("\n");
}
if(hang == 19){
for(lie=0;lie<20;lie++){
printw("--");
}
printw("\n");
}
}
printw("By ShiYaHao!,food.hang = %d,food.lie = %d\n",food.hang,food.lie);
}
/*在地图上打印贪吃蛇的节点*/
int printSnakeNode(int i,int j)
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(p->hang == i && p->lie == j){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
/*初始化贪吃蛇*/
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p = NULL;
if(head != NULL){ //当贪吃蛇死亡后,把多余节点释放
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
creatFood();
dir = RIGHT;
head = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->hang = 1;
head->lie = 1;
head->next = NULL;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
addNode();
}
/*从尾部插入新节点*/
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new = (struct Snake *)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
switch(dir){
case UP:
new->hang = tail->hang-1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case DOWN:
new->hang = tail->hang+1;
new->lie = tail->lie;
break;
case LEFT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie-1;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->hang = tail->hang;
new->lie = tail->lie+1;
break;
}
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
/*删除头结点*/
void deletNode()
{
struct Snake *p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
/*判断贪吃蛇是否死亡*/
int ifSnakeDie()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
if(tail->hang < 0 || tail->hang == 20 || tail->lie == 0 || tail->lie == 20){
return 1;
}
while(p->next != NULL){
if(p->hang == tail->hang && p->lie == tail->lie){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
/*实现贪吃蛇的移动*/
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
if(hasFood(tail->hang,tail->lie)){
creatFood();
}else{
deletNode();
}
if(ifSnakeDie()){
initSnake();
}
}
/*线程实现图像刷新*/
void *refreshScreen()
{
usleep(100000);
while(1){
moveSnake();
gameMap();//刷新地图
refresh();//界面刷新函数
usleep(100000);
}
}
/*防止不合理走位*/
void turn(int direction)
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction)){
dir = direction;
}
}
/*线程实现贪吃蛇方向的改变*/
void *changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_UP:
turn(UP);
break;
case KEY_DOWN:
turn(DOWN);
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
turn(LEFT);
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
turn(RIGHT);
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1;
pthread_t t2;
initNcurses();
initSnake();
gameMap();
pthread_create(&t1,NULL,refreshScreen,NULL);
pthread_create(&t2,NULL,changeDir,NULL);
while(1);
getch();//等待用户的输入,如果没有这句话,程序就退出了,看不到运行的结果,也就是无法看到上面那句话
endwin();//程序退出,恢复shell终端的显示,如果没有这句话,shell终端字乱码,坏掉
return 0;
}